|
1
|
Burger M, Catto JW, Dalbagni G, Grossman
HB, Herr H, Karakiewicz P, Kassouf W, Kiemeney LA, La Vecchia C,
Shariat S and Lotan Y: Epidemiology and risk factors of urothelial
bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 63:234–241. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Menashe I, Figueroa JD, Garcia-Closas M,
Chatterjee N, Malats N, Picornell A, Maeder D, Yang Q,
Prokunina-Olsson L, Wang Z, et al: Large-scale pathway-based
analysis of bladder cancer genome-wide association data from five
studies of European background. PLoS One. 7:e293962012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kumar B, Koul S, Petersen J, Khandrika L,
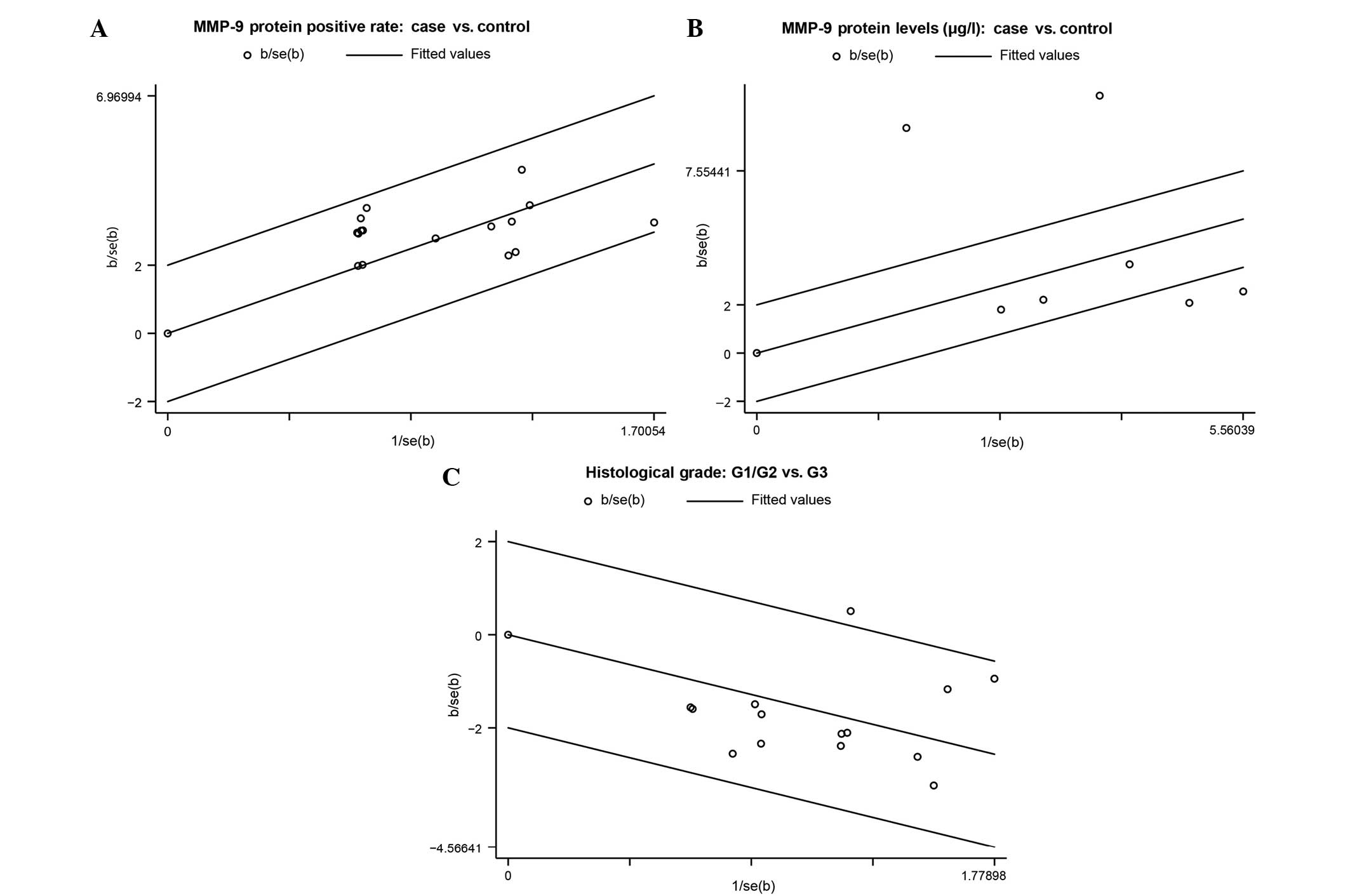
Hwa JS, Meacham RB, Wilson S and Koul HK: p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinase-driven MAPKAPK2 regulates invasion of bladder cancer
by modulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity. Cancer Res. 70:832–841.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gui Y, Guo G, Huang Y, et al: Frequent
mutations of chromatin remodeling genes in transitional cell
carcinoma of the bladder. Nat Genet. 43:875–878. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Samplaski MK, Heston W, Elson P,
Magi-Galluzzi C and Hansel DE: Folate hydrolase (prostate-specific
membrane [corrected] antigen) 1 expression in bladder cancer
subtypes and associated tumor neovasculature. Mod Pathol.
24:1521–1529. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yan Y, Liang H, Li T, Li M, Li R, Qin X
and Li S: The MMP-1, MMP-2, and MMP-9 gene polymorphisms and
susceptibility to bladder cancer: A meta-analysis. Tumour Biol.
35:3047–3052. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Said N, Frierson HF, Sanchez-Carbayo M,
Brekken RA and Theodorescu D: Loss of SPARC in bladder cancer
enhances carcinogenesis and progression. J Clin Invest.
123:751–766. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhuo W, Zhang L, Cai L, Zhu B and Chen Z:
XRCC1 Arg399Gln polymorphism and bladder cancer risk: Updated
meta-analyses based on 5767 cases and 6919 controls. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 238:66–76. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Offersen BV, Knap MM, Horsman MR,
Verheijen J, Hanemaaijer R and Overgaard J: Matrix
metalloproteinase-9 measured in urine from bladder cancer patients
is an independent prognostic marker of poor survival. Acta Oncol.
49:1283–1287. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jacobs BL, Lee CT and Montie JE: Bladder
cancer in: 2010 How far have we come? CA Cancer J Clin. 60:244–272.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Burger M, Oosterlinck W, Konety B, Chang
S, Gudjonsson S, Pruthi R, Soloway M, Solsona E, Sved P, Babjuk M,
et al: International Consultation on Urologic Disease-European
Association of Urology Consultation on Bladder Cancer: 2012 ICUD
EAU International Consultation on Bladder Cancer 2012:
Non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Eur Urol.
63:36–44. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bauvois B: New facets of matrix
metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9 as cell surface transducers:
Outside-in signaling and relationship to tumor progression. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1825:29–36. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zitka O, Kukacka J, Krizkova S, Huska D,
Adam V, Masarik M, Prusa R and Kizek R: Matrix metalloproteinases.
Curr Med Chem. 17:3751–3768. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Surgucheva I, Chidambaram K, Willoughby DA
and Surguchov A: Matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression: New
regulatory elements. J Ocul Biol Dis Infor. 3:41–52. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Eissa S, Badr S, Elhamid SA, Helmy AS,
Nour M and Esmat M: The value of combined use of survivin mRNA and
matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 for bladder cancer detection in
voided urine. Dis Markers. 34:57–62. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vandooren J, Van den Steen PE and
Opdenakker G: Biochemistry and molecular biology of gelatinase B or
matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9): The next decade. Crit Rev
Biochem Mol Biol. 48:222–272. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
141:52–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gunes M, Kemik AS, Pirincci N, Gecit I,
Taken K, Yuksel MB, Kaba M and Eryilmaz R: Preoperative levels of
matrix metalloproteinase-7 and −9 and tissue inhibitor of matrix
metalloproteinase-1 relation to pathologic parameters in bladder
carcinoma patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:873–876. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Urquidi V, Chang M, Dai Y, Kim J, Wolfson
ED, Goodison S and Rosser CJ: IL-8 as a urinary biomarker for the
detection of bladder cancer. BMC Urol. 12:122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Goodison S, Chang M, Dai Y, Urquidi V and
Rosser CJ: A multi-analyte assay for the non-invasive detection of
bladder cancer. PLoS One. 7:e474692012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen H, Manning AK and Dupuis J: A method
of moments estimator for random effect multivariate meta-analysis.
Biometrics. 68:1278–1284. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Higgins JP and Thompson SG: Quantifying
heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 21:1539–1558. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jackson D, White IR and Riley RD:
Quantifying the impact of between-study heterogeneity in
multivariate meta-analyses. Stat Med. 31:3805–3820. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Peters JL, Sutton AJ, Jones DR, Abrams KR
and Rushton L: Comparison of two methods to detect publication bias
in meta-analysis. JAMA. 295:676–680. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zintzaras E and Ioannidis JP:
Heterogeneity testing in meta-analysis of genome searches. Genet
Epidemiol. 28:123–137. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sterne JA and Egger M: Funnel plots for
detecting bias in meta-analysis: Guidelines on choice of axis. J
Clin Epidemiol. 54:1046–1055. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wikstrom EA, Naik S, Lodha N and Cauraugh
JH: Balance capabilities after lateral ankle trauma and
intervention: A meta-analysis. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 41:1287–1295.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Egger M, Smith Davey G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
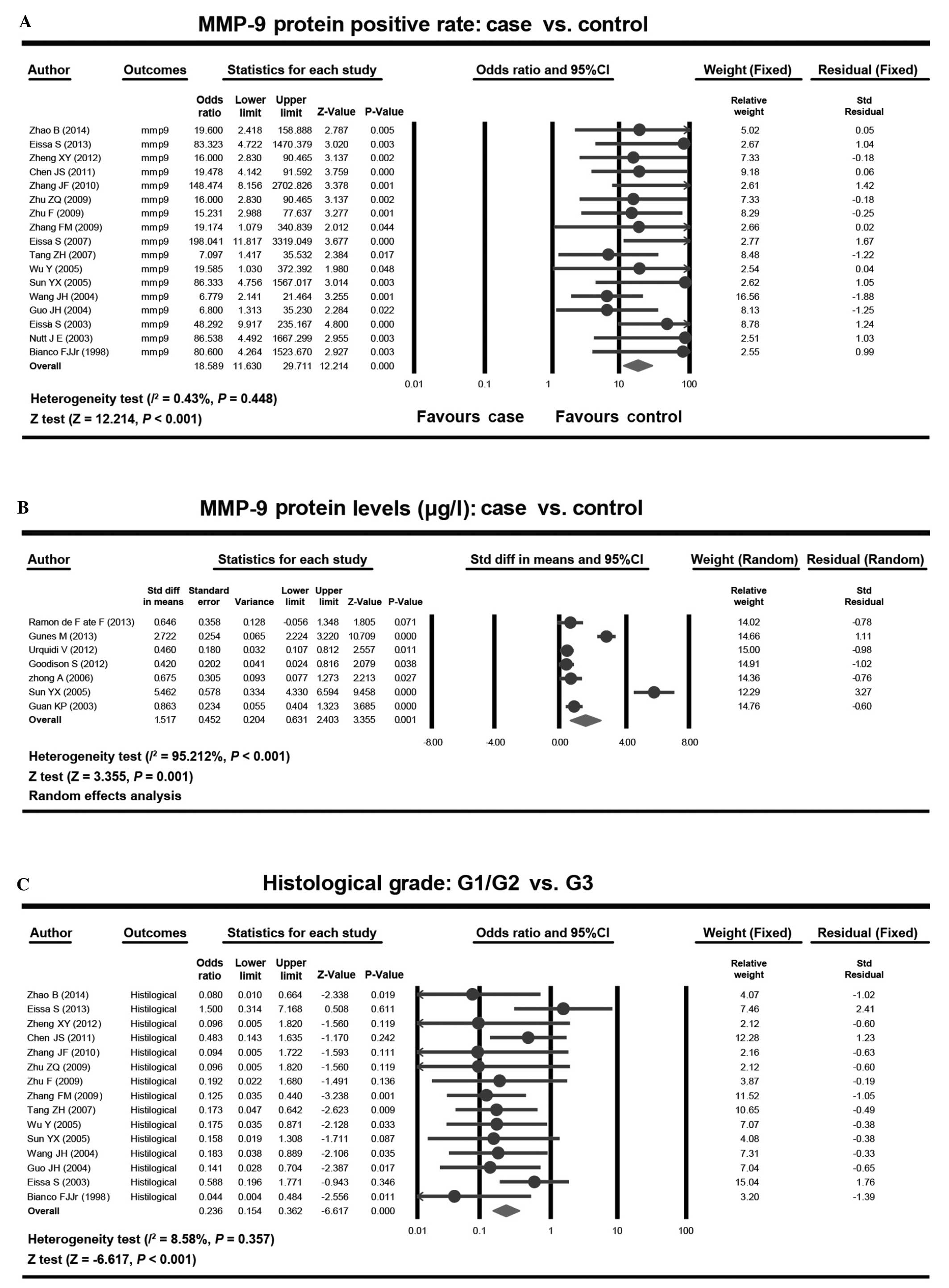
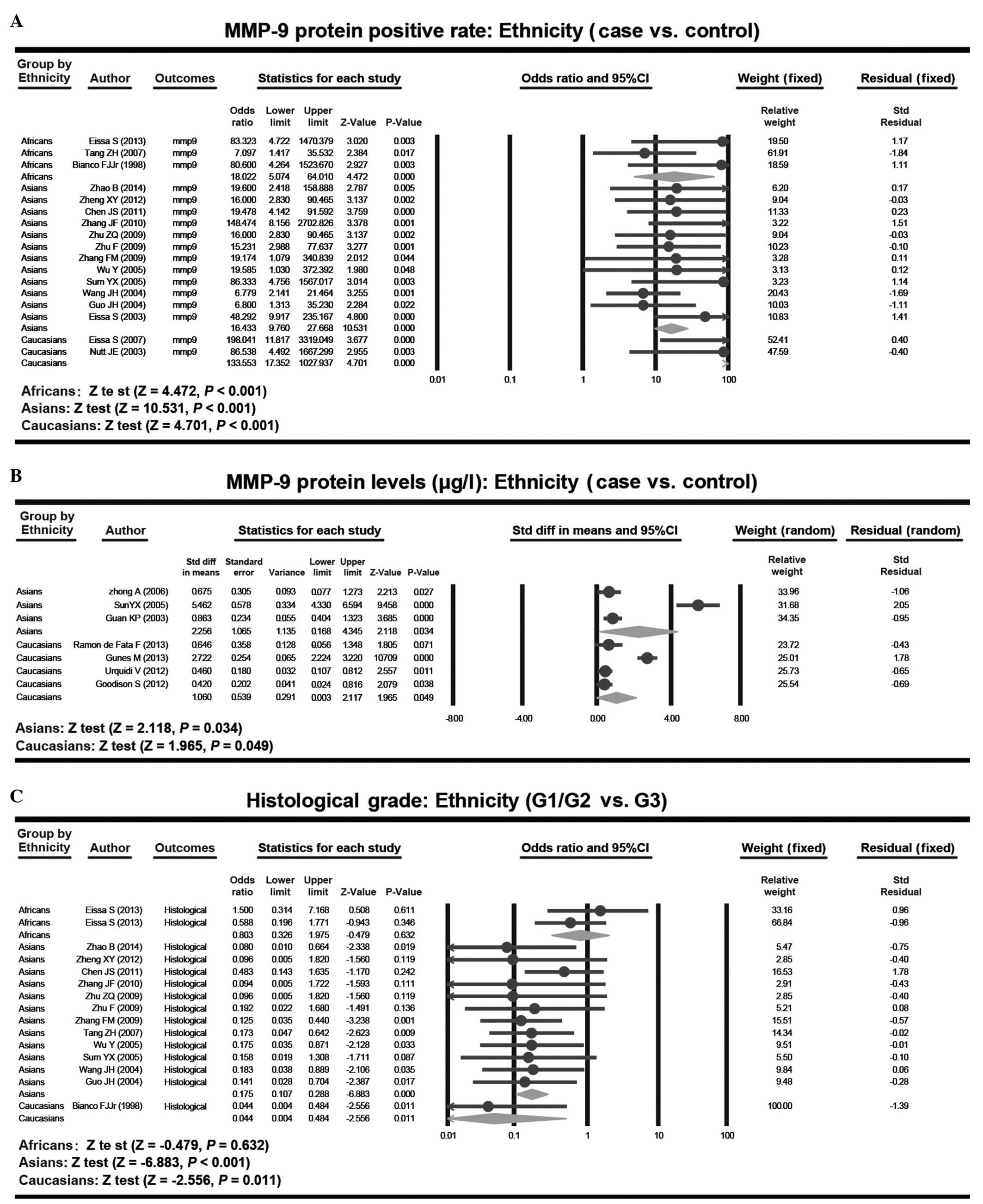
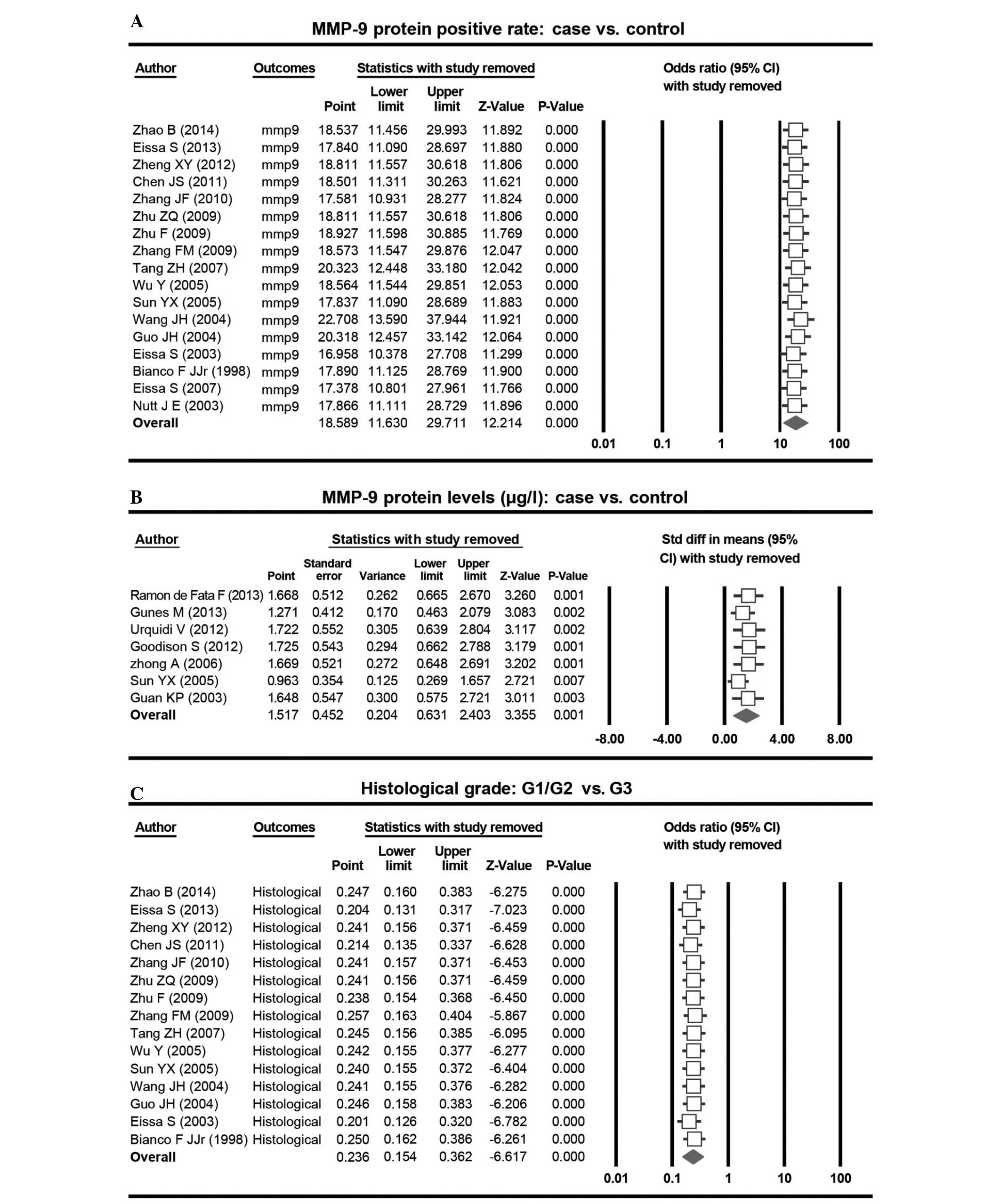
Zhao B, Wang Q, Lei Y, Zhang G, Li R and
Song Z: Study on the expression of MMP-9 and CD34 in bladder
urothelial carcinoma and their correlation. J Clin Res.
31:1518–1521. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
30
|
Bianco FJ Jr, Gervasi DC, Tiguert R,
Grignon DJ, Pontes JE, Crissman JD, Fridman R and Wood DP Jr:
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in bladder washes from
bladder cancer patients predicts pathological stage and grade. Clin
Cancer Res. 4:3011–3016. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Eissa S, Ali-Labib R, Swellam M, Bassiony
M, Tash F and El-Zayat TM: Noninvasive diagnosis of bladder cancer
by detection of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) and
their inhibitor (TIMP-2) in urine. Eur Urol. 52:1388–1396. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Eissa S, Labib RA, Mourad MS, Kamel K and
El-Ahmady O: Comparison of telomerase activity and matrix
metalloproteinase-9 in voided urine and bladder wash samples as a
useful diagnostic tool for bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 44:687–694.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhu F, Zhang Y, Yan R, Zhang HQ and Zhang
YJ: Correlation of expressions of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in the
transitional cell carcinoma of bladder with tremor invasion and
metastasis. Zhong Liu Yan Jiu Yu Lin Chuang. 21:680–682. 2009.(In
Chinese).
|
|
34
|
Zhang FM, Gao XM, Li SS, Li SB, Liu Y and
Xu H: Expressions of MMP-9 and VEGF in 65 cases with bladder
transitional cell carcinoma and their significance. Zhong Liu Xue
Za Zhi. 15:1032–1034. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
35
|
Guan KP, Ye HY, Yan Z, Wang Y and Hou SK:
Serum levels of endostatin and matrix metalloproteinase-9
associated with high stage and grade primary transitional cell
carcinoma of the bladder. Urology. 61:719–723. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang JF, Sun LJ, Luo B, Hao J, Song BL
and Liu P: Expression of survivin, MMP-9 and PTEN proteins in
bladder carcinoma. Xian Dai Yu Fang Yi Xue. 37:4681–4682. 2010.(In
Chinese).
|
|
37
|
Guo JH, Wang HR, Wang J, Zhu J and Song
HY: Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and its correlation
with tumor interstitial microvascular density and tumor metastasis
in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Zhong Guo Ai Zheng
Za Zhi. 14:116–118. 2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
38
|
Wang JH, Chen ZF, Chen WB and Shi Z:
Expression of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in bladder cancer and its
significance. Xian Dai Mi Niao Wai Ke Za Zhi. 9:140–141. 2004.(In
Chinese).
|
|
39
|
Chen JS, Yang WM, Xu YM and Wang SL: The
expression of MMP-9 and cyclin E in bladder urothelial carcinoma
and their clinical significance. Xian Dai Mi Niao Wai Ke Za Zhi.
26:726–731. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
40
|
Nutt JE, Durkan GC, Mellon JK and Lunec J:
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in bladder cancer: The induction
of MMP9 by epidermal growth factor and its detection in urine. BJU
Int. 91:99–104. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
de Ramón Fata F, Ferruelo A, Andrés G,
Gimbernat H, Sánchez-Chapado M and Angulo JC: The role of matrix
metalloproteinase MMP-9 and TIMP-2 tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinases as serum markers of bladder cancer. Actas Urol
Esp. 37:480–488. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zheng XY, Pang X, Wang FJ and Zhu ZQ:
Expression of CXCR4 and MMP-9 in bladder transitional cell
carcinoma tissue. Xian Dai Sheng Wu Yi. 12:5255–5260. 2012.(In
Chinese).
|
|
43
|
Wu Y and Zeng FQ: Expression of
MMP-9/TIMP-1 in bladder and the clinical significance transitional
cell carcinoma. Xian Dai Mi Niao Wai Ke Za Zhi. 20:577–580.
2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
44
|
Sun YX, Zhang ZC, Sun LQ and Gao HW:
Correlation of content and expression of matrix metalloproteinases
in transitional cell carcinoma of bladder with tumor invasion and
metastasis. Ji Lin Da Xue Xue Bao (Yi Xue Ban). 31:127–129.
2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
45
|
Tang ZH, Guo SX, Cai QF and Chen TL:
Expressions of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 and their relationship with the
invasion and metastasis of bladder cancer. Guo Ji Mi Niao Xi Tong
Za Zhi. 27:148–152. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
46
|
Zhong A, Yang WM and Ye ZQ: The expression
of urinary MMP2 and MMP9 in the bladder transitional cell carcinoma
and their correlations to the tumor invasion and metastasis. Chuang
Wai Ke Za Zhi. 14:655–657. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
47
|
Zhu ZQ, Zheng XY, Zhu QH, Wen JH and Fan
CH: Expression and clinical significance of CXCR4 and MMP-9 in
bladder cancer. Zhong Guo Xian Dai Yi Xue Za Zhi. 19:337–340.
2009.(In Chinese), 343.
|
|
48
|
Lu P, Takai K, Weaver VM and Werb Z:
Extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling in development and
disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 3:a0050582011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jacob-Ferreira AL, Lacchini R, Gerlach RF,
Passos CJ, Barbosa F Jr and Tanus-Santos JE: A common matrix
metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 polymorphism affects plasma MMP-2 levels
in subjects environmentally exposed to mercury. Sci Total Environ.
409:4242–4246. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Castro MM, Rizzi E, Rodrigues GJ, Ceron
CS, Bendhack LM, Gerlach RF and Tanus-Santos JE: Antioxidant
treatment reduces matrix metalloproteinase-2-induced vascular
changes in renovascular hypertension. Free Radic Biol Med.
46:1298–1307. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ceron CS, Castro MM, Rizzi E, Montenegro
MF, Fontana V, Salgado MC, Gerlach RF and Tanus-Santos JE:
Spironolactone and hydrochlorothiazide exert antioxidant effects
and reduce vascular matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity and
expression in a model of renovascular hypertension. Br J Pharmacol.
160:77–87. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
O-Charoenrat P and Khantapura P: The role
of genetic polymorphisms in the promoters of the matrix
metalloproteinase-2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2
genes in head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol. 42:257–267. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gialeli C, Theocharis AD and Karamanos NK:
Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their
pharmacological targeting. FEBS J. 278:16–27. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Srivastava P, Mandhani A, Kapoor R and
Mittal RD: Role of MMP-3 and MMP-9 and their haplotypes in risk of
bladder cancer in North Indian cohort. Ann Surg Oncol.
17:3068–3075. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sand JM, Larsen L, Hogaboam C, Martinez F,
Han M, Larsen Røssel M, Nawrocki A, Zheng Q, Karsdal MA and Leeming
DJ: MMP mediated degradation of type IV collagen alpha 1 and alpha
3 chains reflects basement membrane remodeling in experimental and
clinical fibrosis - validation of two novel biomarker assays. PLoS
One. 8:e849342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Reis ST, Leite KR, Piovesan LF,
Pontes-Junior J, Viana NI, Abe DK, Crippa A, Moura CM, Adonias SP,
Srougi M and Dall'Oglio MF: Increased expression of MMP-9 and IL-8
are correlated with poor prognosis of Bladder Cancer. BMC Urol.
12:182012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kumar B, Koul S, Petersen J, Khandrika L,
Hwa JS, Meacham RB, Wilson S and Koul HK: p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinase-driven MAPKAPK2 regulates invasion of bladder cancer
by modulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity. Cancer Res. 70:832–841.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Stankovic S, Konjevic G, Gopcevic K, Jovic
V, Inic M and Jurisic V: Activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in sera of
breast cancer patients. Pathol Res Pract. 206:241–247. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zamilpa R, Ramirez TA, Dai Q, Dayah T,
Nguyen N, Zhang J, Ahuja SS, D'Armiento, Jin YF and Lindsey ML:
MMP-9 overexpression in macrophages regulates the post-myocardial
infarction inflammatory response through SCYE1. FASEB J. 26(Suppl):
399.22012.
|