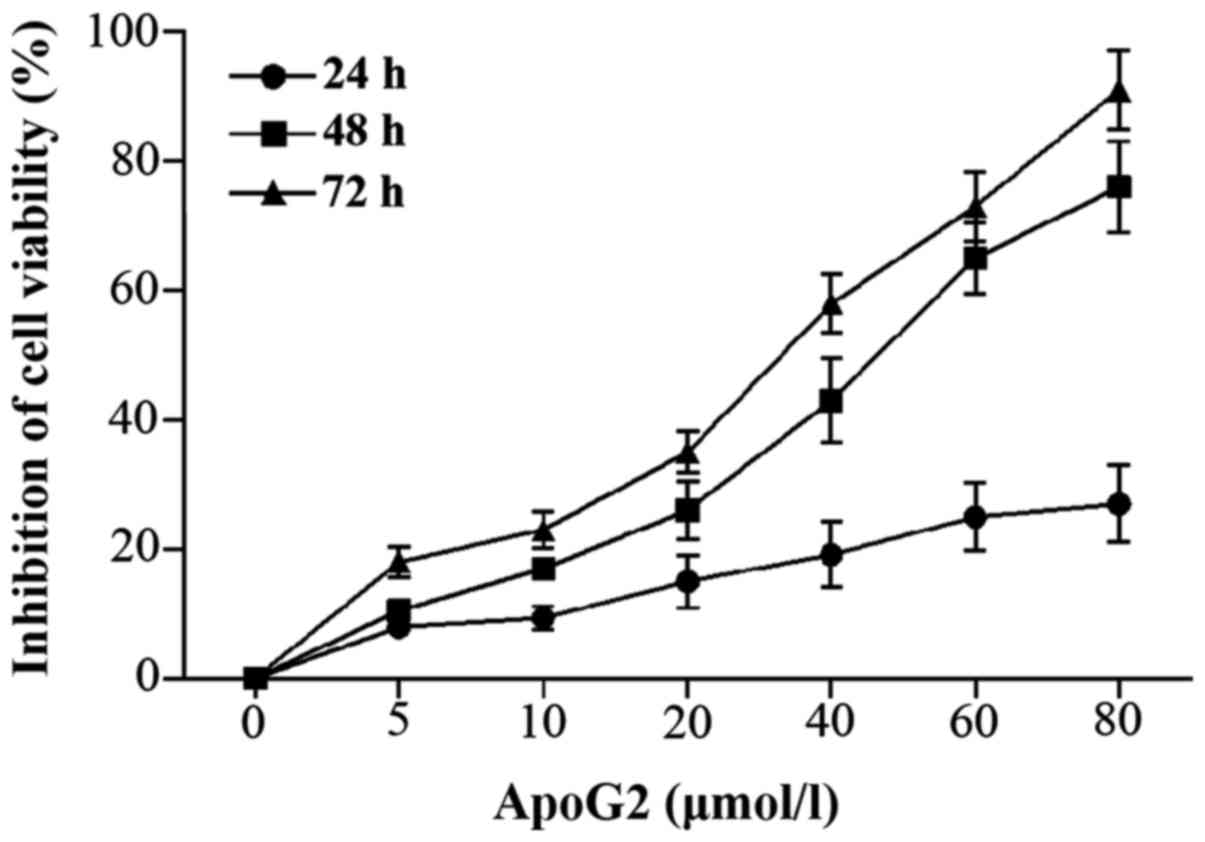
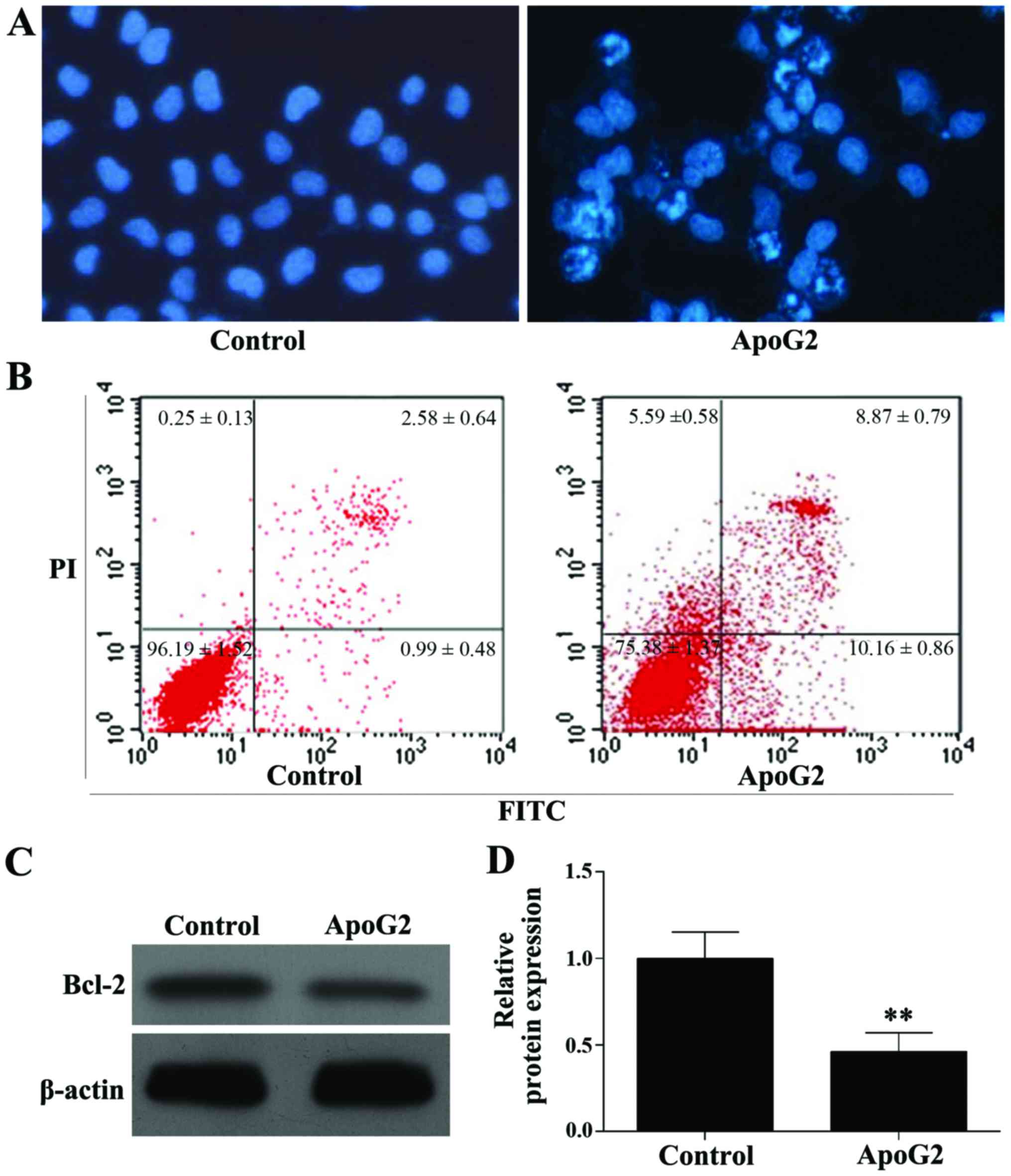
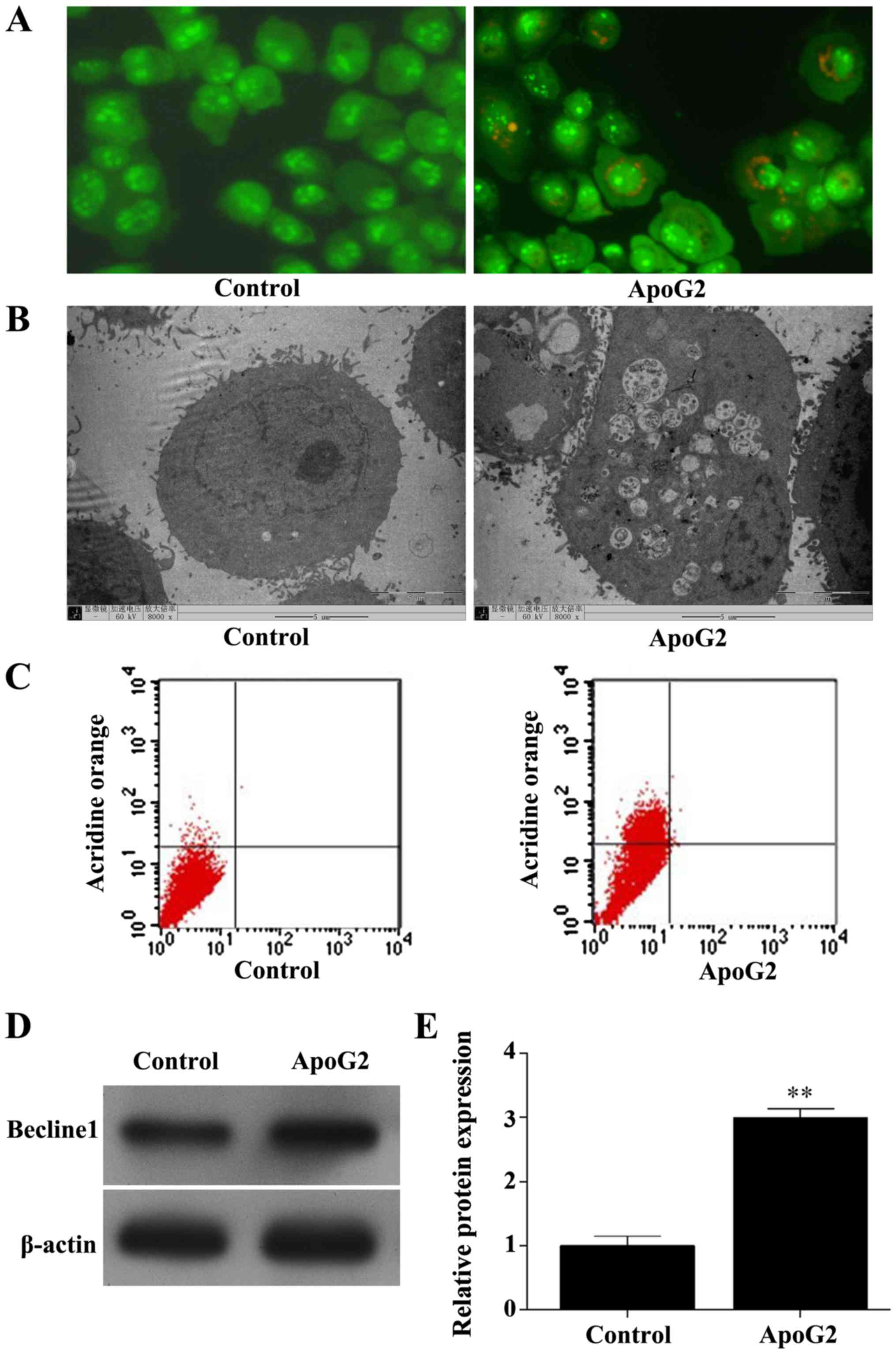
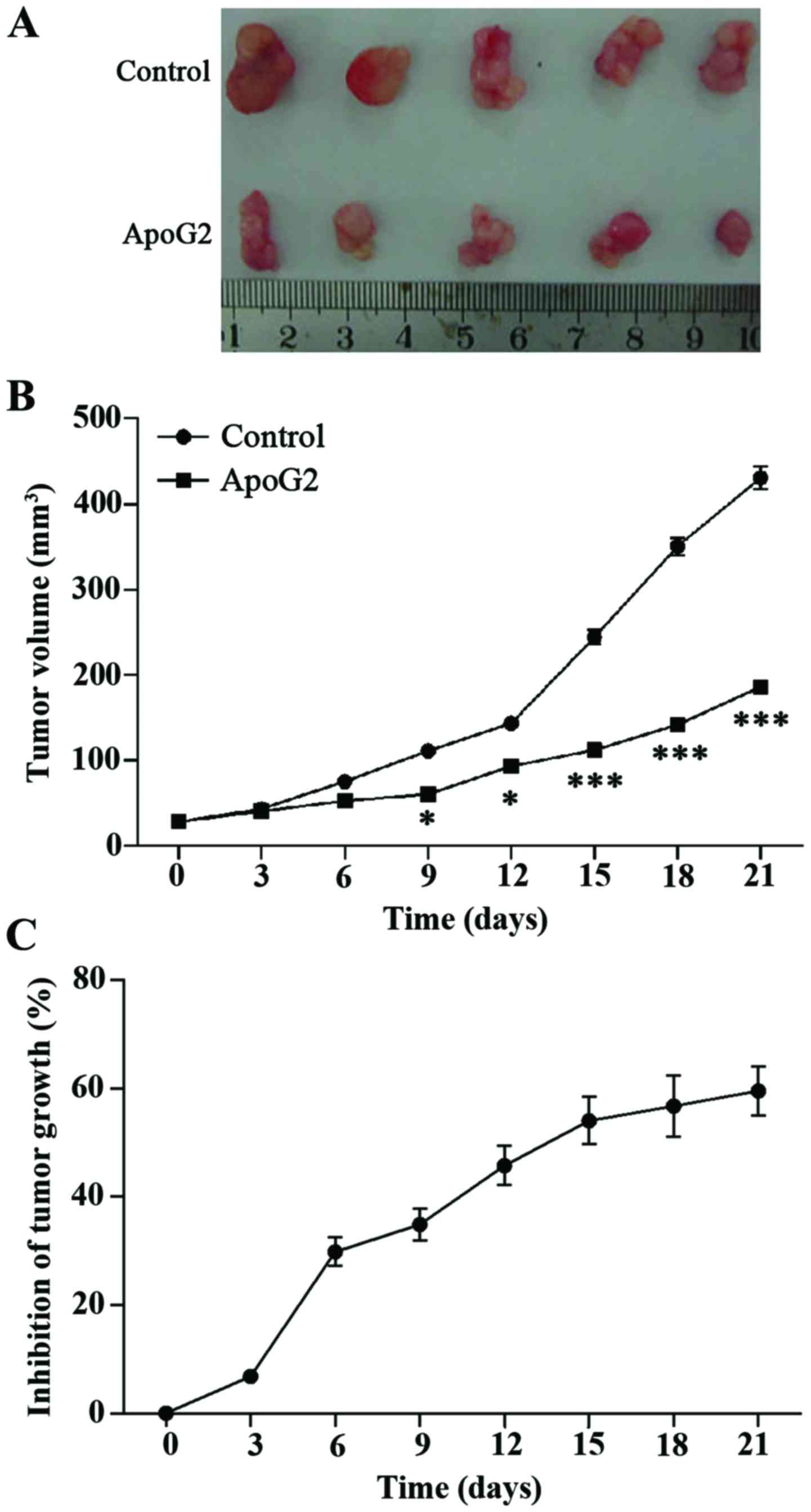
|
1
|
Wang Y, Zhang Y and Ma S: Racial
differences in nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the United States.
Cancer Epidemiol. 37:793–802. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kimura Y, Suzuki D, Tokunaga T,
Takabayashi T, Yamada T, Wakisaka N, Yoshizaki T, Murata H, Miwa K,
Shoujaku H, et al: Epidemiological analysis of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma in the central region of Japan during the period from
1996 to 2005. Auris Nasus Larynx. 38:244–249. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lau HY, Leung CM, Chan YH, Lee AW, Kwong
DL, Lung ML and Lam TH: Secular trends of salted fish consumption
and nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A multi-jurisdiction ecological study
in 8 regions from 3 continents. BMC Cancer. 13:2982013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xu T, Shen C, Ou X, He X, Ying H and Hu C:
The role of adjuvant chemotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma with
bulky neck lymph nodes in the era of IMRT. Oncotarget.
7:21013–21022. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu T, Liu Y, Dou S, Li F, Guan X and Zhu
G: Weekly cetuximab concurrent with IMRT aggravated
radiation-induced oral mucositis in locally advanced nasopharyngeal
carcinoma: Results of a randomized phase II study. 51:875–879.
2015.
|
|
6
|
Li H, Wang DL, Liu XW, Chen MY, Mo YX,
Geng ZJ and Xie CM: MRI signal changes in the skull base bone after
endoscopic nasopharyngectomy for recurrent NPC: A serial study of 9
patients. Eur J Radiol. 82:309–315. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhan YH, Huang XF, Hu XB, An QX, Liu ZX
and Zhang XQ: Growth inhibition and apoptosis induction of human
umbilical vein endothelial cells by apogossypolone. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 14:1791–1795. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Niu X, Li S, Wei F, Huang J, Wu G, Xu L,
Xu D and Wang S: Apogossypolone induces autophagy and apoptosis in
breast cancer MCF-7 cells in vitro and in vivo. Breast Cancer.
21:223–230. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xin J, Zhan YH, Xia LM, Zhu HW, Nie YZ,
Liang JM and Tian J: ApoG2 as the most potent gossypol derivatives
inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis on gastric cancer cells.
Biomed Pharmacother. 67:88–95. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Banerjee S, Choi M, Aboukameel A, Wang Z,
Mohammad M, Chen J, Yang D, Sarkar FH and Mohammad RM: Preclinical
studies of apogossypolone, a novel pan inhibitor of bcl-2 and
mcl-1, synergistically potentiates cytotoxic effect of gemcitabine
in pancreatic cancer cells. Pancreas. 39:323–331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lin J, Wu YJ, Yang DJ and Zhao YQ: Effect
of apogossypolone on induction apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells
and its mechanisms. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 17:92–98.
2009.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Balakrishnan K, Aggarwal S, Wierda W and
Gandhi V: Bax and Bak are required for apogossypolone, a
BH3-mimetic, induced apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
cells. Leuk Lymphoma. 54:1097–1100. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cheng P, Ni Z, Dai X, Wang B, Ding W, Rae
Smith A, Xu L, Wu D, He F and Lian J: The novel BH-3 mimetic
apogossypolone induces Beclin-1- and ROS-mediated autophagy in
human hepatocellular carcinoma [corrected] cells. Cell Death Dis.
4:e4892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun J, Li ZM, Hu ZY, Lin XB, Zhou NN, Xian
LJ, Yang DJ and Jiang WQ: ApoG2 inhibits antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family
proteins and induces mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in human
lymphoma U937 cells. Anticancer Drugs. 19:967–974. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hockenbery DM: Bcl-2 in cancer,
development and apoptosis. J Cell Sci Suppl. 18:51–55. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Raffo AJ, Perlman H, Chen MW, Day ML,
Streitman JS and Buttyan R: Overexpression of bcl-2 protects
prostate cancer cells from apoptosis in vitro and confers
resistance to androgen depletion in vivo. Cancer Res. 55:4438–4445.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
National Research Council (US), .
Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of
Laboratory Animals. ‘Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals. ’ Guide for the Care & Use of Laboratory Animals.
103:1072–1073. 2011.
|
|
18
|
Xu ZJ, Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Zou XN and Chen
WQ: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma incidence and mortality in China in
2009. Chin J Cancer. 32:453–460. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mesia R, Pastor M, Grau JJ and del Barco
E; SEOM: SEOM clinical guidelines for the treatment of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma 2013. Clin Transl Oncol. 15:1025–1029.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Piro LD: Apoptosis, Bcl-2 antisense, and
cancer therapy. Oncology (Williston Park). 18 13 Suppl 10:S5–S10.
2004.
|
|
21
|
Kontos CK, Christodoulou MI and Scorilas
A: Apoptosis-related BCL2-family members: Key players in
chemotherapy. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 14:353–374. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kaneko T, Zhang Z, Mantellini MG, Karl E,
Zeitlin B, Verhaegen M, Soengas MS, Lingen M, Strieter RM, Nunez G
and Nör JE: Bcl-2 orchestrates a cross-talk between endothelial and
tumor cells that promotes tumor growth. Cancer Res. 67:9685–9693.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tucker CA, Kapanen AI, Chikh G, Hoffman
BG, Kyle AH, Wilson IM, Masin D, Gascoyne RD, Bally M and Klasa RJ:
Silencing Bcl-2 in models of mantle cell lymphoma is associated
with decreases in cyclin D1, nuclear factor-kappaB, p53, bax, and
p27 levels. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:749–758. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tekedereli I, Alpay SN, Akar U, Yuka E,
Ayugo-Rodriguez C, Han HD, Sood AK, Lopez-Berestein G and Ozpolat
B: Therapeutic silencing of Bcl-2 by systemically administered
siRNA nanotherapeutics inhibits tumor growth by autophagy and
apoptosis and enhances the efficacy of chemotherapy in orthotopic
xenograft models of ER (−) and ER (+) breast cancer. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 2:e1212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Du P, Cao H, Wu HR, Zhu BS, Wang HW, Gu
CW, Xing CG and Chen W: Blocking Bcl-2 leads to autophagy
activation and cell death of the HEPG2 liver cancer cell line.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:5849–5854. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Akar U, Chaves-Reyez A, Barria M, Tari A,
Sanguino A, Kondo Y, Kondo S, Arun B, Lopez-Berestein G and Ozpolat
B: Silencing of Bcl-2 expression by small interfering RNA induces
autophagic cell death in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Autophagy.
4:669–679. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Paoluzzi L, Gonen M, Gardner JR, Mastrella
J, Yang D, Holmlund J, Sorenen M, Leopold L, Manova K, Marcucci G,
et al: Targeting Bcl-2 family members with the BH3 mimetic AT-101
markedly enhances the therapeutic effects of chemotherapeutic
agents in in vitro and in vivo models of B-cell lymphoma. Blood.
111:5350–5358. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lieber J, Kirchner B, Eicher C, Warman SW,
Seitz G, Fuchs J and Armeanu-Ebinger S: Inhibition of Bcl-2 and
Bcl-X enhances chemotherapy sensitivity in hepatoblastoma cells.
Pediatr Blood Cancer. 55:1089–1095. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lamb CA, Yoshimori T and Tooze SA: The
autophagosome: Origins unknown, biogenesis complex. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 14:759–774. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang Z and Klionsky DJ: Eaten alive: A
history of macroautophagy. Nat Cell Biol. 12:814–822. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu HD, Wu D, Gu JH, Ge JB, Wu JC, Han R,
Liang ZQ and Qin ZH: The pro-survival role of autophagy depends on
Bcl-2 under nutrition stress conditions. PLoS One. 8:e632322013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tian S, Lin J, Jun Zhou J, Wang X, Li Y,
Ren X, Yu W, Zhong W, Xiao J, Sheng F, et al: Beclin 1-independent
autophagy induced by a Bcl-XL/Bcl-2 targeting compound, Z18.
Autophagy. 6:1032–1041. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
He JH, Liao XL, Wang W, Li DD, Chen WD,
Deng R, Yang D, Han ZP, Jiang JW and Zhu XF: Apogossypolone, a
small-molecule inhibitor of Bcl-2, induces radiosensitization of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by stimulating autophagy. Int J
Oncol. 45:1099–1108. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu ZY, Wang J, Cheng G, Zhu XF, Huang P,
Yang D and Zeng YX: Apogossypolone targets mitochondria and light
enhances its anticancer activity by stimulating generation of
singlet oxygen and reactive oxygen species. Chin J Cancer.
30:41–53. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hu ZY, Sun J, Zhu XF, Yang D and Zeng YX:
ApoG2 induces cell cycle arrest of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
by suppressing the c-Myc signaling pathway. J Transl Med. 7:742009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hu ZY, Zhu XF, Zhong ZD, Sun J, Wang J,
Yang D and Zeng YX: ApoG2, a novel inhibitor of antiapoptotic Bcl-2
family proteins, induces apoptosis and suppresses tumor growth in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma xenografts. Int J Cancer. 123:2418–2429.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|