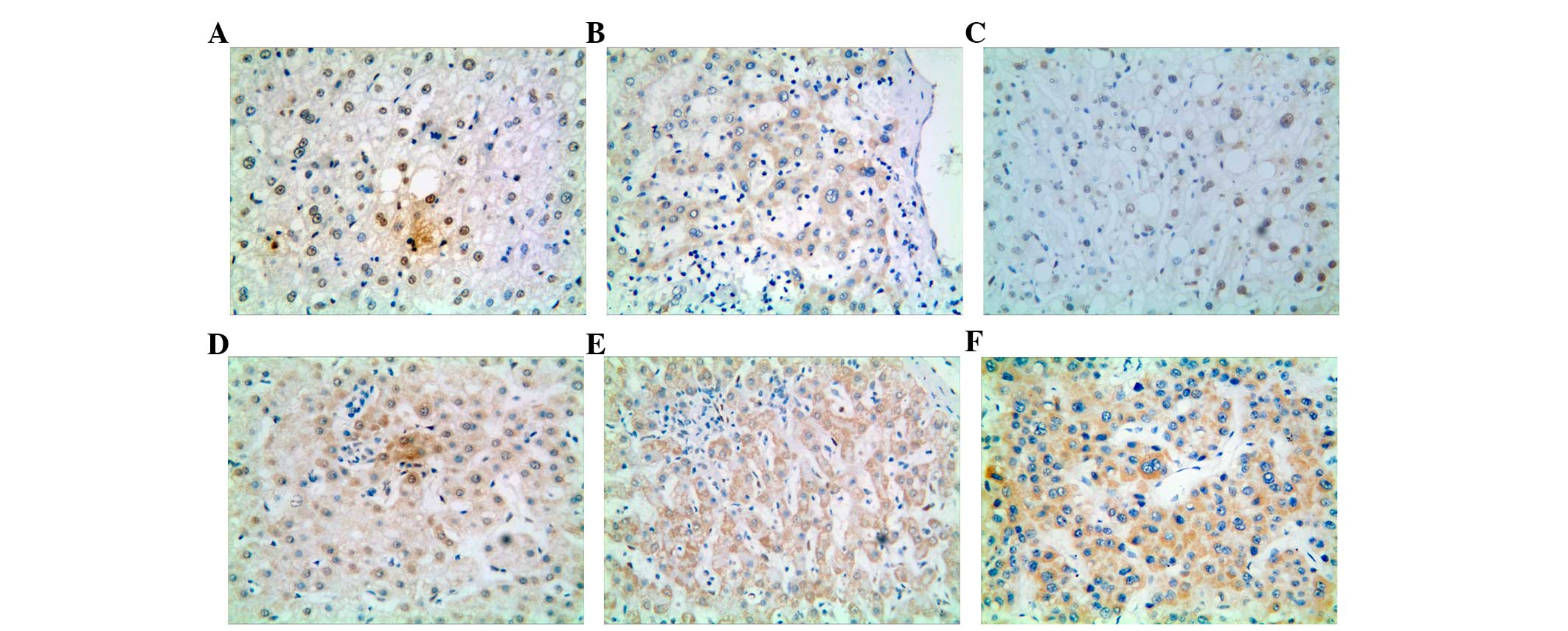
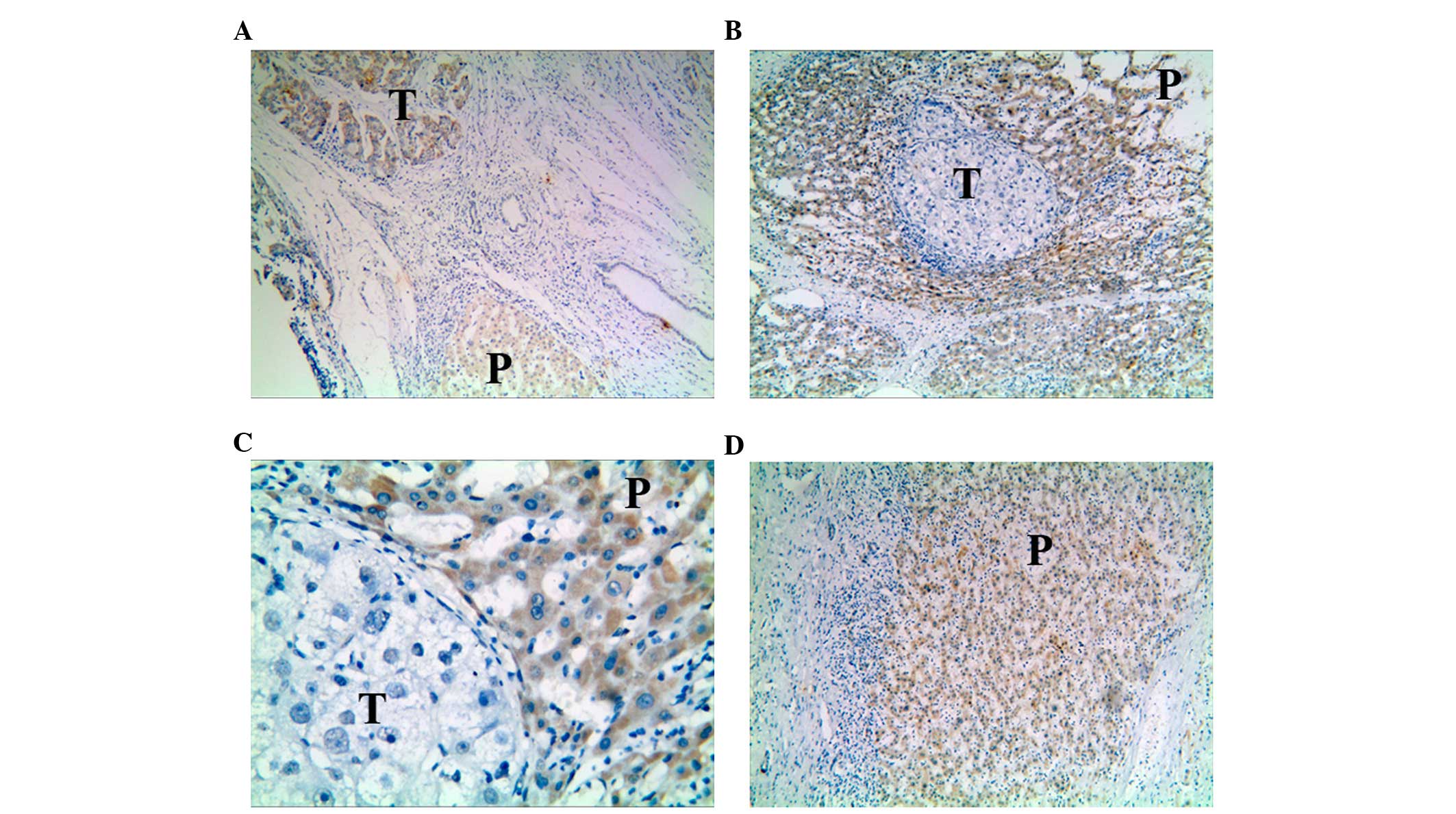
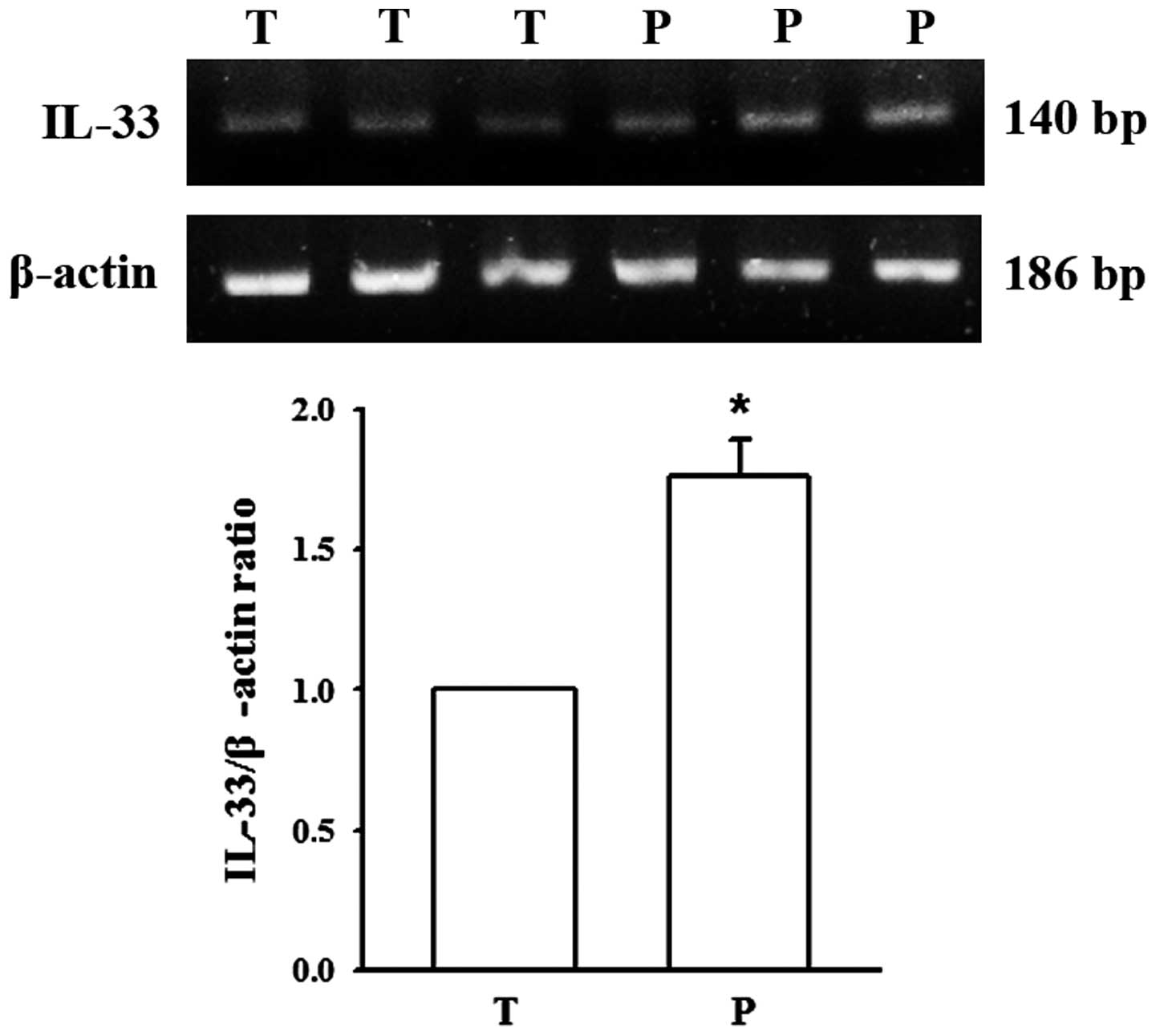
|
1
|
Marx J: Cancer research. Inflammation and
cancer: The link grows stronger. Science. 306:966–968. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hofseth LJ and Ying L: Identifying and
defusing weapons of mass inflammation in carcinogenesis. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1765:74–84. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chew V, Tow C, Teo M, et al: Inflammatory
tumour microenvironment is associated with superior survival in
hepatocellular carcinoma patients. J Hepatol. 52:370–379. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wong CM and Ng IO: Molecular pathogenesis
of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 28:160–174. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y,
Murphy E, McClanahan TK, Zurawski G, Moshrefi M, Qin J, Li X, et
al: IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1
receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated
cytokines. Immunity. 23:479–490. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Milovanovic M, Volarevic V, Radosavljevic
G, Jovanovic I, Pejnovic N, Arsenijevic N and Lukic ML: IL-33/ST2
axis in inflammation and immunopathology. Immunol Res. 52:89–99.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Carriere V, Roussel L, Ortega N, Lacorre
DA, Americh L, Aguilar L, Bouche G and Girard JP: IL-33, the
IL-1-like cytokine ligand for ST2 receptor, is a
chromatin-associated nuclear factor in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 104:282–287. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen SF, Nieh S, Jao SW, Wu MZ, Liu CL,
Chang YC and Lin YS: The paracrine effect of cancer-associated
fibroblast-induced interleukin-33 regulates the invasiveness of
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Pathol. 231:180–189. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jovanovic IP, Pejnovic NN, Radosavljevic
GD, Pantic JM, Milovanovic MZ, Arsenijevic NN and Lukic ML:
Interleukin-33/ST2 axis promotes breast cancer growth and
metastases by facilitating intratumoral accumulation of
immunosuppressive and innate lymphoid cells. Int J Cancer.
134:1669–1682. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun P, Ben Q, Tu S, Dong W, Qi X and Wu Y:
Serum interleukin-33 levels in patients with gastric cancer. Dig
Dis Sci. 56:3596–3601. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hu LA, Fu Y, Zhang DN and Zhang J: Serum
IL-33 as a diagnostic and prognostic marker in non-small cell lung
cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:2563–2566. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu J, Shen JX, Hu JL, Huang WH and Zhang
GJ: Significance of interleukin-33 and its related cytokines in
patients with breast cancers. Front Immunol. 5:1412014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bonilla WV, Fröhlich A, Senn K, Kallert S,
Fernandez M, Johnson S, Kreutzfeldt M, Hegazy AN, Schrick C, Fallon
PG, et al: The alarmin interleukin-33 drives protective antiviral
CD8+ T cell responses. Science. 335:984–989. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Arshad MI, Rauch M, L'Helgoualc'h A, Julia
V, Leite-de-Moraes MC, Lucas-Clerc C, Piquet-Pellorce C and Samson
M: NKT cells are required to induce high IL-33 expression in
hepatocytes during ConA-induced acute hepatitis. Eur J Immunol.
41:2341–2348. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang J, Cai Y, Ji H, Feng J, Ayana DA, Niu
J and Jiang Y: Serum IL-33 levels are associated with liver damage
in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Interferon Cytokine Res.
32:248–253. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Marvie P, Lisbonne M, L'Helgoualc'h A,
Rauch M, Turlin B, Preisser L, Bourd-Boittin K, Théret N, Gascan H,
Piquet-Pellorce C and Samson M: Interleukin-33 overexpression is
associated with liver fibrosis in mice and humans. J Cell Mol Med.
14:1726–1739. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang P, Liu XK, Chu Z, Ye JC, Li KL,
Zhuang WL, Yang DJ and Jiang YF: Detection of interleukin-33 in
serum and carcinoma tissue from patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma and its clinical implications. J Int Med Res.
40:1654–1661. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bergis D, Kassis V, Ranglack A, Koeberle
V, Piiper A, Kronenberger B, Zeuzem S, Waidmann O and Radeke HH:
High serum levels of the interleukin-33 receptor soluble ST2 as a
negative prognostic factor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Transl
Oncol. 6:311–318. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sakai N, Van Sweringen HL, Quillin RC,
Schuster R, Blanchard J, Burns JM, Tevar AD, Edwards MJ and Lentsch
AB: Interleukin-33 is hepatoprotective during liver
ischemia/reperfusion in mice. Hepatology. 56:1468–1478. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Edmondson HA and Steiner PE: Primary
carcinoma of the liver: A study of 100 cases among 48,900
necropsies. Cancer. 7:462–503. 1954. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zheng R, Wang J, Wu Q, Wang Z, Ou Y, Ma L,
Wang M, Wang J and Yang Y: Expression of ALDH1 and TGFβ2 in benign
and malignant breast tumors and their prognostic implications. Int
J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:4173–4183. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
He XD, Wang Y, Wu Q, Wang HX, Chen ZD,
Zheng RS, Wang ZS, Wang JB and Yang Y: Xuebijing protects rats from
sepsis challenged with acinetobacter baumannii by promoting annexin
A1 expression and inhibiting proinflammatory cytokines secretion.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:8049402013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Goncalves CK, Fregnani ER, Leon JE,
Silva-Sousa YT and Perez DE: Immunohistochemical expression of p63,
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and notch-1 in radicular
cysts, dentigerous cysts and keratocystic odontogenic tumors. Braz
Dent J. 23:337–343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang Y, Qin SK, Wu Q, Wang ZS, Zheng RS,
Tong XH, Liu H, Tao L and He XD: Connexin-dependent gap junction
enhancement is involved in the synergistic effect of sorafenib and
all-trans retinoic acid on HCC growth inhibition. Oncol Rep.
31:540–550. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang DY and Friedman SL:
Fibrosis-dependent mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology.
56:769–775. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Baekkevold ES, Roussigné M, Yamanaka T,
Johansen FE, Jahnsen FL, Amalric F, Brandtzaeg P, Erard M,
Haraldsen G and Girard JP: Molecular characterization of NF-HEV, a
nuclear factor preferentially expressed in human high endothelial
venules. Am J Pathol. 163:69–79. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hayakawa H, Hayakawa M, Kume A and
Tominaga S: Soluble ST2 blocks interleukin-33 signaling in allergic
airway inflammation. J Biol Chem. 282:26369–26380. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Arend WP, Palmer G and Gabay C: IL-1,
IL-18, and IL-33 families of cytokines. Immunol Rev. 223:20–38.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lüthi AU, Cullen SP, McNeela EA, Duriez
PJ, Afonina IS, Sheridan C, Brumatti G, Taylor RC, Kersse K,
Vandenabeele P, et al: Suppression of interleukin-33 bioactivity
through proteolysis by apoptotic caspases. Immunity. 31:84–98.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cayrol C and Girard JP: The IL-1-like
cytokine IL-33 is inactivated after maturation by caspase-1. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:9021–9026. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kunes P, Holubcová Z, Kolácková M and
Krejsek J: The counter-regulation of atherogenesis: A role for
interleukin-33. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 53:125–129.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Miller AM: Role of IL-33 in inflammation
and disease. J Inflamm (Lond). 8:222011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|