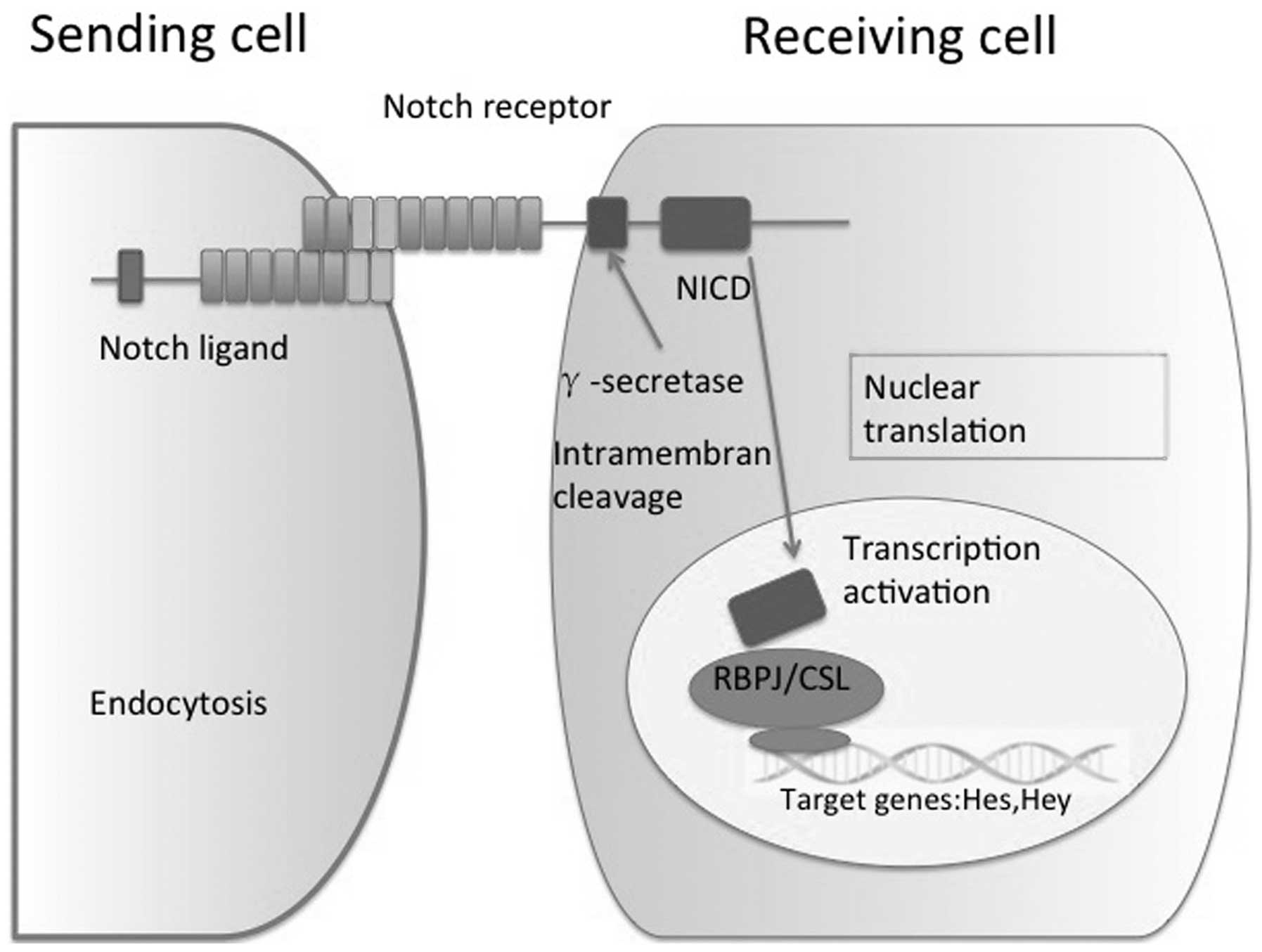
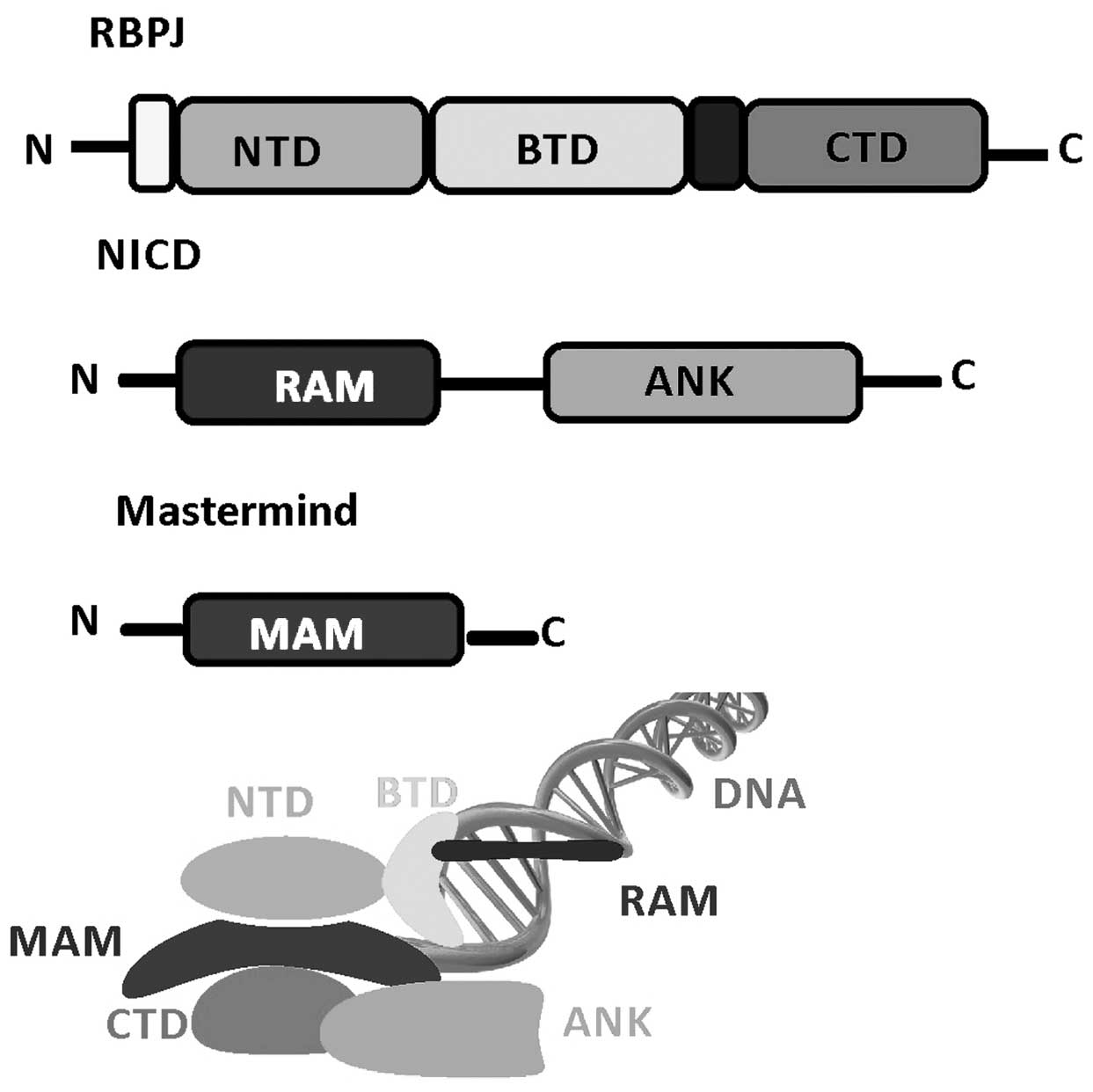
|
1
|
Tinkle CL and Haas-Kogan D: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: natural history, current management, and emerging tools.
Biologics. 6:207–219. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jie L, Fan W, Weiqi D, Yingqun Z, Ling X,
Miao S, Ping C and Chuanyong G: The hippo-yes association protein
pathway in liver cancer. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2013:1870702013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hackl C, Schlitt HJ, Kirchner GI, Knoppke
B and Loss M: Liver transplantation for malignancy: Current
treatment strategies and future perspectives. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:5331–5344. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lam PH, Obirieze AC, Ortega G, Nwokeabia
I, Onyewu S, Purnell SD, Samimi MM, Weeks CB, Lee EL, Shokrani B,
et al: Characterization of hepatitis B and C among liver transplant
recipients with hepatocellular carcinoma: An analysis of the
Nationwide Inpatient Sample Database. Transplant Proc. 48:123–127.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: Globocan 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang F, He L, Dai WQ, Xu YP, Wu D, Lin CL,
Wu SM, Cheng P, Zhang Y, Shen M, et al: Salinomycin inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis of human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 7:e506382012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dai W, Wang F, He L, Lin C, Wu S, Chen P,
Zhang Y, Shen M, Wu D, Wang C, et al: Genistein inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration by reversing the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Partial mediation by the
transcription factor NFAT1. Mol Carcinog. 54:301–311. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Roca C and Adams RH: Regulation of
vascular morphogenesis by notch signaling. Genes Dev. 21:2511–2524.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dou GR, Wang YC, Hu XB, Hou LH, Wang CM,
Xu JF, Wang YS, Liang YM, Yao LB, Yang AG and Han H: RBP-J, the
transcription factor downstream of Notch receptors, is essential
for the maintenance of vascular homeostasis in adult mice. FASEB J.
22:1606–1617. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fortini ME: Notch signaling: The core
pathway and its posttranslational regulation. Dev Cell. 16:633–647.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Coffinier C, Gresh L, Fiette L, Tronche F,
Schütz G, Babinet C, Pontoglio M, Yaniv M and Barra J: Bile system
morphogenesis defects and liver dysfunction upon targeted deletion
of HNF1beta. Development. 129:1829–1838. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zong Y, Panikkar A, Xu J, Antoniou A,
Raynaud P, Lemaigre F and Stanger BZ: Notch signaling controls
liver development by regulating biliary differentiation.
Development. 136:1727–1739. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Morell CM, Fiorotto R, Fabris L and
Strazzabosco M: Notch signalling beyond liver development: emerging
concepts in liver repair and oncogenesis. Clin Res Hepatol
Gastroenterol. 37:447–454. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ahn KJ, Yoon JK, Kim GB, Kwon BS, Go JM,
Moon JS, Bae EJ and Noh CI: Alagille syndrome and a JAG1 mutation:
41 Cases of experience at a single center. Korean J Pediatr.
58:392–397. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu X, Zuo Y, Sun W, Zhang W, Lv H, Huang
Y, Xiao J, Yuan Y and Wang Z: The genetic spectrum and the
evaluation of CADASIL screening scale in Chinese patients with
NOTCH3 mutations. J Neurol Sci. 354:63–69. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Oda T, Elkahloun AG, Pike BL, Okajima K,
Krantz ID, Genin A, Piccoli DA, Meltzer PS, Spinner NB, Collins FS
and Chandrasekharappa SC: Mutations in the human Jagged1 gene are
responsible for alagille syndrome. Nat Genet. 16:235–242. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Brooks AS and Dooijes D: From gene to
disease: Arteriohepatic dysplasia or Alagille syndrome. Ned
Tijdschr Geneeskd. 147:1213–1215. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
McDaniell R, Warthen DM, Sanchez-Lara PA,
Pai A, Krantz ID, Piccoli DA and Spinner NB: NOTCH2 mutations cause
alagille syndrome, a heterogeneous disorder of the notch signaling
pathway. Am J Hum Genet. 79:169–173. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Habib R, Dommergues JP, Gubler MC,
Hadchouel M, Gautier M, Odievre M and Alagille D: Glomerular
mesangiolipidosis in alagille syndrome (arteriohepatic dysplasia).
Pediatr Nephrol. 1:455–464. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nyfeler Y, Kirch RD, Mantei N, Leone DP,
Radtke F, Suter U and Taylor V: Jagged1 signals in the postnatal
subventricular zone are required for neural stem cell self-renewal.
EMBO J. 24:3504–3515. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gridley T: Notch signaling in the
vasculature. Curr Top Dev Biol. 92:277–309. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cheng P, Dai W, Wang F, Lu J, Shen M, Chen
K, Li J, Zhang Y, Wang C, Yang J, et al: Ethyl pyruvate inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma via
regulation of the HMGB1-RAGE and AKT pathways. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 443:1162–1168. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Croquelois A, Blindenbacher A, Terracciano
L, Wang X, Langer I, Radtke F and Heim MH: Inducible inactivation
of Notch1 causes nodular regenerative hyperplasia in mice.
Hepatology. 41:487–496. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dill MT, Rothweiler S, Djonov V, Hlushchuk
R, Tornillo L, Terracciano L, Meili-Butz S, Radtke F, Heim MH and
Semela D: Disruption of Notch1 induces vascular remodeling,
intussusceptive angiogenesis and angiosarcomas in livers of mice.
Gastroenterolog. 142:967–977. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Geisler F, Nagl F, Mazur PK, Lee M,
Zimber-Strobl U, Strobl LJ, Radtke F, Schmid RM and Siveke JT:
Liver-specific inactivation of Notch2, but not Notch1, compromises
intrahepatic bile duct development in mice. Hepatology. 48:607–616.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen JY, Feng L, Zhang HL, Li JC, Yang XW,
Cao XL, Liu L, Qin HY, Liang YM and Han H: Differential regulation
of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells and endothelial
outgrowth cells by the notch signaling pathway. PLoS One.
7:e436432012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Krebs LT, Xue Y, Norton CR, Shutter JR,
Maguire M, Sundberg JP, Gallahan D, Closson V, Kitajewski J,
Callahan R, et al: Notch signaling is essential for vascular
morphogenesis in mice. Genes Dev. 14:1343–1352. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hofmann JJ, Zovein AC, Koh H, Radtke F,
Weinmaster G and Iruela-Arispe ML: Jagged1 in the portal vein
mesenchyme regulates intrahepatic bile duct development: Insights
into alagille syndrome. Development. 137:4061–4072. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang R, Lan Y, Chapman HD, Shawber C,
Norton CR, Serreze DV, Weinmaster G and Gridley T: Defects in limb,
craniofacial and thymic development in Jagged2 mutant mice. Genes
Dev. 12:1046–1057. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Redeker C, Schuster-Gossler K, Kremmer E
and Gossler A: Normal development in mice over-expressing the
intracellular domain of DLL1 argues against reverse signaling by
DLL1 in vivo. PLoS One. 8:e790502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Djokovic D, Trindade A, Gigante J, Badenes
M, Silva L, Liu R, Li X, Gong M, Krasnoperov V, Gill PS and Duarte
A: Combination of Dll4/Notch and Ephrin-B2/EphB4 targeted therapy
is highly effective in disrupting tumor angiogenesis. BMC Cancer.
10:6412010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Turnpenny PD, Whittock N, Duncan J,
Dunwoodie S, Kusumi K and Ellard S: Novel mutations in DLL3, a
somitogenesis gene encoding a ligand for the Notch signalling
pathway, cause a consistent pattern of abnormal vertebral
segmentation in spondylocostal dysostosis. J Med Genet. 40:333–339.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gale NW, Dominguez MG, Noguera I, Pan L,
Hughes V, Valenzuela DM, Murphy AJ, Adams NC, Lin HC, Holash J,
Thurston G and Yancopoulos GD: Haploinsufficiency of delta-like 4
ligand results in embryonic lethality due to major defects in
arterial and vascular development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:15949–15954. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Traustadóttir GÁ, Jensen CH, Thomassen M,
Beck HC, Mortensen SB, Laborda J, Baladrón V, Sheikh SP and
Andersen DC: Evidence of non-canonical NOTCH signaling: Delta-like
1 homolog (DLK1) directly interacts with the NOTCH1 receptor in
mammals. Cell Signal. 28:246–254. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hayashi T, Gust KM, Wyatt AW, Goriki A,
Jäger W, Awrey S, Li N, Oo HZ, Altamirano-Dimas M, Buttyan R, et
al: Not all NOTCH Is Created Equal: The Oncogenic Role of NOTCH2 in
Bladder Cancer and Its Implications for Targeted Therapy. Clin
Cancer Res. Jan 14–2016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Conlon RA, Reaume AG and Rossant J: Notch1
is required for the coordinate segmentation of somites.
Development. 121:1533–1545. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Swiatek PJ, Lindsell CE, del Amo FF,
Weinmaster G and Gridley T: Notch1 is essential for
postimplantation development in mice. Genes Dev. 8:707–719. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kamath BM, Bauer RC, Loomes KM, Chao G,
Gerfen J, Hutchinson A, Hardikar W, Hirschfield G, Jara P, Krantz
ID, et al: NOTCH2 mutations in Alagille syndrome. J Med Genet.
49:138–144. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jeliazkova P1, Jörs S, Lee M,
Zimber-Strobl U, Ferrer J, Schmid RM, Siveke JT and Geisler F:
Canonical Notch2 signaling determines biliary cell fates of
embryonic hepatoblasts and adult hepatocytes independent of Hes1.
Hepatology. 57:2469–2479. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Falix FA, Aronson DC, Lamers WH and
Gaemers IC: Possible roles of DLK1 in the notch pathway during
development and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1822:988–995. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pippucci T, Maresca A, Magini P, Cenacchi
G, Donadio V, Palombo F, Papa V, Incensi A, Gasparre G, Valentino
ML, et al: Homozygous NOTCH3 null mutation and impaired NOTCH3
signaling in recessive early-onset arteriopathy and cavitating
leukoencephalopathy. EMBO Mol Med. 7:848–858. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen YX, Weng ZH and Zhang SL: Notch3
regulates the activation of hepatic stellate cells. World J
Gastroenterol. 18:1397–1403. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Carlson TR, Yan Y, Wu X, Lam MT, Tang GL,
Beverly LJ, Messina LM, Capobianco AJ, Werb Z and Wang R:
Endothelial expression of constitutively active Notch4 elicits
reversible arteriovenous malformations in adult mice. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:9884–9889. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rocha SF, Lopes SS, Gossler A and Henrique
D: Dll1 and Dll4 function sequentially in the retina and pV2 domain
of the spinal cord to regulate neurogenesis and create cell
diversity. Dev Biol. 328:54–65. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
de Hrabĕ Angelis M, McIntyre J II and
Gossler A: Maintenance of somite borders in mice requires the delta
homologue DII1. Nature. 386:717–721. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Maemura K, Yoshikawa H, Yokoyama K, Ueno
T, Kurose H, Uchiyama K and Otsuki Y: Delta-like 3 is silenced by
methylation and induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 42:817–822. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Castel D, Mourikis P, Bartels SJ, Brinkman
AB, Tajbakhsh S and Stunnenberg HG: Dynamic binding of RBPJ is
determined by notch signaling status. Genes Dev. 27:1059–1071.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yuan Z, Friedmann DR, VanderWielen BD,
Collins KJ and Kovall RA: Characterization of CSL (CBF-1, Su (H),
Lag-1) mutants reveals differences in signaling mediated by Notch1
and Notch2. J Biol Chem. 287:34904–34916. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kopan R and Ilagan MX: The canonical notch
signaling pathway: Unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell.
137:216–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Borggrefe T and Oswald F: The notch
signaling pathway: Transcriptional regulation at notch target
genes. Cell Mol Life Sci. 66:1631–1646. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kovall RA and Blacklow SC: Mechanistic
insights into notch receptor signaling from structural and
biochemical studies. Curr Top Dev Biol. 92:31–71. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Clayton T, Poe MM, Rallapalli S, Biawat P,
Savić MM, Rowlett JK, Gallos G, Emala CW, Kaczorowski CC, Stafford
DC, Arnold LA and Cook JM: A Review of the Updated Pharmacophore
for the Alpha 5 GABA(A) Benzodiazepine Receptor Model. Int J Med
Chem. 2015:4302482015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zou JH, Xue TC, Sun C, Li Y, Liu BB, Sun
RX, Chen J, Ren ZG and Ye SL: Prognostic significance of Hes-1, a
downstream target of notch signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma
Asian Pac. J Cancer Prev. 16:3811–3816. 2015.
|
|
54
|
Friedmann DR and Kovall RA: Thermodynamic
and structural insights into CSL-DNA complexes. Protein Sci.
19:34–46. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Dai W, Wang C, Wang F, Wang Y, Shen M,
Chen K, Cheng P, Zhang Y, Yang J, Zhu R, et al: Anti-miR-197
inhibits migration in HCC cells by targeting KAI 1/CD82. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 446:541–548. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang H, Zou J, Zhao B, Johannsen E,
Ashworth T, Wong H, Pear WS, Schug J, Blacklow SC, Arnett KL, et
al: Genome-wide analysis reveals conserved and divergent features
of Notch1/RBPJ binding in human and murine T-lymphoblastic leukemia
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:14908–14913. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ridgway J, Zhang G, Wu Y, Stawicki S,
Liang WC, Chanthery Y, Kowalski J, Watts RJ, Callahan C, Kasman I,
et al: Inhibition of Dll4 signalling inhibits tumour growth by
deregulating angiogenesis. Nature. 444:1083–1087. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Sumazaki R, Shiojiri N, Isoyama S, Masu M,
Keino-Masu K, Osawa M, Nakauchi H, Kageyama R and Matsui A:
Conversion of biliary system to pancreatic tissue in Hes1-deficient
mice. Nat Genet. 36:83–87. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wolfe MS, Esler WP and Das C: Continuing
strategies for inhibiting alzheimer's gamma-secretase. J Mol
Neurosci. 19:83–87. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Tchorz JS, Kinter J, Müller M, Tornillo L,
Heim MH and Bettler B: Notch2 signaling promotes biliary epithelial
cell fate specification and tubulogenesis during bile duct
development in mice. Hepatology. 50:871–879. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhang QD, Xu MY, Cai XB, Qu Y, Li ZH and
Lu LG: Myofibroblastic transformation of rat hepatic stellate
cells: The role of Notch signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition regulation. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 19:4130–4138.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wen L, Liang C, Chen E, Chen W, Liang F,
Zhi X, Wei T, Xue F, Li G, Yang Q, Gong W, Feng X, Bai X and Liang
T: Regulation of Multi-drug Resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells is TRPC6/Calcium Dependent. Sci Rep. 6:232692016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Chen QY, Jiao DM, Wang J, Hu H, Tang X,
Chen J, Mou H and Lu W: miR-206 regulates cisplatin resistance and
EMT in human lung adenocarcinoma cells partly by targeting MET.
Oncotarget. Mar 21–2016.(Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.18632/oncotarget.8229. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Lombardo Y, Faronato M, Filipovic A,
Vircillo V, Magnani L and Coombes RC: Nicastrin and Notch4 drive
endocrine therapy resistance and epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in MCF7 breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res.
16:R622014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Espinoza I, Pochampally R, Xing F, Watabe
K and Miele L: Notch signaling: Targeting cancer stem cells and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Onco Targets Ther.
6:1249–1259. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kang H, An HJ, Song JY, Kim TH, Heo JH,
Ahn DH and Kim G: Notch3 and Jagged2 contribute to gastric cancer
development and to glandular differentiation associated with MUC2
and MUC5AC expression. Histopathology. 61:576–586. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kodama Y, Hijikata M, Kageyama R,
Shimotohno K and Chiba T: The role of notch signaling in the
development of intrahepatic bile ducts. Gastroenterology.
127:1775–1786. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Cheng HT, Kim M, Valerius MT, Surendran K,
Schuster-Gossler K, Gossler A, McMahon AP and Kopan R: Notch2, but
not Notch1, is required for proximal fate acquisition in the
mammalian nephron. Development. 134:801–811. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Loomes KM, Taichman DB, Glover CL,
Williams PT, Markowitz JE, Piccoli DA, Baldwin HS and Oakey RJ:
Characterization of notch receptor expression in the developing
mammalian heart and liver. Am J Med Genet. 112:181–189. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Pei J, Tang Z, Zang G and Yu Y: Blockage
of Notch1 signaling modulates the T-helper (Th)1/Th2 cell balance
in chronic hepatitis B patients. Hepatol Res. 40:799–805. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Nijjar SS, Crosby HA, Wallace L, Hubscher
SG and Strain AJ: Notch receptor expression in adult human liver: A
possible role in bile duct formation and hepatic
neovascularization. Hepatology. 34:1184–1192. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Alvaro D, Bragazzi MC, Benedetti A, Fabris
L, Fava G, Invernizzi P, Marzioni M, Nuzzo G, Strazzabosco M and
Stroffolini T: Cholangiocarcinoma in Italy: A national survey on
clinical characteristics, diagnostic modalities and treatment.
Results from the ‘Cholangiocarcinoma’ committee of the Italian
association for the study of liver disease. Dig Liver Dis.
43:60–65. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Lee JS, Heo J, Libbrecht L, Chu IS,
Kaposi-Novak P, Calvisi DF, Mikaelyan A, Roberts LR, Demetris AJ,
Sun Z, et al: A novel prognostic subtype of human hepatocellular
carcinoma derived from hepatic progenitor cells. Nat Med.
12:410–416. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Gao J, Chen Y, Wu KC, Liu J, Zhao YQ, Pan
YL, Du R, Zheng GR, Xiong YM, Xu HL and Fan DM: RUNX3 directly
interacts with intracellular domain of Notch1 and suppresses notch
signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res.
316:149–157. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Sekiya S and Suzuki A: Intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma can arise from Notch-mediated conversion of
hepatocytes. J Clin Invest. 122:3914–3918. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Weng AP and Aster JC: Multiple niches for
notch in cancer: Context is everything. Curr Opin Genet De.
14:48–54. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Lu J, Zhou Y, Hu T, Zhang H, Shen M, Cheng
P, Dai W, Wang F, Chen K, Zhang Y, et al: Notch Signaling
Coordinates Progenitor Cell-Mediated Biliary Regeneration Following
Partial Hepatectomy. Sci Rep. 6:227542016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Espinoza I and Miele L: Notch inhibitors
for cancer treatment. Pharmacol Ther. 139:95–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Hayashi Y, Osanai M and Lee GH: NOTCH2
signaling confers immature morphology and aggressiveness in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 34:1650–1658.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Kohn A, Rutkowski TP, Liu Z, Mirando AJ,
Zuscik MJ, O'Keefe RJ and Hilton MJ: Notch signaling controls
chondrocyte hypertrophy via indirect regulation of Sox9. Bone Res.
3:150212015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Fowlkes BJ and Robey EA: A reassessment of
the effect of activated Notch1 on CD4 and CD8 T cell development. J
Immunol. 169:1817–1821. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zhu R, Yang J, Xu L, Dai W, Wang F, Shen
M, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Chen K, Cheng P, et al: Diagnostic performance
of des-γ-carboxy prothrombin for hepatocellular carcinoma: A
meta-analysis. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2014:5293142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Nalesnik MA, Tseng G, Ding Y, Xiang GS,
Zheng ZL, Yu Y, Marsh JW, Michalopoulos GK and Luo JH: Gene
deletions and amplifications in human hepatocellular carcinomas:
Correlation with hepatocyte growth regulation. Am J Pathol.
180:1495–1508. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Villanueva A, Alsinet C, Yanger K, Hoshida
Y, Zong Y, Toffanin S, Rodriguez-Carunchio L, Solé M, Thung S,
Stanger BZ and Llovet JM: Notch signaling is activated in human
hepatocellular carcinoma and induces tumor formation in mice.
Gastroenterology. 143:1660–1669. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Fan B, Malato Y, Calvisi DF, Naqvi S,
Razumilava N, Ribback S, Gores GJ, Dombrowski F, Evert M, Chen X
and Willenbring H: Cholangiocarcinomas can originate from
hepatocytes in mice. J Clin Invest. 122:2911–2915. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Viatour P, Ehmer U, Saddic LA, Dorrell C,
Andersen JB, Lin C, Zmoos AF, Mazur PK, Schaffer BE, Ostermeier A,
et al: Notch signaling inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma following
inactivation of the RB pathway. J Exp Med. 208:1963–1976. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Vincent F, Bonnin P, Clemessy M, Contrerès
JO, Lamandé N, Gasc JM, Vilar J, Hainaud P, Tobelem G, Corvol P and
Dupuy E: Angiotensinogen delays angiogenesis and tumor growth of
hepatocarcinoma in transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 69:2853–2860. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Wang F, Dai W, Wang Y, Shen M, Chen K,
Cheng P, Zhang Y, Wang C, Li J, Zheng Y, et al: The synergistic in
vitro and in vivo antitumor effect of combination therapy with
salinomycin and 5-fluorouracil against hepatocellular carcinoma.
PLoS One. 9:e974142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Sekiya S and Suzuki A: Intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma can arise from notch-mediated conversion of
hepatocytes. J Clin Invest. 122:3914–3918. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Ishimura N, Bronk SF and Gores GJ:
Inducible nitric oxide synthase up-regulates notch-1 in mouse
cholangiocytes: Implications for carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology.
128:1354–1368. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Roma J, Masià A, Reventós J, de Sánchez
Toledo J and Gallego S: Notch Pathway Inhibition Significantly
Reduces Rhabdomyosarcoma Invasiveness and Mobility. Vitro Clin
Cancer Res. 17:505–513. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Olsauskas-Kuprys R, Zlobin A and Osipo C:
Gamma secretase inhibitors of notch signaling. Onco Targets Ther.
6:943–955. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|