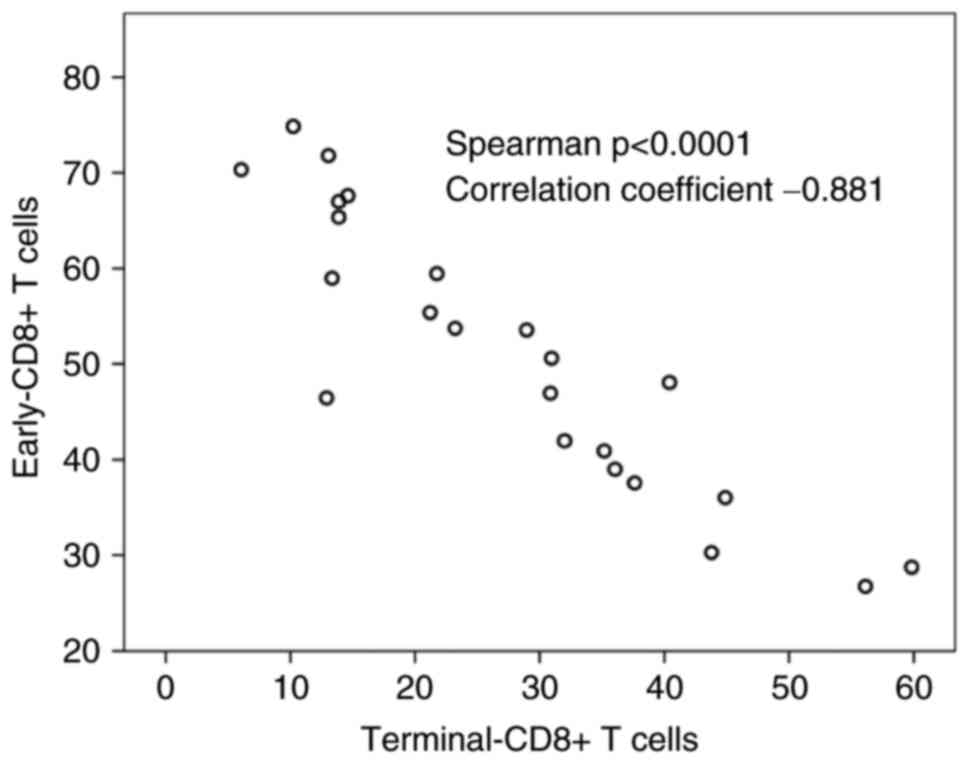
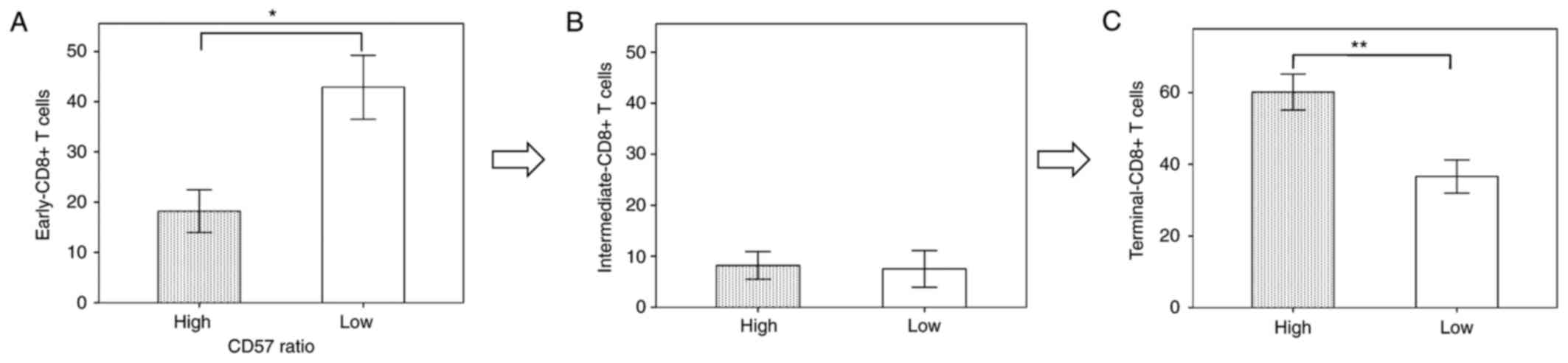
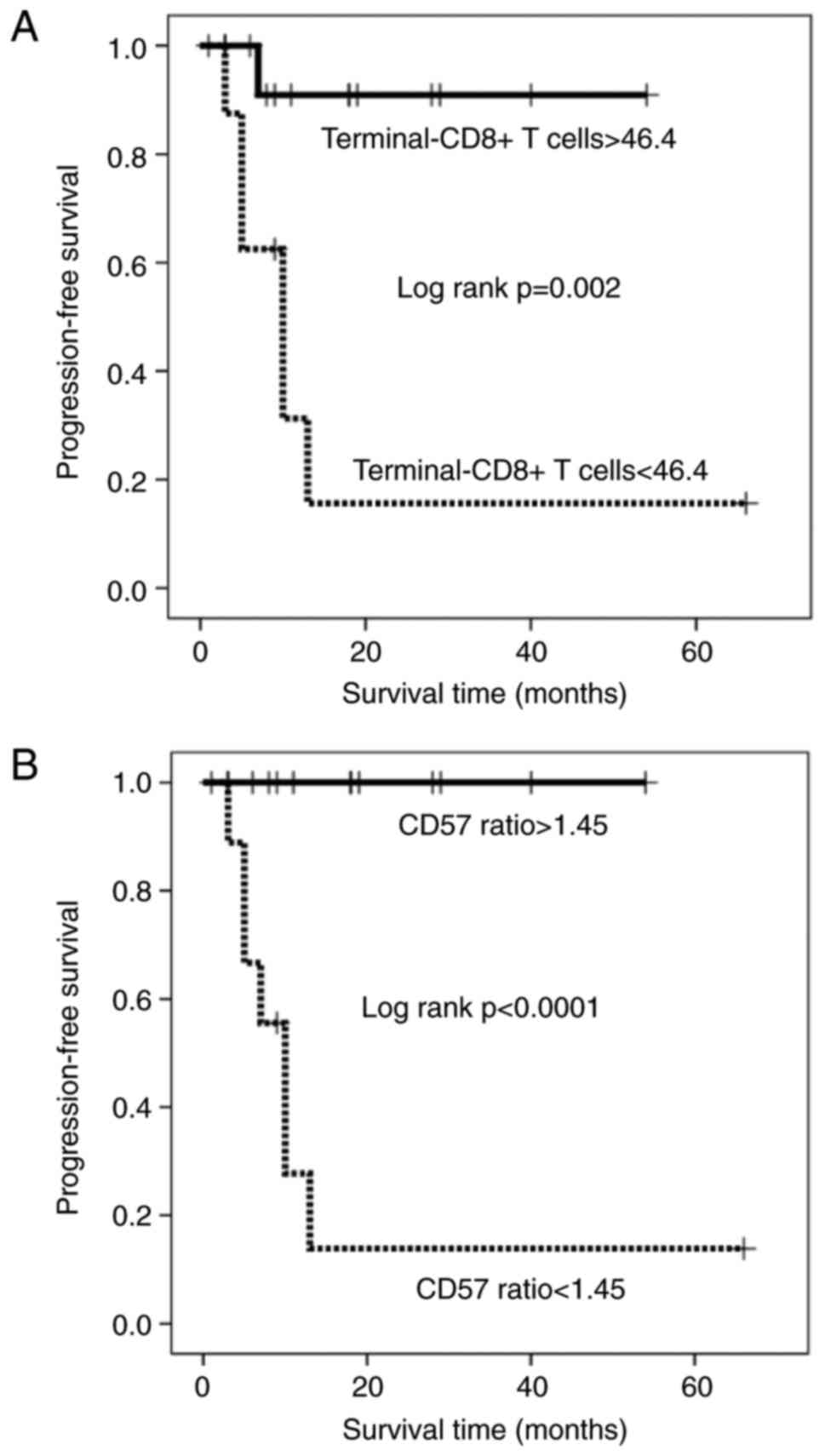
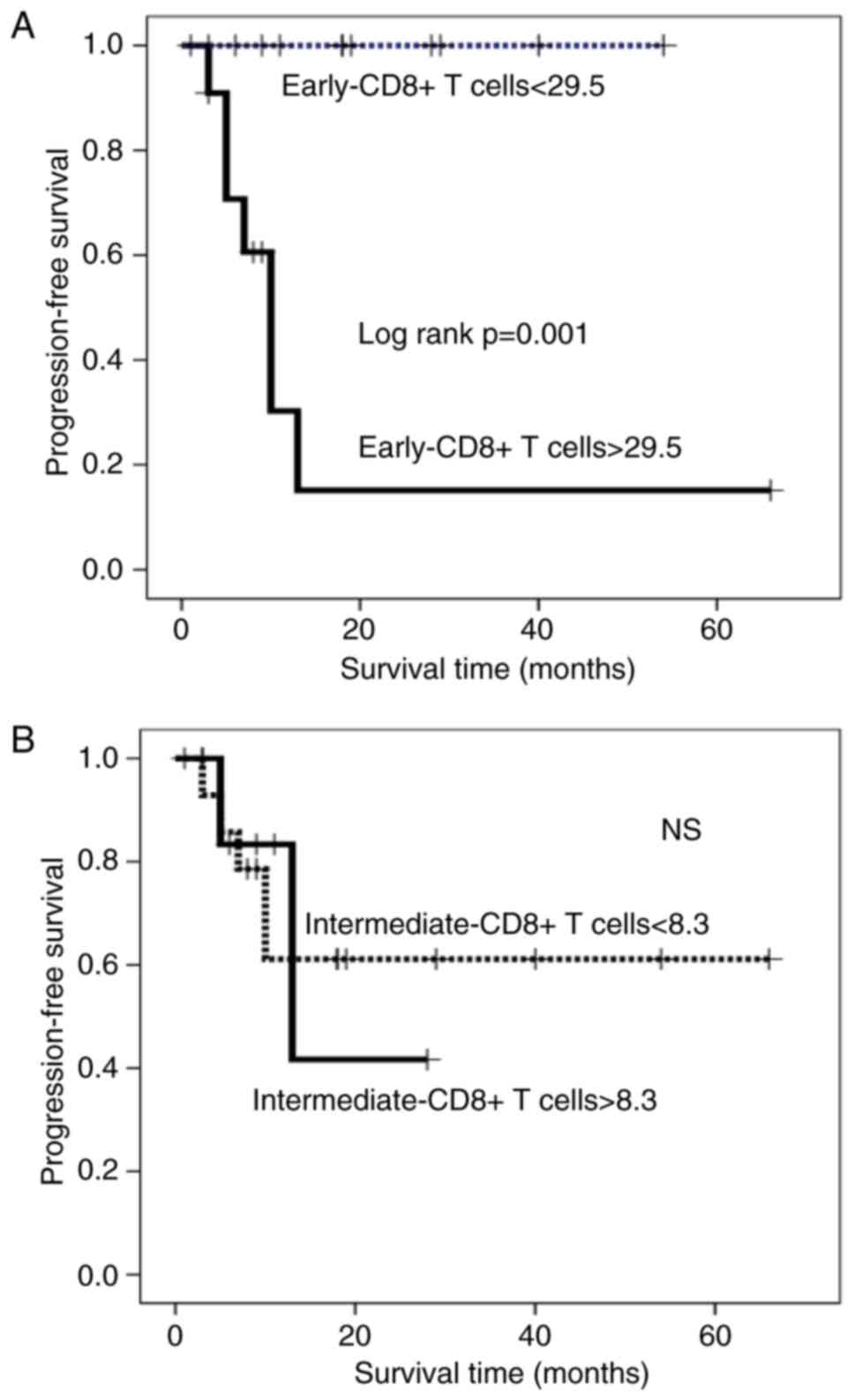
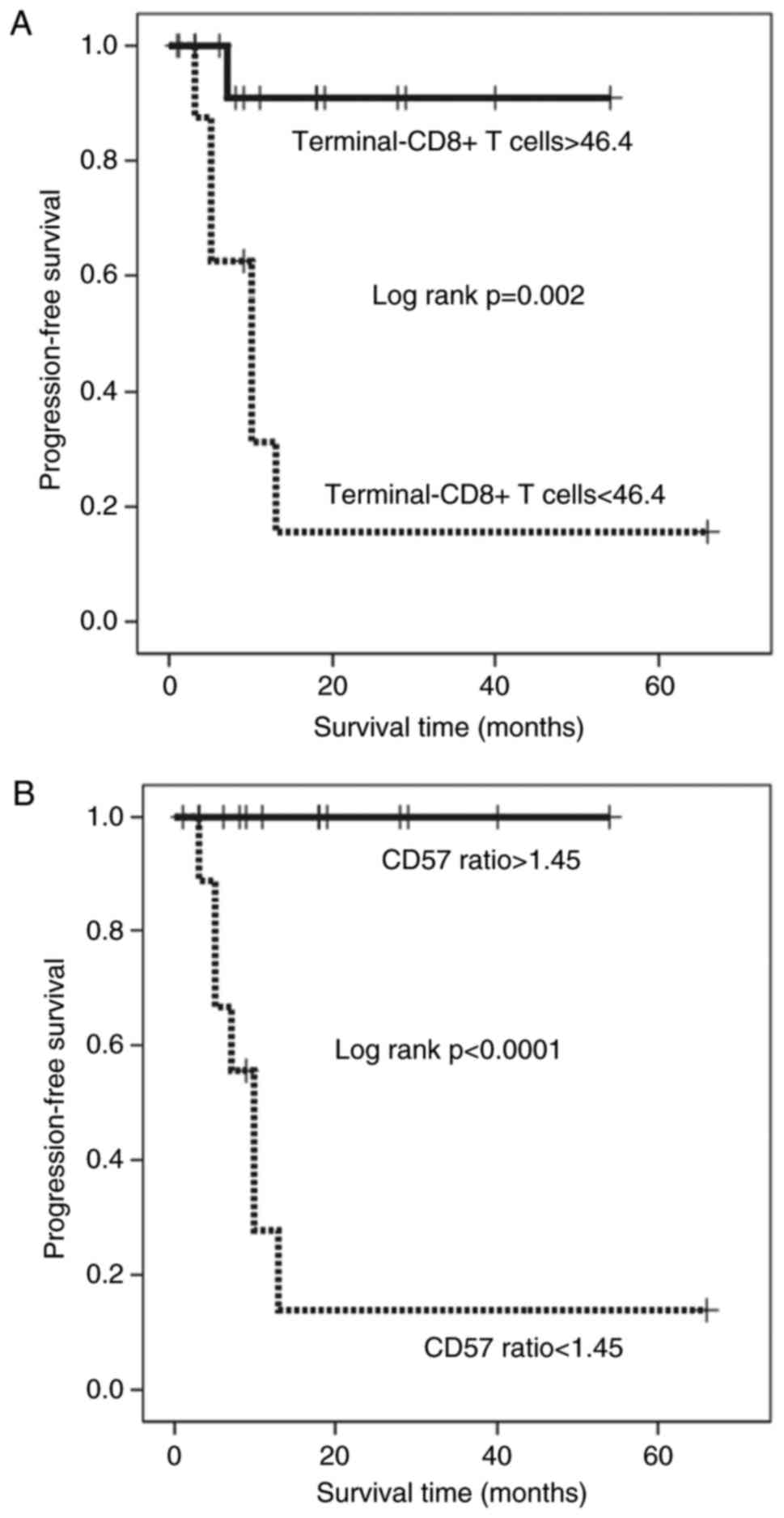
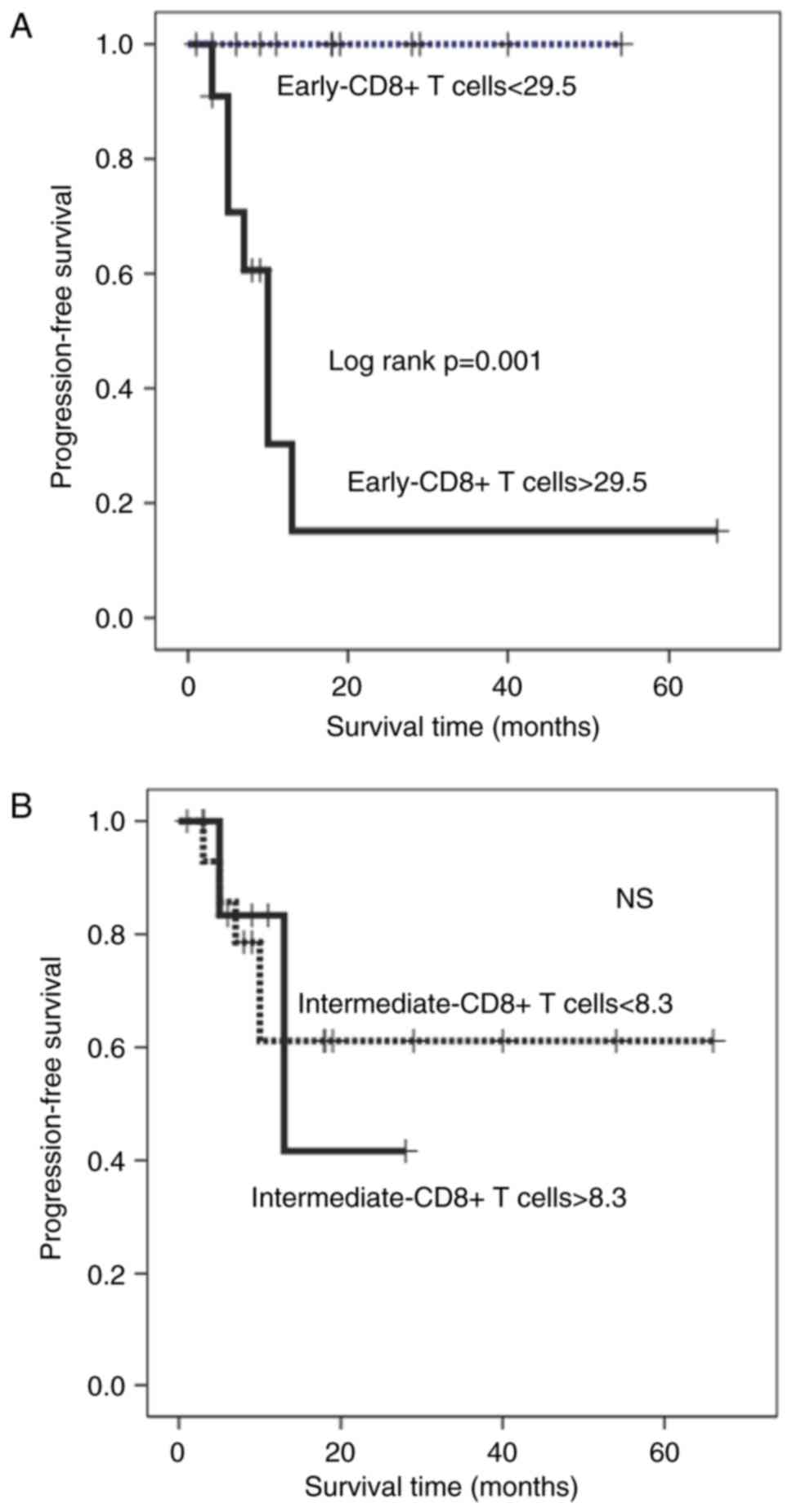
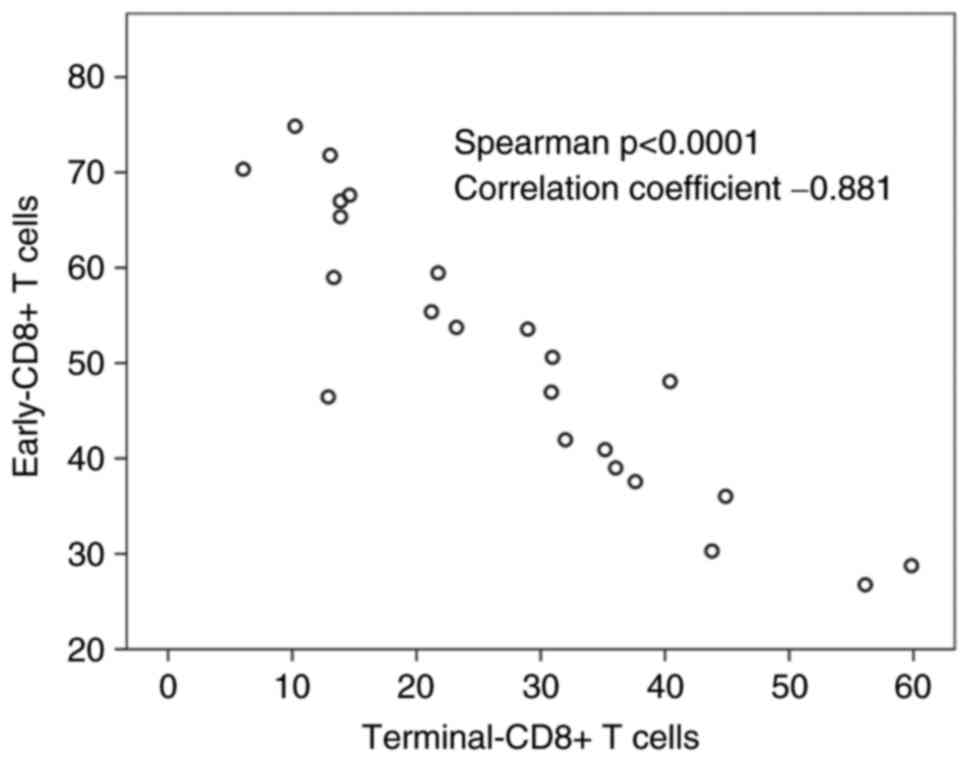
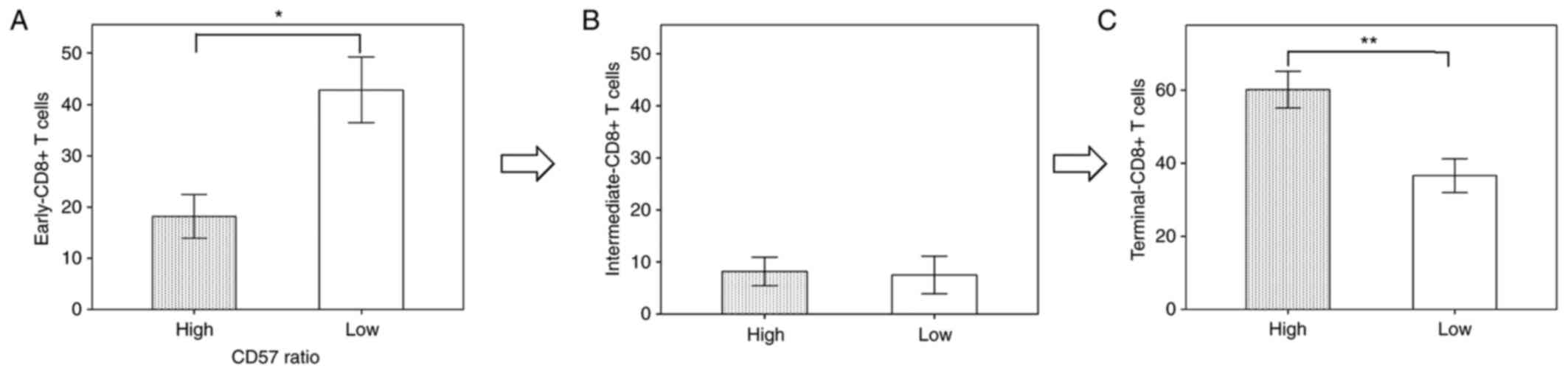
|
1
|
Akagi J and Baba H: Prognostic value of
CD57(+) T lymphocytes in the peripheral blood of patients with
advanced gastric cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 13:528–535. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Characiejus D, Pasukoniene V, Kazlauskaite
N, Valuckas KP, Petraitis T, Mauricas M and Den Otter W: Predictive
value of CD8highCD57+ lymphocyte subset in interferon therapy of
patients with renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 22:3679–3683.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Focosi D, Bestagno M, Burrone O and
Petrini M: CD57+ T lymphocytes and functional immune deficiency. J
Leuloc Biol. 87:107–116. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Dondi E, Roué G, Yuste VJ, Susin SA and
Pellegrini S: A dual role of IFN-alpha in the balance between
proliferation and death of human CD4+ T lymphocytes during primary
response. J Immunol. 173:3740–3747. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Characiejus D, Pasukoniene V,
Jonusauskaite R, Azlauskaite N, Aleknavicius E, Mauricas M and
Otter WD: Peripheral blood CD8high CD57+ lymphocyte levels may
predict outcome in melanoma patients treated with adjuvant
interferon-alpha. Anticancer Res. 28:1139–1142. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu RC, Hwu P and Radvanyi LG: New insights
on the role of CD8(+)CD57(+) T-cells in cancer. Oncoimmunology.
1:954–956. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brenchley JM, Karandikar NJ, Betts MR,
Ambrozak DR, Hill BJ, Crotty LE, Casazza JP, Kuruppu J, Migueles
SA, Connors M, et al: Expression of CD57 defines replicative
senescence and antigen-induced apoptotic death of CD8+ T cells.
Blood. 101:2711–2720. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sobin LH and Wittekind CH: UICC TNM
Classification of malignant tumours. John Wiley and Sons; New York:
1997
|
|
9
|
Papagno L, Spina CA, Marchant A, Salio M,
Rufer N, Little S, Dong T, Chesney G, Waters A, Easterbrook P, et
al: Immune activation and CD8+ T-cell differentiation towards
senescence in HIV-1 infection. PLoS Biol. 2:E202004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nolte MA, van Olffen RW, van Gisbergen KP
and van Lier RA: Timing and tuning of CD27-CD70 interactions: The
impact of signal strength in setting the balance between adaptive
responses and immunopathology. Immunol Rev. 229:216–231. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Matter M, Odermatt B, Yagita H, Nuoffer JM
and Ochsenbein AF: Elimination of chronic viral infection by
blocking CD27 signaling. J Exp Med. 203:2145–2155. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Penaloza-MacMaster P, Rasheed Ur A, Iyer
SS, Yagita H, Blazar BR and Ahmed R: Opposing effects of CD70
costimulation during acute and chronic lymphocytic choriomeningitis
virus infection of mice. J Virol. 85:6168–6174. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Borst J, Hendriks J and Xiao Y: CD27 and
CD70 in T cell and B cell activation. Curr Opin Immunol.
17:275–281. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wischhusen J, Jung G, Radovanovic I, Beier
C, Steinbach JP, Rimner A, Huang H, Schulz JB, Ohgaki H, Aguzzi A,
et al: Identification of CD70-mediated apoptosis of immune effector
cells as a novel immune escape pathway of human glioblastoma.
Cancer Res. 62:2592–2599. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Claus C, Riether C, Schürch C, Matter MS,
Hilmenyuk T and Ochsenbein AF: CD27 signaling increases the
frequency of regulatory T cells and promotes tumor growth. Cancer
Res. 72:3664–3676. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|