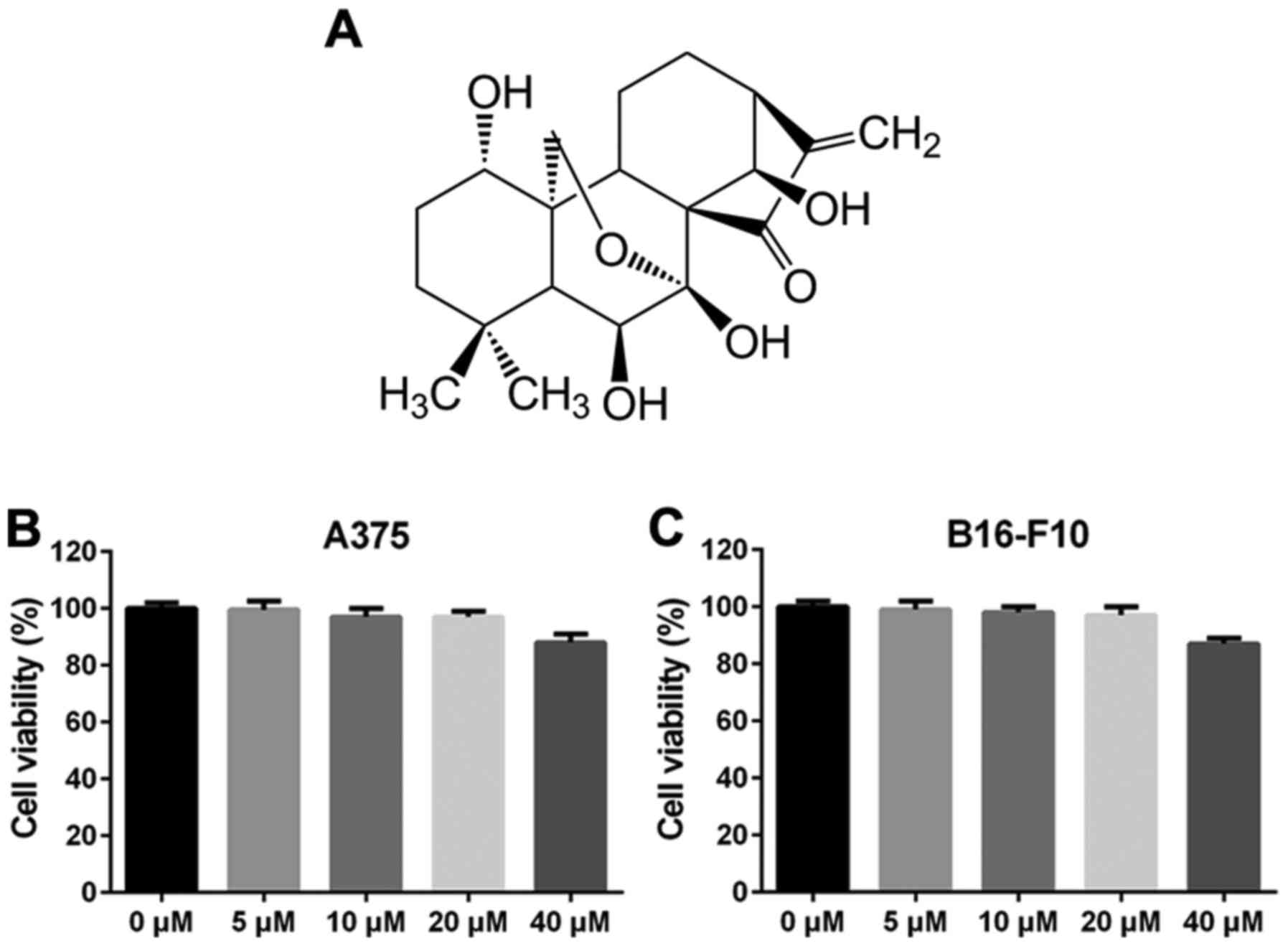
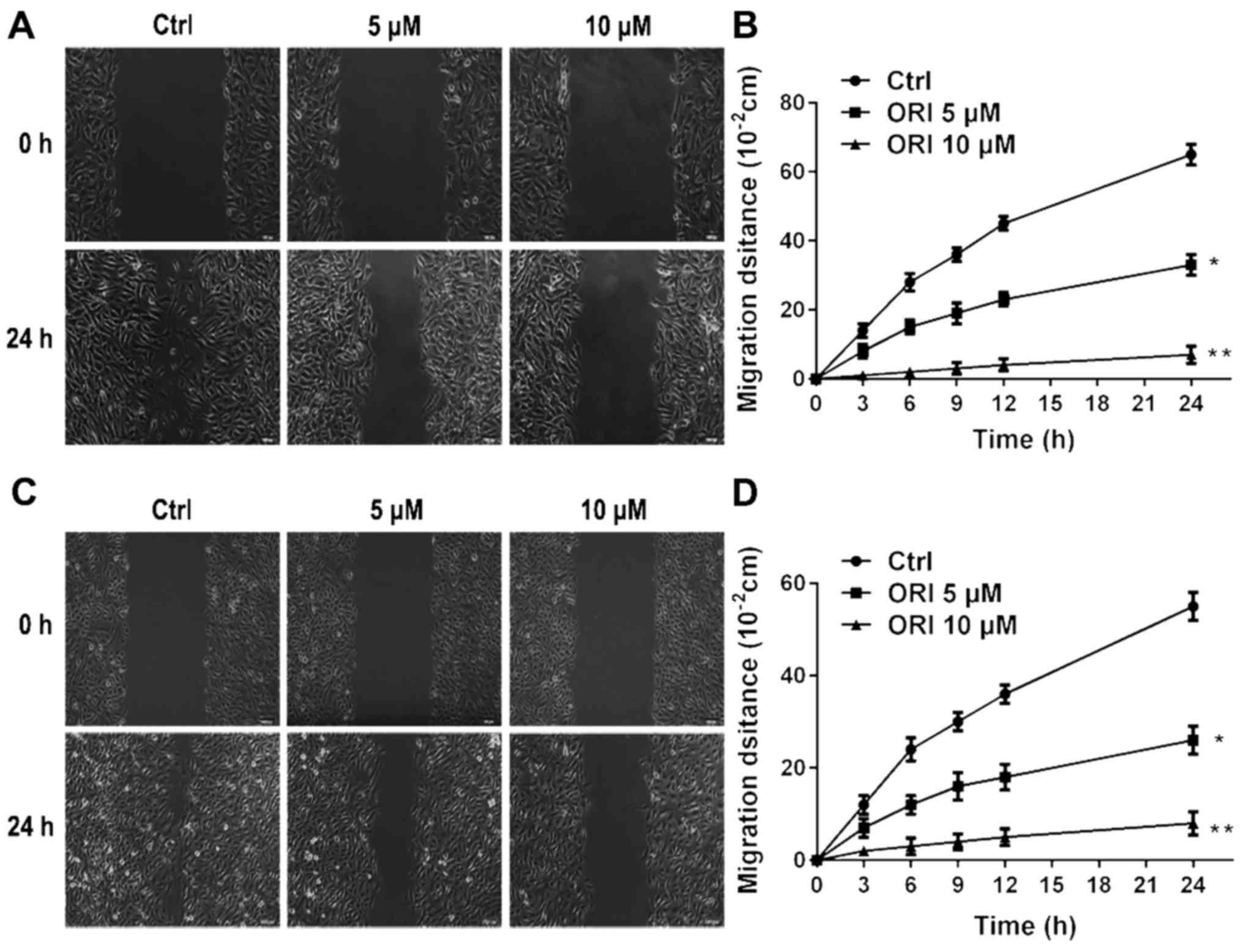
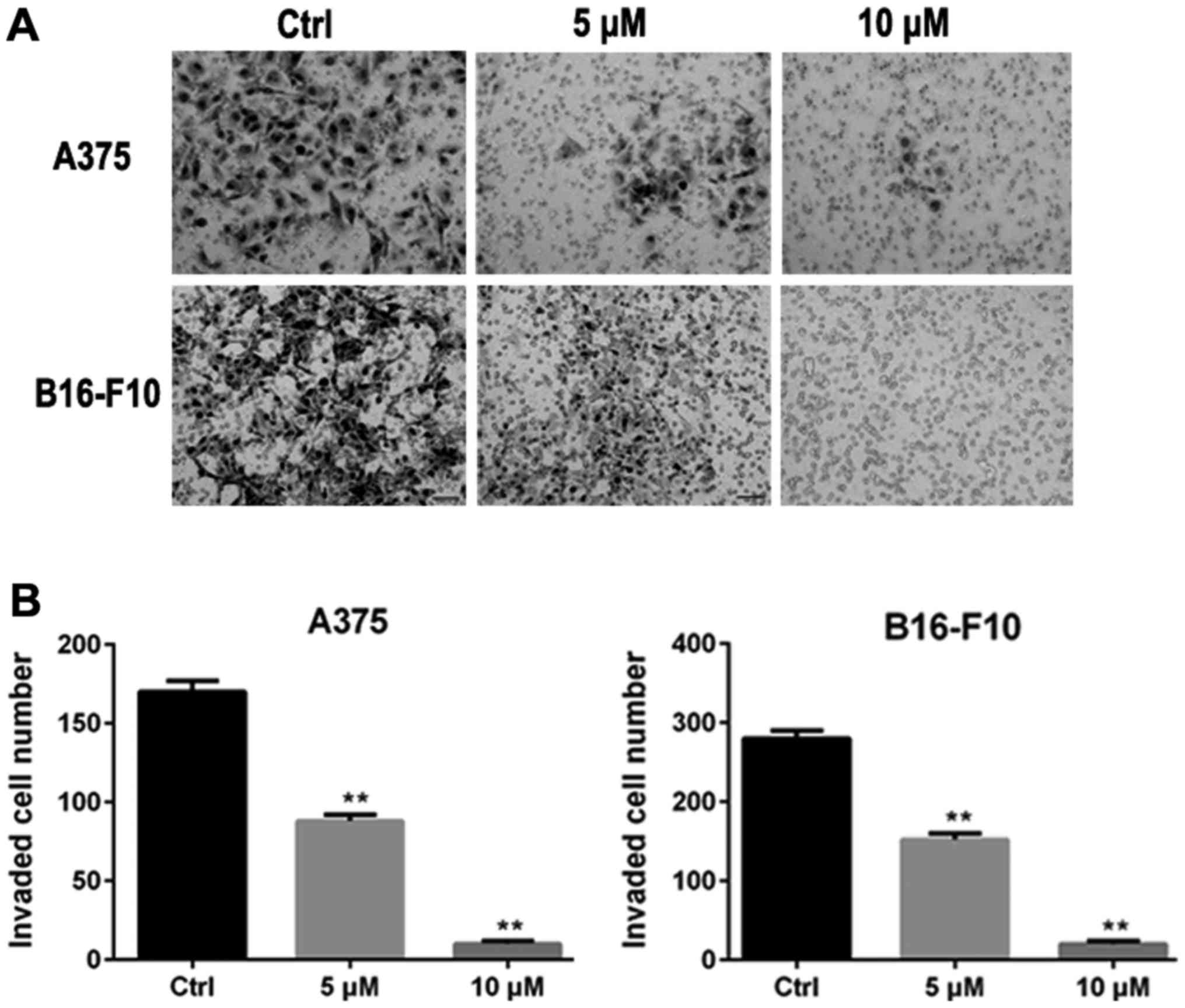
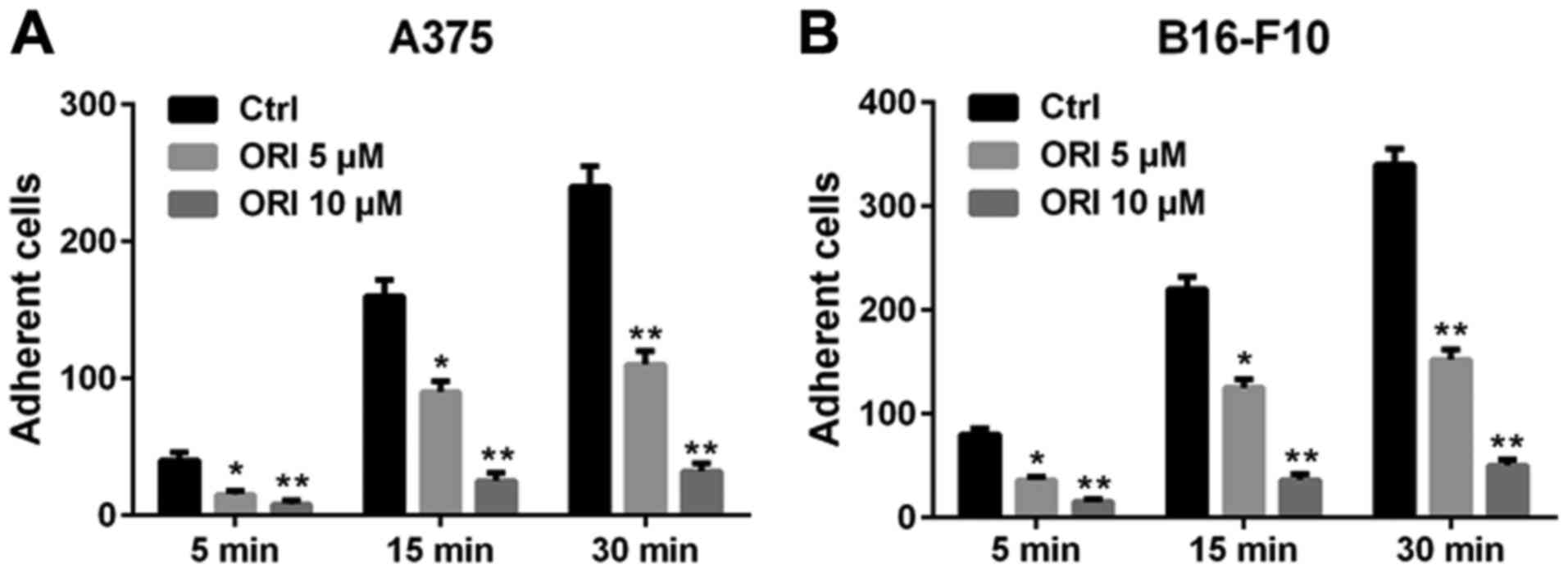
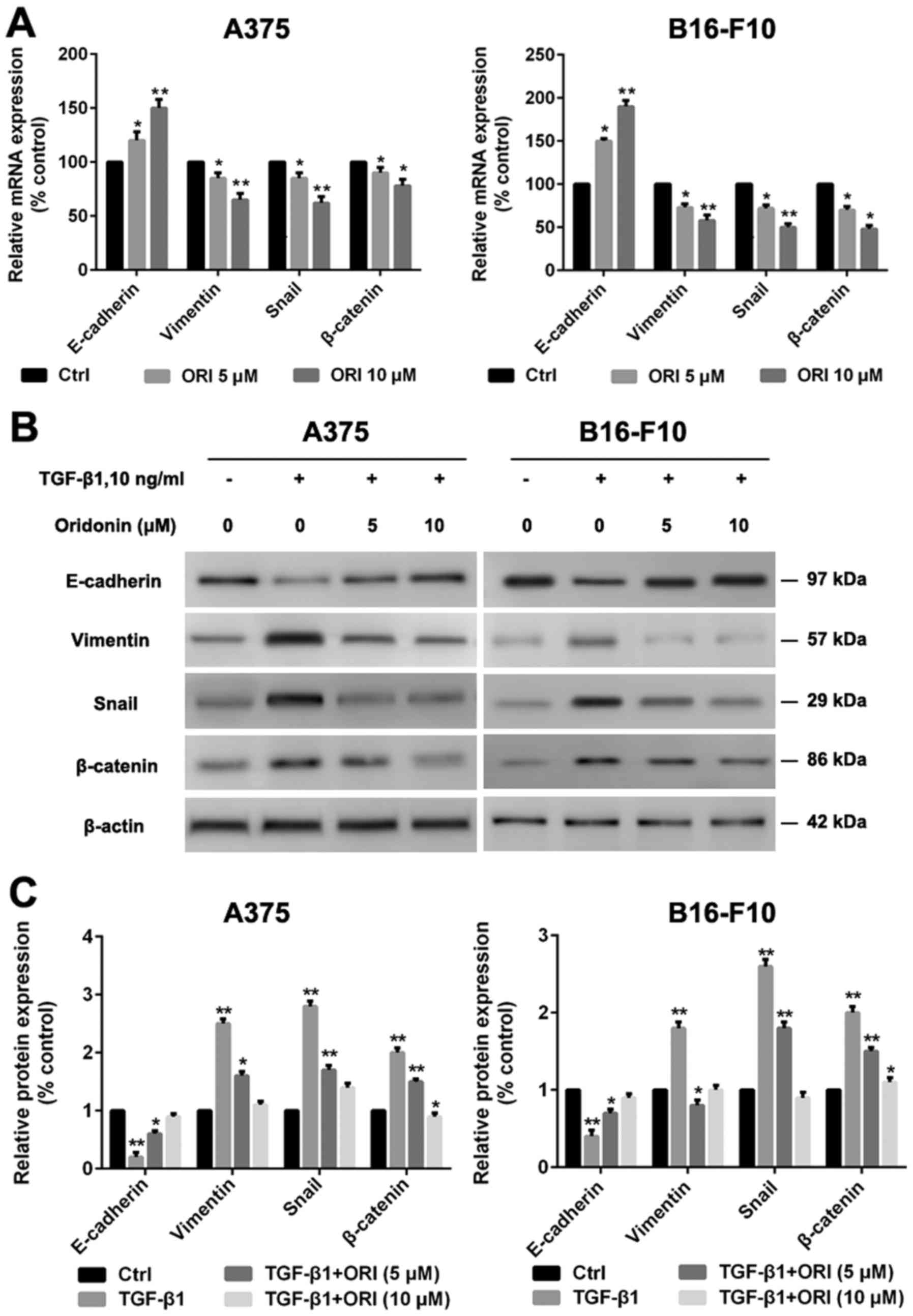
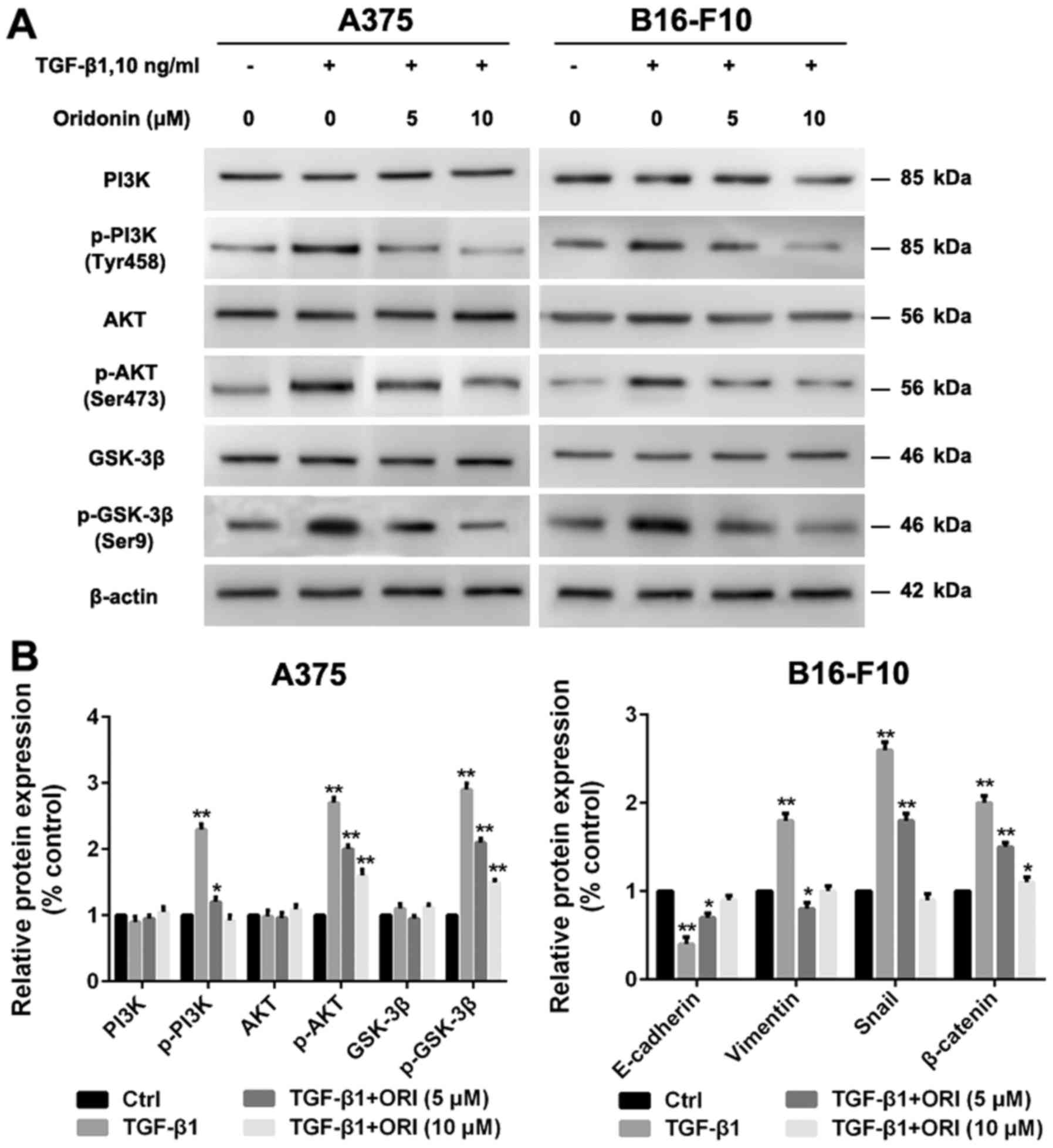
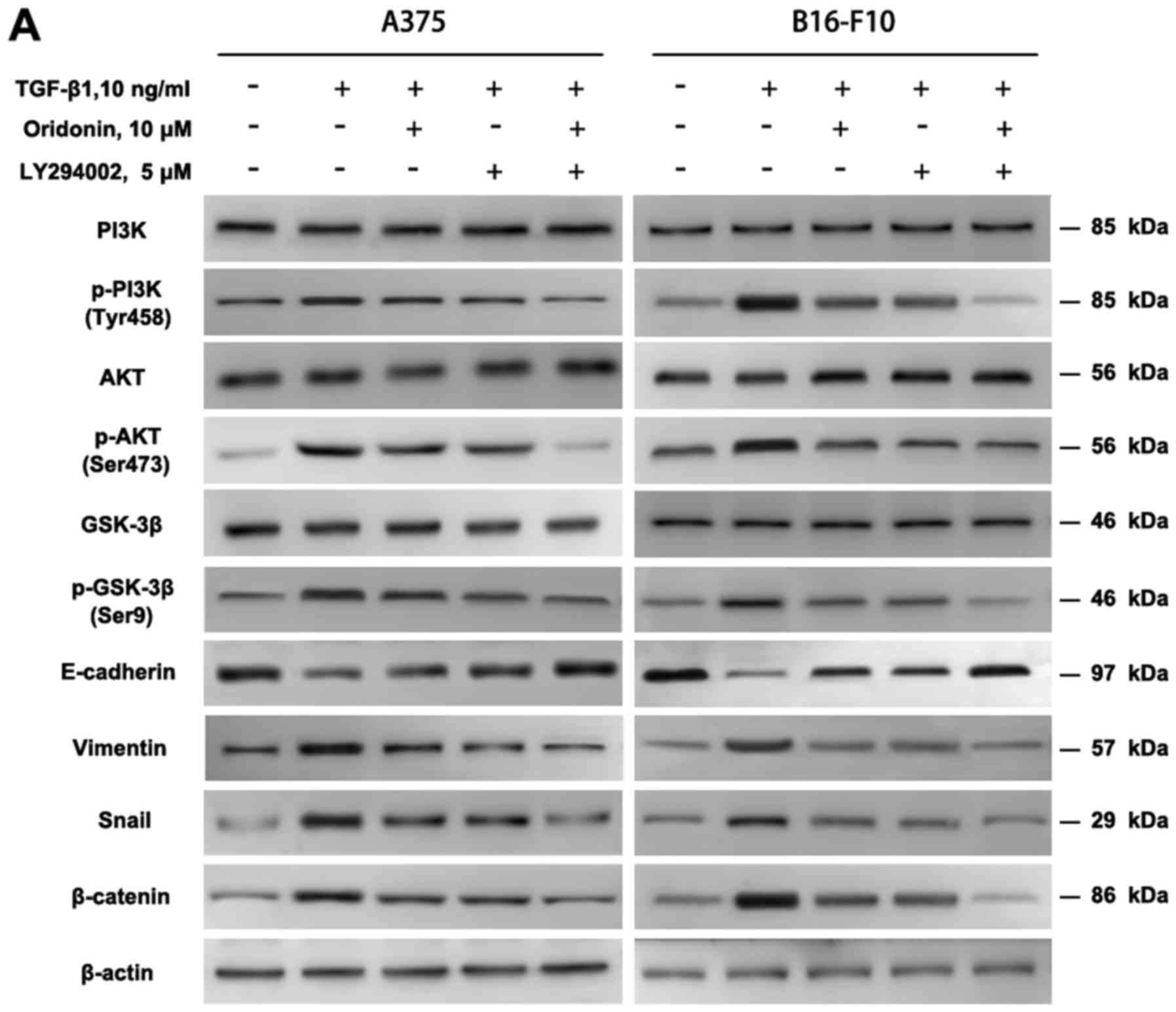
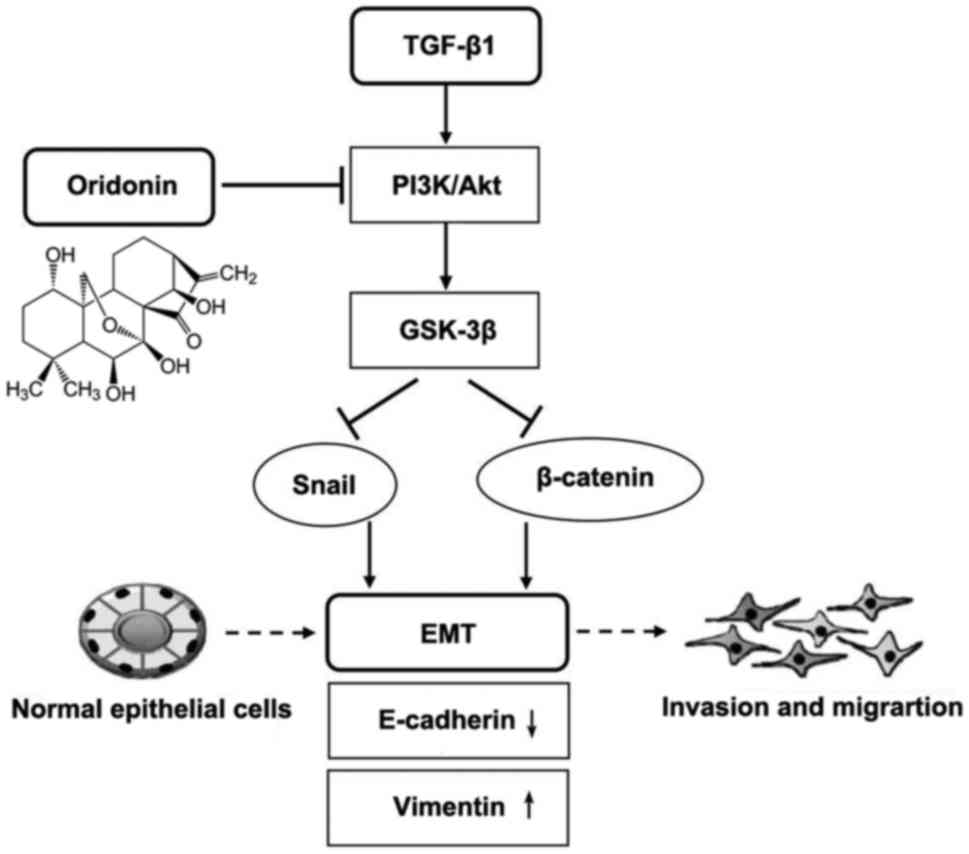
|
1
|
Aviles-Izquierdo JA, Molina-Lopez I,
Rodriguez-Lomba E, Marquez-Rodas I, Suarez-Fernandez R and
Lazaro-Ochaita P: Who detects melanoma? Impact of detection
patterns on characteristics and prognosis of patients with
melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 75:967–974. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bowyer S, Prithviraj P, Lorigan P, Larkin
J, McArthur G, Atkinson V, Millward M, Khou M, Diem S, Ramanujam S,
et al: Efficacy and toxicity of treatment with the anti-CTLA-4
antibody ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma after
prior anti-PD-1 therapy. Br J Cancer. 114:1084–1089. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Balch CM, Gershenwald JE, Soong SJ,
Thompson JF, Atkins MB, Byrd DR, Buzaid AC, Cochran AJ, Coit DG,
Ding S, et al: Final version of 2009 AJCC melanoma staging and
classification. J Clin Oncol. 27:6199–6206. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Duan H, Ma L, Liu H, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Yan
X and Li X: Tanshinone IIA attenuates epithelial-mesenchymal
transition to inhibit the tracheal narrowing. J Surg Res.
206:252–262. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ling G, Ji Q, Ye W, Ma D and Wang Y:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulated by p38/MAPK signaling
pathways participates in vasculogenic mimicry formation in SHG44
cells transfected with TGF-β cDNA loaded lentivirus in vitro and in
vivo. Int J Oncol. 49:2387–2398. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ma Y, Xu X and Luo M: CXCR6 promotes tumor
cell proliferation and metastasis in osteosarcoma through the Akt
pathway. Cell Immunol. 311:80–85. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Le Coz V, Zhu C, Devocelle A, Vazquez A,
Boucheix C, Azzi S, Gallerne C, Eid P, Lecourt S and Giron-Michel
J: IGF-1 contributes to the expansion of melanoma-initiating cells
through an epithelial-mesenchymal transition process. Oncotarget.
7:82511–82527. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mao XY, Li QQ, Gao YF, Zhou HH, Liu ZQ and
Jin WL: Gap junction as an intercellular glue: Emerging roles in
cancer EMT and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 381:133–137. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Menezes ME, Shen XN, Das SK, Emdad L,
Sarkar D and Fisher PB: MDA-9/Syntenin (SDCBP) modulates small
GTPases RhoA and Cdc42 via transforming growth factor β1 to enhance
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Oncotarget.
7:80175–80189. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Da C, Liu Y, Zhan Y, Liu K and Wang R:
Nobiletin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human
non-small cell lung cancer cells by antagonizing the TGF-β1/Smad3
signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 35:2767–2774. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim YJ, Jeon Y, Kim T, Lim WC, Ham J, Park
YN, Kim TJ and Ko H: Combined treatment with zingerone and its
novel derivative synergistically inhibits TGF-β1 induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion of human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 27:1081–1088.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu Y, Yuan X, Li W, Cao Q and Shu Y:
Aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 inhibits TGF-β1-induced EMT through
the inhibition of the mTOR pathway by reducing the expression of
PKM2 and is closely linked to oxidative stress. Int J Mol Med.
38:1235–1242. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang H, Zhang C, Xu L, Zang K, Ning Z,
Jiang F, Chi H, Zhu X and Meng Z: Bufalin suppresses hepatocellular
carcinoma invasion and metastasis by targeting HIF-1α via the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Oncotarget. 7:20193–20208. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chang CC, Ling XH, Hsu HF, Wu JM, Wang CP,
Yang JF, Fang LW and Houng JY: Siegesbeckia orientalis extract
inhibits TGFβ1-induced migration and invasion of endometrial cancer
cells. Molecules. 21:E10212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Feng LX, Sun P, Mi T, Liu M, Liu W, Yao S,
Cao YM, Yu XL, Wu WY, Jiang BH, et al: Agglutinin isolated from
Arisema heterophyllum Blume induces apoptosis and autophagy in A549
cells through inhibiting PI3K/Akt pathway and inducing ER stress.
Chin J Nat Med. 14:856–864. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li D, Han T, Liao J, Hu X, Xu S, Tian K,
Gu X, Cheng K, Li Z, Hua H and Xu J: Oridonin, a promising
ent-Kaurane diterpenoid lead compound. Int J Mol Sci. 17:E13952016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li D, Han T, Xu S, Zhou T, Tian K, Hu X,
Cheng K, Li Z, Hua H and Xu J: Antitumor and antibacterial
derivatives of oridonin: A main composition of Dong-Ling-Cao.
Molecules. 21:E5752016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu J, Chen X, Qu S, Yao B, Xu Y, Wu J, Jin
Y and Ma C: Oridonin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in hormone-independent prostate
cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 13:2838–2846. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang XH, Zhang SF, Bao JT and Liu FY:
Oridonin synergizes with Nutlin-3 in osteosarcoma cells by
modulating the levels of multiple Bcl-2 family proteins. Tumour
Biol. 39:10104283177016382017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xia S, Zhang X, Li C and Guan H: Oridonin
inhibits breast cancer growth and metastasis through blocking the
Notch signaling. Saudi Pharm J. 25:638–643. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Y, Wang L, Zi Y, Zhang L, Guo Y and
Huang Y: Oridonin effectively reverses the drug resistance of
cisplatin involving induction of cell apoptosis and inhibition of
MMP expression in human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Saudi J Biol
Sci. 24:678–686. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gu Z, Wang X, Qi R, Wei L, Huo Y, Ma Y,
Shi L, Chang Y, Li G and Zhou L: Oridonin induces apoptosis in
uveal melanoma cells by upregulation of Bim and downregulation of
fatty acid synthase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 457:187–193. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang HJ, Li D, Yang FY, Tashiro S, Onodera
S and Ikejima T: Oridonin induces human melanoma A375-S2 cell death
partially through inhibiting insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
signaling. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 10:787–798. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang G, Li J, Zhang L, Huang S and Zhao X
and Zhao X: Celecoxib induced apoptosis against different breast
cancer cell lines by down-regulated NF-κB pathway. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 490:969–976. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang JJ, Sanderson BJ and Zhang W:
Significant anti-invasive activities of α-mangostin from the
mangosteen pericarp on two human skin cancer cell lines. Anticancer
Res. 32:3805–3816. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cui S, Wang J, Wu Q, Qian J, Yang C and Bo
P: Genistein inhibits the growth and regulates the migration and
invasion abilities of melanoma cells via the FAK/paxillin and MAPK
pathways. Oncotarget. 8:21674–21691. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu ZY, Lien JC, Huang YP, Liao CL, Lin JJ,
Fan MJ, Ko YC, Hsiao YP, Lu HF and Chung JG: Casticin inhibits
A375.S2 human melanoma cell migration/invasion through
downregulating NF-κB and matrix metalloproteinase-2 and −1.
Molecules. 21:3842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Abu R, Jiang Z, Ueno M, Isaka S, Nakazono
S, Okimura T, Cho K, Yamaguchi K, Kim D and Oda T: Anti-metastatic
effects of the sulfated polysaccharide ascophyllan isolated from
Ascophyllum nodosum on B16 melanoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
458:727–732. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Saviola AJ, Burns PD, Mukherjee AK and
Mackessy SP: The disintegrin tzabcanin inhibits adhesion and
migration in melanoma and lung cancer cells. Int J Biol Macromol.
88:457–464. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao S, Wang J and Qin C: Blockade of
CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling inhibits intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
progression and metastasis via inactivation of canonical Wnt
pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:1032014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hsu YY, Shi GY, Wang KC, Ma CY, Cheng TL
and Wu HL: Thrombomodulin promotes focal adhesion kinase activation
and contributes to angiogenesis by binding to fibronectin.
Oncotarget. 7:68122–68139. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shih YL, Chou HM, Chou HC, Lu HF, Chu YL,
Shang HS and Chung JG: Casticin impairs cell migration and invasion
of mouse melanoma B16F10 cells via PI3K/AKT and NF-κB signaling
pathways. Environ Toxicol. 32:2097–2112. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ruan JS, Liu YP, Zhang L, Yan LG, Fan FT,
Shen CS, Wang AY, Zheng SZ, Wang SM and Lu Y: Luteolin reduces the
invasive potential of malignant melanoma cells by targeting β3
integrin and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 33:1325–1331. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Feng J, Cen J, Li J, Zhao R, Zhu C, Wang
Z, Xie J and Tang W: Histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid
(VPA) promotes the epithelial mesenchymal transition of colorectal
cancer cells via up regulation of Snail. Cell Adh Migr. 9:495–501.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pearlman RL, Montes de Oca MK, Pal HC and
Afaq F: Potential therapeutic targets of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in melanoma. Cancer Lett. 391:125–140. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li F, Wang Y and Yan Y: Gambogenic acid
induces cell growth inhibition, cell cycle arrest and metastasis
inhibition in choroidal melanoma in a dose-dependent manner. Exp
Ther Med. 13:2456–2462. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhu Y, Cheng Y, Guo Y, Chen J, Chen F, Luo
R and Li A: Protein kinase D2 contributes to TNF-α-induced
epithelial mesenchymal transition and invasion via the
PI3K/GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 7:5327–5341. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhou SL, Zhou ZJ, Hu ZQ, Li X, Huang XW,
Wang Z, Fan J, Dai Z and Zhou J: CXCR2/CXCL5 axis contributes to
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of HCC cells through activating
PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β/Snail signaling. Cancer Lett. 358:124–135. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sadok A, McCarthy A, Caldwell J, Collins
I, Garrett MD, Yeo M, Hooper S, Sahai E, Kuemper S, Mardakheh FK
and Marshall CJ: Rho kinase inhibitors block melanoma cell
migration and inhibit metastasis. Cancer Res. 75:2272–2284. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Noguchi K, Dalton AC, Howley BV, McCall
BJ, Yoshida A, Diehl JA and Howe PH: Interleukin-like EMT inducer
regulates partial phenotype switching in MITF-low melanoma cell
lines. PLoS One. 12:e01778302017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Miao M, Yan X, Guo L and Shao S: Effects
of the Rabdosia rubescens total flavonoids on focal cerebral
ischemia reperfusion model in rats. Saudi Pharm J. 25:607–614.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ren CM, Li Y, Chen QZ, Zeng YH, Shao Y, Wu
QX, Yuan SX, Yang JQ, Yu Y, Wu K, et al: Oridonin inhibits the
proliferation of human colon cancer cells by upregulating BMP7 to
activate p38 MAPK. Oncol Rep. 35:2691–2698. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhao J, Zhang M, He P, Zhao J, Chen Y, Qi
J and Wang Y: Proteomic analysis of oridonin-induced apoptosis in
multiple myeloma cells. Mol Med Rep. 15:1807–1815. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hao Y, Zhao F, Luo Y, Zhang M and Li S:
Inhibitory effect of oridonin on proliferation of RPMI8226 cells
and the possible underlying mechanism. J Tradit Chin Med.
36:225–230. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Staton CA, Reed MW and Brown NJ: A
critical analysis of current in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis
assays. Int J Exp Pathol. 90:195–221. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nakamura K, Peng Y, Utsumi F, Tanaka H,
Mizuno M, Toyokuni S, Hori M, Kikkawa F and Kajiyama H: Novel
intraperitoneal treatment with non-thermal plasma-activated medium
inhibits metastatic potential of ovarian cancer cells. Sci Rep.
7:60852017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wu QX, Yuan SX, Ren CM, Yu Y, Sun WJ, He
BC and Wu K: Oridonin upregulates PTEN through activating p38 MAPK
and inhibits proliferation in human colon cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
35:3341–3348. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xia R, Chen SX, Qin Q, Chen Y, Zhang WW,
Zhu RR and Deng AM: Oridonin suppresses proliferation of human
ovarian cancer cells via blockage of mTOR signaling. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 17:667–671. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bauer D, Werth F, Nguyen HA, Kiecker F and
Eberle J: Critical role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) for
synergistic enhancement of apoptosis by vemurafenib and the
potassium channel inhibitor TRAM-34 in melanoma cells. Cell Death
Dis. 8:e25942017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang Y, Sun Y, Wu Y and Zhang J:
Cucurbitacin E inhibits osteosarcoma cells proliferation and
invasion through attenuation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Biosci
Rep. 36:e004052016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Cha BK, Kim YS, Hwang KE, Cho KH, Oh SH,
Kim BR, Jun HY, Yoon KH, Jeong ET and Kim HR: Celecoxib and
sulindac inhibit TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and suppress lung cancer migration and invasion via downregulation
of sirtuin 1. Oncotarget. 7:57213–57227. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lee YJ and Han HJ: Troglitazone
ameliorates high glucose-induced EMT and dysfunction of SGLTs
through PI3K/Akt, GSK-3β, Snail1, and β-catenin in renal proximal
tubule cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 298:F1263–F1275. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Baek SH, Ko JH, Lee JH, Kim C, Lee H, Nam
D, Lee J, Lee SG, Yang WM, Um JY, et al: Ginkgolic acid inhibits
invasion and migration and TGF-β-induced EMT of lung cancer cells
through PI3K/Akt/mTOR inactivation. J Cell Physiol. 232:346–354.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Petanidis S, Kioseoglou E, Domvri K,
Zarogoulidis P, Carthy JM, Anestakis D, Moustakas A and Salifoglou
A: In vitro and ex vivo vanadium antitumor activity in
(TGF-β)-induced EMT. Synergistic activity with carboplatin and
correlation with tumor metastasis in cancer patients. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 74:121–134. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Balakrishnan S, Mukherjee S, Das S, Bhat
FA, Raja Singh P, Patra CR and Arunakaran J: Gold
nanoparticles-conjugated quercetin induces apoptosis via inhibition
of EGFR/PI3K/Akt-mediated pathway in breast cancer cell lines
(MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231). Cell Biochem Funct. 35:217–231. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chen XH, Lu LL, Ke HP, Liu ZC, Wang HF,
Wei W, Qi YF, Wang HS, Cai SH and Du J: The TGF-β-induced
up-regulation of NKG2DLs requires AKT/GSK-3β-mediated stabilization
of SP1. J Cell Mol Med. 21:860–870. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
He F, Chen H, Yang P, Wu Q, Zhang T, Wang
C, Wei J, Chen Z, Hu H, Li W and Cao J: Gankyrin sustains
PI3K/GSK-3β/β-catenin signal activation and promotes colorectal
cancer aggressiveness and progression. Oncotarget. 7:81156–81171.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Qin CD, Ma DN, Ren ZG, Zhu XD, Wang CH,
Wang YC, Ye BG, Cao MQ, Gao DM and Tang ZY: Astragaloside IV
inhibits metastasis in hepatoma cells through the suppression of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Akt/GSK-3β/β-catenin
pathway. Oncol Rep. 37:1725–1735. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Guo H, Luo H, Yuan H, Xia Y, Shu P, Huang
X, Lu Y, Liu X, Keller ET, Sun D, et al: Litchi seed extracts
diminish prostate cancer progression via induction of apoptosis and
attenuation of EMT through Akt/GSK-3β signaling. Sci Rep.
7:416562017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|