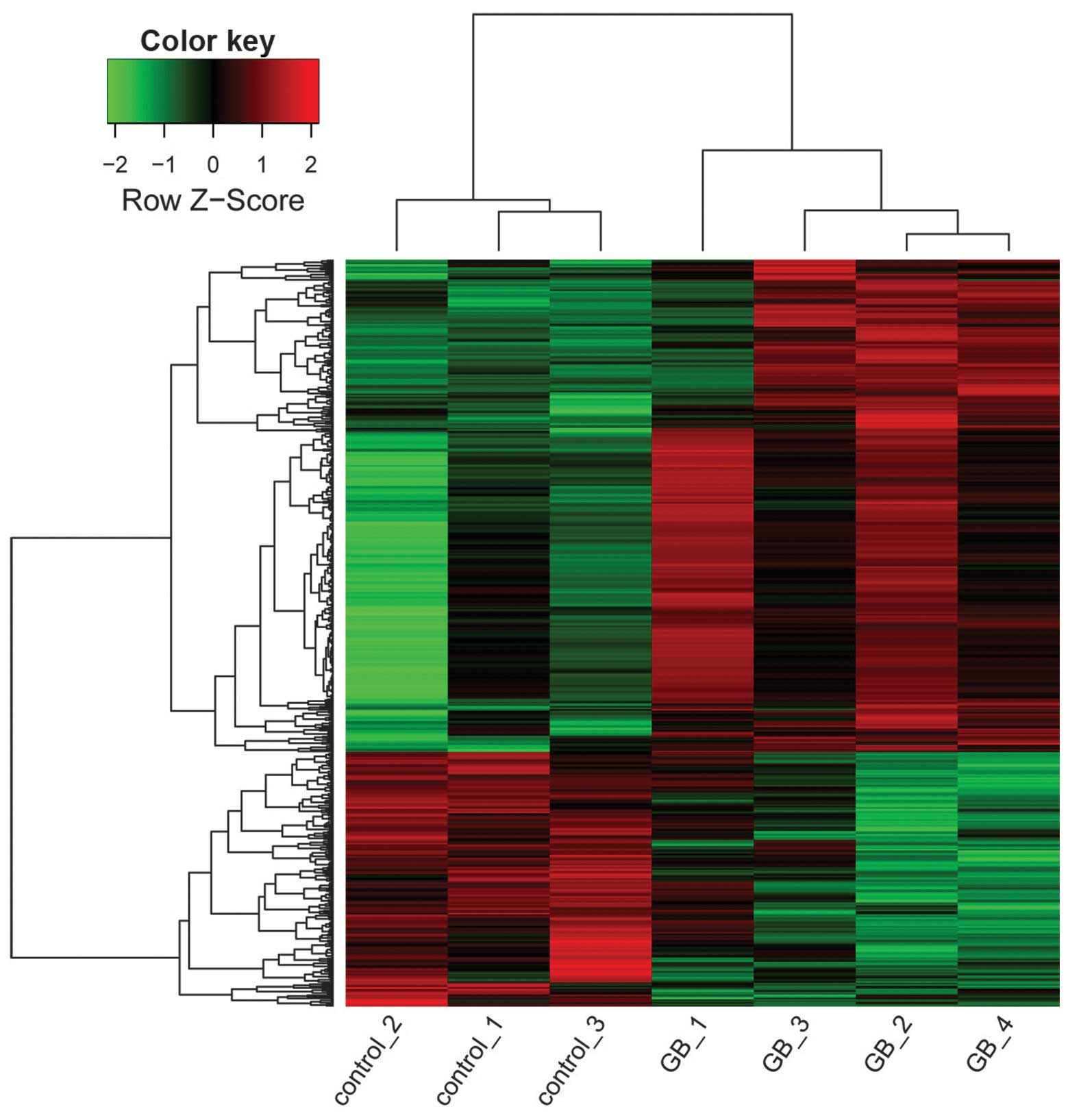
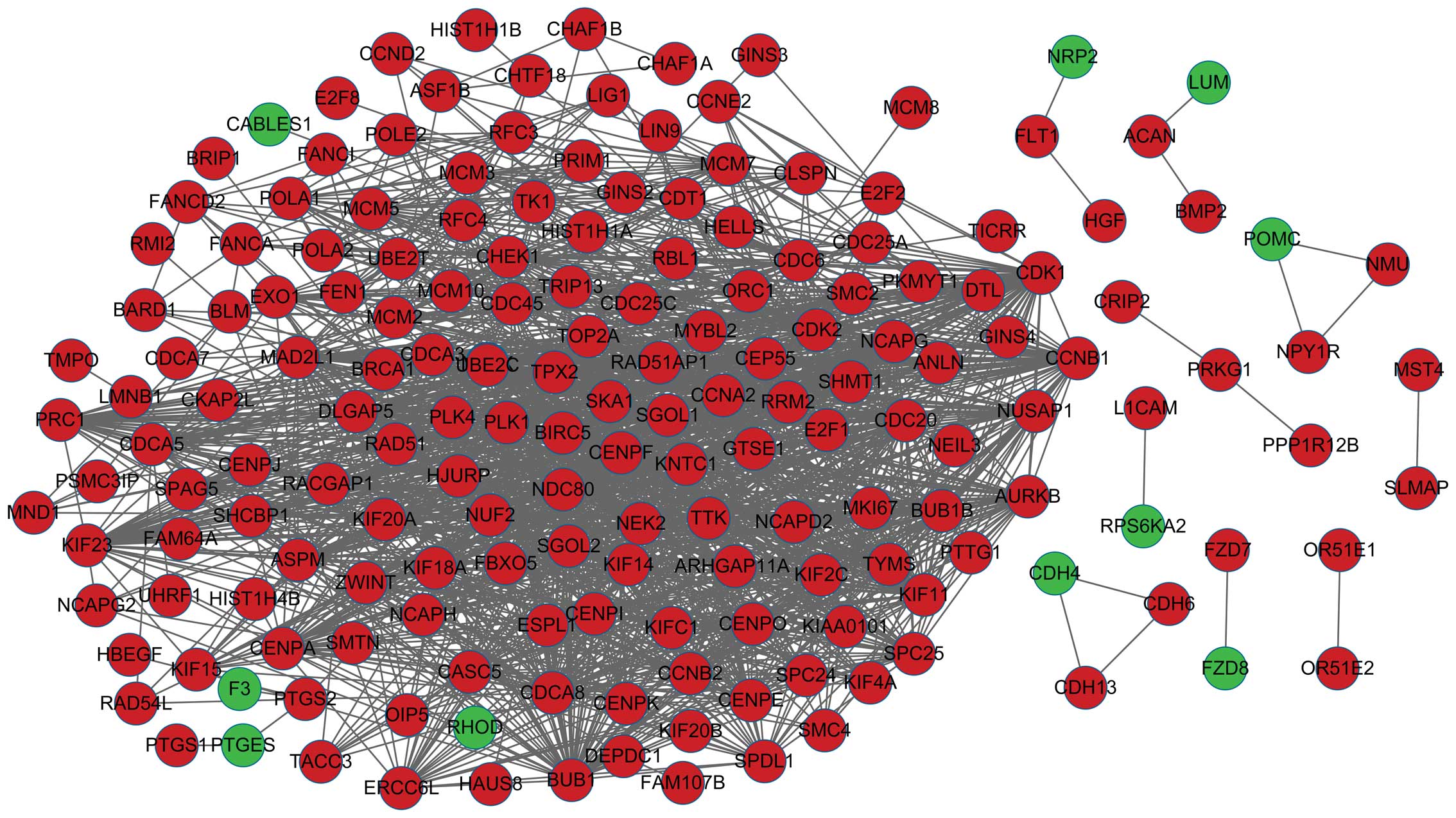
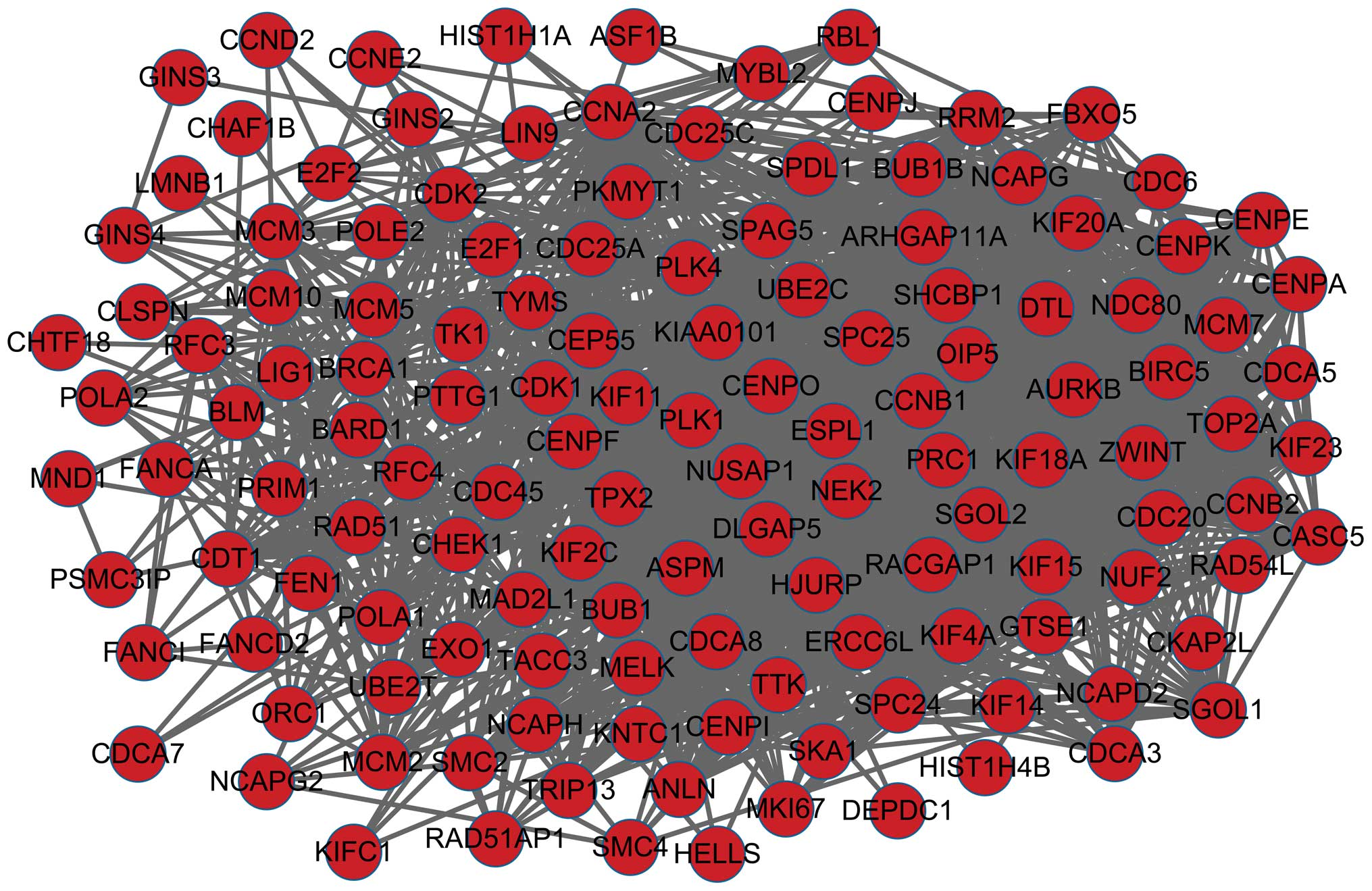
|
1
|
McLendon RE and Rich JN: Glioblastoma stem
cells: A Neuropathologist's View. J Oncol. 2011:3971952011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
States CBTRotU: CBTRUS statistical report:
primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the
United States in 2004–2006. 2010.
|
|
3
|
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent
MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B,
Belanger K, et al: European Organisation for Research and
Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumour and Radiation Oncology Groups;
National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group:
Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide
versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a
randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC
trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:459–466. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thumma SR, Fairbanks RK, Lamoreaux WT,
Mackay AR, Demakas JJ, Cooke BS, Elaimy AL, Hanson PW and Lee CM:
Effect of pretreatment clinical factors on overall survival in
glioblastoma multiforme: A surveillance epidemiology and end
results (SEER) population analysis. World J Surg Oncol. 10:752012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tseng YY, Liao JY, Chen WA, Kao YC and Liu
SJ: Sustainable release of carmustine from biodegradable
poly[(d,l)-lactide-co-glycolide] nanofibrous membranes in the
cerebral cavity: In vitro and in vivo studies. Expert
Opin Drug Deliv. 10:879–888. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gangemi RM, Griffero F, Marubbi D, Perera
M, Capra MC, Malatesta P, Ravetti GL, Zona GL, Daga A and Corte G:
SOX2 silencing in glioblastoma tumor-initiating cells causes stop
of proliferation and loss of tumorigenicity. Stem Cells. 27:40–48.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Clavreul A, Etcheverry A, Chassevent A,
Quillien V, Avril T, Jourdan ML, Michalak S, François P, Carré JL,
Mosser J, et al: Isolation of a new cell population in the
glioblastoma microenvironment. J Neurooncol. 106:493–504. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mao Y, Keller ET, Garfield DH, Shen K and
Wang J: Stromal cells in tumor microenvironment and breast cancer.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 32:303–315. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Calon A, Espinet E, Palomo-Ponce S,
Tauriello DV, Iglesias M, Céspedes MV, Sevillano M, Nadal C, Jung
P, Zhang XH, et al: Dependency of colorectal cancer on a
TGF-β-driven program in stromal cells for metastasis initiation.
Cancer cell. 22:571–584. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Östman A and Augsten M: Cancer-associated
fibroblasts and tumor growth-bystanders turning into key players.
Curr Opin Genet Dev. 19:67–73. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
López-Romero P, González MA, Callejas S,
Dopazo A and Irizarry RA: Processing of agilent microRNA array
data. BMC Res Notes. 3:182010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hulsegge I, Kommadath A and Smits MA:
Globaltest and GOEAST: Two different approaches for gene ontology
analysis. BMC Proc. 3(Suppl 4): S102009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for Annotation,
Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao M, Sun J and Zhao Z: TSGene: A web
resource for tumor suppressor genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 41(Database
issue): D970–D976. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen JS, Hung WS, Chan HH, Tsai SJ and Sun
HS: In silico identification of oncogenic potential of fyn-related
kinase in hepatocellular carcinoma. Bioinformatics. 29:420–427.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Kuhn M,
Simonovic M, Roth A, Minguez P, Doerks T, Stark M, Muller J, Bork
P, et al: The STRING database in 2011: Functional interaction
networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39(Database issue): D561–D568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Adamcsek B, Palla G, Farkas IJ, Derényi I
and Vicsek T: CFinder: Locating cliques and overlapping modules in
biological networks. Bioinformatics. 22:1021–1023. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ding T, Ma Y, Li W, Liu X, Ying G, Fu L
and Gu F: Role of aquaporin-4 in the regulation of migration and
invasion of human glioma cells. Int J Oncol. 38:1521–1531.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Baldwin RM, Barrett GM, Parolin DA,
Gillies JK, Paget JA, Lavictoire SJ, Gray DA and Lorimer IA:
Coordination of glioblastoma cell motility by PKCι. Mol Cancer.
9:2332010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schwartz GK and Shah MA: Targeting the
cell cycle: A new approach to cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol.
23:9408–9421. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mo W, Chen J, Patel A, Zhang L, Chau V, Li
Y, Cho W, Lim K, Xu J, Lazar AJ, et al: CXCR4/CXCL12 mediate
autocrine cell-cycle progression in NF1-associated malignant
peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Cell. 152:1077–1090. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang TH, Huo L, Wang YN, Xia W, Wei Y,
Chang SS, Chang WC, Fang YF, Chen CT, Lang JY, et al: EGFR
potentiates MCM7-mediated DNA replication through tyrosine
phosphorylation of Lyn kinase in human cancers. Cancer Cell.
23:796–810. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ubersax JA, Woodbury EL, Quang PN, Paraz
M, Blethrow JD, Shah K, Shokat KM and Morgan DO: Targets of the
cyclin-dependent kinase Cdk1. Nature. 425:859–864. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Stegh AH, Brennan C, Mahoney JA, Forloney
KL, Jenq HT, Luciano JP, Protopopov A, Chin L and Depinho RA:
Glioma oncoprotein Bcl2L12 inhibits the p53 tumor suppressor. Genes
Dev. 24:2194–2204. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao R, Gish K, Murphy M, Yin Y, Notterman
D, Hoffman WH, Tom E, Mack DH and Levine AJ: Analysis of
p53-regulated gene expression patterns using oligonucleotide
arrays. Genes Dev. 14:981–993. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Levine A, Hu W and Feng Z: The P53
pathway: What questions remain to be explored? Cell Death Differ.
13:1027–1036. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schwermer M, Lee S, Köster J, van Maerken
T, Stephan H, Eggert A, Morik K, Schulte JH and Schramm A:
Sensitivity to cdk1-inhibition is modulated by p53 status in
preclinical models of embryonal tumors. Oncotarget. 6:154252015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Grabsch H, Takeno S, Parsons WJ, Pomjanski
N, Boecking A, Gabbert HE and Mueller W: Overexpression of the
mitotic checkpoint genes BUB1, BUBR1 and BUB3 in gastric
cancer-association with tumour cell proliferation. J Pathol.
200:16–22. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tang Z, Shu H, Qi W, Mahmood NA, Mumby MC
and Yu H: PP2A is required for centromeric localization of Sgo1 and
proper chromosome segregation. Dev Cell. 10:575–585. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ricke RM, Jeganathan KB and van Deursen
JM: Bub1 overexpression induces aneuploidy and tumor formation
through Aurora B kinase hyperactivation. J Cell Biol.
193:1049–1064. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kawashima SA, Yamagishi Y, Honda T,
Ishiguro K and Watanabe Y: Phosphorylation of H2A by Bub1 prevents
chromosomal instability through localizing shugoshin. Science.
327:172–177. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Myrie KA, Percy MJ, Azim JN, Neeley CK and
Petty EM: Mutation and expression analysis of human BUB1 and BUB1B
in aneuploid breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Lett. 152:193–199.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Telentschak S, Soliwoda M, Nohroudi K,
Addicks K and Klinz FJ: Cytokinesis failure and successful
multipolar mitoses drive aneuploidy in glioblastoma cells. Oncology
Rep. 33:2001–2008. 2015.
|
|
36
|
Hadjihannas MV, Bernkopf DB, Brückner M
and Behrens J: Cell cycle control of Wnt/β-catenin signalling by
conductin/axin2 through CDC20. EMBO Rep. 13:347–354. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Frescas D and Pagano M: Deregulated
proteolysis by the F-box proteins SKP2 and β-TrCP: Tipping the
scales of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:438–449. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang Z, Wan L, Zhong J, Inuzuka H, Liu P,
Sarkar FH and Wei W: Cdc20: A potential novel therapeutic target
for cancer treatment. Curr Pharm Des. 19:3210–3214. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jiang J, Jedinak A and Sliva D:
Ganodermanontriol (GDNT) exerts its effect on growth and
invasiveness of breast cancer cells through the down-regulation of
CDC20 and uPA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 415:325–329. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rajkumar T, Sabitha K, Vijayalakshmi N,
Shirley S, Bose MV, Gopal G and Selvaluxmy G: Identification and
validation of genes involved in cervical tumourigenesis. BMC
Cancer. 11:802011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Marucci G, Morandi L, Magrini E, Farnedi
A, Franceschi E, Miglio R, Calò D, Pession A, Foschini MP and
Eusebi V: Gene expression profiling in glioblastoma and
immunohistochemical evaluation of IGFBP-2 and CDC20. Virchows
Archiv. 453:599–609. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bie L, Zhao G, Cheng P, Rondeau G,
Porwollik S, Ju Y, Xia XQ and McClelland M: The accuracy of
survival time prediction for patients with glioma is improved by
measuring mitotic spindle checkpoint gene expression. PloS one.
6:e256312011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bae I, Rih JK, Kim HJ, Kang HJ, Haddad B,
Kirilyuk A, Fan S, Avantaggiati ML and Rosen EM: BRCA1 regulates
gene expression for orderly mitotic progression. Cell Cycle.
4:1641–1666. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bogdani M, Teugels E, De Grève J, Bourgain
C, Neyns B and Pipeleers-Marichal M: Loss of nuclear BRCA1
localization in breast carcinoma is age dependent. Virchows Arch.
440:274–279. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lee C, Fotovati A, Triscott J, Chen J,
Venugopal C, Singhal A, Dunham C, Kerr JM, Verreault M, Yip S, et
al: Polo-like kinase 1 inhibition kills glioblastoma multiforme
brain tumor cells in part through loss of SOX2 and delays tumor
progression in mice. Stem Cells. 30:1064–1075. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Roshak AK, Capper EA, Imburgia C, Fornwald
J, Scott G and Marshall LA: The human polo-like kinase, PLK,
regulates cdc2/cyclin B through phosphorylation and activation of
the cdc25c phosphatas. Cell Signal. 12:405–411. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Casenghi M, Barr FA and Nigg EA:
Phosphorylation of Nlp by Plk1 negatively regulates its
dynein-dynactin-dependent targeting to the centrosome. J Cell Sci.
118:5101–5108. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Feng Y, Yuan JH, Maloid SC, Fisher R,
Copeland TD, Longo DL, Conrads TP, Veenstra TD, Ferris A, Hughes S,
et al: Polo-like kinase 1-mediated phosphorylation of the
GTP-binding protein Ran is important for bipolar spindle formation.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 349:144–152. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hansen DV, Loktev AV, Ban KH and Jackson
PK: Plk1 regulates activation of the anaphase promoting complex by
phosphorylating and triggering SCFbetaTrCP-dependent destruction of
the APC inhibitor Emi1. Mol Biol Cell. 15:5623–5634. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Niiya F, Tatsumoto T, Lee KS and Miki T:
Phosphorylation of the cytokinesis regulator ECT2 at G2/M phase
stimulates association of the mitotic kinase Plk1 and accumulation
of GTP-bound RhoA. Oncogene. 25:827–837. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Foong CS, Sandanaraj E, Brooks HB,
Campbell RM, Ang BT, Chong YK and Tang C: Glioma-propagating cells
as an in vitro screening platform PLK1 as a case study. J
Biomol Screen. 17:1136–1150. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hu K, Lee C, Qiu D, Fotovati A, Davies A,
Abu-Ali S, Wai D, Lawlor ER, Triche TJ, Pallen CJ and Dunn SE:
Small interfering RNA library screen of human kinases and
phosphatases identifies polo-like kinase 1 as a promising new
target for the treatment of pediatric rhabdomyosarcomas. Mol Cancer
Ther. 8:3024–3035. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ko E, Kim Y, Cho EY, Han J, Shim YM, Park
J and Kim DH: Synergistic effect of Bcl-2 and Cyclin A2 on adverse
recurrence-free survival in stage i non-small cell lung cancer. Ann
Surg Oncol. 20:1005–1012. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Arsic N, Bendris N, Peter M, Begon-Pescia
C, Rebouissou C, Gadéa G, Bouquier N, Bibeau F, Lemmers B and
Blanchard JM: A novel function for Cyclin A2: Control of cell
invasion via RhoA signaling. J Cell Biol. 196:147–162. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Uhlen M, Oksvold P, Fagerberg L, Lundberg
E, Jonasson K, Forsberg M, Zwahlen M, Kampf C, Wester K, Hober S,
et al: Towards a knowledge-based human protein atlas. Nature
Biotechnol. 28:1248–1250. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Koyama-Nasu R, Nasu-Nishimura Y, Todo T,
Ino Y, Saito N, Aburatani H, Funato K, Echizen K, Sugano H, Haruta
R, et al: The critical role of cyclin D2 in cell cycle progression
and tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem cells. Oncogene.
32:3840–3845. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|