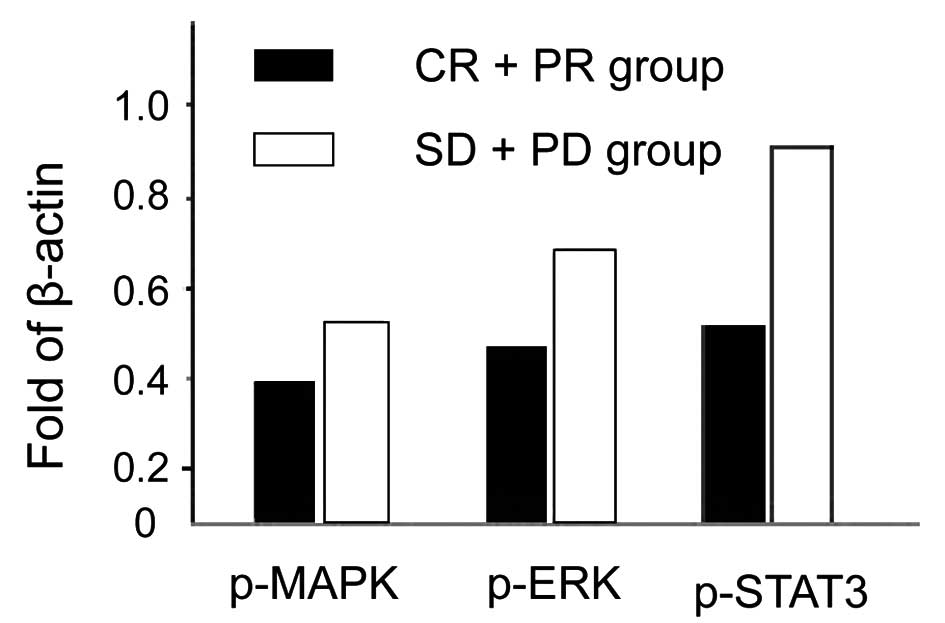
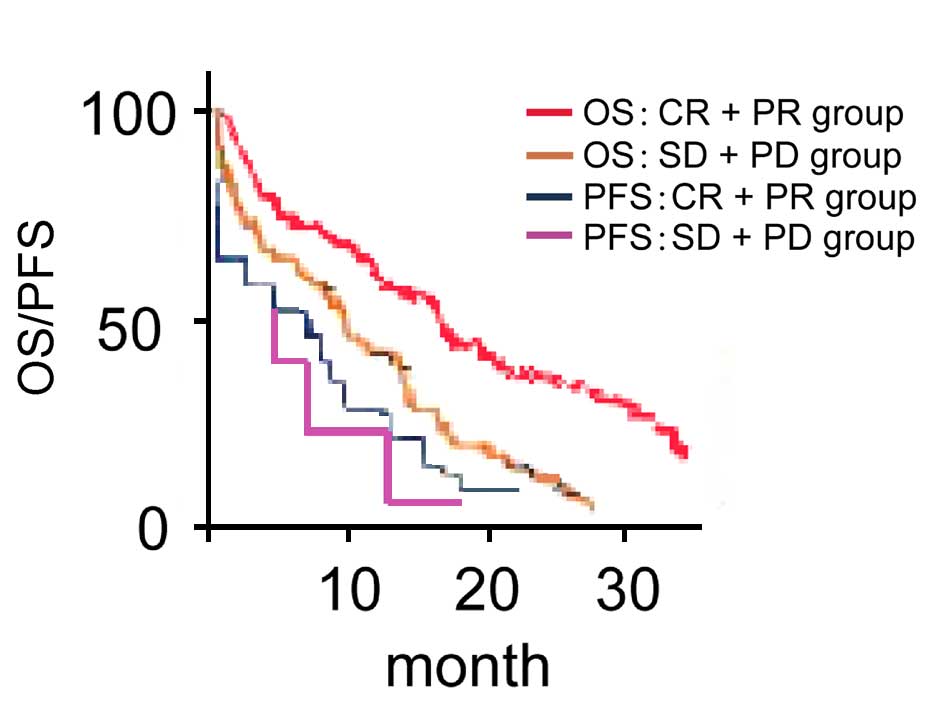
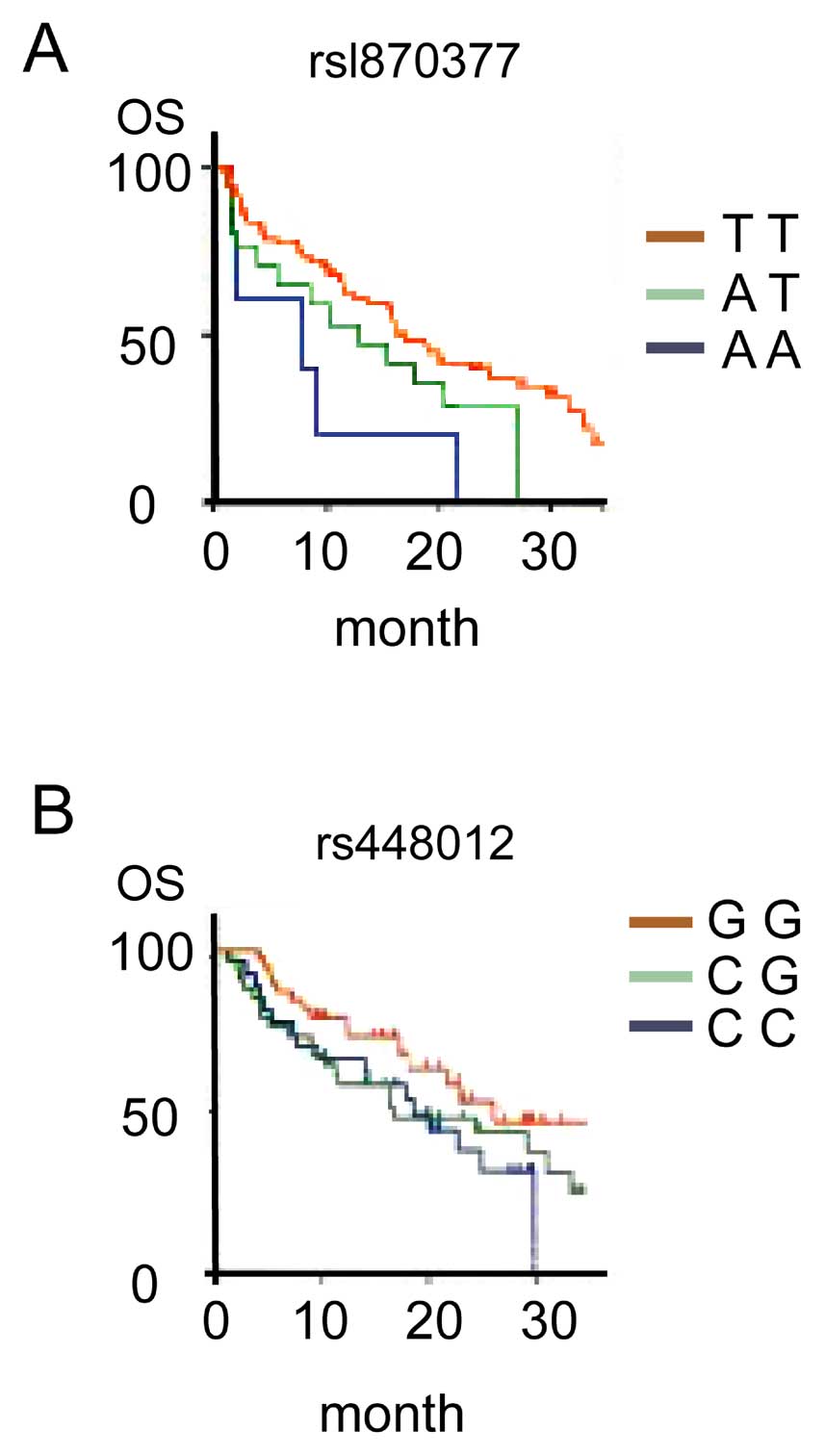
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2011: The impact of eliminating socioeconomic
and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:212–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zimmermann K, Schmittel A, Steiner U,
Asemissen AM, Knoedler M, Thiel E, Miller K and Keilholz U:
Sunitinib treatment for patients with advanced clear-cell
renal-cell carcinoma after progression on sorafenib. Oncology.
76:350–354. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P,
Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik
C, Kim ST, et al: Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic
renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 356:115–124. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yamamoto K, Mizumoto A, Nishimura K, Uda
A, Mukai A, Yamashita K, Kume M, Makimoto H, Bito T, Nishigori C,
et al: Association of toxicity of sorafenib and sunitinib for human
keratinocytes with inhibition of signal transduction and activator
of transcription 3 (STAT3). PLoS One. 9:e1021102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Finley DS, Pantuck AJ and Belldegrun AS:
Tumor biology and prognostic factors in renal cell carcinoma.
Oncologist. 16:(Suppl 2). 4–13. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rock EP, Goodman V, Jiang JX, Mahjoob K,
Verbois SL, Morse D, Dagher R, Justice R and Pazdur R: Food and
Drug Administration drug approval summary: Sunitinib malate for the
treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumor and advanced renal cell
carcinoma. Oncologist. 12:107–113. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Motzer RJ, Michaelson MD, Redman BG, Hudes
GR, Wilding G, Figlin RA, Ginsberg MS, Kim ST, Baum CM, DePrimo SE,
et al: Activity of SU11248, a multitargeted inhibitor of vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor and platelet-derived growth
factor receptor, in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.
J Clin Oncol. 24:16–24. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Miyake H, Muramaki M, Imai S, Harada KI
and Fujisawa M: Changes in renal function of patients with
metastatic renal cell carcinoma during treatment with
molecular-targeted agents. Target Oncol. 11:329–335. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Korashy HM, Al-Suwayeh HA, Maayah ZH,
Ansari MA, Ahmad SF and Bakheet SA: Mitogen-activated protein
kinases pathways mediate the sunitinib-induced hypertrophy in rat
cardiomyocyte H9c2 cells. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 15:41–51. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shi WH, Bian YH, Song XH and Wu JC:
Coadministration of sorafenib with adriamycin inhibits cell
proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells HepG2. Prog Modern
Biomed. 24:4845–3848. 2011.
|
|
11
|
Diekstra MH, Belaustegui A, Swen JJ, Boven
E, Castellano D, Gelderblom H, Mathijssen RH, García-Donas J,
Rodríguez-Antona C, Rini BI, et al: Sunitinib-induced hypertension
in CYP3A4 rs4646437 A-allele carriers with metastatic renal cell
carcinoma. Pharmacogenomics J. 26:2–4. 2016.
|
|
12
|
Diekstra MH, Swen JJ, Boven E, Castellano
D, Gelderblom H, Mathijssen RH, Rodríguez-Antona C, García-Donas J,
Rini BI and Guchelaar HJ: CYP3A5 and ABCB1 polymorphisms as
predictors for sunitinib outcome in metastatic renal cell
carcinoma. Eur Urol. 68:621–629. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Boers-Sonderen MJ, Desar IM, Fütterer JJ,
Mulder SF, De Geus-Oei LF, Mulders PF, Van Der Graaf WT, Oyen WJ
and Van Herpen CM: Biological Effects After Discontinuation of
VEGFR Inhibitors in Metastatic Renal Cell Cancer. Anticancer Res.
35:5601–5606. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bruyère F, Hovens CM, Marson MN, d'Arcier
BF, Costello AJ, Watier H, Linassier C and Ohresser M: VEGF
polymorphisms are associated with an increasing risk of developing
renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 184:1273–1278. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Purdue MP, Ye Y, Wang Z, Colt JS, Schwartz
KL, Davis FG, Rothman N, Chow WH, Wu X and Chanock SJ: A
genome-wide association study of renal cell carcinoma among African
Americans. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 23:209–214. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Harten SK, Shukla D, Barod R, Hergovich A,
Balda MS, Matter K, Esteban MA and Maxwell PH: Regulation of renal
epithelial tight junctions by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor
suppressor gene involves occludin and claudin 1 and is independent
of E-cadherin. Mol Biol Cell. 20:1089–1101. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|