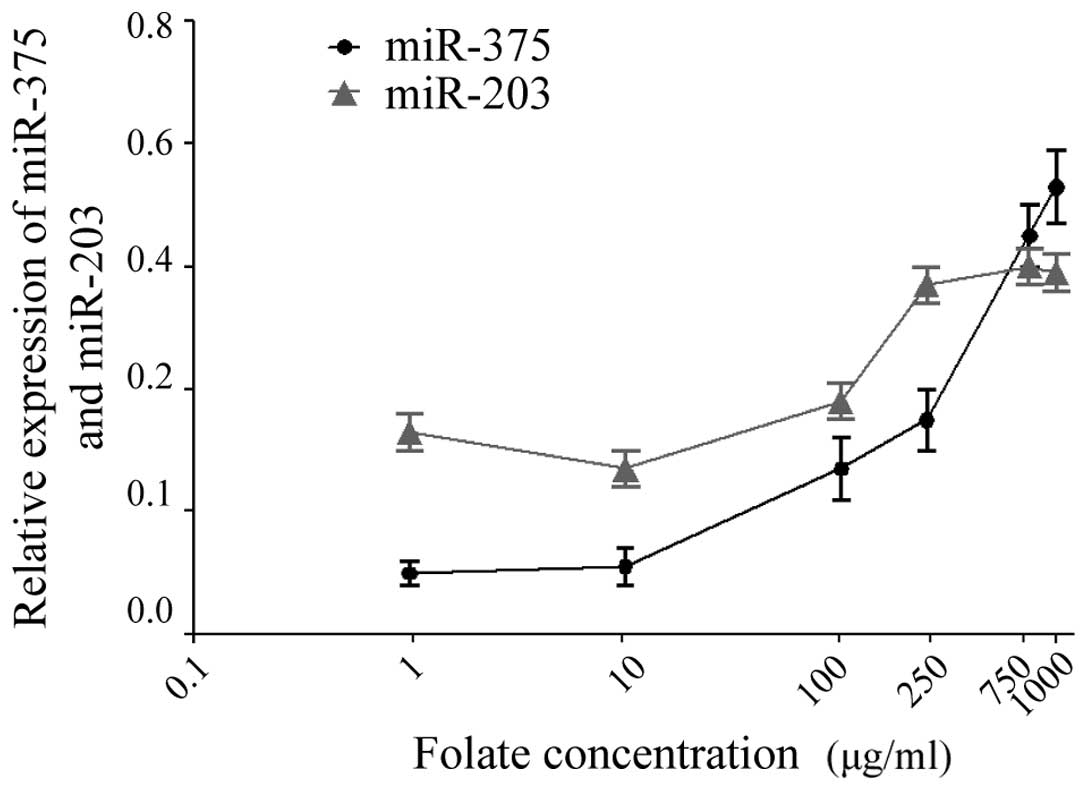
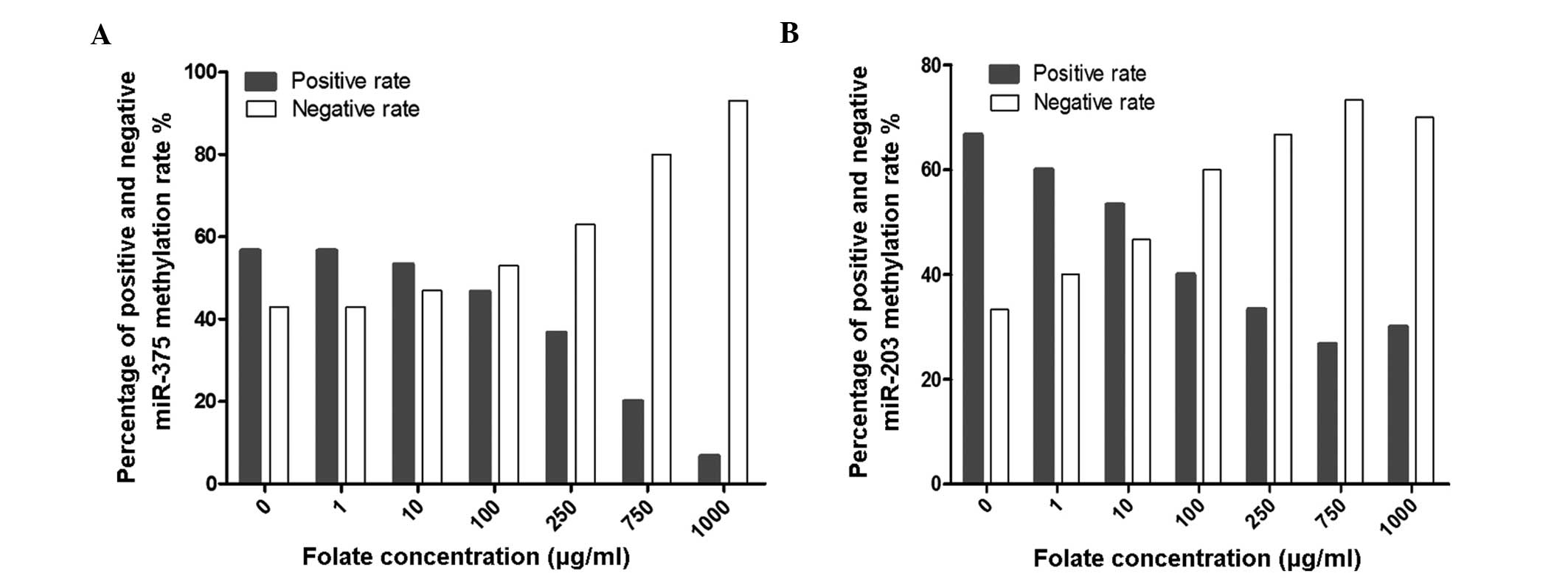
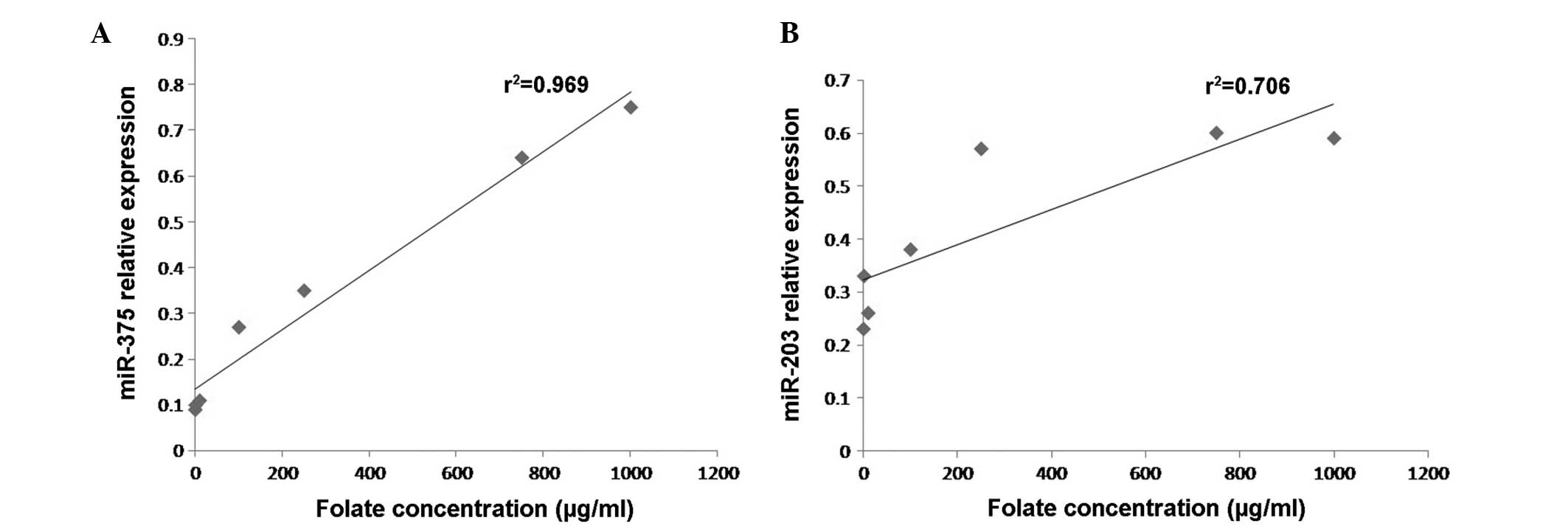
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schiffman MH and Castle P: Epidemiologic
studies of a necessary causal risk factor: Human papillomavirus
infection and cervical neoplasia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 95:E22003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Choi YJ and Park JS: Clinical significance
of human papillomavirus genotyping. J Gynecol Oncol. 27:e212016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ho GY, Bierman R, Beardsley L, Chang CJ
and Burk RD: Natural history of cervicovaginal papillomavirus
infection in young women. N Engl J Med. 338:423–428. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhao WH, Hao M, Cheng XT, Yang X, Wang ZL,
Cheng KY, Liu FL and Bai YX: c-myc gene copy number variation in
cervical exfoliated cells detected on fluorescence in situ
hybridization for cervical cancer screening. Gynecol Obstet Invest.
Jan 26–2016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wilting SM, Snijders PJ, Verlaat W,
Jaspers A, van de Wiel MA, van Wieringen WN, Meijer GA, Kenter GG,
Yi Y, le Sage C, et al: Altered microRNA expression associated with
chromosomal changes contributes to cervical carcinogenesis.
Oncogene. 32:106–116. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang L, Yue Y, Wang X and Jin H: Function
and clinical potential of microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncol Lett. 10:3345–3353. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lo R and Weksberg R: Biological and
biochemical modulation of DNA methylation. Epigenomics. 6:593–602.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sarkar D, Leung EY, Baguley BC, Finlay GJ
and Askarian-Amiri ME: Epigenetic regulation in human melanoma:
Past and future. Epigenetics. 10:103–121. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang LQ and Chim CS: DNA methylation of
tumor-suppressor miRNA genes in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Epigenomics. 7:461–473. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang JT, Ding L, Jiang SW, Hao J, Zhao WM,
Zhou Q, Yang ZK and Zhang L: Folate deficiency and aberrant
expression of DNA methyltransferase 1 were associated with cervical
cancerization. Curr Pharm Des. 20:1639–1646. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Flatley JE, McNeir K, Balasubramani L,
Tidy J, Stuart EL, Young TA and Powers HJ: Folate status and
aberrant DNA methylation are associated with HPV infection and
cervical pathogenesis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
18:2782–2789. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Flatley JE, Sargent A, Kitchener HC,
Russell JM and Powers HJ: Tumour suppressor gene methylation and
cervical cell folate concentration are determinants of high-risk
human papillomavirus persistence: A nested case control study. BMC
Cancer. 14:8032014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bai LX, Wang JT, Ding L, Jiang SW, Kang
HJ, Gao CF, Chen X, Chen C and Zhou Q: Folate deficiency and FHIT
hypermethylation and HPV 16 infection promote cervical
cancerization. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:9313–9317. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lewin SN, Herzog TJ, Barrena Medel NI,
Deutsch I, Burke WM, Sun X and Wright JD: Comparative performance
of the 2009 International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics'
staging system for uterine corpus cancer. Obstet Gynecol.
116:1141–1149. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu HQ, Wang YH, Wang LL and Hao M:
P16INK4A and survivin: Diagnostic and prognostic markers in
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical squamous cell
carcinoma. Exp Mol Pathol. 99:44–49. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wright TC, Ronnett BM, Kurman RJ and
Ferenczy A: Precancerous lesions of the cervix. Kurman RJ, Ellenson
LH and Ronnett BM: Blaustein's Pathology of the Female Genital
Tract (6th). Springer US. (New York, NY). 193–252. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xiao W, Zhao H, Dong W, Li Q, Zhu J, Li G,
Zhang S and Ye M: Quantitative detection of methylated NDRG4 gene
as a candidate biomarker for diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Oncol
Lett. 9:1383–1387. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shi JF, Canfell K, Lew JB and Qiao YL: The
burden of cervical cancer in China: Synthesis of the evidence. Int
J Cancer. 130:641–652. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang JT, Ma XC, Cheng YY, Ding L and Zhou
Q: A case-control study on the association between folate and
cervical cancer. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 27:424–427.
2006.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cheung TH, Man KN, Yu MY, Yim SF, Siu NS,
Lo KW, Doran G, Wong RR, Wang VW, Smith DI, et al: Dysregulated
microRNAs in the pathogenesis and progression of cervical neoplasm.
Cell Cycle. 11:2876–2884. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiménez-Wences H, Peralta-Zaragoza O and
Fernández-Tilapa G: Human papilloma virus, DNA methylation and
microRNA expression in cervical cancer (Review). Oncol Rep.
31:2467–2476. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yao T, Rao Q, Liu L, Zheng C, Xie Q, Liang
J and Lin Z: Exploration of tumor-suppressive microRNAs silenced by
DNA hypermethylation in cervical cancer. Virol J. 10:1752013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Michel CI and Malumbres M: microRNA-203:
Tumor suppression and beyond. Microrna. 2:118–126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen T, Xu C, Chen J, Ding C, Xu Z, Li C
and Zhao J: MicroRNA-203 inhibits cellular proliferation and
invasion by targeting Bmi1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol
Lett. 9:2639–2646. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gocze K, Gombos K, Juhasz K, Kovacs K,
Kajtar B, Benczik M, Gocze P, Patczai B, Arany I and Ember I:
Unique microRNA expression profiles in cervical cancer. Anticancer
Res. 33:2561–2567. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gocze K, Gombos K, Kovacs K, Juhasz K,
Gocze P and Kiss I: MicroRNA expressions in HPV-induced cervical
dysplasia and cancer. Anticancer Res. 35:523–530. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Melar-New M and Laimins LA: Human
papillomaviruses modulate expression of microRNA 203 upon
epithelial differentiation to control levels of p63 proteins. J
Virol. 84:5212–5221. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Greco D, Kivi N, Qian K, Leivonen SK,
Auvinen P and Auvinen E: Human papillomavirus 16 E5 modulates the
expression of host microRNAs. PLoS One. 6:e216462011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Costa-Pinheiro P, Ramalho-Carvalho J,
Vieira FQ, Torres-Ferreira J, Oliveira J, Gonçalves CS, Costa BM,
Henrique R and Jerónimo C: MicroRNA-375 plays a dual role in
prostate carcinogenesis. Clin Epigenetics. 7:422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang F, Li Y, Zhou J, Xu J, Peng C, Ye F,
Shen Y, Lu W, Wan X and Xie X: miR-375 is down-regulated in
squamous cervical cancer and inhibits cell migration and invasion
via targeting transcription factor SP1. Am J Pathol. 179:2580–2588.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shen Y, Wang P, Li Y, Ye F, Wang F, Wan X,
Cheng X, Lu W and Xie X: miR-375 is upregulated in acquired
paclitaxel resistance in cervical cancer. Br J Cancer. 109:92–99.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shen Y, Zhou J, Li Y, Ye F, Wan X, Lu W,
Xie X and Cheng X: miR-375 mediated acquired chemo-resistance in
cervical cancer by facilitating EMT. PLoS One. 9:e1092992014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Adams BD, Kasinski AL and Slack FJ:
Aberrant regulation and function of microRNAs in cancer. Curr Biol.
24:R762–776. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wilting SM, Verlaat W, Jaspers A, Makazaji
NA, Agami R, Meijer CJ, Snijders PJ and Steenbergen RD:
Methylation-mediated transcriptional repression of microRNAs during
cervical carcinogenesis. Epigenetics. 8:220–228. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Geng Y, Gao R, Chen X, Liu X, Liao X, Li
Y, Liu S, Ding Y, Wang Y and He J: Folate deficiency impairs
decidualization and alters methylation patterns of the genome in
mice. Mol Hum Reprod. 21:844–856. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ho E, Beaver LM, Williams DE and Dashwood
RH: Dietary factors and epigenetic regulation for prostate cancer
prevention. Adv Nutr. 2:497–510. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|