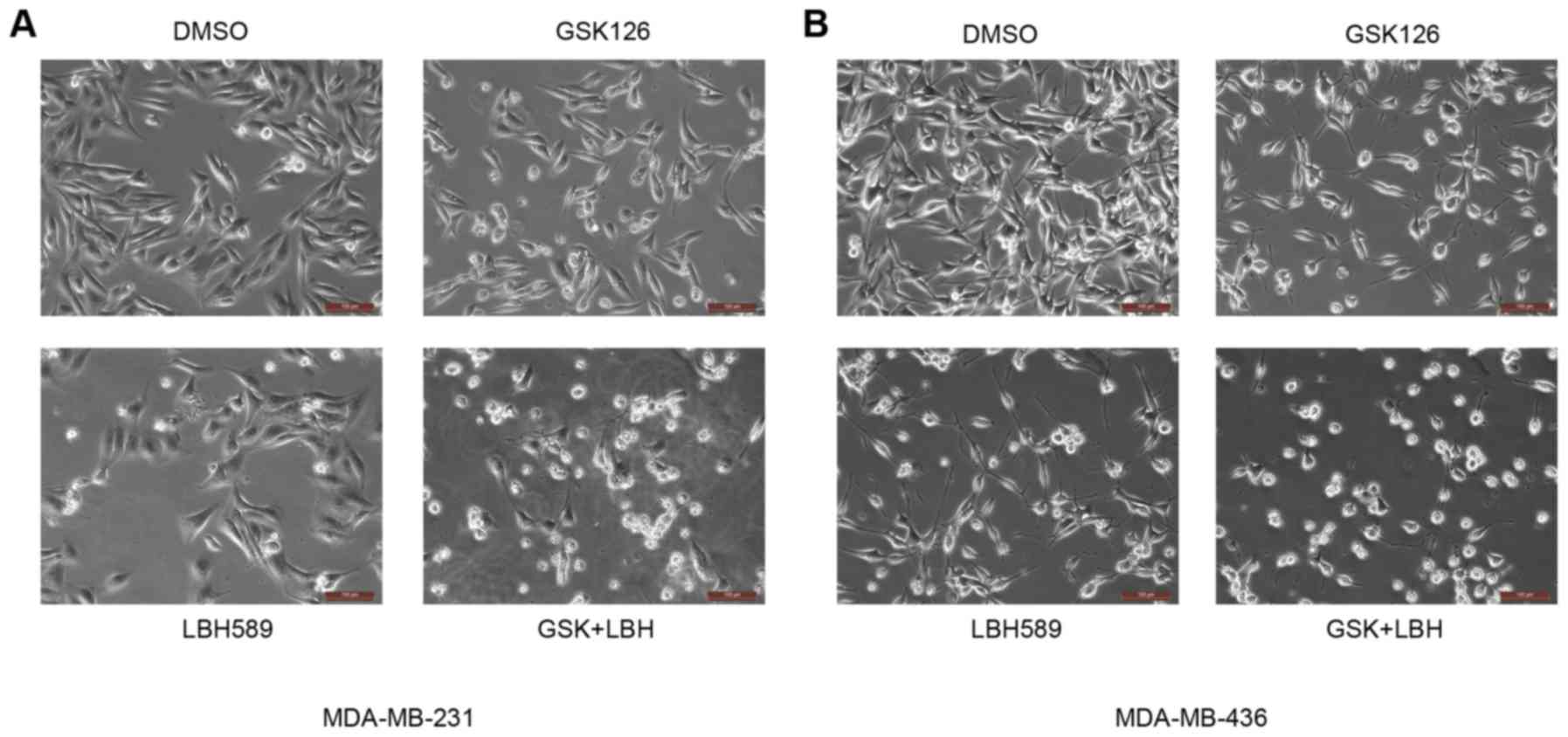
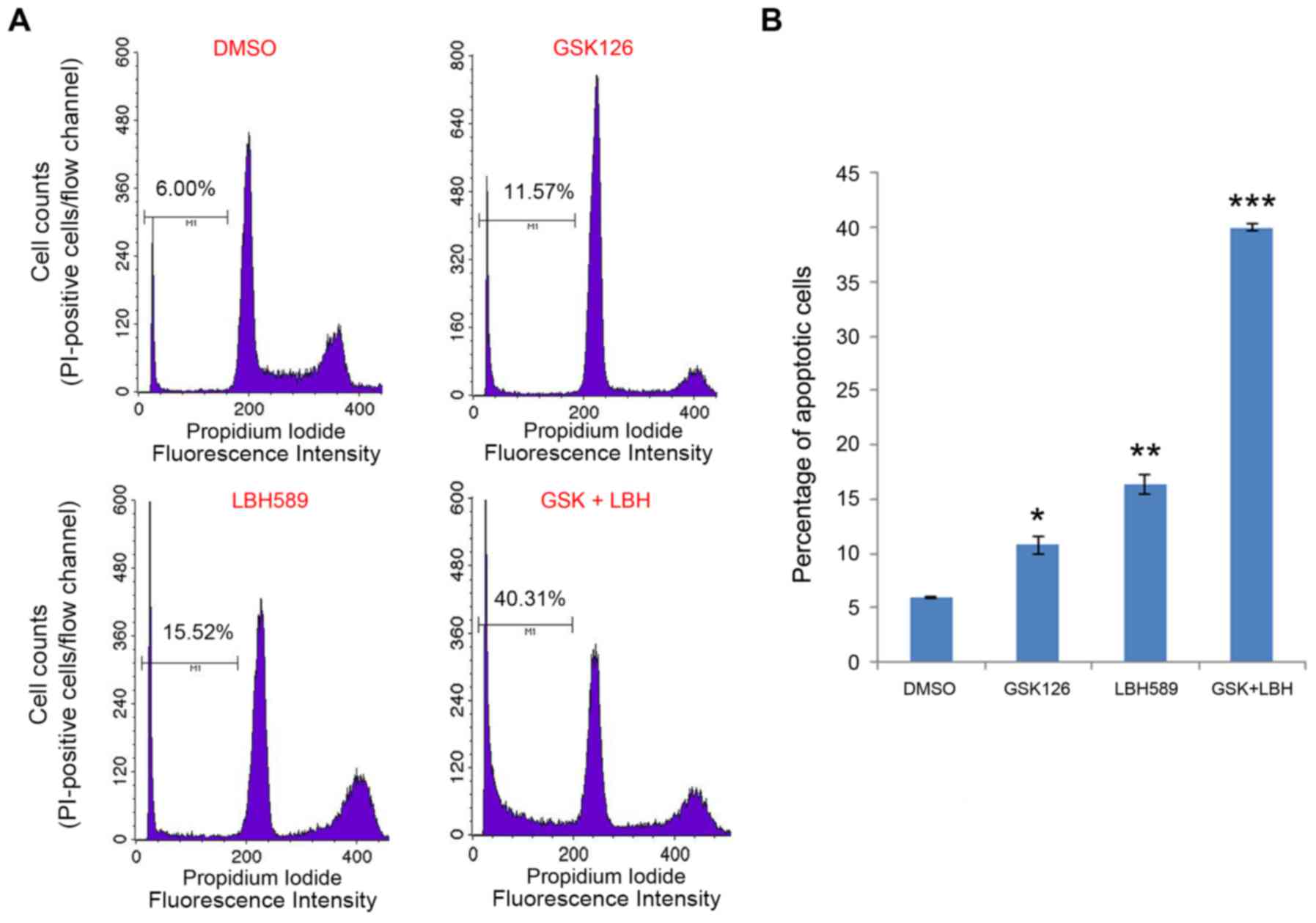
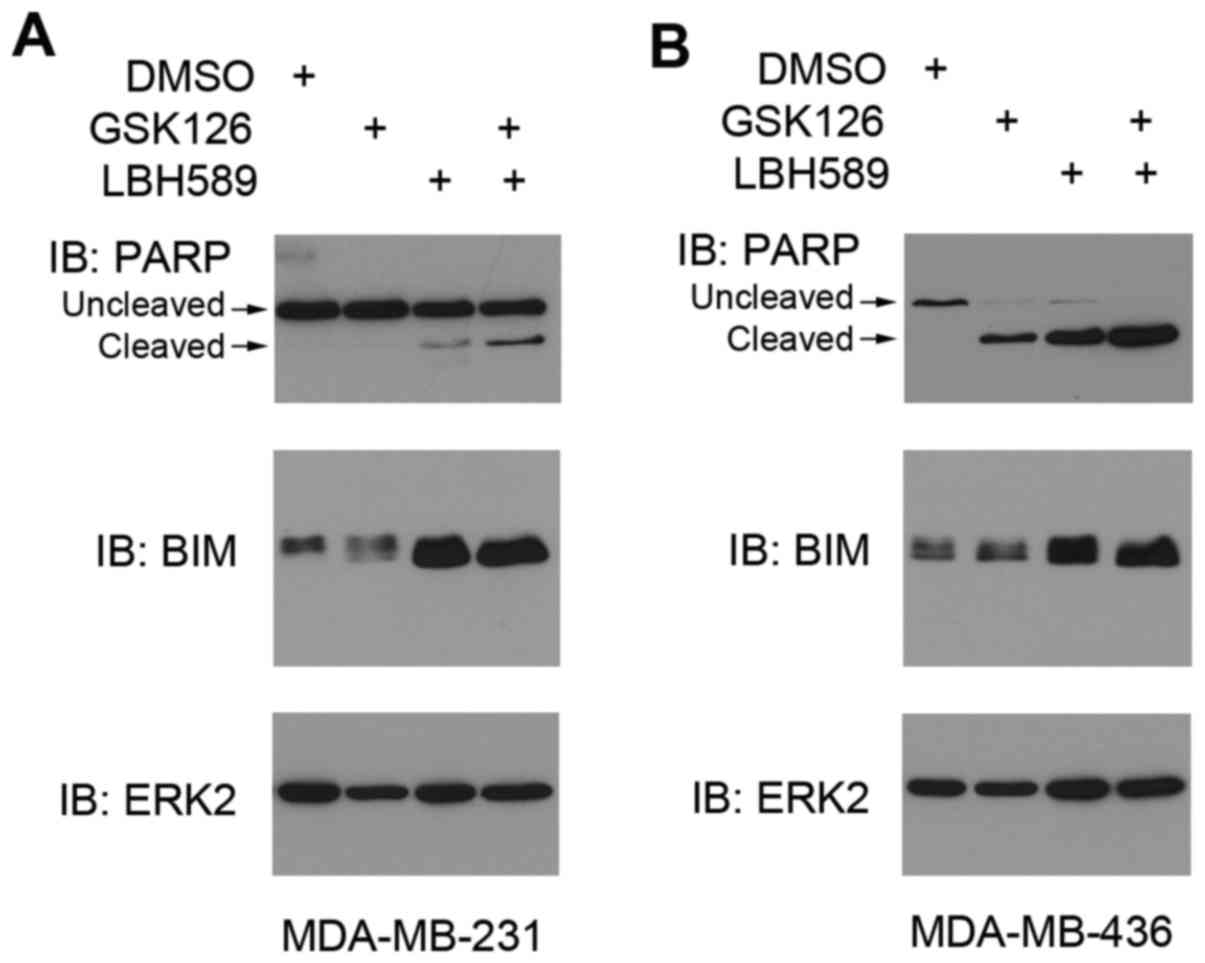
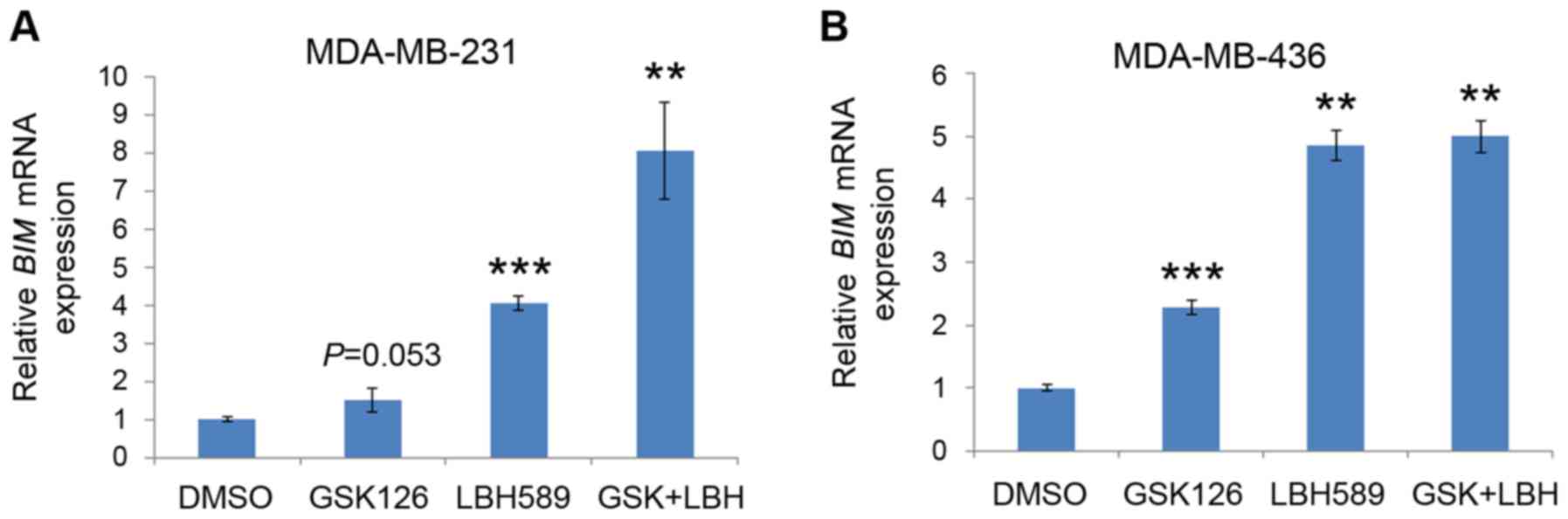
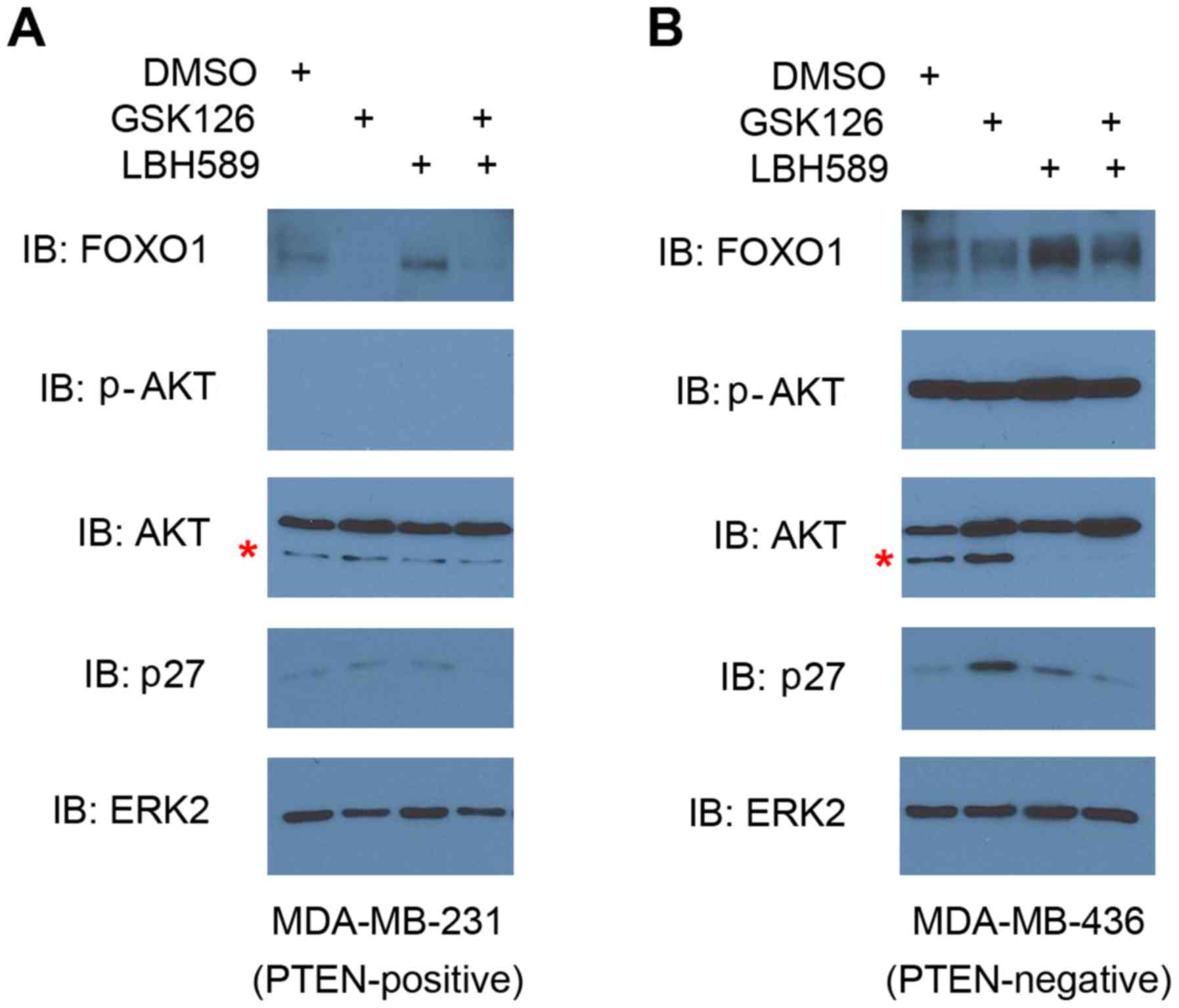
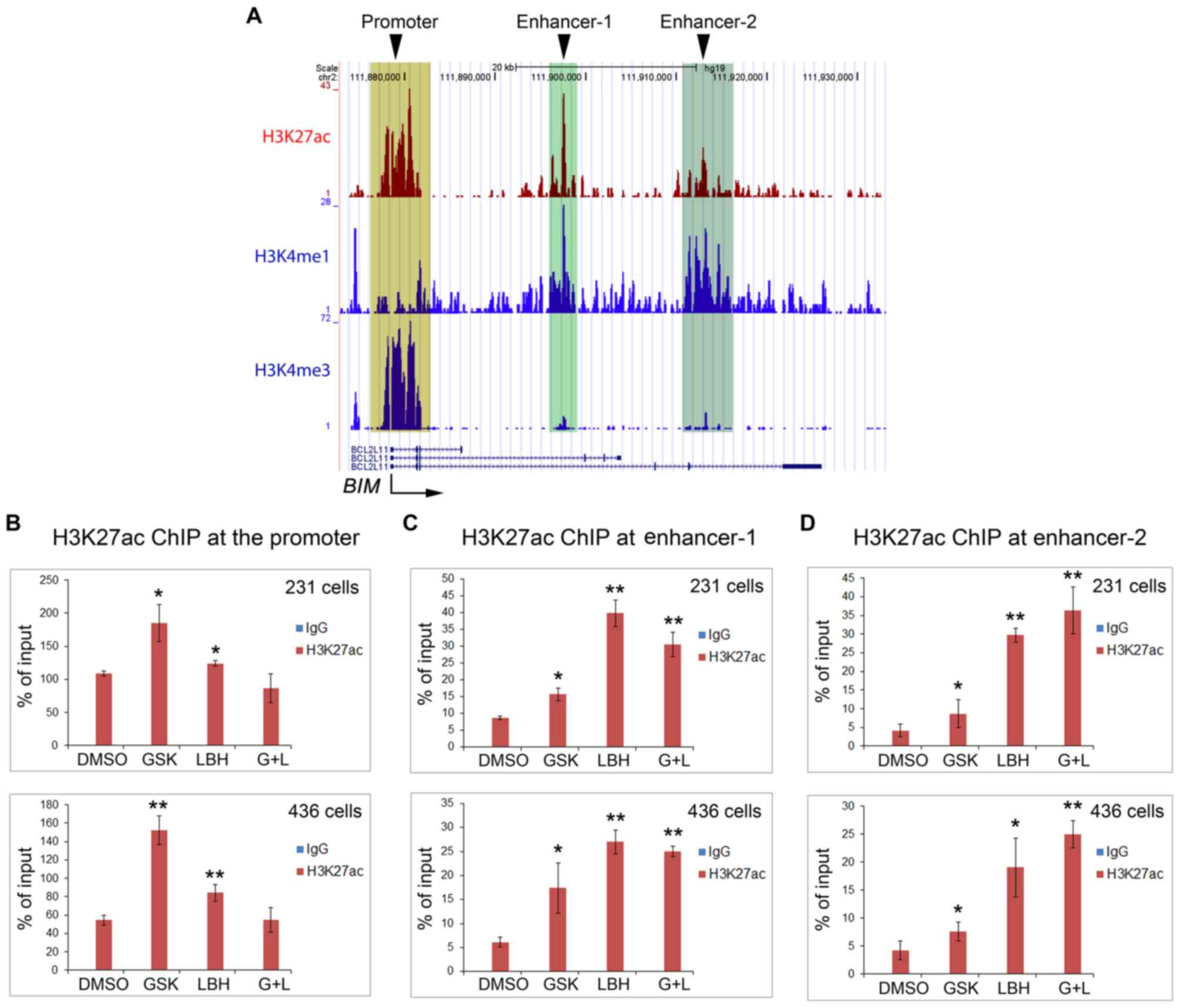
|
1
|
Donepudi MS, Kondapalli K, Amos SJ and
Venkanteshan P: Breast cancer statistics and markers. J Cancer Res
Ther. 10:506–511. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
DeSantis CE, Fedewa SA, Sauer Goding A,
Kramer JL, Smith RA and Jemal A: Breast cancer statistics, 2015:
Convergence of incidence rates between black and white women. CA
Cancer J Clin. 66:31–42. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schnitt SJ: Classification and prognosis
of invasive breast cancer: From morphology to molecular taxonomy.
Mod Pathol. 23 Suppl 2:S60–S64. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Callahan R and Hurvitz S: Human epidermal
growth factor receptor-2-positive breast cancer: Current management
of early, advanced, and recurrent disease. Curr Opin Obstet
Gynecol. 23:37–43. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Andre F and Zielinski CC: Optimal
strategies for the treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast
cancer with currently approved agents. Ann Oncol. 23 Suppl
6:vi46–vi51. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Simon JA and Kingston RE: Mechanisms of
polycomb gene silencing: Knowns and unknowns. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 10:697–708. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim KH and Roberts CW: Targeting EZH2 in
cancer. Nat Med. 22:128–134. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Simon JA and Lange CA: Roles of the EZH2
histone methyltransferase in cancer epigenetics. Mutat Res.
647:21–29. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kleer CG, Cao Q, Varambally S, Shen R, Ota
I, Tomlins SA, Ghosh D, Sewalt RG, Otte AP, Hayes DF, et al: EZH2
is a marker of aggressive breast cancer and promotes neoplastic
transformation of breast epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:11606–11611. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Varambally S, Dhanasekaran SM, Zhou M,
Barrette TR, Kumar-Sinha C, Sanda MG, Ghosh D, Pienta KJ, Sewalt
RG, Otte AP, et al: The polycomb group protein EZH2 is involved in
progression of prostate cancer. Nature. 419:624–629. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gilbert PM, Mouw JK, Unger MA, Lakins JN,
Gbegnon MK, Clemmer VB, Benezra M, Licht JD, Boudreau NJ, Tsai KK,
et al: HOXA9 regulates BRCA1 expression to modulate human breast
tumor phenotype. J Clin Invest. 120:1535–1550. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang L, Zeng X, Chen S, Ding L, Zhong J,
Zhao JC, Wang L, Sarver A, Koller A, Zhi J, et al: BRCA1 is a
negative modulator of the PRC2 complex. Embo J. 32:1584–1597. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen H, Tu SW and Hsieh JT:
Down-regulation of human DAB2IP gene expression mediated by
polycomb Ezh2 complex and histone deacetylase in prostate cancer. J
Biol Chem. 280:22437–22444. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
McCabe MT, Ott HM, Ganji G, Korenchuk S,
Thompson C, Van Aller GS, Liu Y, Graves AP, Pietra A Della III,
Diaz E, et al: EZH2 inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for
lymphoma with EZH2-activating mutations. Nature. 492:108–112. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kurmasheva RT, Sammons M, Favours E, Wu J,
Kurmashev D, Cosmopoulos K, Keilhack H, Klaus CR, Houghton PJ and
Smith MA: Initial testing (stage 1) of tazemetostat (EPZ-6438), a
novel EZH2 inhibitor, by the Pediatric Preclinical Testing Program.
Pediatr Blood Cancer. 64:2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
van der Vlag J and Otte AP:
Transcriptional repression mediated by the human polycomb-group
protein EED involves histone deacetylation. Nat Genet. 23:474–478.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang T, Cooper S and Brockdorff N: The
interplay of histone modifications-writers that read. EMBO Rep.
16:1467–1481. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu P, Kao TP and Huang H: CDK1 promotes
cell proliferation and survival via phosphorylation and inhibition
of FOXO1 transcription factor. Oncogene. 27:4733–4744. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Heintzman ND, Stuart RK, Hon G, Fu Y,
Ching CW, Hawkins RD, Barrera LO, Van Calcar S, Qu C, Ching KA, et
al: Distinct and predictive chromatin signatures of transcriptional
promoters and enhancers in the human genome. Nat Genet. 39:311–318.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang D, Garcia-Bassets I, Benner C, Li W,
Su X, Zhou Y, Qiu J, Liu W, Kaikkonen MU, Ohgi KA, et al:
Reprogramming transcription by distinct classes of enhancers
functionally defined by eRNA. Nature. 474:390–394. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Boyer LA, Lee TI, Cole MF, Johnstone SE,
Levine SS, Zucker JP, Guenther MG, Kumar RM, Murray HL, Jenner RG,
et al: Core transcriptional regulatory circuitry in human embryonic
stem cells. Cell. 122:947–956. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Riccardi C and Nicoletti I: Analysis of
apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. Nat
Protoc. 1:1458–1461. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chaitanya GV, Steven AJ and Babu PP:
PARP-1 cleavage fragments: Signatures of cell-death proteases in
neurodegeneration. Cell Commun Signal. 8:312010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gogada R, Yadav N, Liu J, Tang S, Zhang D,
Schneider A, Seshadri A, Sun L, Aldaz CM, Tang DG and Chandra D:
Bim, a proapoptotic protein, up-regulated via transcription factor
E2F1-dependent mechanism, functions as a prosurvival molecule in
cancer. J Biol Chem. 288:368–381. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gilley J, Coffer PJ and Ham J: FOXO
transcription factors directly activate bim gene expression and
promote apoptosis in sympathetic neurons. J Cell Biol. 162:613–622.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pei Y, Liu KW, Wang J, Garancher A, Tao R,
Esparza LA, Maier DL, Udaka YT, Murad N, Morrissy S, et al: HDAC
and PI3K Antagonists Cooperate to Inhibit Growth of MYC-Driven
Medulloblastoma. Cancer Cell. 29:311–323. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang Y, Zhao Y, Liao W, Yang J, Wu L,
Zheng Z, Yu Y, Zhou W, Li L, Feng J, et al: Acetylation of FoxO1
activates Bim expression to induce apoptosis in response to histone
deacetylase inhibitor depsipeptide treatment. Neoplasia.
11:313–324. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gong C, Yao S, Gomes AR, Man EP, Lee HJ,
Gong G, Chang S, Kim SB, Fujino K, Kim SW, et al: BRCA1 positively
regulates FOXO3 expression by restricting FOXO3 gene methylation
and epigenetic silencing through targeting EZH2 in breast cancer.
Oncogenesis. 5:e2142016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang J, Zhang P, Wei Y, Piao HL, Wang W,
Maddika S, Wang M, Chen D, Sun Y, Hung MC, et al: Deubiquitylation
and stabilization of PTEN by USP13. Nat Cell Biol. 15:1486–1494.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nakamura N, Ramaswamy S, Vazquez F,
Signoretti S, Loda M and Sellers WR: Forkhead transcription factors
are critical effectors of cell death and cell cycle arrest
downstream of PTEN. Mol Cell Biol. 20:8969–8982. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Medema RH, Kops GJ, Bos JL and Burgering
BM: AFX-like forkhead transcription factors mediate cell-cycle
regulation by Ras and PKB through p27kip1. Nature. 404:782–787.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hussein YR, Sood AK, Bandyopadhyay S,
Albashiti B, Semaan A, Nahleh Z, Roh J, Han HD, Lopez-Berestein G
and Ali-Fehmi R: Clinical and biological relevance of enhancer of
zeste homolog 2 in triple-negative breast cancer. Hum Pathol.
43:1638–1644. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Stahl M, Dijkers PF, Kops GJ, Lens SM,
Coffer PJ, Burgering BM and Medema RH: The forkhead transcription
factor FoxO regulates transcription of p27Kip1 and Bim in response
to IL-2. J Immunol. 168:5024–5031. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|