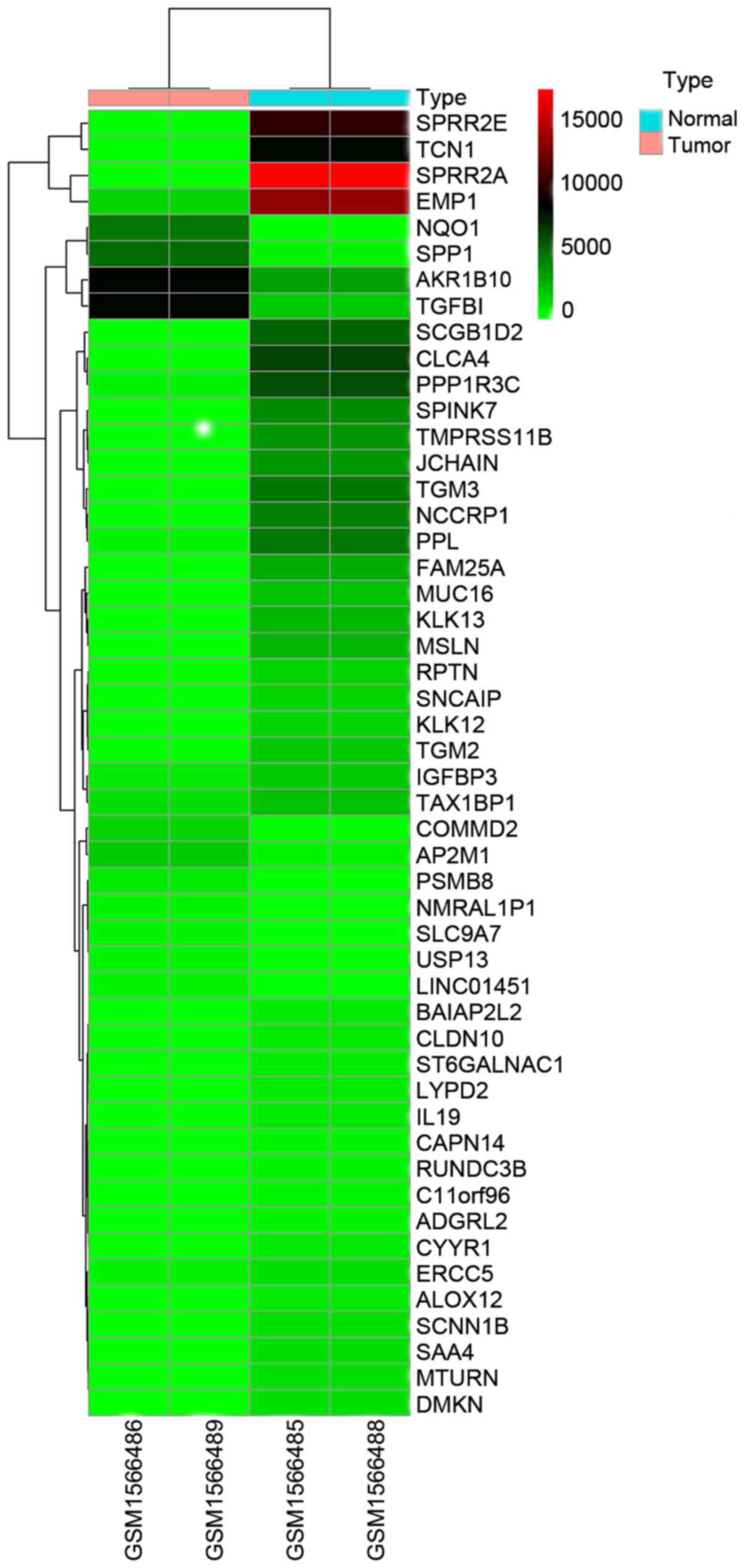
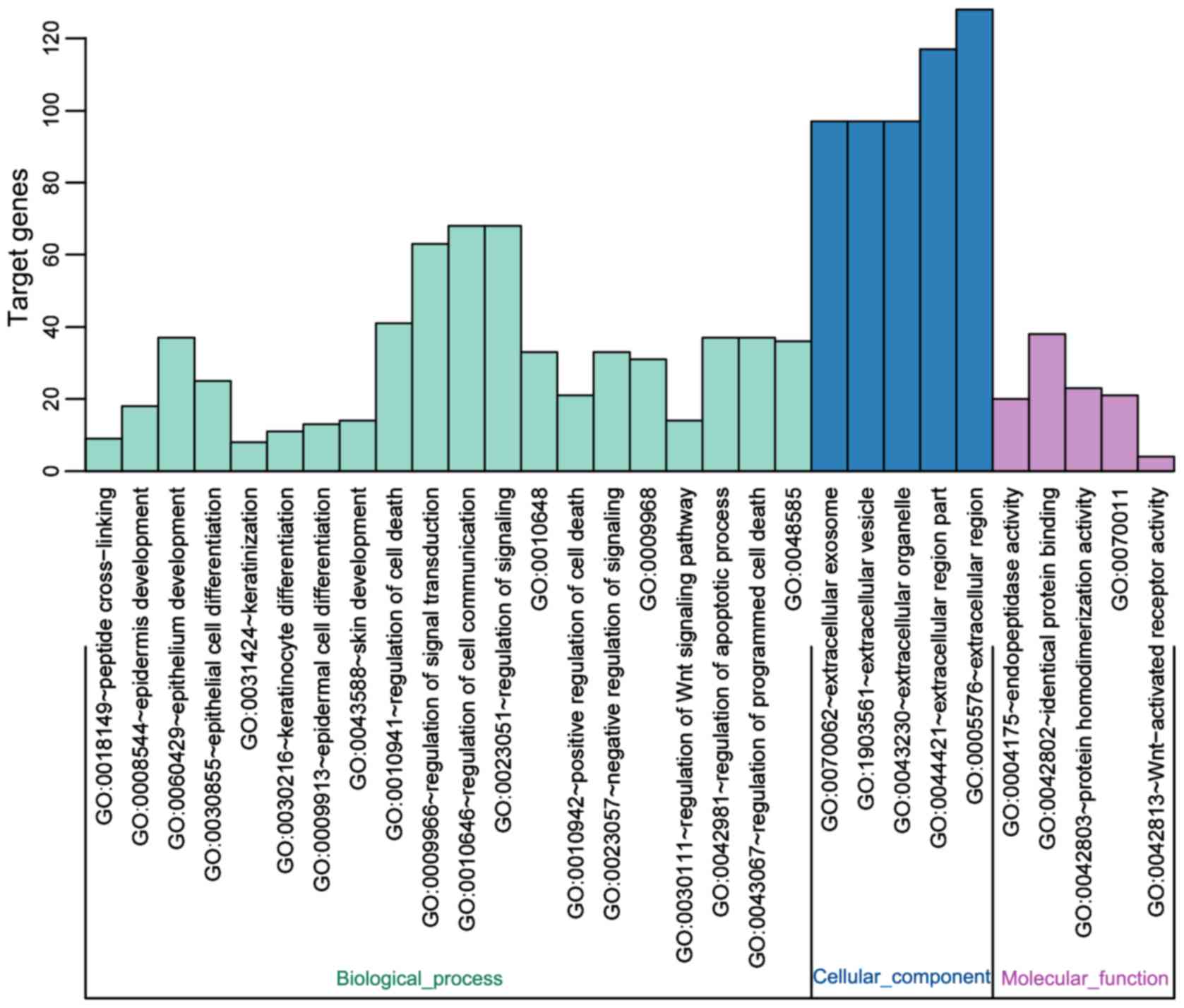
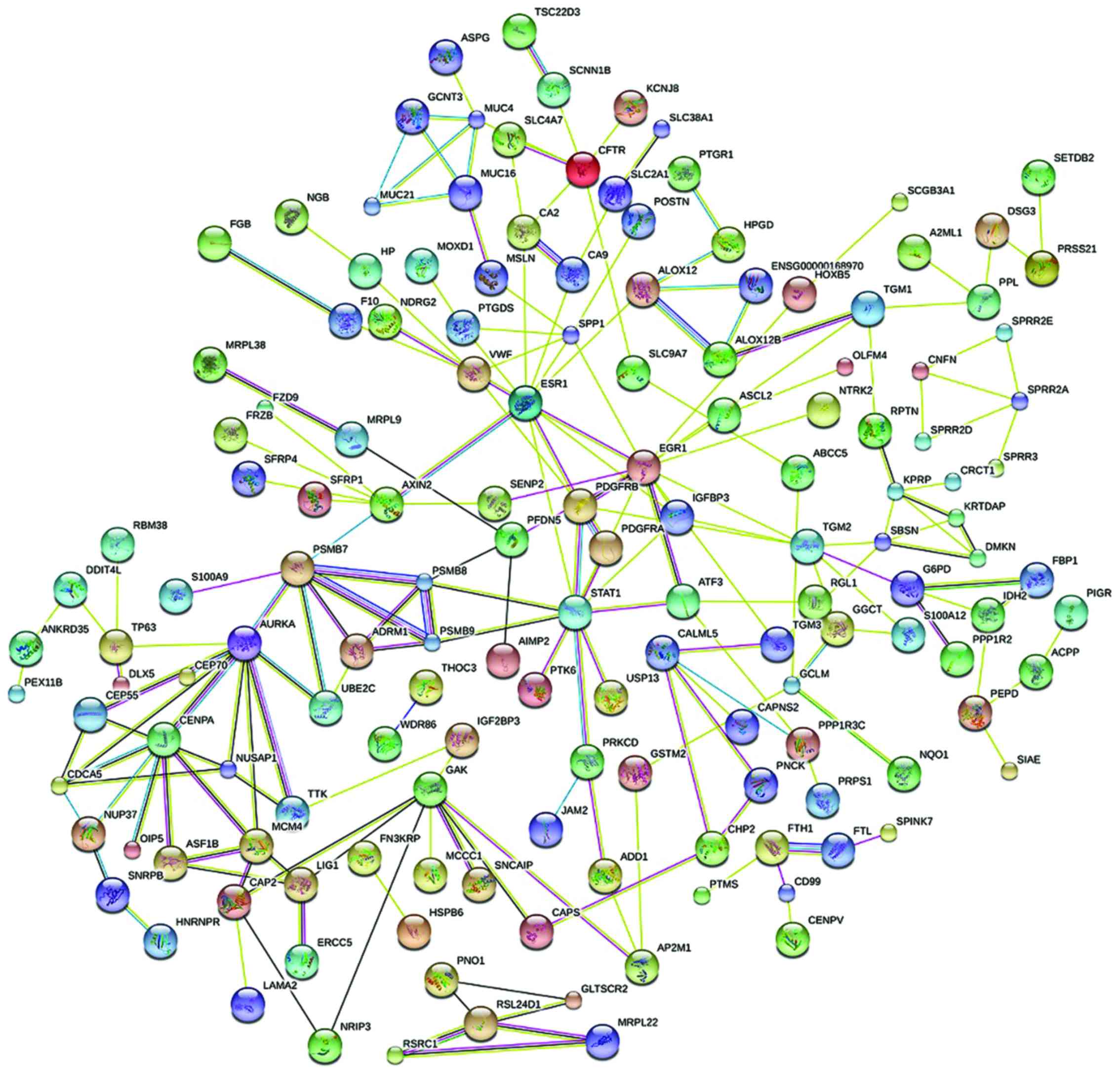
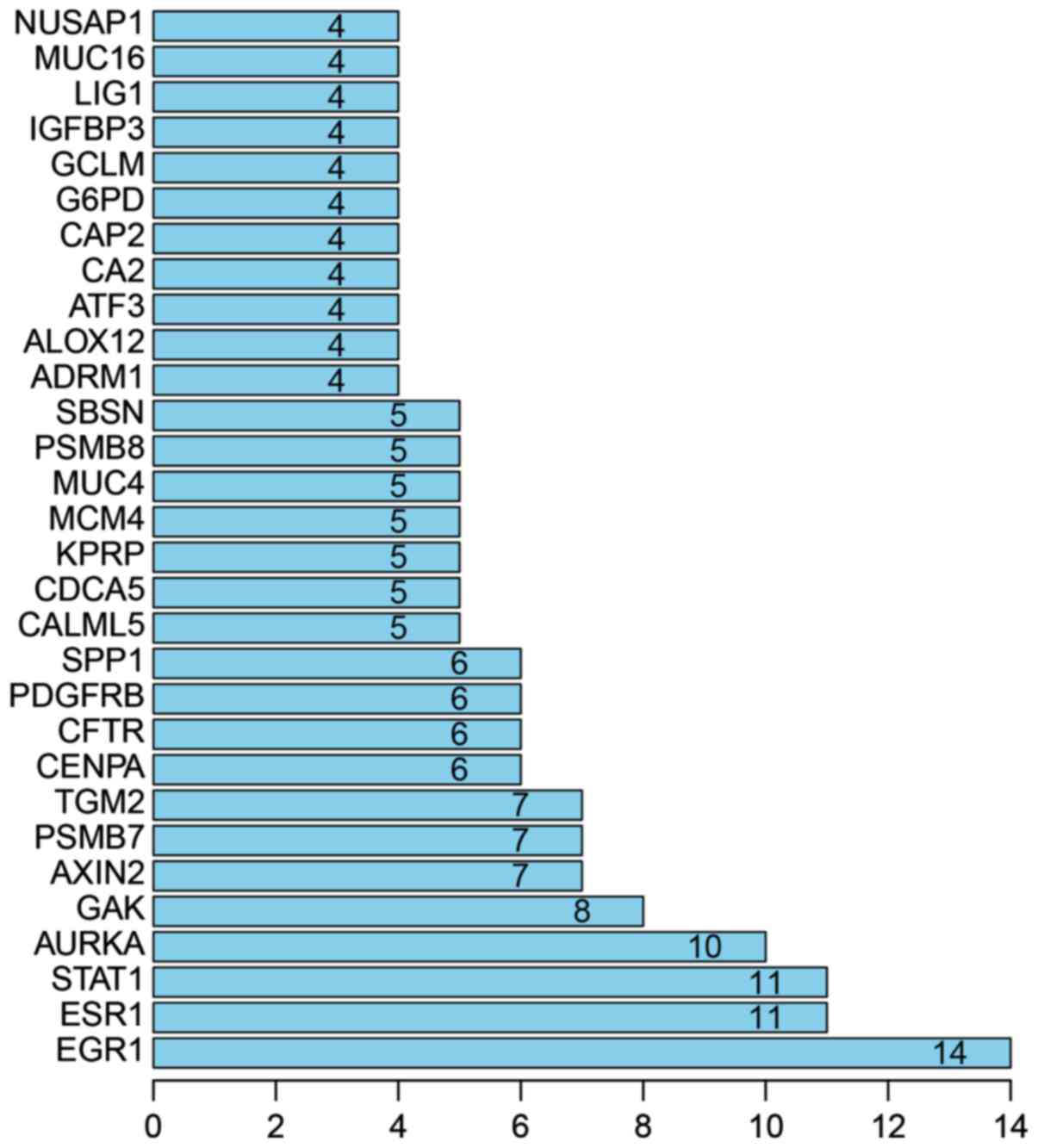
|
1
|
Luo Q, Lei B, Liu S, Chen Y, Sheng W, Lin
P, Li W, Zhu H and Shen H: Expression of PBK/TOPK in cervical
cancer and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 7:8059–8064. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ni L, Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Zhou XN, Zeng HM
and Chen WQ: An analysis of incidence and mortality of cervical
cancer in China 2003–2007. China Cancer. 21:801–804. 2012.
|
|
3
|
Shi YH, Wang BW, Tuokan T, Li QZ and Zhang
YJ: Association between micronucleus frequency and cervical
intraepithelial neoplasia grade in Thinprep cytological test and
its significance. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:8426–8432.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miller JW, Hanson V, Johnson GD, Royalty
JE and Richardson LC: From cancer screening to treatment: Service
delivery and referral in the National Breast and Cervical Cancer
Early Detection Program. Cancer. 120:2549–2556. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bueno CT, da Silva Dornelles CM, Barcellos
RB, da Silva J, Dos Santos CR, Menezes JE, Menezes HS and Rossetti
ML: Association between cervical lesion grade and micronucleus
frequency in the Papanicolaou test. Genet Mol Biol. 37:496–499.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li Q, Liu S, Liu H, Zhang J, Guo S and
Wang L: Significance and implication on changes of serum squamous
cell carcinoma antigen in the diagnosis of recurrence squamous cell
carcinoma of cervix. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 50:131–136.
2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rebolj M, Helmerhorst T, Habbema D, Looman
C, Boer R, van Rosmalen J and van Ballegooijen M: Risk of cervical
cancer after completed post-treatment follow-up of cervical
intraepithelial neoplasia: Population based cohort study. BMJ.
345:e68552012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Luesley D and Leeson S: Colposcopy and
programme management: Guidelines for the NHS Cervical Screening
Programme2nd edition. SBA Questions for the MRCOG. Jones A: NHSCSP
Publication No. 20. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: pp.
1262010
|
|
10
|
Leinonen M, Nieminen P, Kotaniemi-Talonen
L, Malila N, Tarkkanen J, Laurila P and Anttila A: Age-specific
evaluation of primary human papillomavirus screening vs
conventional cytology in a randomized setting. J Natl Cancer Inst.
101:1612–1623. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
McCredie MR, Sharples KJ, Paul C, Baranyai
J, Medley G, Jones RW and Skegg DC: Natural history of cervical
neoplasia and risk of invasive cancer in women with cervical
intraepithelial neoplasia 3: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet
Oncol. 9:425–434. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hakama M, Miller AB and Day NE: Screening
for cancer of the uterine cervix. Oxford University Press; UK:
2012
|
|
13
|
Cuzick J, Arbyn M, Sankaranarayanan R, Tsu
V, Ronco G, Mayrand MH, Dillner J and Meijer CJ: Overview of human
papillomavirus-based and other novel options for cervical cancer
screening in developed and developing countries. Vaccine. 26:29–41.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bulkmans NW, Berkhof J, Rozendaal L, van
Kemenade FJ, Boeke AJ, Bulk S, Voorhorst FJ, Verheijen RH, van
Groningen K, Boon ME, et al: Human papillomavirus DNA testing for
the detection of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 3 and
cancer: 5-year follow-up of a randomised controlled implementation
trial. Lancet. 370:1764–1772. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ronco G, Sideri MG and Ciatto S: Cervical
intraepithelial neoplasia and higher long term risk of cancer. BMJ.
335:1053–1054. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Werkgroep Oncologische Gynaecologie, .
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), nationwide guidelines.
1.1. 2011.(in Dutch).
|
|
17
|
Van den Brandt PA, Schouten LJ, Goldbohm
RA, Dorant E and Hunen PM: Development of a record linkage protocol
for use in the Dutch Cancer Registry for Epidemiological Research.
Int J Epidemiol. 19:553–558. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Van den Akker-van Marle ME, van
Ballegooijen M and Habbema JD: Low risk of cervical cancer during a
long period after negative screening in the Netherlands. Br J
Cancer. 88:1054–1057. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schiavon G, Hrebien S, Garcia-Murillas I,
Cutts RJ, Pearson A, Tarazona N, Fenwick K, Kozarewa I,
Lopez-Knowles E, Ribas R, et al: Analysis of ESR1 mutation in
circulating tumor DNA demonstrates evolution during therapy for
metastatic breast cancer. Sci Transl Med. 7:313ra1822015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nagaoka K: Zhang H, Watanabe G and Taya K:
Epithelial cell differentiation regulated by McroRNA-200a in
mammary glands. PLoS One. 8:e651272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu Y, Hyde AS, Simpson MA and Barycki JJ:
Emerging regulatory paradigms in glutathione metabolism. Adv Cancer
Res. 122:69–101. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|