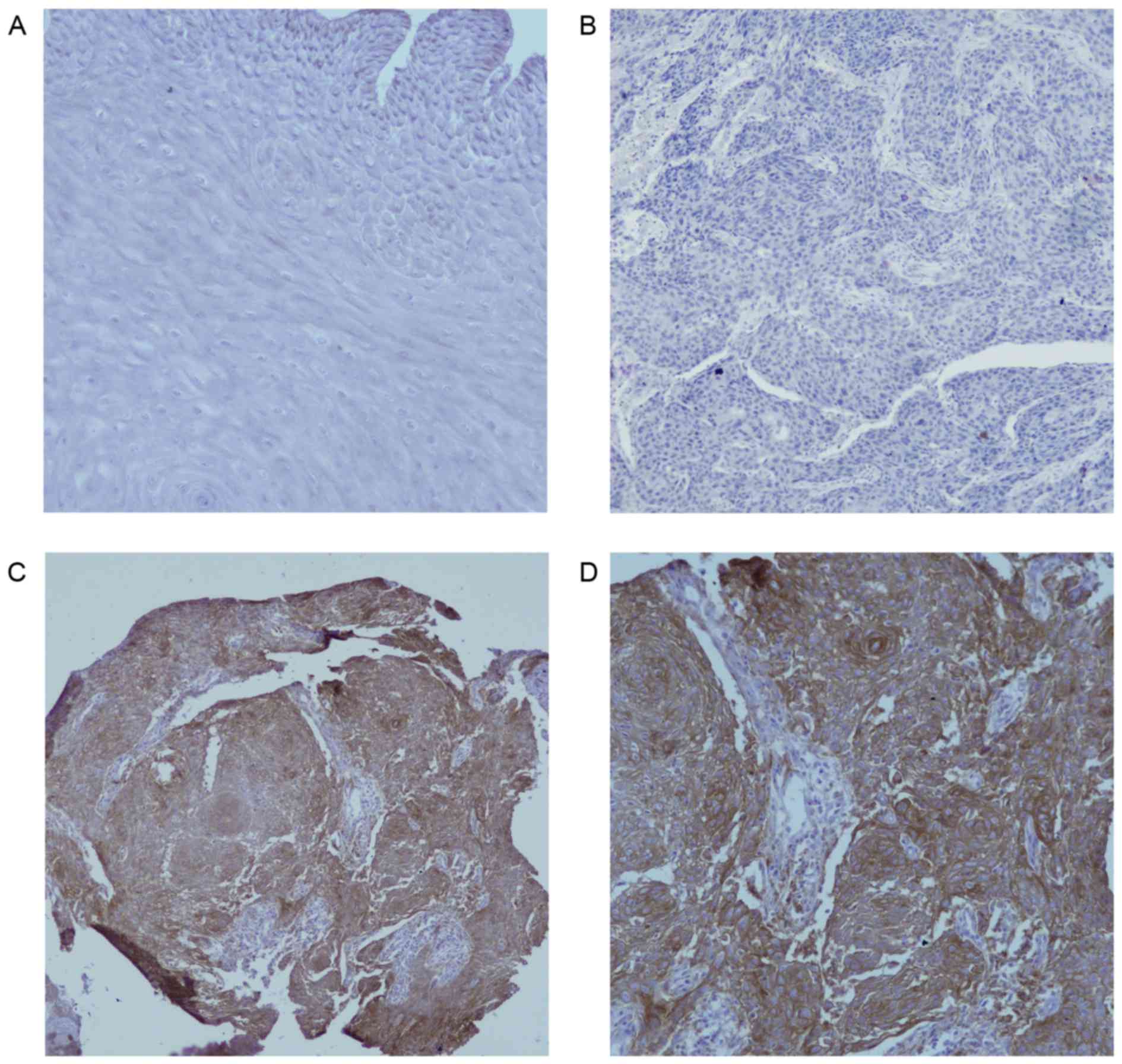
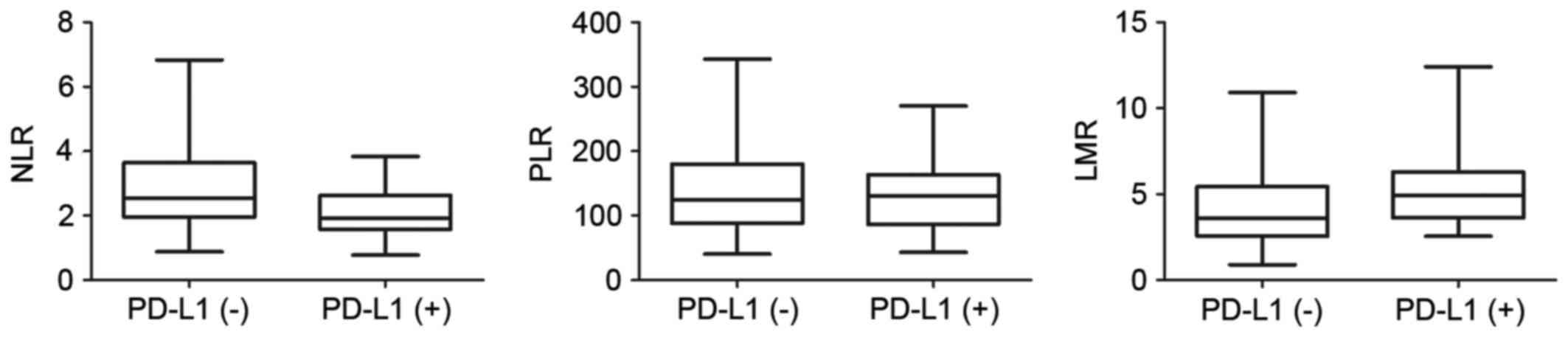
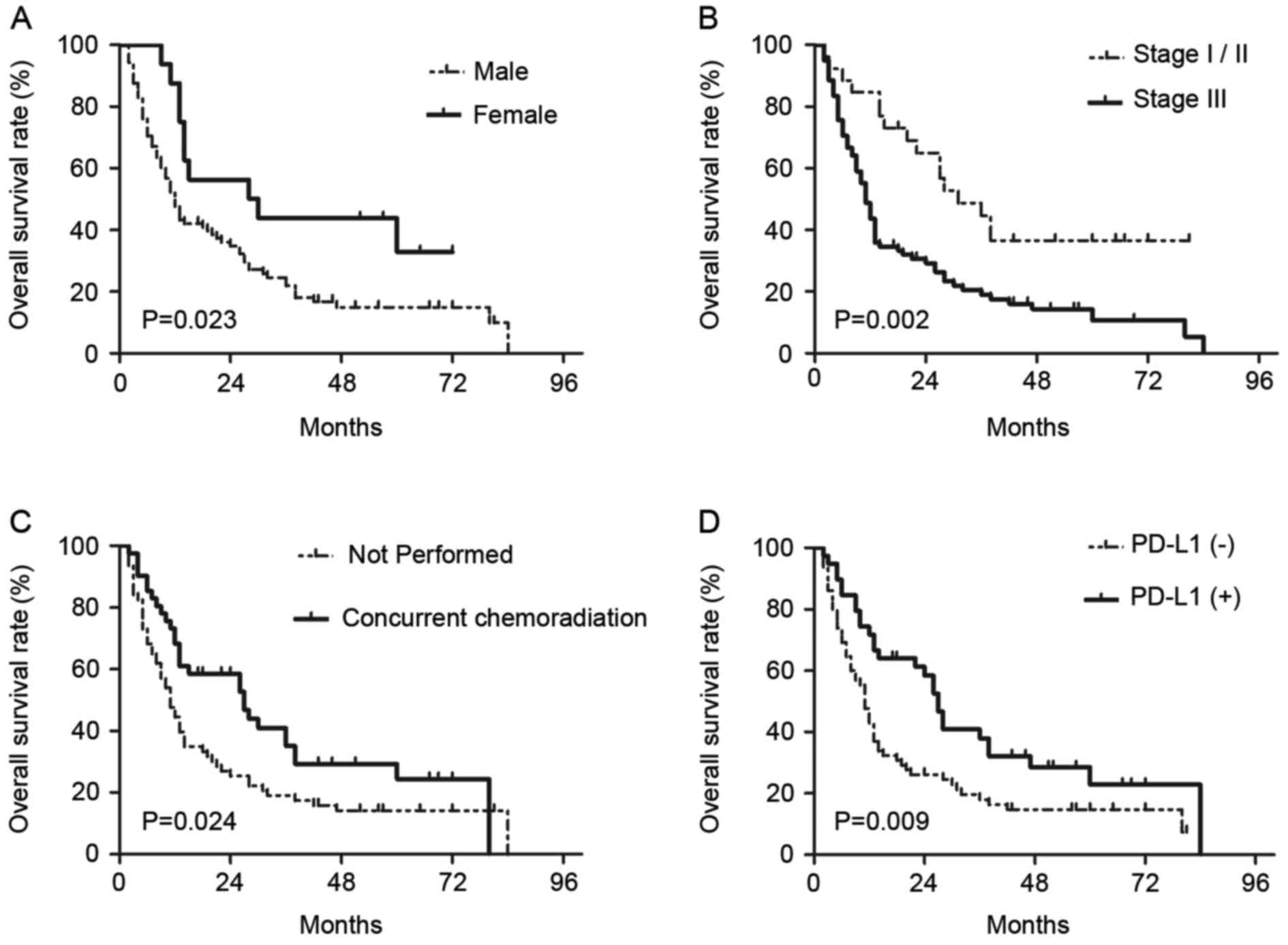
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zeng H and Zhang S: The
incidence and mortality of major cancers in China, 2012. Chin J
Cancer. 35:732016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parkin DM, Läärä E and Muir CS: Estimates
of the worldwide frequency of sixteen major cancers in 1980. Int J
Cancer. 41:184–197. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cooper JS, Guo MD, Herskovic A, Macdonald
JS, Martenson JA Jr, Al-Sarraf M, Byhardt R, Russell AH, Beitler
JJ, Spencer S, et al: Chemoradiotherapy of locally advanced
esophageal cancer: Long-term follow-up of a prospective randomized
trial (RTOG 85-01). Radiation therapy oncology group. JAMA.
281:1623–1627. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ajani JA, Winter K, Komaki R, Kelsen DP,
Minsky BD, Liao Z, Bradley J, Fromm M, Hornback D and Willett CG:
Phase II randomized trial of two nonoperative regimens of induction
chemotherapy followed by chemoradiation in patients with localized
carcinoma of the esophagus: RTOG 0113. J Clin Oncol. 26:4551–4556.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Robert C, Schachter J, Long GV, Arance A,
Grob JJ, Mortier L, Daud A, Carlino MS, McNeil C, Lotem M, et al:
Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med.
372:2521–2532. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Forde PM, Reiss KA, Zeidan AM and Brahmer
JR: What lies within: Novel strategies in immunotherapy for
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncologist. 18:1203–1213. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ritprajak P and Azuma M: Intrinsic and
extrinsic control of expression of the immunoregulatory molecule
PD-L1 in epithelial cells and squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol.
51:221–228. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen MF, Chen PT, Chen WC, Lu MS, Lin PY
and Lee KD: The role of PD-L1 in the radiation response and
prognosis for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma related to IL-6
and T-cell immunosuppression. Oncotarget. 7:7913–7924.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brodská B, Otevřelová P and Kuželová K:
Correlation of PD-L1 surface expression on leukemia cells with the
ratio of PD-L1 mRNA variants and with electrophoretic mobility.
Cancer Immunol Res. 4:815–819. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gu X, Gao XS, Xiong W, Guo W, Han L, Bai
Y, Peng C, Cui M and Xie M: Increased programmed death ligand-1
expression predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma
patients. Onco Targets Ther. 9:4805–4813. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Inamura K, Yokouchi Y, Sakakibara R,
Kobayashi M, Subat S, Ninomiya H, Nagano H, Nomura K, Okumura S and
Ishikawa Y: Relationship of tumor PD-L1 expression with EGFR
wild-type status and poor prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. Jpn J
Clin Oncol. 46:935–941. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Joneja U, Vranic S, Swensen J, Feldman R,
Chen W, Kimbrough J, Xiao N, Reddy S, Palazzo J and Gatalica Z:
Comprehensive profiling of metaplastic breast carcinomas reveals
frequent overexpression of programmed death-ligand 1. J Clin
Pathol. 70:255–259. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zou MX, Peng AB, Lv GH, Wang XB, Li J, She
XL and Jiang Y: Expression of programmed death-1 ligand (PD-L1) in
tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is associated with favorable spinal
chordoma prognosis. Am J Transl Res. 8:3274–3287. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Aguiar P Jr, Lopes G, Santoro I, Tadokoro
H, Barreto C and De Mello R: P2.47 (also presented as PD1.02): The
role of PD-L1 expression as a predictive biomarker in advanced
NSCLC: An update of a network meta-analysis: Track: Immunotherapy.
J Thorac Oncol. 11 Suppl:S247–S248. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen CL, Pan QZ, Zhao JJ, Wang Y, Li YQ,
Wang QJ, Pan K, Weng DS, Jiang SS, Tang Y, et al: PD-L1 expression
as a predictive biomarker for cytokine-induced killer cell
immunotherapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncoimmunology. 5:e11766532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Loos M, Langer R, Schuster T, Gertler R,
Walch A, Rauser S, Friess H and Feith M: Clinical significance of
the costimulatory molecule B7-H1 in Barrett carcinoma. Ann Thorac
Surg. 91:1025–1031. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hatogai K, Kitano S, Fujii S, Kojima T,
Daiko H, Nomura S, Yoshino T, Ohtsu A, Takiguchi Y, Doi T and
Ochiai A: Comprehensive immunohistochemical analysis of tumor
microenvironment immune status in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:47252–47264. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang N, Zeng Y, Du W, Zhu J, Shen D, Liu
Z and Huang JA: The EGFR pathway is involved in the regulation of
PD-L1 expression via the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway in
EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Oncol. 49:1360–1368.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen PC and Feng JF: A novel
inflammation-based stage (I Stage) in patients with resectable
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mediators Inflamm.
2016:53967472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kara M, Uysal S, Altinisik U, Cevizci S,
Güçlü O and Dereköy FS: The pre-treatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte
ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and red cell distribution
width predict prognosis in patients with laryngeal carcinoma. Eur
Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 274:535–542. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
van Kessel KE, de Haan LM, Fransen van de
Putte EE, van Rhijn BW, de Wit R, van der Heijden MS, Zwarthoff EC
and Boormans JL: Elevated derived neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
corresponds with poor outcome in patients undergoing pre-operative
chemotherapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Bladder Cancer.
2:351–360. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American joint
committee on cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tanaka K, Miyata H, Sugimura K, Kanemura
T, Hamada-Uematsu M, Mizote Y, Yamasaki M, Wada H, Nakajima K,
Takiguchi S, et al: Negative influence of programmed
death-1-ligands on the survival of esophageal cancer patients
treated with chemotherapy. Cancer Sci. 107:726–733. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen K, Cheng G, Zhang F, Zhang N, Li D,
Jin J, Wu J, Ying L, Mao W and Su D: Prognostic significance of
programmed death-1 and programmed death-ligand 1 expression in
patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget.
7:30772–30780. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Takada K, Toyokawa G, Okamoto T, Akamine
T, Takamori S, Katsura M, Fujishita T, Shoji F, Oda Y and Maehara
Y: An immunohistochemical analysis of PD-L1 protein expression in
surgically resected small cell lung cancer using different
antibodies and criteria. Anticancer Res. 36:3409–3412.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, McDermott DF,
George S, Hammers HJ, Srinivas S, Tykodi SS, Sosman JA, Procopio G,
Plimack ER, et al: Nivolumab versus everolimus in advanced
renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 373:1803–1813. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Taube JM, Anders RA, Young GD, Xu H,
Sharma R, McMiller TL, Chen S, Klein AP, Pardoll DM, Topalian SL
and Chen L: Colocalization of inflammatory response with B7-h1
expression in human melanocytic lesions supports an adaptive
resistance mechanism of immune escape. Sci Transl Med.
4:127ra372012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Grimm M, Rieth J, Hoefert S, Krimmel M,
Rieth S, Teriete P, Kluba S, Biegner T, Munz A and Reinert S:
Standardized pretreatment inflammatory laboratory markers and
calculated ratios in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 273:3371–3384. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee SM, Russell A and Hellawell G:
Predictive value of pretreatment inflammation-based prognostic
scores (neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte
ratio, and lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio) for invasive bladder
carcinoma. Korean J Urol. 56:749–755. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu JS, Huang Y, Yang X and Feng JF: A
nomogram to predict prognostic values of various inflammatory
biomarkers in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am
J Cancer Res. 5:2180–2189. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Stotz M, Liegl-Atzwanger B, Posch F, Mrsic
E, Thalhammer M, Stojakovic T, Bezan A, Pichler M, Gerger A and
Szkandera J: Blood-based biomarkers are associated with disease
recurrence and survival in gastrointestinal stroma tumor patients
after surgical resection. PLoS One. 11:e01594482016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Q, Blank S, Fiel MI, Kadri H, Luan W,
Warren L, Zhu A, Deaderick PA, Sarpel U, Labow DM and Hiotis SP:
The severity of liver fibrosis influences the prognostic value of
inflammation-based scores in hepatitis B-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 22 Suppl 3:S1125–S1132. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
He G, Zhang H, Zhou J, Wang B, Chen Y,
Kong Y, Xie X, Wang X, Fei R, Wei L, et al: Peritumoural
neutrophils negatively regulate adaptive immunity via the
PD-L1/PD-1 signalling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 34:1412015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bankey PE, Banerjee S, Zucchiatti A, De M,
Sleem RW, Lin CF, Miller-Graziano CL and De AK: Cytokine induced
expression of programmed death ligands in human neutrophils.
Immunol Lett. 129:100–107. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Thorn M, Guha P, Cunetta M, Espat NJ,
Miller G, Junghans RP and Katz SC: Tumor-associated GM-CSF
overexpression induces immunoinhibitory molecules via STAT3 in
myeloid-suppressor cells infiltrating liver metastases. Cancer Gene
Ther. 23:188–198. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Han S, Liu Y, Li Q, Li Z, Hou H and Wu A:
Pre-treatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with
neutrophil and T-cell infiltration and predicts clinical outcome in
patients with glioblastoma. BMC Cancer. 15:6172015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee VH, Lo AW, Leung CY, Shek WH, Kwong
DL, Lam KO, Tong CC, Sze CK and Leung TW: Correlation of PD-L1
expression of tumor cells with survival outcomes after radical
intensity-modulated radiation therapy for non-metastatic
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One. 11:e01579692016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Song Z, Yu X and Zhang Y: Altered
expression of programmed death-ligand 1 after neo-adjuvant
chemotherapy in patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma. Lung
Cancer. 99:166–171. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wei Y, Huang H, Qiu Z, Li H, Tan J, Ren G
and Wang X: NLRP1 overexpression is correlated with the
tumorigenesis and proliferation of human breast tumor. Biomed Res
Int. 2017:49384732017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pang X, Li R, Shi D, Pan X, Ma C, Zhang G,
Mu C and Chen W: Knockdown of Rhotekin 2 expression suppresses
proliferation and induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Oncol
Lett. 14:8028–8034. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lim SH, Hong M, Ahn S, Choi YL, Kim KM, Oh
D, Ahn YC, Jung SH, Ahn MJ, Park K, et al: Changes in tumour
expression of programmed death-ligand 1 after neoadjuvant
concurrent chemoradiotherapy in patients with squamous oesophageal
cancer. Eur J Cancer. 52:1–9. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Demaria S, Golden EB and Formenti SC: Role
of local radiation therapy in cancer immunotherapy. JAMA Oncol.
1:1325–1332. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Takeshima T, Pop LM, Laine A, Iyengar P,
Vitetta ES and Hannan R: Key role for neutrophils in
radiation-induced antitumor immune responses: Potentiation with
G-CSF. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:pp. 11300–11305. 2016;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ohigashi Y, Sho M, Yamada Y, Tsurui Y,
Hamada K, Ikeda N, Mizuno T, Yoriki R, Kashizuka H, Yane K, et al:
Clinical significance of programmed death-1 ligand-1 and programmed
death-1 ligand-2 expression in human esophageal cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 11:2947–2953. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen L, Deng H, Lu M, Xu B, Wang Q, Jiang
J and Wu C: B7-H1 expression associates with tumor invasion and
predicts patient's survival in human esophageal cancer. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 7:6015–6023. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Leng C, Li Y, Qin J, Ma J, Liu X, Cui Y,
Sun H, Wang Z, Hua X, Yu Y, et al: Relationship between expression
of PD-L1 and PD-L2 on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and the
antitumor effects of CD8+ T cells. Oncol Rep.
35:699–708. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhu Y, Li M, Mu D, Kong L, Zhang J, Zhao
F, Li Z, Liu X, Bo C and Yu J: CD8+/FOXP3+ ratio and PD-L1
expression associated with survival in pT3N0M0 stage esophageal
squamous cell cancer. Oncotarget. 7:71455–71465. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ito S, Okano S, Morita M, Saeki H,
Tsutsumi S, Tsukihara H, Nakashima Y, Ando K, Imamura Y, Ohgaki K,
et al: Expression of PD-L1 and HLA class I in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma: Prognostic factors for patient outcome. Ann Surg
Oncol. 23 Suppl 4:S508–S515. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|