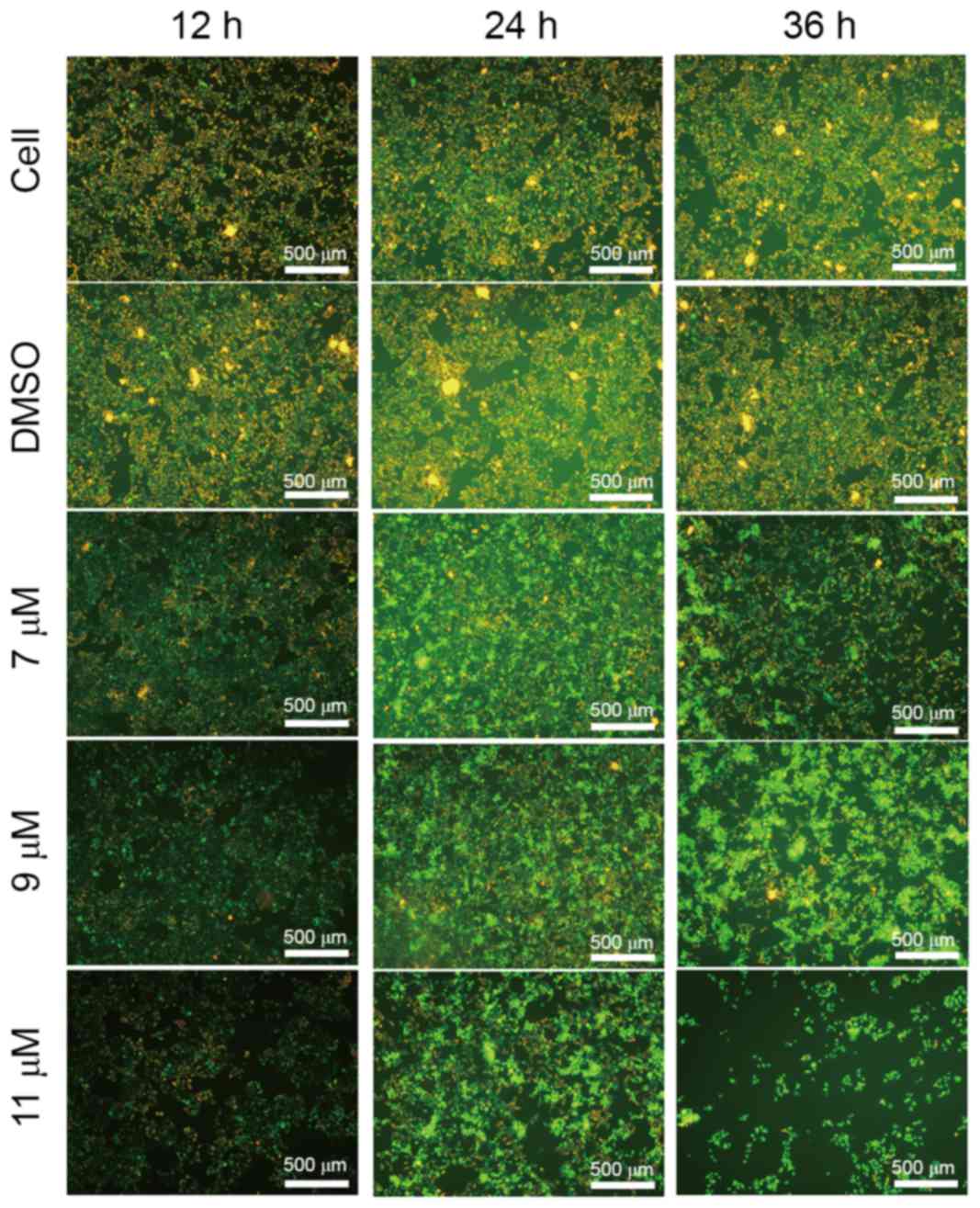
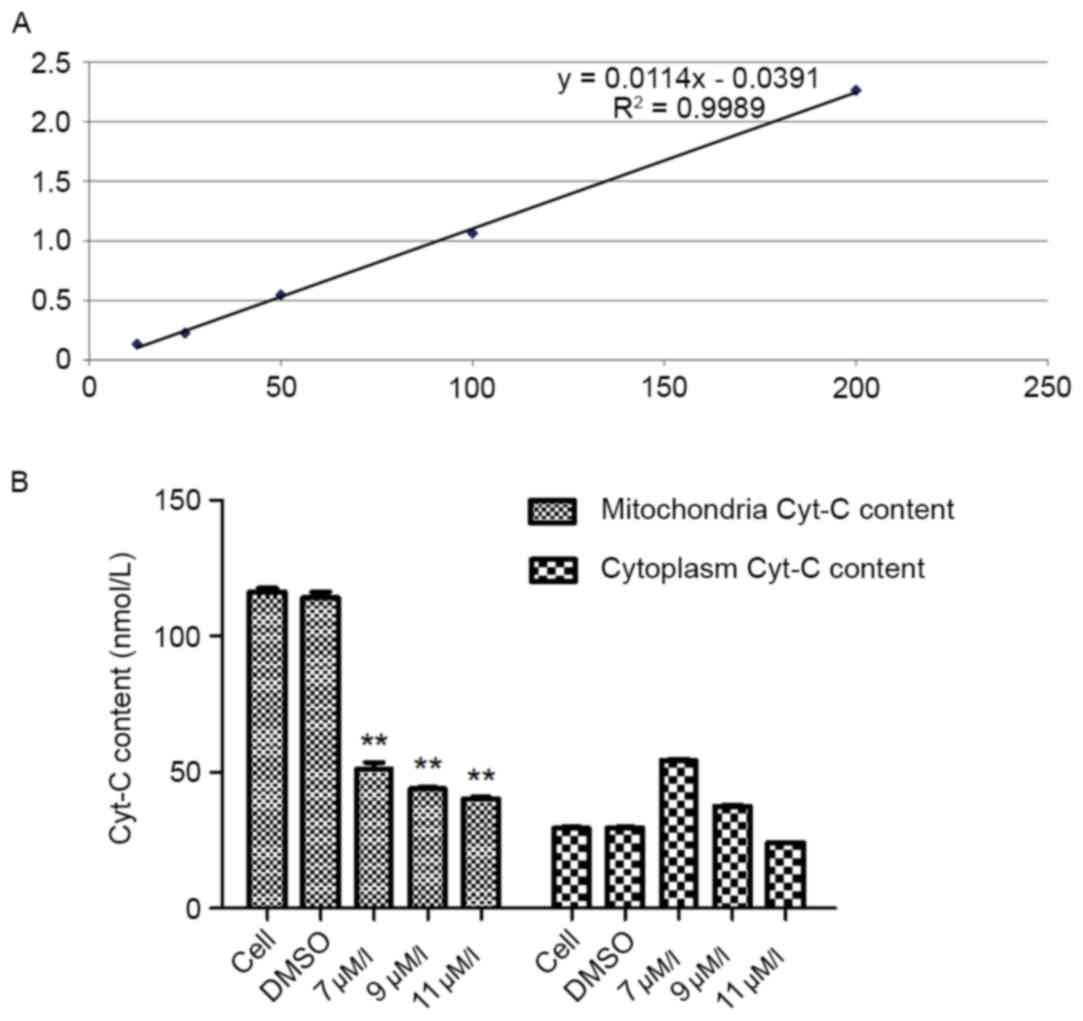
|
1
|
El-Serag HB: Epidemiology of viral
hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
142:1264–1273.e1. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bruix J and Sherman M: American
Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ng IO, Liu CL, Fan ST and Ng M: Expression
of P-glycoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma. A determinant of
chemotherapy response. Am J Clin Pathol. 113:355–363. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Vitale A, Volk ML, Pastorelli D, Lonardi
S, Farinati F, Burra P, Angeli P and Cillo U: Use of sorafenib in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma before liver
transplantation: A cost-benefit analysis while awaiting data on
sorafenib safety. Hepatology. 51:165–173. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Liu L, Fu J, Li T, Cui R, Ling J, Yu X, Ji
H and Zhang Y: NG, a novel PABA/NO-based oleanolic acid derivative,
induces human hepatoma cell apoptosis via a ROS/MAPK-dependent
mitochondrial pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 691:61–68. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wei J, Liu M, Liu H, Wang H, Wang F, Zhang
Y, Han L and Lin X: Oleanolic acid arrests cell cycle and induces
apoptosis via ROS-mediated mitochondrial depolarization and
lysosomal membrane permeabilization in human pancreatic cancer
cells. J Appl Toxicol. 33:756–765. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zheng QY, Li PP, Jin FS, Yao C, Zhang GH,
Zang T and Ai X: Ursolic acid induces ER stress response to
activate ASK1-JNK signaling and induce apoptosis in human bladder
cancer T24 cells. Cell Signal. 25:206–213. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Arur S, Uche UE, Rezaul K, Fong M,
Scranton V, Cowan AE, Mohler W and Han DK: Annexin I is an
endogenous ligand that mediates apoptotic cell engulfment. Dev
Cell. 4:587–598. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kuida K: Caspase-9. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 32:121–124. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Bossy-Wetzel E, Newmeyer DD and Green DR:
Mitochondrial cytochrome c release in apoptosis occurs upstream of
DEVD-specific caspase activation and independently of mitochondrial
transmembrane depolarization. EMBO J. 17:37–49. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Mourdjeva M, Kyurkchiev D, Mandinova A,
Altankova I, Kehayov I and Kyurkchiev S: Dynamics of membrane
translocation of phosphatidylserine during apoptosis detected by a
monoclonal antibody. Apoptosis. 10:209–217. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Joza N, Susin SA, Daugas E, Stanford WL,
Cho SK, Li CY, Sasaki T, Elia AJ, Cheng HY, Ravagnan L, et al:
Essential role of the mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor in
programmed cell death. Nature. 410:549–554. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Houston MA, Augenlicht LH and Heerdt BG:
Stable differences in intrinsic mitochondrial membrane potential of
tumor cell subpopulations reflect phenotypic heterogeneity. Int J
Cell Biol. 2011:9785832011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hao Z, Duncan GS, Chang CC, Elia A, Fang
M, Wakeham A, Okada H, Calzascia T, Jang Y, You-Ten A, et al:
Specific ablation of the apoptotic functions of cytochrome C
reveals a differential requirement for cytochrome C and Apaf-1 in
apoptosis. Cell. 121:579–591. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Samuel S, Tumilasci VF, Oliere S, Nguyên
TL, Shamy A, Bell J and Hiscott J: VSV oncolysis in combination
with the BCL-2 inhibitor obatoclax overcomes apoptosis resistance
in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Mol Ther. 18:2094–2103. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Barbu EM, Shirazi F, McGrath DM, Albert N,
Sidman RL, Pasqualini R, Arap W and Kontoyiannis DP: An
antimicrobial peptidomimetic induces Mucorales cell death through
mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. PLoS One. 8:e769812013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jang JH, Cho YC, Kim KH, Lee KS, Lee J,
Kim DE, Park JS, Jang BC, Kim S, Kwon TK and Park JW: BAI, a novel
Cdk inhibitor, enhances farnesyltransferase inhibitor
LB42708-mediated apoptosis in renal carcinoma cells through the
downregulation of Bcl-2 and c-FLIP (L). Int J Oncol. 45:1680–1690.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang X, Beitler JJ, Wang H, Lee MJ, Huang
W, Koenig L, Nannapaneni S, Amin AR, Bonner M, Shin HJ, et al:
Honokiol enhances paclitaxel efficacy in multi-drug resistant human
cancer model through the induction of apoptosis. PLoS One.
9:e863692014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Vacca RA, Valenti D, Bobba A, Merafina RS,
Passarella S and Marra E: Cytochrome c is released in a reactive
oxygen species-dependent manner and is degraded via caspase-like
proteases in tobacco Bright-Yellow 2 cells en route to heat
shock-induced cell death. Plant Physiol. 141:208–219. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bobba A, Atlante A, Giannattasio S,
Sgaramella G, Calissano P and Marra E: Early release and subsequent
caspase-mediated degradation of cytochrome c in apoptotic
cerebellar granule cells. FEBS Lett. 457:126–130. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I,
Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES and Wang X: Cytochrome c and
dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an
apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 91:479–489. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zou H, Li Y, Liu X and Wang X: An
APAF1.cytochrome c multimeric complex is a functional apoptosome
that activates procaspase-9. J Biol Chem. 274:11549–11556. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yoshida T, Okuyama H, Nakayama M,
Nishimura K, Nonomura N and Inoue M: Rapid decrease of ATP followed
by necrosis-like cell death in bladder cancer cells after exposure
to high-dose chemotherapeutics used in intravesical therapy. Cancer
Res. 74:13412014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Galluzzi L and Kroemer G: Necroptosis: A
specialized pathway of programmed necrosis. Cell. 135:1161–1163.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|