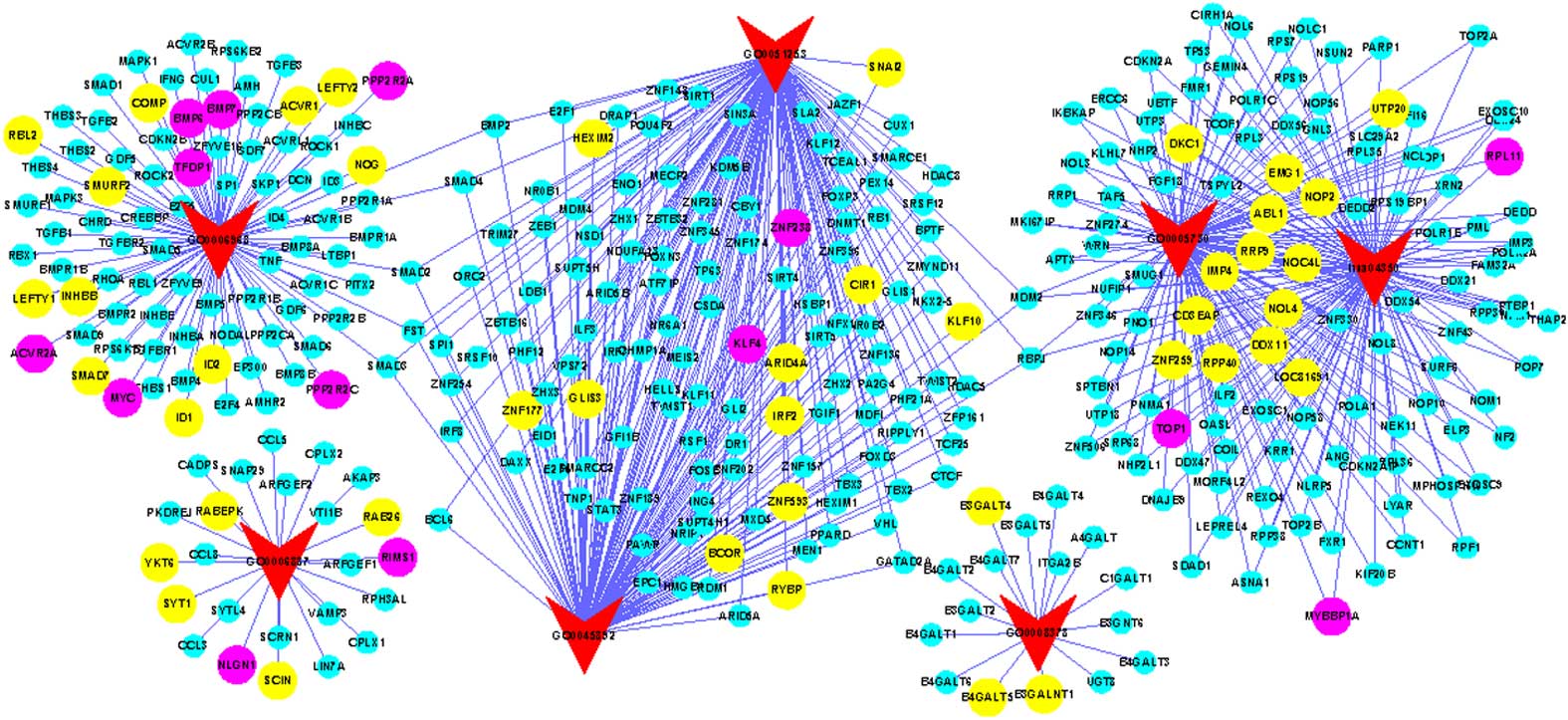
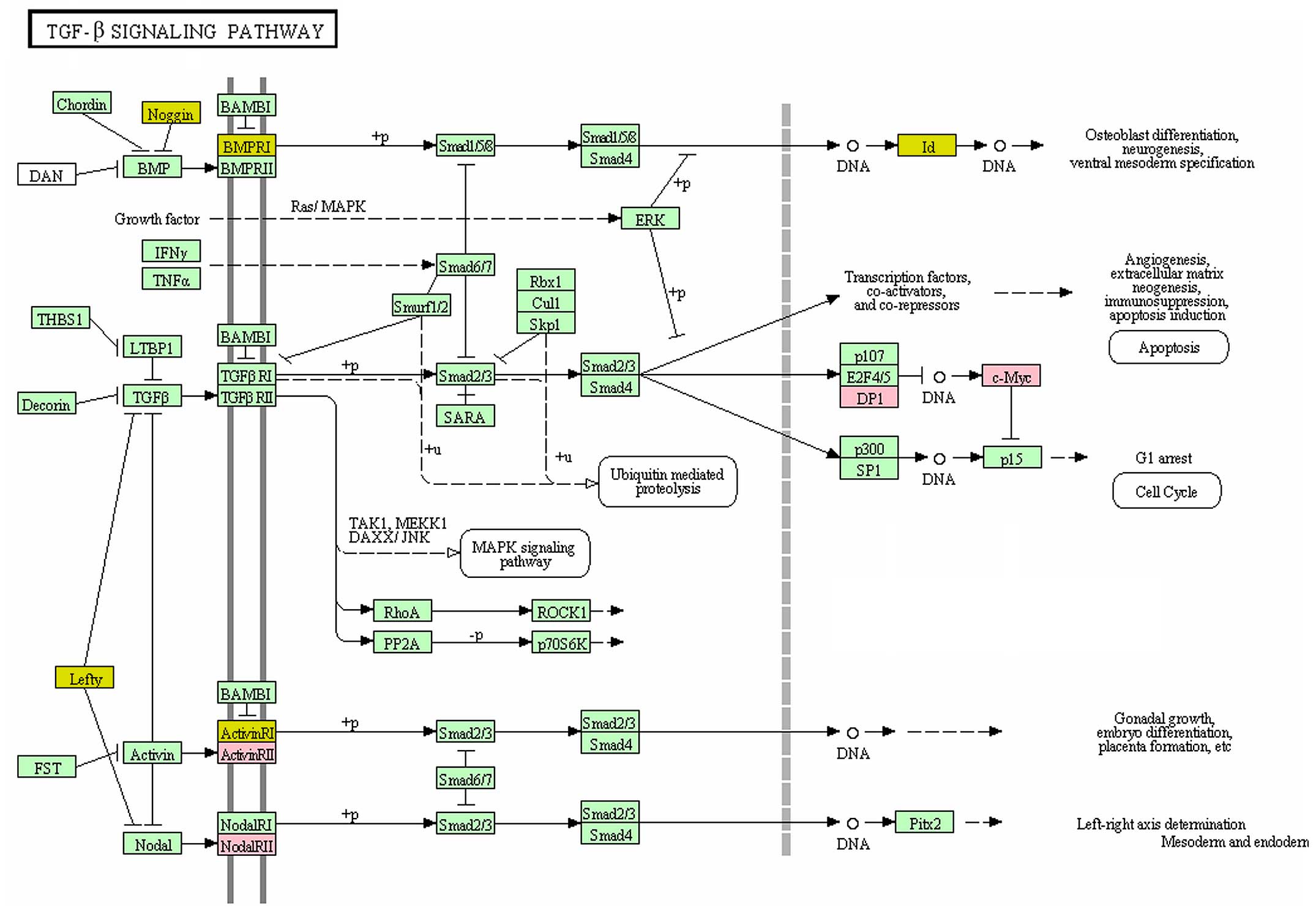
|
1
|
Thomas J, Kim M, Balakrishnan L, Nanjappa
V, Raju R, Marimuthu A, Radhakrishnan A, Muthusamy B, Khan AA,
Sakamuri S, et al: Pancreatic cancer database: An integrative
resource for pancreatic cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 15:963–967. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lowenfels AB and Maisonneuve P:
Epidemiology and risk factors for pancreatic cancer. Best Pract Res
Clin Gastroenterol. 20:197–209. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hruban RH, Adsay NV, Albores-Saavedra J,
Compton C, Garrett ES, Goodman SN, Kern SE, Klimstra DS, Klöppel G,
Longnecker DS, et al: Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia: A new
nomenclature and classification system for pancreatic duct lesions.
Am J Surg Pathol. 25:579–586. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Griffin CA, Hruban RH, Long PP, Morsberger
LA, Douna-Issa F and Yeo CJ: Chromosome abnormalities in pancreatic
adenocarcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 9:93–100. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sarkar FH, Banerjee S and Li Y: Pancreatic
cancer: Pathogenesis, prevention and treatment. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 224:326–336. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thayer SP, di Magliano MP, Heiser PW,
Nielsen CM, Roberts DJ, Lauwers GY, Qi YP, Gysin S, Fernández-del
Castillo C, Yajnik V, et al: Hedgehog is an early and late mediator
of pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis. Nature. 425:851–856. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Strimpakos A, Saif MW and Syrigos KN:
Pancreatic cancer: From molecular pathogenesis to targeted therapy.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 27:495–522. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hingorani SR, Petricoin EF, Maitra A,
Rajapakse V, King C, Jacobetz MA, Ross S, Conrads TP, Veenstra TD,
Hitt BA, et al: Preinvasive and invasive ductal pancreatic cancer
and its early detection in the mouse. Cancer Cell. 4:437–450. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Goldstein AM, Fraser MC, Struewing JP,
Hussussian CJ, Ranade K, Zametkin DP, Fontaine LS, Organic SM,
Dracopoli NC, Clark WH Jr, et al: Increased risk of pancreatic
cancer in melanoma-prone kindreds with p16INK4 mutations. N Engl J
Med. 333:970–975. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pellegata N, Sessa F, Renault B, Bonato M,
Leone BE, Solcia E and Ranzani GN: K-ras and p53 gene mutations in
pancreatic cancer: Ductal and nonductal tumors progress through
different genetic lesions. Cancer Res. 54:1556–1560.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Grau AM, Zhang L, Wang W, Ruan S, Evans
DB, Abbruzzese JL, Zhang W and Chiao PJ: Induction of p21waf1
expression and growth inhibition by transforming growth factor beta
involve the tumor suppressor gene DPC4 in human pancreatic
adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 57:3929–3934. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sorio C, Baron A, Orlandini S, Zamboni G,
Pederzoli P, Huebner K and Scarpa A: The FHIT gene is expressed in
pancreatic ductular cells and is altered in pancreatic cancers.
Cancer Res. 59:1308–1314. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jones S, Zhang X, Parsons DW, Lin JC,
Leary RJ, Angenendt P, Mankoo P, Carter H, Kamiyama H, Jimeno A, et
al: Core signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancers revealed by
global genomic analyses. Science. 321:1801–1806. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Biankin AV, Waddell N, Kassahn KS, Gingras
MC, Muthuswamy LB, Johns AL, Miller DK, Wilson PJ, Patch AM, Wu J,
et al: Pancreatic cancer genomes reveal aberrations in axon
guidance pathway genes. Nature. 491:399–405. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rosenfeldt MT, O'Prey J, Morton JP, Nixon
C, MacKay G, Mrowinska A, Au A, Rai TS, Zheng L, Ridgway R, et al:
p53 status determines the role of autophagy in pancreatic tumour
development. Nature. 504:296–300. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cantor RM, Lange K and Sinsheimer JS:
Prioritizing GWAS results: A review of statistical methods and
recommendations for their application. Am J Hum Genet. 86:6–22.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Croteau-Chonka DC, Qiu W, Carey VJ, Weiss
ST and Raby BA: Gene set enrichment analyses of gene expression
associations with asthma control hint at candidate drug pathways.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 189:A52742014.
|
|
18
|
Kato S, Hayakawa Y, Sakurai H, Saiki I and
Yokoyama S: Mesenchymal-transitioned cancer cells instigate the
invasion of epithelial cancer cells through secretion of WNT3 and
WNT5B. Cancer Sci. 105:281–289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu H and Liu B: CPEB4 is a candidate
biomarker for defining metastatic cancers and directing
personalized therapies. Med Hypotheses. 81:875–877. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gröger C: The role of Neuropilin 2 in
hepatocellular carcinoma: From meta-analysis to target
characterization. Journal. 2013.
|
|
21
|
Amundadottir L, Kraft P,
Stolzenberg-Solomon RZ, Fuchs CS, Petersen GM, Arslan AA,
Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, Gross M, Helzlsouer K, Jacobs EJ, et al:
Genome-wide association study identifies variants in the ABO locus
associated with susceptibility to pancreatic cancer. Nat Genet.
41:986–990. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Maupin KA, Sinha A, Eugster E, Miller J,
Ross J, Paulino V, Keshamouni VG, Tran N, Berens M, Webb C and Haab
BB: Glycogene expression alterations associated with pancreatic
cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition in complementary model
systems. PloS One. 5:e130022010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Joslyn G, Ravindranathan A, Brush G,
Schuckit M and White RL: Human variation in alcohol response is
influenced by variation in neuronal signaling genes. Alcohol Clin
Exp Res. 34:800–812. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mootha VK, Lindgren CM, Eriksson KF,
Subramanian A, Sihag S, Lehar J, Puigserver P, Carlsson E,
Ridderstråle M, Laurila E, et al: PGC-1alpha-responsive genes
involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately
downregulated in human diabetes. Nat Genet. 34:267–273. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Furumichi M
and Tanabe M: KEGG for integration and interpretation of
large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 40(Database
Issue): D109–D114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rice WR: A consensus combined P-value test
and the family-wide significance of component tests. Biometrics.
303–308. 1990. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Edwards YJ, Beecham GW, Scott WK, Khuri S,
Bademci G, Tekin D, Martin ER, Jiang Z, Mash DC, ffrench-Mullen J,
et al: Identifying consensus disease pathways in Parkinson's
disease using an integrative systems biology approach. PLoS One.
6:e169172011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Unsicker K, Spittau B and Krieglstein K:
The multiple facets of the TGF-β family cytokine
growth/differentiation factor-15/macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 24:373–384. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shi Y and Massagué J: Mechanisms of
TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell.
113:685–700. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Murre C, McCaw PS and Baltimore D: A new
DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer
binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 56:777–783.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dang CV: MYC on the path to cancer. Cell.
149:22–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dominguez-Sola D, Ying CY, Grandori C,
Ruggiero L, Chen B, Li M, Galloway DA, Gu W, Gautier J and
Dalla-Favera R: Non-transcriptional control of DNA replication by
c-Myc. Nature. 448:445–451. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Asano T, Yao Y, Zhu J, Li D, Abbruzzese JL
and Reddy SA: The PI 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway is activated
due to aberrant Pten expression and targets transcription factors
NF-kappaB and c-Myc in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene.
23:8571–8580. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Grippo PJ and Sandgren EP:
Acinar-to-ductal metaplasia accompanies c-myc-induced exocrine
pancreatic cancer progression in transgenic rodents. Int J Cancer.
131:1243–1248. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Köenig A, Linhart T, Schlengemann K,
Reutlinger K, Wegele J, Adler G, Singh G, Hofmann L, Kunsch S, Büch
T, et al: NFAT-induced histone acetylation relay switch promotes
c-Myc-dependent growth in pancreatic cancer cells.
Gastroenterology. 138:1189–1199, e1–e2. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Calzone L, Gelay A, Zinovyev A, Radvanyi F
and Barillot E: A comprehensive modular map of molecular
interactions in RB/E2F pathway. Mol Syst Biol. 4:1732008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Abba MC, Fabris VT, Hu Y, Kittrell FS, Cai
WW, Donehower LA, Sahin A, Medina D and Aldaz CM: Identification of
novel amplification gene targets in mouse and human breast cancer
at a syntenic cluster mapping to mouse ch8A1 and human ch13q34.
Cancer Res. 67:4104–4112. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tarragona M, Pavlovic M, Arnal-Estapé A,
Urosevic J, Morales M, Guiu M, Planet E, González-Suárez E and
Gomis RR: Identification of NOG as a specific breast cancer bone
metastasis-supporting gene. J Biol Chem. 287:21346–21355. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yasui K, Okamoto H, Arii S and Inazawa J:
Association of over-expressed TFDP1 with progression of
hepatocellular carcinomas. J Hum Genet. 48:609–613. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kebebew E, Peng M, Treseler PA, Clark OH,
Duh QY, Ginzinger D and Miner R: Id1 gene expression is
up-regulated in hyperplastic and neoplastic thyroid tissue and
regulates growth and differentiation in thyroid cancer cells. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 89:6105–6111. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gumireddy K, Li A, Gimotty PA,
Klein-Szanto AJ, Showe LC, Katsaros D, Coukos G, Zhang L and Huang
Q: KLF17 is a negative regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and metastasis in breast cancer. Nat Cell Biol.
11:1297–1304. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
D'Abronzo FH, Swearingen B, Klibanski A
and Alexander JM: Mutational Analysis of activin/transforming
growth factor-beta type I and type II receptor kinases in human
pituitary tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 84:1716–1721. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Casey B and Hackett BP: Left-right axis
malformations in man and mouse. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 10:257–261.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shore EM, Xu M, Feldman GJ, Fenstermacher
DA, Cho TJ, Choi IH, Connor JM, Delai P, Glaser DL, LeMerrer M, et
al: A recurrent mutation in the BMP type I receptor ACVR1 causes
inherited and sporadic fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. Nat
Genet. 38:525–527. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Masui T, Long Q, Beres TM, Magnuson MA and
MacDonald RJ: Early pancreatic development requires the vertebrate
Suppressor of Hairless (RBPJ) in the PTF1 bHLH complex. Genes Dev.
21:2629–2643. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sasaki M, Kawahara K, Nishio M, Mimori K,
Kogo R, Hamada K, Itoh B, Wang J, Komatsu Y, Yang YR, et al:
Regulation of the MDM2-P53 pathway and tumor growth by PICT1 via
nucleolar RPL11. Nat Med. 17:944–951. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mayo LD and Donner DB: A
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway promotes translocation of
Mdm2 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:11598–11603. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Greuber EK, Smith-Pearson P, Wang J and
Pendergast AM: Role of ABL family kinases in cancer: From leukaemia
to solid tumours. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:559–571. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Shaul Y and Ben-Yehoyada M: Role of c-Abl
in the DNA damage stress response. Cell Res. 15:33–35. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Barilá D and Superti-Furga G: An
intramolecular SH3-domain interaction regulates c-Abl activity. Nat
Genet. 18:280–282. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Greither T, Grochola LF, Udelnow A,
Lautenschläger C, Würl P and Taubert H: Elevated expression of
microRNAs 155, 203, 210 and 222 in pancreatic tumors is associated
with poorer survival. Int J Cancer. 126:73–80. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|