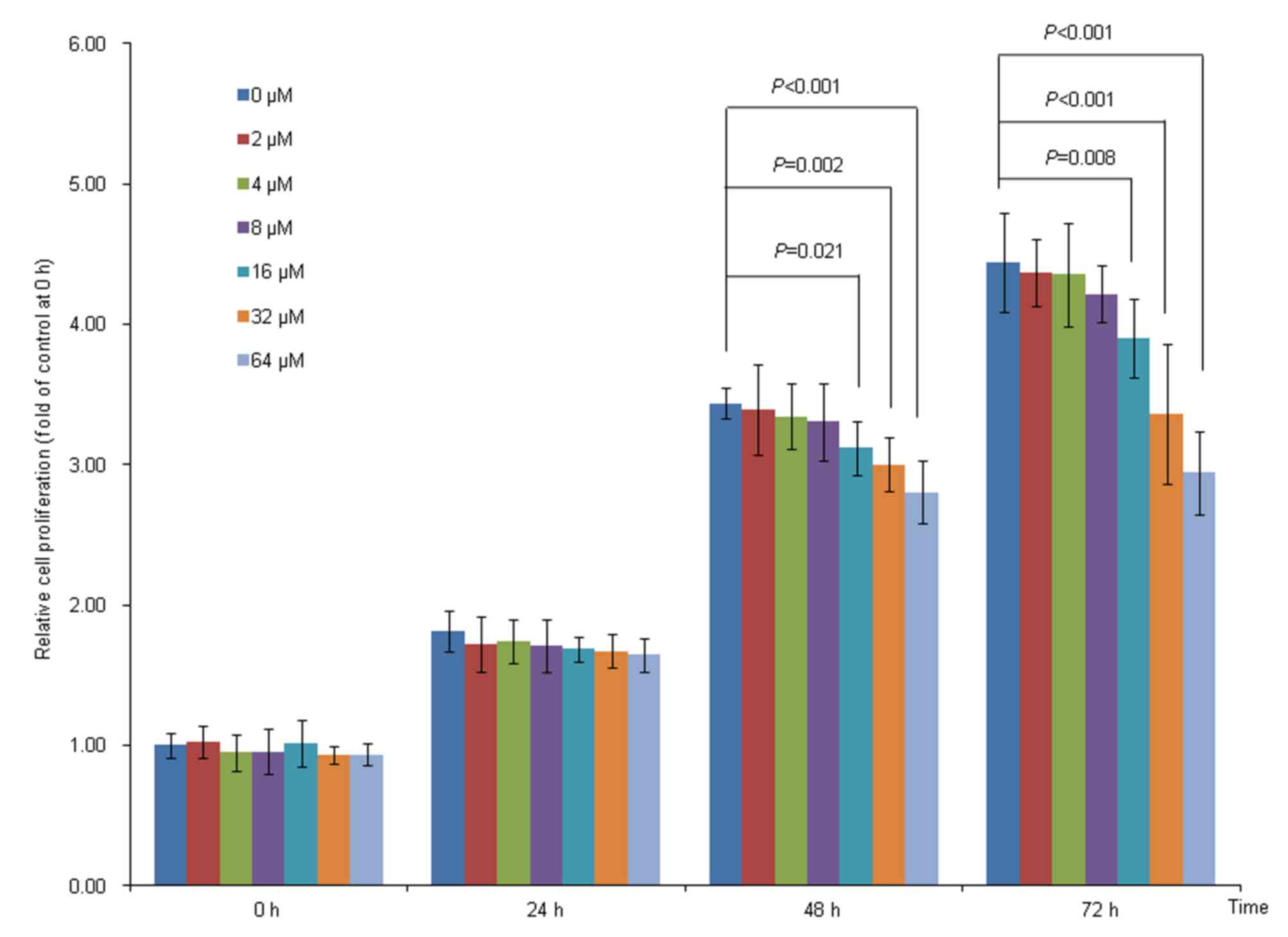
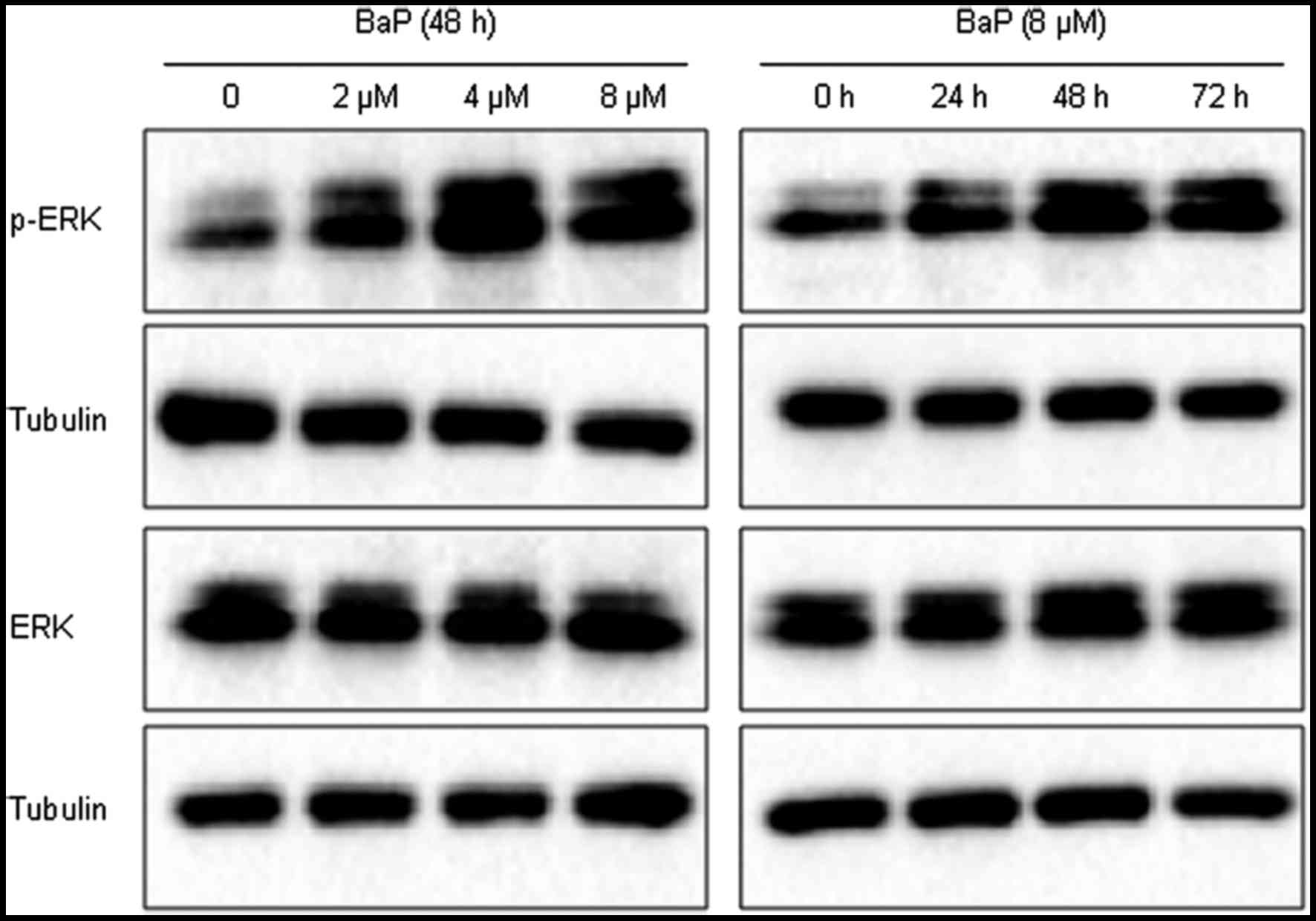
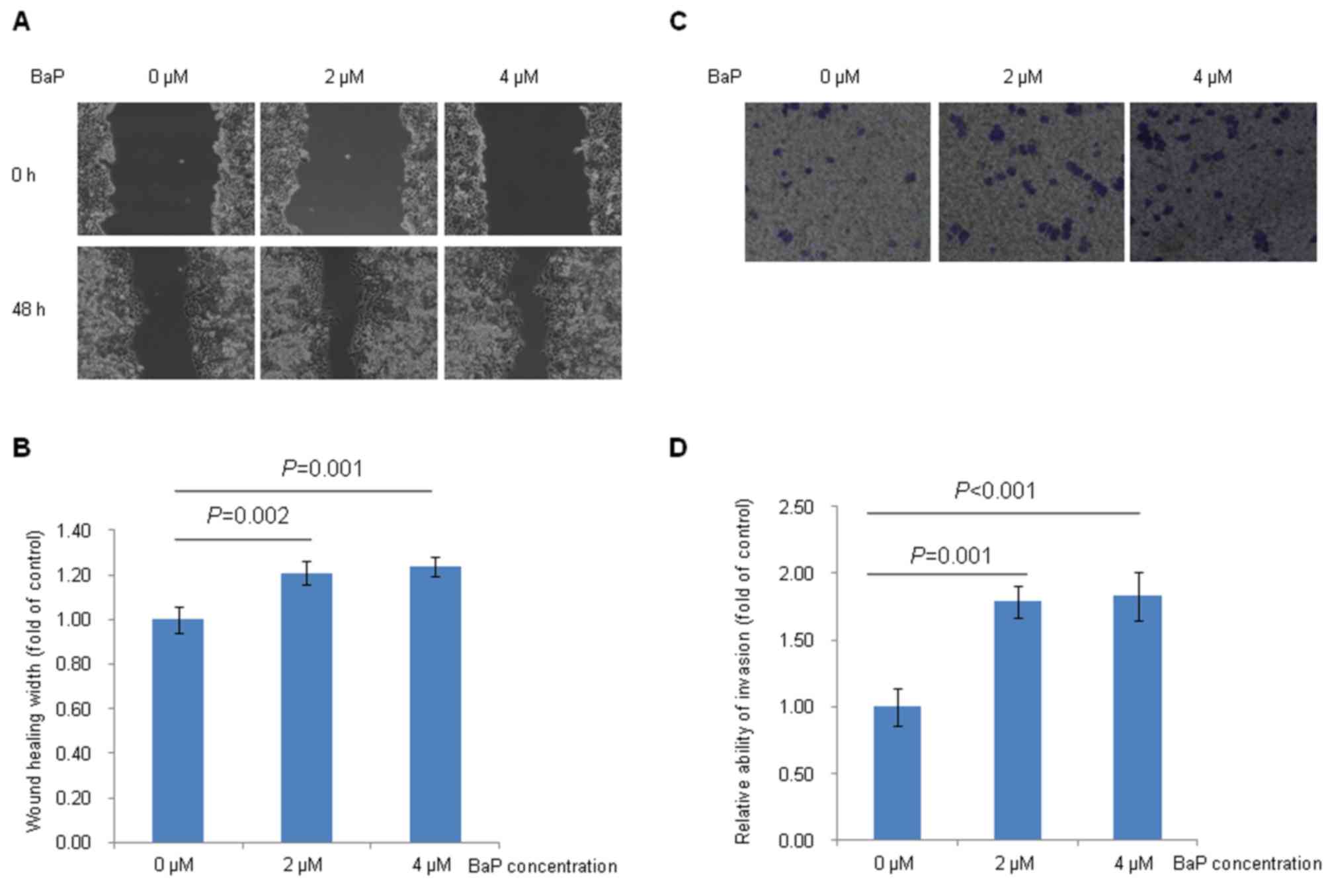
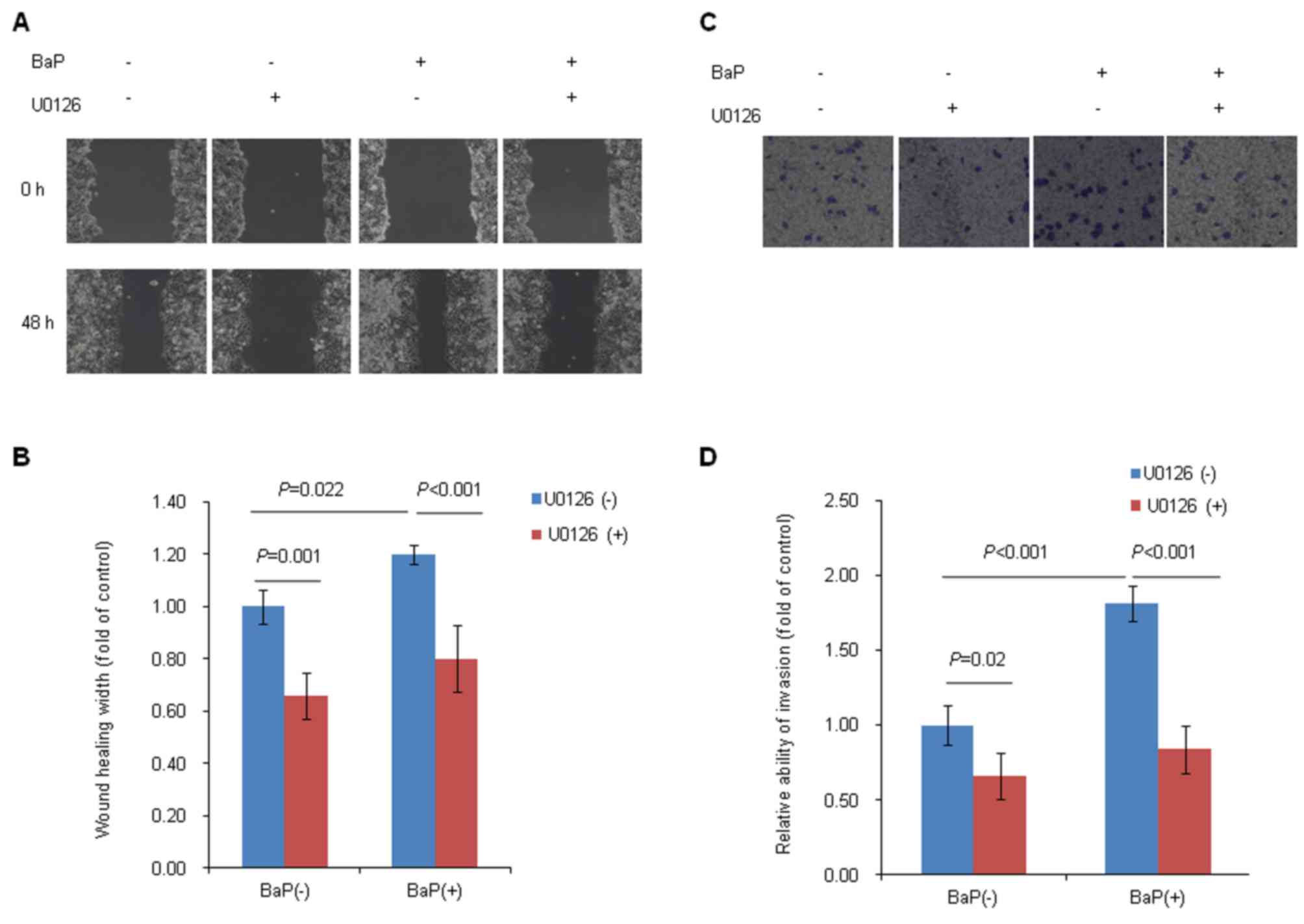
|
1
|
IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of
Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Some non-heterocyclic polycyclic
aromatic hydrocarbons and some related exposures. IARC Monogr Eval
Carcinog Risks Hum. 92:1–853. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
He XZ, Chen W, Liu ZY and Chapman RS: An
epidemiological study of lung cancer in Xuan Wei County, China:
Current progress. Case-control study on lung cancer and cooking
fuel. Environ Health Perspect. 94:9–13. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yoshimoto T, Inoue T, Iizuka H, Nishikawa
H, Sakatani M, Ogura T, Hirao F and Yamamura Y: Differential
induction of squamous cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas in mouse
lung by intratracheal instillation of benzo(a)pyrene and charcoal
powder. Cancer Res. 40:4301–4307. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Senthilnathan P, Padmavathi R, Magesh V
and Sakthisekaran D: Chemotherapeutic efficacy of paclitaxel in
combination with Withania somnifera on benzo(a)pyrene-induced
experimental lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 97:658–664. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Anderson KE, Kadlubar FF, Kulldorff M,
Harnack L, Gross M, Lang NP, Barber C, Rothman N and Sinha R:
Dietary intake of heterocyclic amines and benzo(a)pyrene:
Associations with pancreatic cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 14:2261–2265. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li D, Day RS, Bondy ML, Sinha R, Nguyen
NT, Evans DB, Abbruzzese JL and Hassan MM: Dietary mutagen exposure
and risk of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
16:655–661. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ronco AL, De Stefani E, Correa P,
Deneo-Pellegrini H, Boffetta P, Acosta G and Mendilaharsu M:
Dietary benzo[a]pyrene, alcohol drinking, and risk of breast
cancer: A case-control study in Uruguay. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
12:1463–1467. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Roe FJ and Waters MA: Induction of
hepatoma in mice by carcinogens of the polycyclic hydrocarbon type.
Nature. 214:299–300. 1967. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vesselinovitch SD, Kyriazis AP,
Mihailovich N and Rao KV: Conditions modifying development of
tumors in mice at various sites by benzo(a)pyrene. Cancer Res.
35:2948–2953. 1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Su Y, Zhao B, Guo F, Bin Z, Yang Y, Liu S,
Han Y, Niu J, Ke X, Wang N, et al: Interaction of benzo[a]pyrene
with other risk factors in hepatocellular carcinoma: A case-control
study in Xiamen, China. Ann Epidemiol. 24:98–103. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Abe S, Nemoto N and Sasaki M:
Sister-chromatid exchange induction by indirect
mutagens/carcinogens, aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity and
benzo[alpha]pyrene metabolism in cultured human hepatoma cells.
Mutat Res. 109:83–90. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cherpillod P and Amstad PA:
Benzo[a]pyrene-induced mutagenesis of p53 hot-spot codons 248 and
249 in human hepatocytes. Mol Carcinog. 13:15–20. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Park SY, Lee SM, Ye SK, Yoon SH, Chung MH
and Choi J: Benzo[a]pyrene-induced DNA damage and p53 modulation in
human hepatoma HepG2 cells for the identification of potential
biomarkers for PAH monitoring and risk assessment. Toxicol Lett.
167:27–33. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Delgado ME, Haza AI, Arranz N, Garcia A
and Morales P: Dietary polyphenols protect against N-nitrosamines
and benzo(a)pyrene-induced DNA damage (strand breaks and oxidized
purines/pyrimidines) in HepG2 human hepatoma cells. Eur J Nutr.
47:479–490. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tian M, Zhao B, Zhang J, Martin FL, Huang
Q, Liu L and Shen H: Association of environmental benzo[a]pyrene
exposure and DNA methylation alterations in hepatocellular
carcinoma: A Chinese case-control study. Sci Total Environ.
541:1243–1252. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ba Q, Li J, Huang C, Qiu H, Li J, Chu R,
Zhang W, Xie D, Wu Y and Wang H: Effects of benzo[a]pyrene exposure
on human hepatocellular carcinoma cell angiogenesis, metastasis,
and NF-κB signaling. Environ Health Perspect. 123:246–254.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun Y, Liu WZ, Liu T, Feng X, Yang N and
Zhou HF: Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation,
differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J Recept
Signal Transduct Res. 35:600–604. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Osaki LH and Gama P: MAPKs and signal
transduction in the control of gastrointestinal epithelial cell
proliferation and differentiation. Int J Mol Sci. 14:10143–10161.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li L, Zhao GD, Shi Z, Qi LL, Zhou LY and
Fu ZX: The Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway and its role in the
occurrence and development of HCC. Oncol Lett. 12:3045–3050. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH,
Abrams SL, Wong EW, Chang F, Lehmann B, Terrian DM, Milella M,
Tafuri A, et al: Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth,
malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1773:1263–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang S and Liu G: Targeting the
Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett.
13:1041–1047. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mehdizadeh A, Somi MH, Darabi M and
Jabbarpour-Bonyadi M: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2
in cancer therapy: A focus on hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Biol
Rep. 43:107–116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen Y, Liu Q, Wu M, Li M, Ding H, Shan X,
Liu J, Tao T, Ni R and Chen X: GAB2 promotes cell proliferation by
activating the ERK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Tumour Biol. 37:11763–11773. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ito Y, Sasaki Y, Horimoto M, Wada S,
Tanaka Y, Kasahara A, Ueki T, Hirano T, Yamamoto H, Fujimoto J, et
al: Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases/extracellular
signal-regulated kinases in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 27:951–958. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schmitz KJ, Wohlschlaeger J, Lang H,
Sotiropoulos GC, Malago M, Steveling K, Reis H, Cicinnati VR,
Schmid KW and Baba HA: Activation of the ERK and AKT signalling
pathway predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma and ERK
activation in cancer tissue is associated with hepatitis C virus
infection. J Hepatol. 48:83–90. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang L, Yan Q, Fang S, Liu M, Li Y, Yuan
YF, Li Y, Zhu Y, Qi J, Yang X, et al: Calcium-binding protein 39
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis by
activating extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway.
Hepatology. 66:1529–1545. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dang Z, Shangguan J, Zhang C, Hu P, Ren Y,
Lv Z, Xiang H and Wang X: Loss of protocadherin-17 (PCDH-17)
promotes metastasis and invasion through hyperactivation of
EGFR/MEK/ERK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour
Biol. 37:2527–2535. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
López-Terrada D, Cheung SW, Finegold MJ
and Knowles BB: Hep G2 is a hepatoblastoma-derived cell line. Hum
Pathol. 40:1512–1515. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Guo J, Xu Y, Ji W, Song L, Dai C and Zhan
L: Effects of exposure to benzo[a]pyrene on metastasis of breast
cancer are mediated through ROS-ERK-MMP9 axis signaling. Toxicol
Lett. 234:201–210. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang Y, Zhai W, Wang H, Xia X and Zhang C:
Benzo(a)pyrene promotes A549 cell migration and invasion through
up-regulating twist. Arch Toxicol. 89:451–458. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Z, Shen M, Lu P, Li X, Zhu S and Yue
S: NEDD9 may regulate hepatocellular carcinoma cell metastasis by
promoting epithelial-mesenchymal-transition and stemness via
repressing Smad7. Oncotarget. 8:1714–1724. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang C, Ruan P, Zhao Y, Li X, Wang J, Wu
X, Liu T, Wang S, Hou J, Li W, et al: Spermidine/spermine
N1-acetyltransferase regulates cell growth and metastasis via
AKT/β-catenin signaling pathways in hepatocellular and colorectal
carcinoma cells. Oncotarget. 8:1092–1109. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ye Y, Long X, Zhang L, Chen J, Liu P, Li
H, Wei F, Yu W, Ren X and Yu J: NTS/NTR1 co-expression enhances
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and promotes tumor metastasis
by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:70303–70322. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dong Q, Zhu X, Dai C, Zhang X, Gao X, Wei
J, Sheng Y, Zheng Y, Yu J, Xie L, et al: Osteopontin promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma
through regulating vimentin. Oncotarget. 7:12997–13012. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bolotina NA, Gasparian AV, Dubovaja TK,
Evteev VA and Kobliakov VA: Benzo[a]pyrene-dependent activation of
transcription factors NF-kappaB and AP-1 related to tumor promotion
in hepatoma cell cultures. Biochemistry (Mosc). 72:552–557. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cui H, Gu X, Chen J, Xie Y, Ke S, Wu J,
Golovko A, Morpurgo B, Yan C, Phillips TD, et al: Pregnane X
receptor regulates the AhR/Cyp1A1 pathway and protects liver cells
from benzo-[α]-pyrene-induced DNA damage. Toxicol Lett. 275:67–76.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Marrone AK, Tryndyak V, Beland FA and
Pogribny IP: MicroRNA responses to the genotoxic carcinogens
aflatoxin B1 and Benzo[a]pyrene in human HepaRG cells. Toxicol Sci.
149:496–502. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Souza T, Jennen D, van Delft J, van
Herwijnen M, Kyrtoupolos S and Kleinjans J: New insights into
BaP-induced toxicity: Role of major metabolites in transcriptomics
and contribution to hepatocarcinogenesis. Arch Toxicol.
90:1449–1458. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ueng TH, Chang YL, Tsai YY, Su JL, Chan
PK, Shih JY, Lee YC, Ma YC and Kuo ML: Potential roles of
fibroblast growth factor-9 in the benzo(a)pyrene-induced invasion
in vitro and the metastasis of human lung adenocarcinoma. Arch
Toxicol. 84:651–660. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Miller ME, Holloway AC and Foster WG:
Benzo-[a]-pyrene increases invasion in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer
cells via increased COX-II expression and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)
output. Clin Exp Metastasis. 22:149–156. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hitt Patten E, DeLong MJ and Merrill AH
Jr: Benzo(a)pyrene activates extracellular signal-related and p38
mitogen-activated protein kinases in HT29 colon adenocarcinoma
cells: Involvement in NAD(P)H:quinone reductase activity and cell
proliferation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 183:160–167. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang BY, Wu SY, Tang SC, Lai CH, Ou CC, Wu
MF, Hsiao YM and Ko JL: Benzo[a]pyrene-induced cell cycle
progression occurs via ERK-induced Chk1 pathway activation in human
lung cancer cells. Mutat Res. 773:1–8. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kometani T, Yoshino I, Miura N, Okazaki H,
Ohba T, Takenaka T, Shoji F, Yano T and Maehara Y: Benzo[a]pyrene
promotes proliferation of human lung cancer cells by accelerating
the epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway. Cancer
Lett. 278:27–33. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Castillo-Sanchez R, Villegas-Comonfort S,
Galindo-Hernandez O, Gomez R and Salazar EP: Benzo-[a]-pyrene
induces FAK activation and cell migration in MDA-MB-231 breast
cancer cells. Cell Biol Toxicol. 29:303–319. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hu L, Lau SH, Tzang CH, Wen JM, Wang W,
Xie D, Huang M, Wang Y, Wu MC, Huang JF, et al: Association of
Vimentin overexpression and hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis.
Oncogene. 23:298–302. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wei PL, Kuo LJ, Wang W, Lin FY, Liu HH,
How T, Ho YS, Huang MT, Wu CH and Chang YJ: Silencing of
glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) enhances cell migration
through the upregulation of vimentin in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Ann Surg Oncol. 19 Suppl 3:S572–S579. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang TH, Lin YS, Chen Y, Yeh CT, Huang YL,
Hsieh TH, Shieh TM, Hsueh C and Chen TC: Long non-coding RNA AOC4P
suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by enhancing
vimentin degradation and inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Oncotarget. 6:23342–23357. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xie X, Zhu H, Zhang J, Wang M, Zhu L, Guo
Z, Shen W and Wang D: Solamargine inhibits the migration and
invasion of HepG2 cells by blocking epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Oncol Lett. 14:447–452. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chen C, Xue Y, Zhang D, Xu W, Xu H, Yao H,
Pei D and Gu Y: Short hairpin RNA silencing of TGF-βRII and FZD-7
synergistically suppresses proliferation and metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett. 11:2039–2046. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
He S, Lin J, Yu S and Sun S: Upregulation
of PREX2 promotes the proliferation and migration of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells via PTEN-AKT signaling. Oncol Lett. 11:2223–2228.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Liu Z, Wang J, Mao Y, Zou B and Fan X:
MicroRNA-101 suppresses migration and invasion via targeting
vascular endothelial growth factor-C in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Oncol Lett. 11:433–438. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhao X, Yang W, Pei F, Ma W and Wang Y:
Downregulation of matrix metalloproteinases contributes to the
inhibition of cell migration and invasion in HepG2 cells by sodium
valproate. Oncol Lett. 10:531–535. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|