Introduction
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most lethal types
of cancer and has been increasing in incidence and mortality over
the last several decades. In China, it has been estimated that
~464,000 new cases were diagnosed in 2012, which accounts for over
40% of the total cases (~989,600) worldwide (1). According to evidence from clinical
studies, the majority of patients with GC are diagnosed at an
advanced stage and are thus not suitable for radical surgery
(2). Previous studies have also
reported that earlier diagnosis and treatment of GC could produce a
5-year survival rate of >90% (3).
Recent developments in the field of digestive system
endoscopy have been remarkable due to their association with
decreased trauma, accelerated recovery and fewer complications
(4,5).
However, endoscopic biopsy and observation of pathological
morphology are unable to detect all precancerous lesions associated
with early GC (6). Therefore,
improvements in the early-stage diagnosis of GC and identification
of sensitive and specific biomarkers for early detection are
important research topics. These issues will be resolved by further
investigation into the pathogenesis of GC as well as the
identification of novel and reliable biomarkers for early diagnosis
or molecular therapeutic targets for the treatment of this
disease.
Over the past decade, various studies have indicated
that the human transcriptome comprises not only of protein-coding
mRNAs, but also a large number of non-protein-coding RNAs (7). Although a large number of studies focus
on microRNAs (miRNAs; 18–200 nucleotides), a wide array of critical
regulatory roles in biology have been associated with long
non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) (8).
lncRNAs, which are tentatively defined as a series of RNA
transcripts that are >200 nucleotides in length, have been
confirmed as essential regulators in almost all aspects of biology
(9). Accumulating evidence suggests
that lncRNAs are important in tumorigenesis (10). As it is the functional end-product,
the level of lncRNA expression correlates directly with the level
of the active molecule (11). Thus,
the use of lncRNAs in diagnostics has inherent advantages over the
use of protein-coding RNAs. In addition, lncRNAs exhibit greater
tissue specificity compared with protein-coding mRNAs and miRNAs,
making them appealing in the search for novel diagnostic and
prognostic cancer biomarkers (12).
Therefore, further studies on GC tissues from endoscopic biopsy may
aid in establishing the associations between lncRNAs and GC.
Previous studies have identified a subset of lncRNAs
that are associated with GC, indicating their wide participation in
the development and progression of GC (13,14).
However, the biological functions and mechanisms of these lncRNAs
remain unexplored (11). In the
present study, differential expression profiles of lncRNAs and
mRNAs were detected in advanced GC tissues and adjacent non-tumor
tissues by microarray analysis. In addition, the present study
aimed to identify the associations between significant differences
in lncRNA levels and the clinicopathological characteristics of GC
in order to elucidate the specific functions and mechanisms of
these lncRNAs during GC development.
Materials and methods
Patients and tissue sample
collection
Specimens from 10 patients with advanced GC, as well
as their paired adjacent non-cancerous tissue specimens, were
included in the lncRNA microarray analysis, and tissues from 82
patients, including 59 males and 23 females aged between 45 and 70
years, were collected for reverse transcription-quantitative
polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) analysis from the Gansu Wuwei
Cancer Hospital (Wuwei, China) between September 2014 and May 2015.
The present study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Gansu
Wuwei Cancer Hospital. All patients provided written informed
consent to participate in the present study. All patients were
assigned a diagnosis of GC based on histopathology and clinical
history.
In addition, clinical information was recorded for
each patient, including age, gender, tumor grade, tumor location,
tumor stage, degree of differentiation, tumor-node-metastasis (TNM)
stage, lymph node metastasis status and date of resection. The
pathologist assessed the tumor by microscopic examination in every
case, and the percentage of tumor tissue was estimated to be ≥80%.
No patients had received preoperative radiotherapy or chemotherapy.
Adjacent non-cancerous tissues were located ≥5 cm from the tumor
edge. Tissue samples were immersed in RNAlater (Ambion; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc., Austin, TX, USA) and stored at −80°C until
use.
Isolation of RNA
Total RNA was isolated from the GC tissues and
adjacent non-tumor gastric mucosal epithelium using TRIzol reagent
(Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Carlsbad, CA, USA)
according to the manufacturer's instructions. The concentration and
integrity of isolated RNA was assessed using a NanoDrop 1000
spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc., Wilmington, DE, USA). Finally, total RNA integrity was
assessed by agarose gel electrophoresis.
lncRNA microarray analysis
RNA samples were isolated from 10 patients by
pooling RNA from 2, 4 and 4 patients, respectively, into three
groups as ‘one sample’. Thus, three pairs of pooled RNA samples
were generated from GC specimens and their paired adjacent
non-cancerous tissues. These three pairs of RNA samples were
subjected to microarray analysis using a RiboArray Custom Array
1*90K (Guangzhou RiboBio Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China), which could
detect 32,987 lncRNAs from a number of authoritative data sources,
including RefSeq (National Center for Biotechnology Information)
(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/?term=), H-invDB
(http://h-invitational.jp/hinv/ahg-db/index.jsp), UCSC
(http://genome.ucsc.edu/) LncRNAdb (http://www.lncrnadb.org/#opennewwindow),
and GENCODE LncRNA (https://www.gencodegenes.org). Signals were normalized
using the median center tool for the genes. Analysis of variance
(ANOVA) was used to compare differentially expressed lncRNAs and
mRNAs.
In a previous study, we built an lncRNA-mRNA
co-expression network that was based on the theory of competing
endogenous RNAs, and the differentially expressed lncRNAs and mRNAs
that were selected from GC specimens and their paired adjacent
non-cancerous tissues (15). In the
present study, standard selection criteria to identify
differentially expressed lncRNAs and mRNAs were established at
P<0.05 and fold change >2. The lncRNA-mRNA networks were
constructed based on the associations between the differentially
expressed lncRNAs and mRNAs in the previous study (15), and visualized using Cytoscape v3.0
(National Institute of General Medical Sciences, National
Institutes of Health, Rockville, MD, USA).
RT-qPCR analysis
GAPDH was selected as the endogenous standard. RT
reactions were conducted in two steps. First, the mixture
containing 1 µg of RNA samples was incubated in a 96-well plate for
10 min at 70°C and held at 4°C. Subsequently, the 11.1-µl mixture,
which comprised 4 µl MgCl2 (25 mM), 2 µl 10X RT buffer
(Promega Corporation, Madison, WI, USA), 2 µl dNTPs (10 mM; Promega
Corporation), 0.6 µl AMV reverse transcriptase (15 U/µl), 0.5 µl
RNAsin, 2 µl random primers, and 6.9 µl ddH2O, was
incubated in a 96-well plate at 25°C for 10 min, 42°C for 15 min,
95°C for 5 min, and subsequently held at 4°C.
qPCR was performed to detect the expression levels
of candidate lncRNAs with the StepOnePlus™ Real-Time PCR System
(Applied Biosystems; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA,
USA) and GoTaq® qPCR Master Mix (Promega Corporation),
according to the manufacturer's protocol. The total PCR reaction
volume was 10 µl and included 1 µl cDNA, 5 µl GoTaq®
qPCR Master Mix, 0.2 µM PCR primers (Shanghai Generay Biotech Co.,
Ltd., Shanghai, China) and RNase-free water. The reaction was
performed at 95°C for 2 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 15
sec, 60°C for 30 sec and 72°C for 30 sec. A dissociation curve was
analyzed from 60–95°C. Primers used for real-time RT-PCR as shown
in Table I. RT-qPCR relative
fold-change results were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCq
method [where ΔCq=(CqRNAs-CqGAPDH); and
ΔΔCq=ΔCqtumor tissues-ΔCqadjacent non-tumor
tissues] (16). All experiments
were repeated three times.
 | Table I.Primer sequences used in the reverse
transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction validation of
long non-coding RNAs. |
Table I.
Primer sequences used in the reverse
transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction validation of
long non-coding RNAs.
| Gene symbol | Primer sequences,
5′-3′ | Target size,
bp | Tm, °C |
|---|
| RP5-919F19-F |
TGGAGGAAGGAGAAGGTCAT | 88 | 59 |
| RP5-919F19-R |
CGTGTCAGGTAGCCAAGG |
|
|
| CTD-2541M15-F |
GATACTGCCTGTGACCTG | 120 | 59 |
| CTD-2541M15-R |
GACTAAGCGTGACTCCTG |
|
|
| UCA1-F |
TCCACACCCAAAACAAAA | 200 | 59 |
| UCA1-R |
GCCCTCTAACAACAAACAAC |
|
|
| AP000459-F |
CCATCTTTGAGGGCTTTT | 141 | 59 |
| AP000459-R |
GGTGTGTCATTTTGTTTTCC |
|
|
| LOC101928316-F |
AACAACGGGGACATTAGG | 119 | 59 |
| LOC101928316-R |
AACTGGAAACATCACATAGCA |
|
|
| LINC01071-F |
TTTCCATAAGGCACGATT | 220 | 59 |
| LINC01071-R |
CCTAACCCACCACATTCA |
|
|
| MEG3-F |
TGCCCATCTACACCTCAC | 112 | 59 |
| MEG3-R |
TCCTCTTCATCCTTTGCC |
|
|
| GAPDH-F |
GGGAGCCAAAAGGGTCATCA | 203 | 60 |
| GAPDH-R |
TGATGGCATGGACTGTGGTC |
|
|
Statistical analysis
SPSS software version 18.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL,
USA) was used to perform the data analysis. Results are presented
as mean ± standard error. Statistical analysis was performed using
a Student's t-test for comparison of two groups in the microarray
analysis, and one-way analysis of variance for multiple comparisons
with the Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test. For all comparisons,
differences with P<0.05 were considered statistically
significant. In addition, a conditional logistic regression
analysis was used to evaluate any association between
differentially expressed lncRNAs and the characteristics of
patients with GC.
Results
Screening of candidate lncRNAs by
microarray and bioinformatics analysis
Previous microarray analysis identified that 1,046
lncRNAs, including 427 upregulated and 619 downregulated lncRNAs,
were significantly differentially expressed (fold-change ≥2.0)
between advanced GC lesions and adjacent non-tumor tissues. The
present study identified key lncRNAs, and a total of 6 key lncRNAs
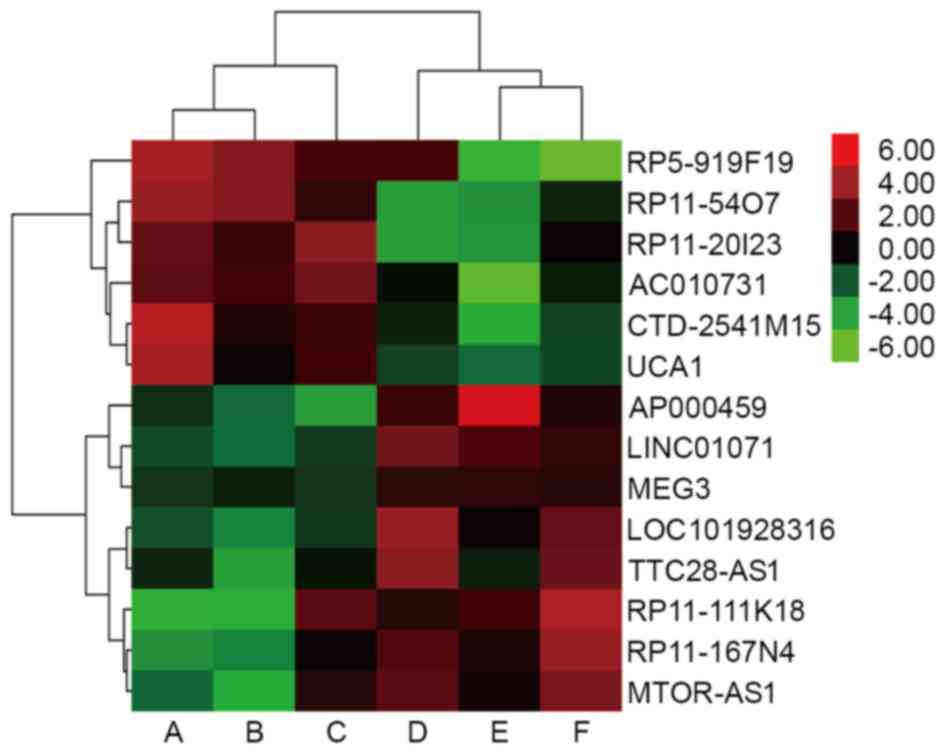
were revealed to be overexpressed in tumor tissues [RP5-919F19,
RP11-54O7, RP11-20I23, MCPH1 antisense RNA 1
(CTD-2541M15), AC010731, and urothelial
carcinoma-associated 1 (UCA1); Table II], in addition, there were 8 key
lncRNAs were found to be downregulated in tumor tissues
[AP000459, LOC101928316, RP11-167N4, tumor suppressor
candidate 8 (LINC01071), RP11-111K18, TTC28 antisense
RNA 1 (TTC28-AS1), MTOR antisense RNA 1 (MTOR-AS1),
and maternally expressed 3 (MEG3); Table II]. The data also revealed that there
were significant differences in the expression levels of
RP5-919F19, CTD-2541M15, UCA1, AP000459, LOC101928316,
LINC01071 and MEG3 in tumor tissues compared with
adjacent non-tumor tissues (P<0.05). Clustering analysis was
performed for all 14 abnormally expressed key lncRNAs (Fig. 1).
 | Table II.Differential expression of key
lncRNAs in gastric cancer. |
Table II.
Differential expression of key
lncRNAs in gastric cancer.
| Name (lncRNA) | Transcript-ID | Regulation | Fold-change |
|---|
|
RP5-919F19a | URS0000515CAC | Up | 36.92 |
|
RP11-54O7 | URS00005B803E | Up | 32.52 |
|
RP11-20I23 | URS00002B7786 | Up | 32.43 |
|
CTD-2541M15a | URS0000359EF8 | Up | 28.03 |
|
AC010731 |
ENST00000543490 | Up | 25.33 |
|
UCA1a | NR_015379 | Up | 11.51 |
|
AP000459a | URS000048CBED | Down | −23.26 |
|
LOC101928316a | XR_428890 | Down | −22.73 |
|
RP11-167N4 |
ENST00000537019 | Down | −22.73 |
|
RP11-111K18 | URS00002FCA1A | Down | −18.52 |
|
LINC01071a | NR_104174 | Down | −18.52 |
|
TTC28-AS1 |
ENST00000430525 | Down | −17.88 |
|
MTOR-AS1 | NR_046600 | Down | −16.67 |
|
MEG3a | NR_046473 | Down | −2.19 |
Verification of selected lncRNA
expression in GC tissues
RT-qPCR was performed to confirm the reliability and
validity of the detected expression levels of the selected lncRNAs
in 82 GC tissues and adjacent non-tumor tissues. The results
demonstrated that RP5-919F19, CTD-2541M15 and UCA1
showed consistent upregulation compared with adjacent non-tumor
tissues, while AP000459, LOC101928316, LINC01071 and
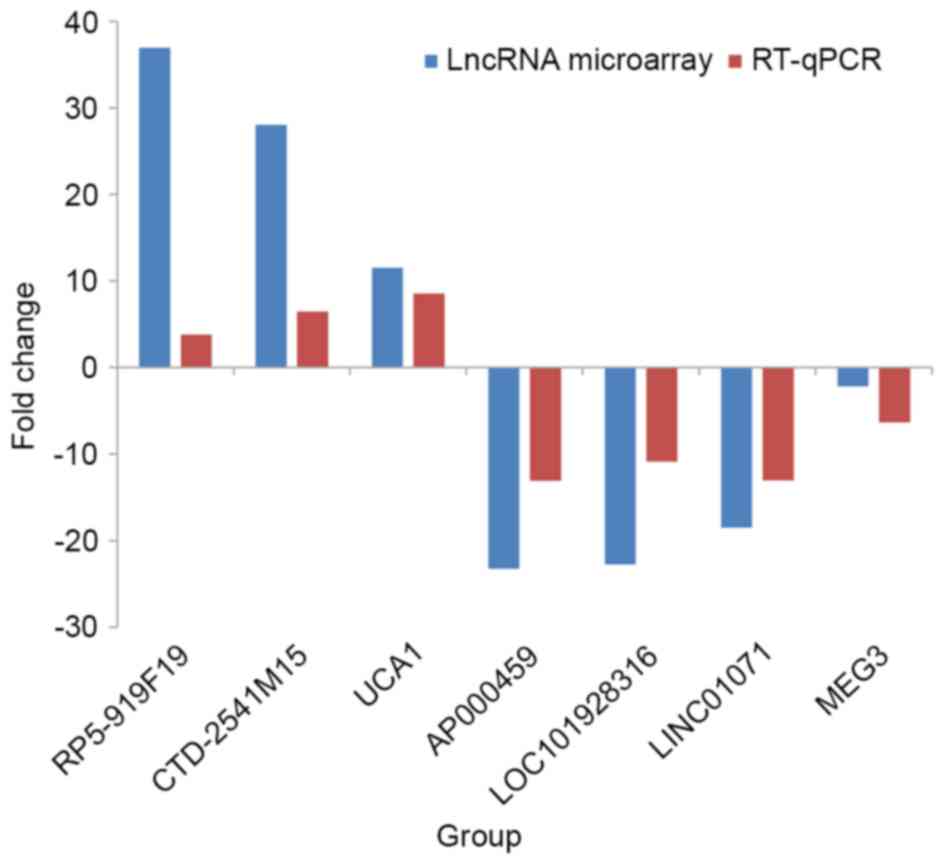
MEG3 showed consistent downregulation (Table III). A histogram (Fig. 2) shows the fold-changes detected by
RT-qPCR (2−ΔΔCq) and lncRNA microarray data. The
consistency between the microarray and RT-qPCR data confirms the
reliability of the results.
 | Table III.Relative expression levels of lncRNAs
in 82 pairs of GC and non-tumor tissues. |
Table III.
Relative expression levels of lncRNAs
in 82 pairs of GC and non-tumor tissues.
|
| lncRNA expression,
ΔCq (mean ± standard deviation) |
|
|
|
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Gene symbol | GC tissues | Adjacent non-tumor
tissues |
2−ΔΔCq | Change in
expression in GC | P-value |
|---|
|
RP5-919F19 | 11.448±4.136 | 12.393±3.613 | 3.778 | Up | 0.000a |
|
CTD-2541M15 | 8.041±2.734 | 8.729±2.633 | 6.459 | Up | 0.001a |
| UCA1 | 9.666±3.459 | 10.764±4.011 | 8.521 | Up | 0.000a |
|
AP000459 | 12.234±5.216 | 10.460±4.938 | −13.073 | Down | 0.000a |
|
LOC101928316 | 10.198±3.749 | 8.789±3.677 | −10.878 | Down | 0.000a |
|
LINC01071 | 13.757±4.260 | 12.152±4.809 | −13.062 | Down | 0.000a |
| MEG3 | 8.079±4.892 | 7.159±4.479 | −6.322 | Down | 0.003a |
Association between the identified
lncRNAs and clinicopathological characteristics of GC
The associations between the expression levels of
the seven selected lncRNAs in GC samples and the
clinicopathological characteristics of the patients were analyzed.
The results identified that one lncRNA, AP000459, had no
statistically significant associations with the following
clinicopathological characteristics: Patient gender or age; tumor
size or differentiation degree; TNM stage; or lymph node metastasis
status. However, the remaining six lncRNAs each demonstrated
significant associations with certain characteristics:
RP5-919F19, LOC101928316 and MEG3 were significantly
associated with tumor differentiation degree; RP5-919F19,
UCA1 and MEG3 were significantly associated with lymph
node metastasis status; and RP5-919F19, CTD-2541M15 and
UCA1 were significantly associated with TNM stage (all
P<0.05). In addition, LINC01071 expression was associated
with patient age; UCA1 was associated with tumor size; and
LOC101928316 was associated with the sex of the patient (all
P<0.05; Tables IV–X).
 | Table IV.Association between the expression of
RP5-919F19 and clinicopathological characteristics of
gastric cancer patients. |
Table IV.
Association between the expression of
RP5-919F19 and clinicopathological characteristics of
gastric cancer patients.
| Variable | Cases, n (%) | Expression of
RP5-919F19 2−ΔΔCq (mean ± standard
deviation) | P-value |
|---|
| Gender |
|
| 0.672 |
|
Male | 59 (72) | 4.284±11.597 |
|
|
Female | 23 (28) | 3.059±9.363 |
|
| Age, years |
|
| 0.405 |
|
≤50 | 30 (37) | 2.446±12.746 |
|
|
>50 | 52 (63) | 4.617±9.843 |
|
| Tumor size, cm |
|
| 0.238 |
| ≤5 | 43 (52) | 2.434±11.066 |
|
|
>5 | 39 (48) | 5.404±10.823 |
|
| Degree of
differentiation |
|
| 0.006a |
|
Well/moderately | 28 (34) | −0.638±6.568 |
|
|
Poorly | 54 (66) | 6.452±12.135 |
|
| TNM stage |
|
| 0.015a |
|
I/II | 44 (54) | 1.170±7.709 |
|
|
III/IV | 38 (46) | 7.264±13.440 |
|
| Lymph node
status |
|
| 0.029a |
| No
metastasis | 36 (44) | 0.890±7.236 |
|
|
Metastasis | 46 (56) | 6.337±12.893 |
|
 | Table X.Association between the expression of
MEG3 and clinicopathological characteristics of gastric
cancer patients. |
Table X.
Association between the expression of
MEG3 and clinicopathological characteristics of gastric
cancer patients.
| Variable | Cases, n (%) | Expression of
MEG3 2−ΔΔCq (mean ± standard deviation) | P-value |
|---|
| Gender |
|
| 0.674 |
|
Male | 59 (72) | −4.960±15.210 |
|
|
Female | 23 (28) | −3.492±7.248 |
|
| Age, years |
|
| 0.841 |
|
≤50 | 30 (37) | −5.008±11.633 |
|
|
>50 | 52 (63) | −4.342±14.338 |
|
| Tumor size, cm |
|
| 0.791 |
| ≤5 | 43 (52) | −4.067±13.301 |
|
|
>5 | 39 (48) | −4.911±13.640 |
|
| Degree of
differentiation |
|
| 0.036a |
|
Well/moderately | 28 (34) | −1.220±12.479 |
|
|
Poorly | 54 (66) | −8.317±13.822 |
|
| TNM stage |
|
| 0.778 |
|
I/II | 44 (54) | −4.064±13.291 |
|
|
III/IV | 38 (46) | −4.968±13.672 |
|
| Lymph node
status |
|
| 0.024a |
| No
metastasis | 36 (44) | 0.822±11.519 |
|
|
Metastasis | 46 (56) | −6.447±14.730 |
|
Association between candidate lncRNAs
and the lymph node metastasis of GC
Conditional logistic regression analysis was used to
evaluate the association between differentially expressed lncRNAs
and the lymph node metastasis status of GC. As shown in Table XI, a significantly increased risk of
lymph node metastasis was associated with the increased expression
of RP5-919F19 [odds ratio (OR), 1.199] and reduced
expression of MEG3 (OR, 0.924). This suggested that
RP5-919F19 and MEG3 may participate in the lymphatic
metastasis of GC.
 | Table XI.Associations between aberrant
expression of long non-coding RNAs and lymph node metastasis status
of gastric cancer by logistic regression analysis. |
Table XI.
Associations between aberrant
expression of long non-coding RNAs and lymph node metastasis status
of gastric cancer by logistic regression analysis.
| Gene symbol | β | Standard error | Wald | P-value | Odds ratio | 95% confidence
interval |
|---|
|
RP5-919F19 | 0.181 | 0.070 | 6.639 | 0.010a | 1.199 | 1.044–1.376 |
| UCA1 | 0.071 | 0.045 | 2.476 | 0.116 | 1.073 | 0.983–1.172 |
| MEG3 | −0.079 | 0.033 | 5.689 | 0.017a | 0.924 | 0.866–0.986 |
Discussion
Although there appears to have been a steady global
decline in the incidence of GC and associated mortality over
several decades (17), it is still a
disease of substantial incidence and mortality in China, with a
large number of patients diagnosed at an advanced stage and with a
poor prognosis (18). Furthermore,
endoscopic biopsy and pathological morphological observation cannot
detect all precancerous lesions and early stages of GC (19). Therefore, in order to improve this
situation, the identification of the genes and regulatory
mechanisms involved in lymph node metastasis has become a research
area of increasing interest. In recent years, a large number of
lncRNAs have been identified in genetic studies, and have been
found to be associated with various diseases (20). The mechanisms by which lncRNAs may
participate in cancer development are currently being studied
(21–23). However, lncRNAs in GC have
predominantly been reported in Western countries and in Japan,
whereas few studies have been performed on Chinese populations
(24). Although the mechanism of GC
has been widely studied, the exact pathogenesis of this disease
remains unclear (25). The molecular
pathology of GC also varies among populations, mainly due to
differential exposures to disease risk factors, including customs
and habits, Helicobacter pylori variants, and medical
conditions (26). In the present
study, the aim was to establish lncRNA expression profiles for GC
in a known high-risk population in Wuwei, north-west China, and to
investigate the association between significant differential
expression of various lncRNAs and the clinicopathological
characteristics of GC.
To the best of our knowledge, the present study is
the first report on differential lncRNA expression in a population
of patients with GC from Wuwei. The results revealed that certain
lncRNA expression levels in GC samples differed from those in
adjacent non-tumor tissues. Prior to this research, we had detected
mRNA expression profiles with a lncRNA-mRNA combined microarray
(15). Through constructing the
lncRNA-mRNA co-expression network and with bioinformatics analysis,
14 key lncRNAs were identified, of which the majority were reported
for the first time. Our previous research results also revealed
that there were significant differences in the levels of
RP5-919F19, CTD-2541M15, UCA1, AP000459, LOC101928316,
LINC01071 and MEG3 in tumor tissues compared with
adjacent non-tumor tissues (P<0.05). In the present study, these
seven lncRNAs were selected for further validation by RT-qPCR in 82
pairs of human primary GC tissues and their adjacent non-tumor
tissues. Subsequently, the associations between the expression
levels of the seven selected lncRNAs in the GC samples and various
clinicopathological characteristics were analyzed. Finally,
logistic regression analysis was used to evaluate the association
between differentially expressed lncRNAs and the lymph node
metastasis status of GC.
In the present study, the results from the
microarray and RT-qPCR experiments were in 100% agreement.
Correlation analyses of the expression levels of the seven
differentially expressed lncRNAs and the associated
clinicopathological characteristics were performed. The results
identified that six lncRNAs (RP5-919F19, CTD-2541M15, UCA1,
LOC101928316, LINC01071 and MEG3) were associated with
some of the following clinicopathological parameters: Patient
gender, patient age, tumor size, tumor differentiation degree, TNM
stage and lymph node metastasis status. Statistics revealed that
RP5-919F19, LOC101928316 and MEG3 were associated
with tumor differentiation degree, and RP5-919F19, UCA1 and
MEG3 were significantly associated with lymph node
metastasis (P<0.05), indicating that these lncRNAs are possibly
involved in the invasion and metastasis of GC. In addition,
logistic regression analysis suggested that RP5-919F19 and
MEG3 may participate in the lymphatic metastasis of GC.
Thus, the present findings may provide a novel method of
exploration that will improve the prediction of lymphatic
metastatic status in patients with GC post-surgery. Notably, the
abnormal expression levels of LINC01071 and
LOC101928316 were significantly associated with the age and
gender of the patients, respectively (P<0.05).
An increasing number of studies have also identified
a biological link between aberrant expression of lncRNAs and GC
(27). Differential expression of
certain lncRNAs, including H19, UCA1, HOTAIR, PVTI, CCAT1
and MEG3, have been hypothesized to be important features of
GC (28). In combining the results of
our studies, only UCA1 and MEG3 have been reported
previously, and there was limited information available regarding
the other lncRNAs.
The LncRNAdb and LncRNA Diseases databases indicated
that UCA1, which is located on chromosome 19, comprises
three exons. UCA1 was initially found and established in
bladder transitional cell carcinoma (29). A recent study also reported that its
expression was markedly increased in GC tissues and cell lines
compared with that in the normal control tissues, and that high
UCA1 expression correlated with poorer differentiation,
tumor size, invasion depth and TNM stage in GC; furthermore,
increased UCA1 expression was associated with decreased
overall and disease-free survival times of the patients (30).
The present study identified downregulated levels of
MEG3 (which is located on the chromosome 14q32, and acts as
a tumor suppressor gene) in GC tissues compared with healthy
tissues; MEG3 downregulation is associated with poor
prognosis and promotes cell proliferation in GC (31). These results indicate that UCA1
and MEG3 lncRNAs are important factors in the development of
GC, as well as in the invasion and lymphatic metastasis of this
cancer type.
The present study found that RP5-919F19,
LOC101928316 and MEG3 were significantly associated with the degree
of tumor differentiation; RP5-919F19, UCA1 and MEG3 were
significantly associated with lymph node metastasis status; and
RP5-919F19, CTD-2541M15 and UCA1 were significantly associated with
TNM stage of GC patients These lncRNAs may prove useful for further
study as novel candidate biomarkers in the diagnosis and
classification of GC.
The current results indicate that RP5-919F19,
CTD-2541M15, UCA1, LOC101928316 and MEG3 are potential
novel molecular biomarkers that may be involved in the infiltration
and metastasis of GC. In addition, according to epidemiological
reports, the incidence of GC significantly increases with age, with
a peak age of 50–65 years (32), and
men are 2–3-fold more likely to develop GC compared with females
(33). Thus, the significant
associations identified between the differential expression of
LINC01071 and LOC101928316 in GC tissues and patient
age and gender may be of importance for diagnosis.
In conclusion, the present study revealed that
RP5-919F19, CTD-2541M15, UCA1, LOC101928316, LINC01071 and
MEG3 are involved in the development of GC. This provides
preliminary data that may aid in increasing the understanding of
the potential functions of these lncRNAs. The results also suggest
that RP5-919F19, LOC101928316, CTD-2541M15, UCA1 and
MEG3 are closely associated with the invasion and metastasis
of GC, which suggests that these lncRNAs may have potential as
biomarkers for the diagnosis, prognosis and classification of GC.
Further studies of these targets are required to assess their
potential clinical uses.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was financially supported by the
National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 81673132,
81472939 and 8117261), the Qing Lan Project (grant no. 2012), the
333 Project of Jiangsu Province (grant no. 2012), the Liu Da Ren
Cai Gao Feng Project of Jiangsu Province (grant no. 2013-WSW-053)
and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central
Universities.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are
included in this published article.
Authors' contributions
CYL and GYL conceived and designed the study. CYL,
WZY, JS and SY performed the experiments. YQZ and SMM analyzed and
interpreted the results. YCY, ZYZ and WHZ performed the gastric
cancer patients' tissue sample collection and quality control. LHY
and YPP assisted with study design and provided advice throughout.
CYL performed analysis and quality control, and was a major
contributor in writing the manuscript. All authors read and
approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved by the Ethics
Committee of the Gansu Wuwei Tumor Hospital. All patients provided
written informed consent to participate in the present study.
Consent for publication
All participants confirmed that the data can be
published.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Lan H, Zhu N, Lan Y, Jin K and Teng L:
Laparoscopic gastrectomy for gastric cancer in China: An overview.
Hepatogastroenterology. 62:234–239. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yajima H, Omura N, Takahashi N, Yoshida K
and Yanaga K: Additional gastrectomy after endoscopic mucosal
resection for early gastric cancer. Int Surg. 100:169–172. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maruyama K and Katai H: Surgical treatment
of gastric cancer in Japan, trend from standardization to
individualization. Chirurgia (Bucur). 109:722–730. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kwon KA: Is the double channel gastroscope
useful in endoscopic mucosal resection for large sessile colon
polyps? Clin Endosc. 48:89–90. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Qian Y, Huang J, Zhang Y, Ma LM and Fan
ZN: Using a gastroscope to accomplish ERCP: A forward-viewing
endoscope for cannulation of the intradiverticular papilla.
Endoscopy. 46 Suppl 1:UCTN: E139. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ju H, Ma Y, Liang K, Zhang C and Tian Z:
Function of high-resolution manometry in the analysis of peroral
endoscopic myotomy for achalasia. Surg Endosc. 30:1094–1099. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang F, Zhang L, Huo XS, Yuan JH, Xu D,
Yuan SX, Zhu N, Zhou WP, Yang GS, Wang YZ, et al: Long noncoding
RNA high expression in hepatocellular carcinoma facilitates tumor
growth through enhancer of zeste homolog 2 in humans. Hepatology.
54:1679–1689. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ponting CP, Oliver PL and Reik W:
Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 136:629–641.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu YP, Bian XJ, Ye DW, Yao XD, Zhang SL,
Dai B, Zhang HL and Shen YJ: Long noncoding RNA expression
signatures of bladder cancer revealed by microarray. Oncol Lett.
7:1197–1202. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheng WS, Tao H, Hu EP, Liu S, Cai HR, Tao
XL, Zhang L, Mao JJ and Yan DL: Both genes and lncRNAs can be used
as biomarkers of prostate cancer by using high throughput
sequencing data. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 18:3504–3510.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang S and Tran EJ: Unexpected functions
of lncRNAs in gene regulation. Commun Integr Biol. 6:e276102013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hung T and Chang HY: Long noncoding RNA in
genome regulation: Prospects and mechanisms. RNA Biol. 7:582–585.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin XC, Zhu Y, Chen WB, Lin LW, Chen DH,
Huang JR, Pan K, Lin Y, Wu BT, Dai Y and Tu ZG: Integrated analysis
of long non-coding RNAs and mRNA expression profiles reveals the
potential role of lncRNAs in gastric cancer pathogenesis. Int J
Oncol. 45:619–628. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gu Y, Chen T, Li G, Yu X, Lu Y, Wang H and
Teng L: LncRNAs: Emerging biomarkers in gastric cancer. Future
Oncol. 11:2427–2441. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li C, Liang G, Yao W, Sui J, Shen X, Zhang
Y, Ma S, Ye Y, Zhang Z, Zhang W, et al: Differential expression
profiles of long non-coding RNAs reveal potential biomarkers for
identification of human gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 35:1529–1540.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Patru CL, Surlin V, Georgescu I and Patru
E: Current issues in gastric cancer epidemiology. Rev Med Chir Soc
Med Nat Iasi. 117:199–204. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li G, Hu Y and Liu H: Current status of
randomized controlled trials for laparoscopic gastric surgery for
gastric cancer in China. Asian J Endosc Surg. 8:263–267. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rajan E, Gostout CJ, Aimore BE, Moran EA,
Locke RG, Szarka LA, Talley NJ, Deters JL, Miller CA, Knipschield
MA, et al: Endoscopic full-thickness biopsy of the gastric wall
with defect closure by using an endoscopic suturing device:
Survival porcine study. Gastrointest Endosc. 76:1014–1019. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen G, Wang Z, Wang D, Qiu C, Liu M, Chen
X, Zhang Q, Yan G and Cui Q: LncRNADisease: A database for
long-non-coding RNA-associated diseases. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:(Database issue). D983–D986. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings
HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kogo R, Shimamura T, Mimori K, Kawahara K,
Imoto S, Sudo T, Tanaka F, Shibata K, Suzuki A, Komune S, et al:
Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR regulates polycomb-dependent chromatin
modification and is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal
cancers. Cancer Res. 71:6320–6326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tsai MC, Spitale RC and Chang HY: Long
intergenic noncoding RNAs: New links in cancer progression. Cancer
Res. 71:3–7. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang YY, Ye ZY, Zhao ZS, Tao HQ and Li SG:
Systems biology approach to identification of biomarkers for
metastatic progression in gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
136:135–141. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao Z, Song Y, Piao D, Liu T and Zhao L:
Identification of genes and long non-coding RNAs associated with
the pathogenesis of gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 34:1301–1310. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pizzi M, Saraggi D, Fassan M, Megraud F,
Di Mario F and Rugge M: Secondary prevention of epidemic gastric
cancer in the model of Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis.
Dig Dis. 32:265–274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen X, Sun J, Song Y, Gao P, Zhao J,
Huang X, Liu B, Xu H and Wang Z: The novel long noncoding RNA
AC138128.1 may be a predictive biomarker in gastric cancer. Med
Oncol. 31:2622014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li PF, Chen SC, Xia T, Jiang XM, Shao YF,
Xiao BX and Guo JM: Non-coding RNAs and gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:5411–5419. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xie XJ, Li X, Wang F and Chen W: Cellular
localization and tissue expression pattern of UCA1, a non-coding
RNA. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 30:57–60. 2010.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zheng Q, Wu F, Dai WY, Zheng DC, Zheng C,
Ye H, Zhou B, Chen JJ and Chen P: Aberrant expression of UCA1 in
gastric cancer and its clinical significance. Clin Transl Oncol.
17:640–646. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun M, Xia R, Jin F, Xu T, Liu Z, De W and
Liu X: Downregulated long noncoding RNA MEG3 is associated with
poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation in gastric cancer.
Tumour Biol. 35:1065–1073. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Oh S, Kim N, Yoon H, Choi YJ, Lee JY, Park
KJ, Kim HJ, Kang KK, Oh DH, Seo AY, et al: Risk factors of atrophic
gastritis and intestinal metaplasia in first-degree relatives of
gastric cancer patients compared with age-sex matched controls. J
Cancer Prev. 18:149–160. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu J and Zhao Q: The demographic
characteristics of histological types of gastric cancer with
gender, age, and tumor location. J Gastrointest Cancer. 40:98–100.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|