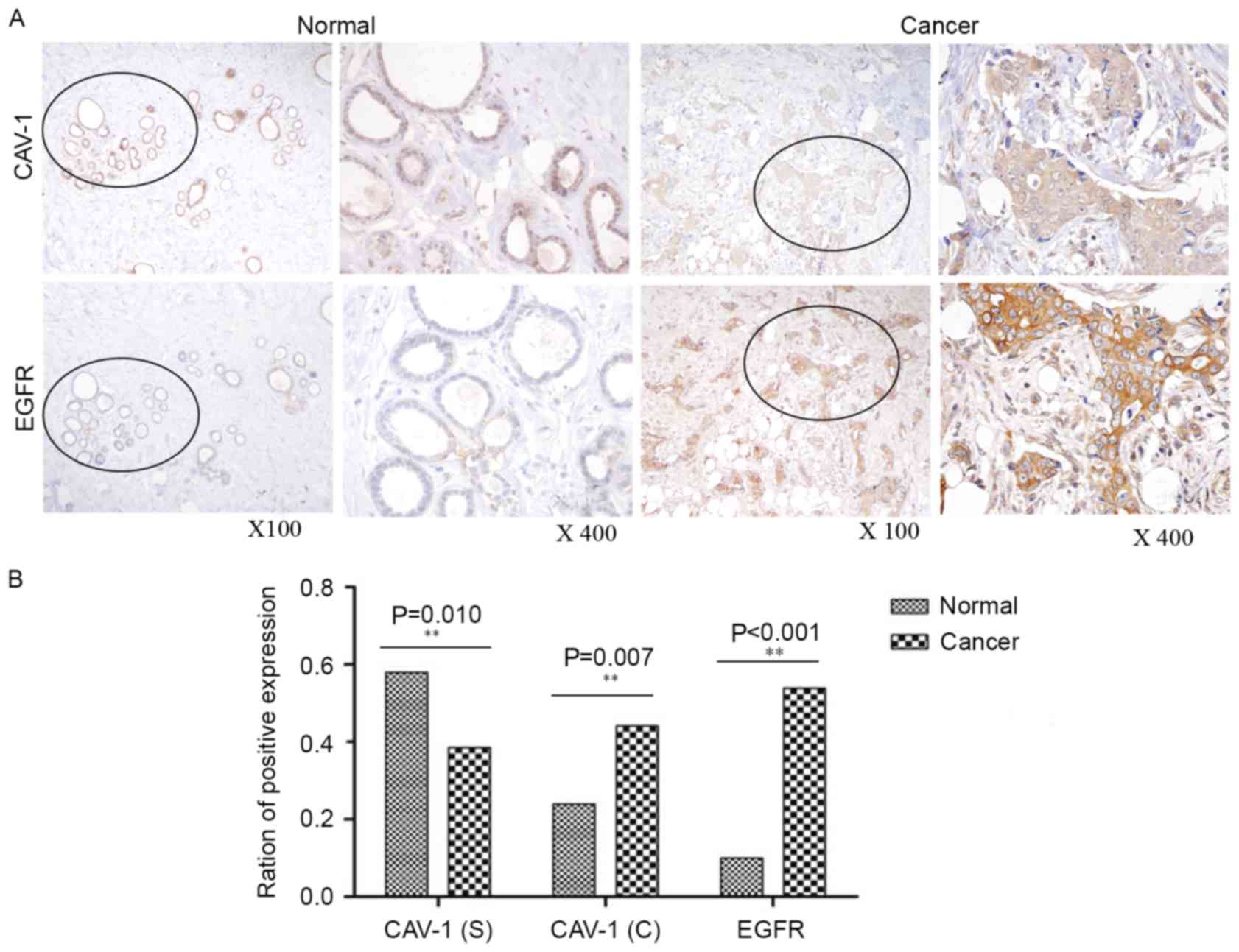
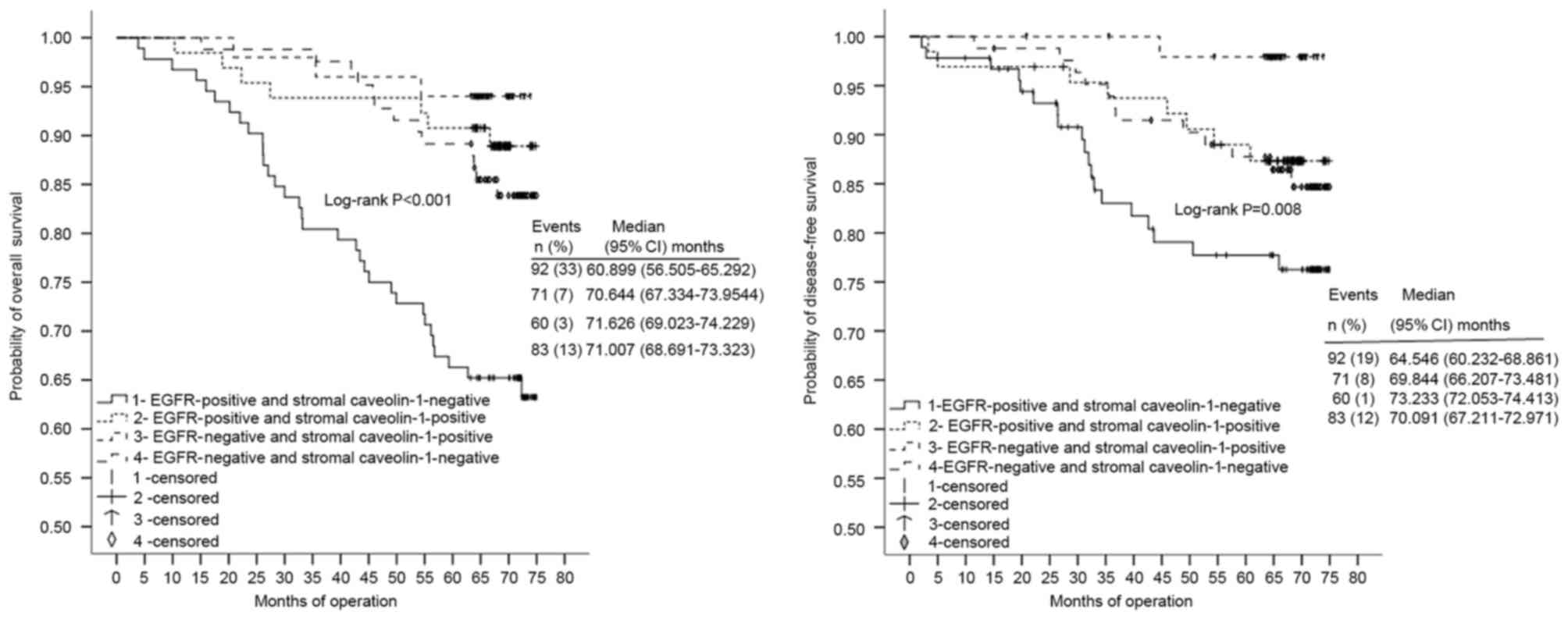
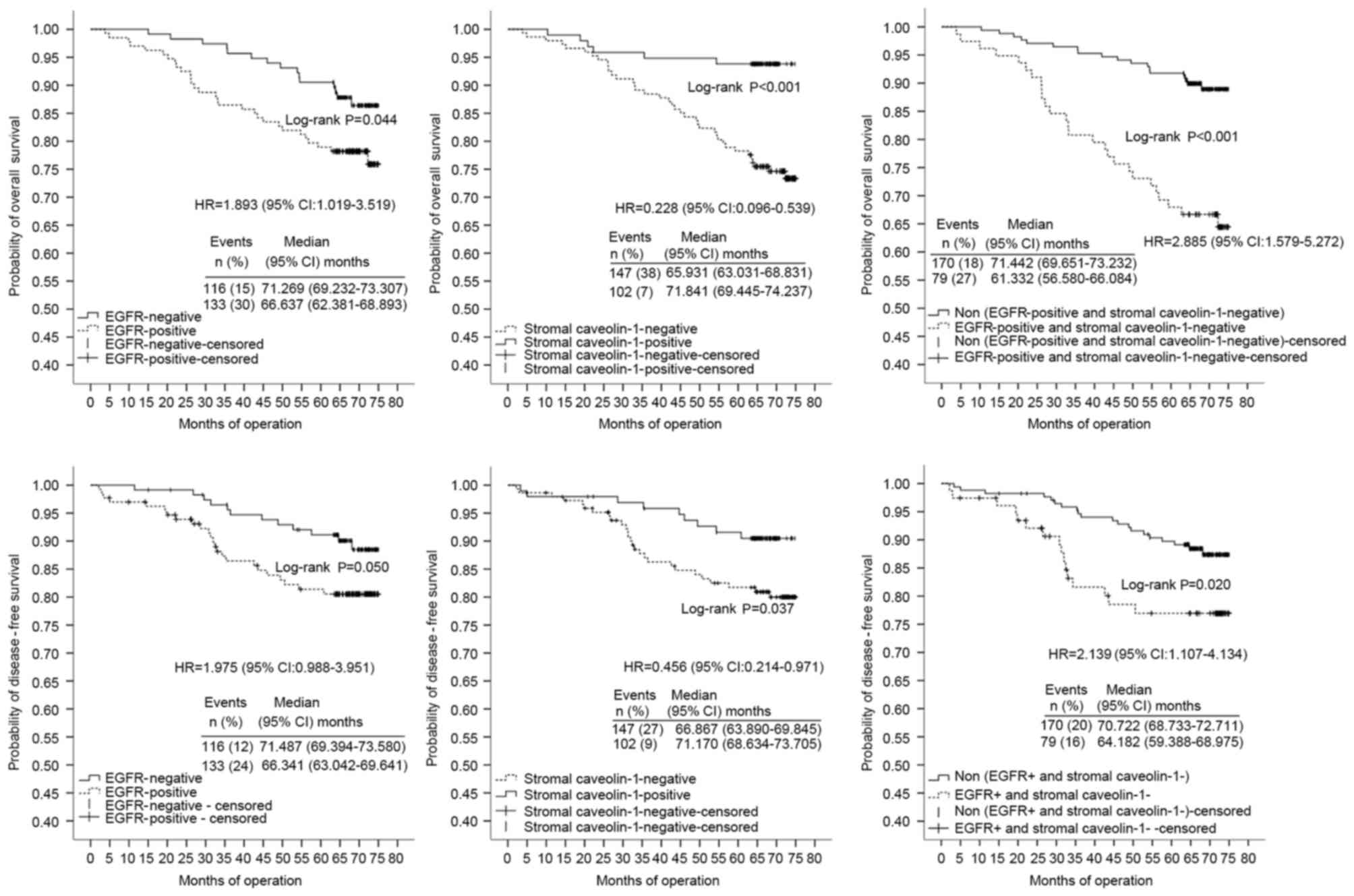
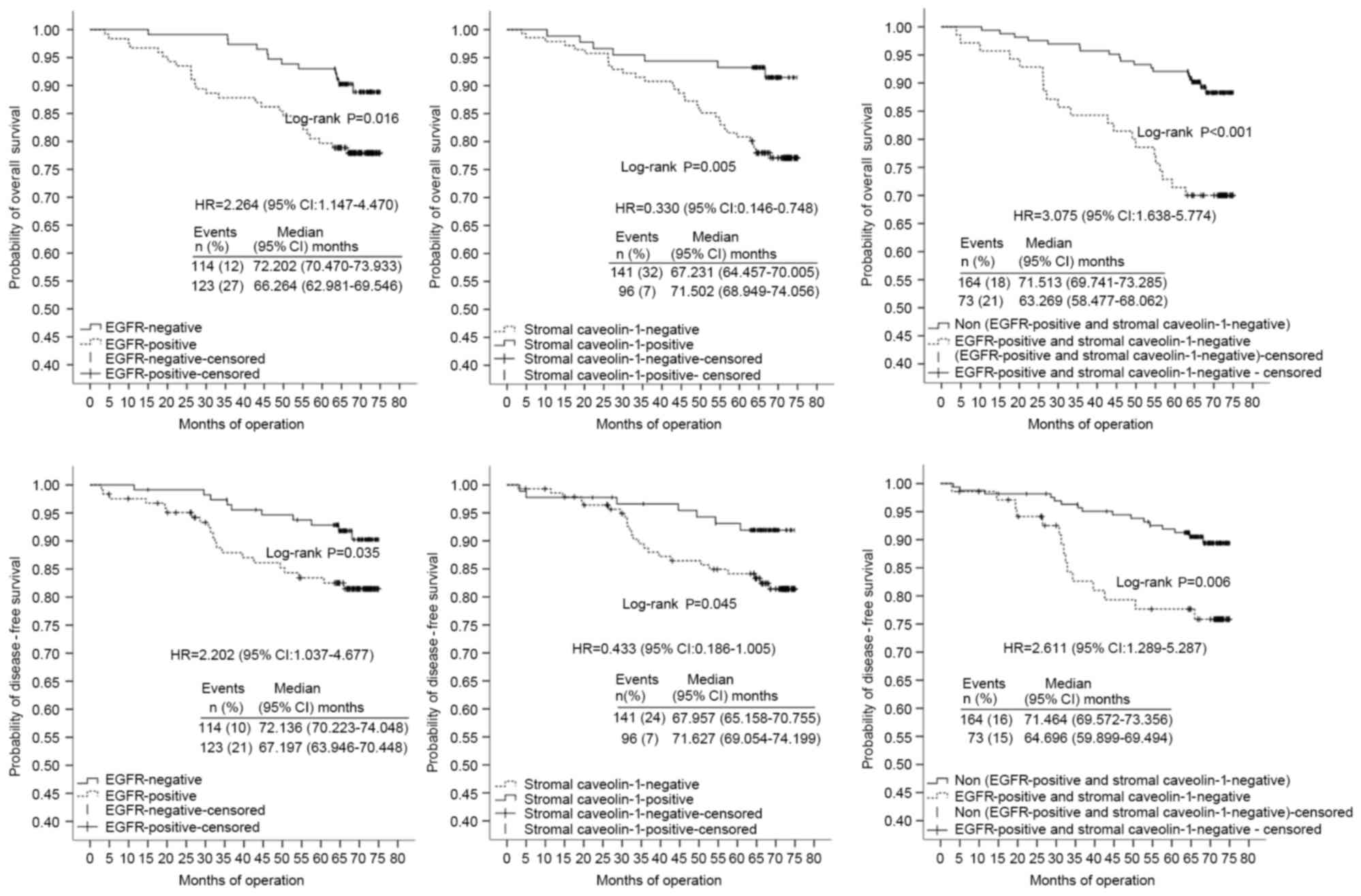
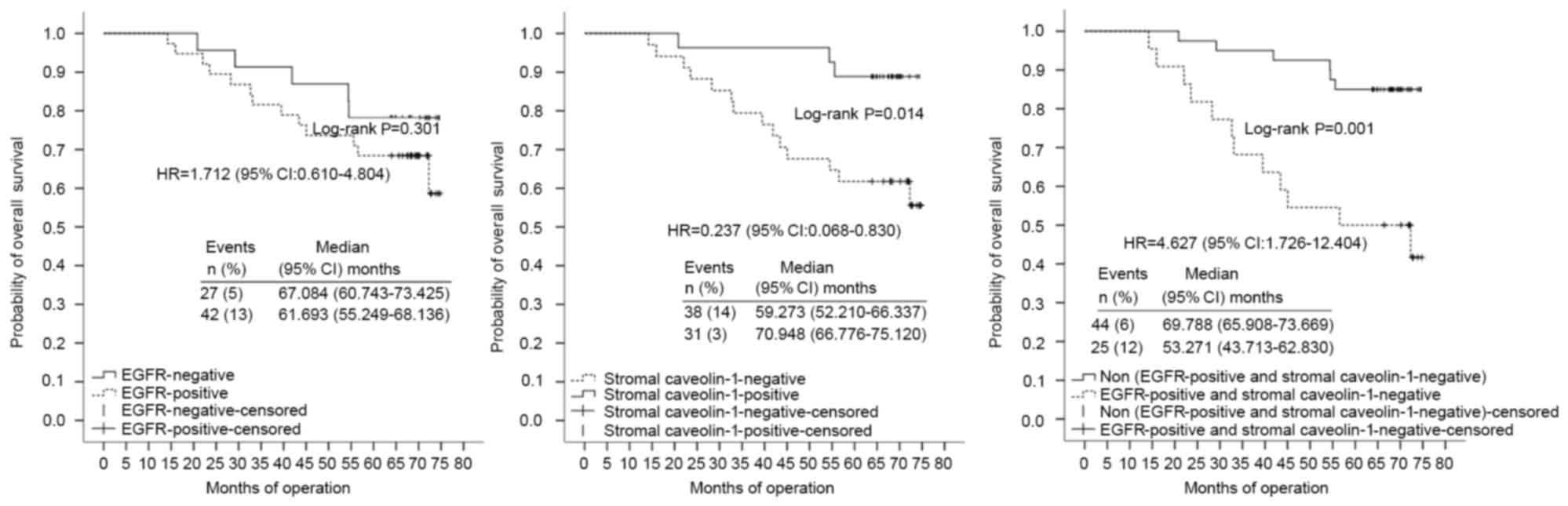
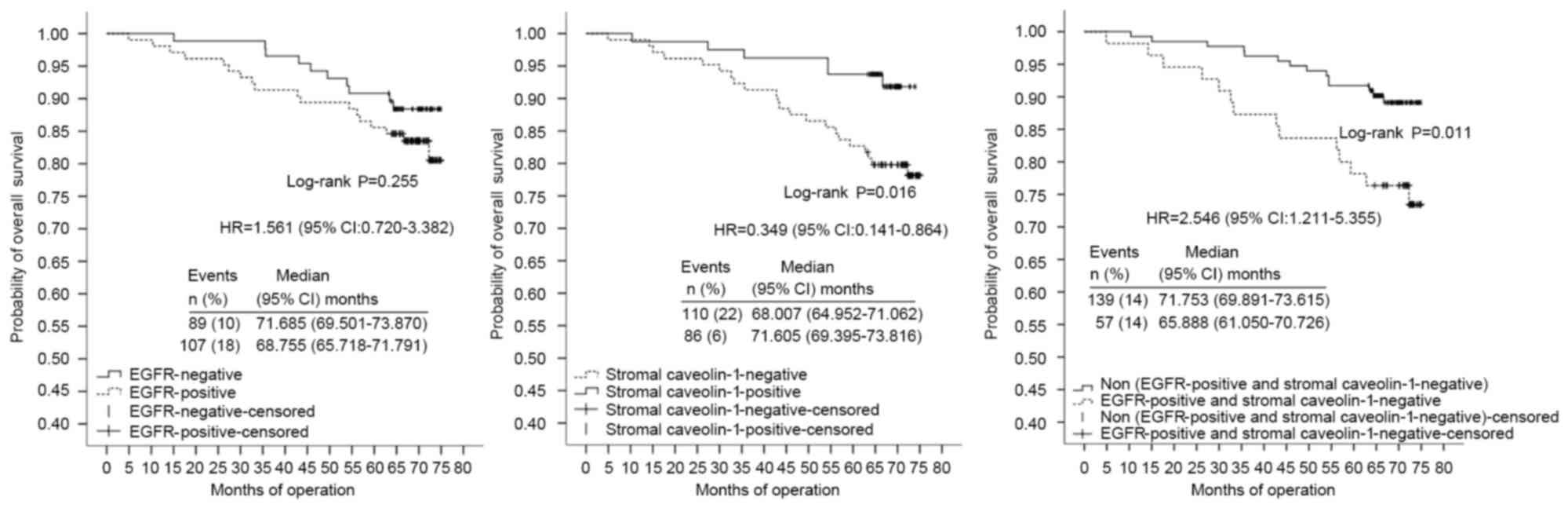
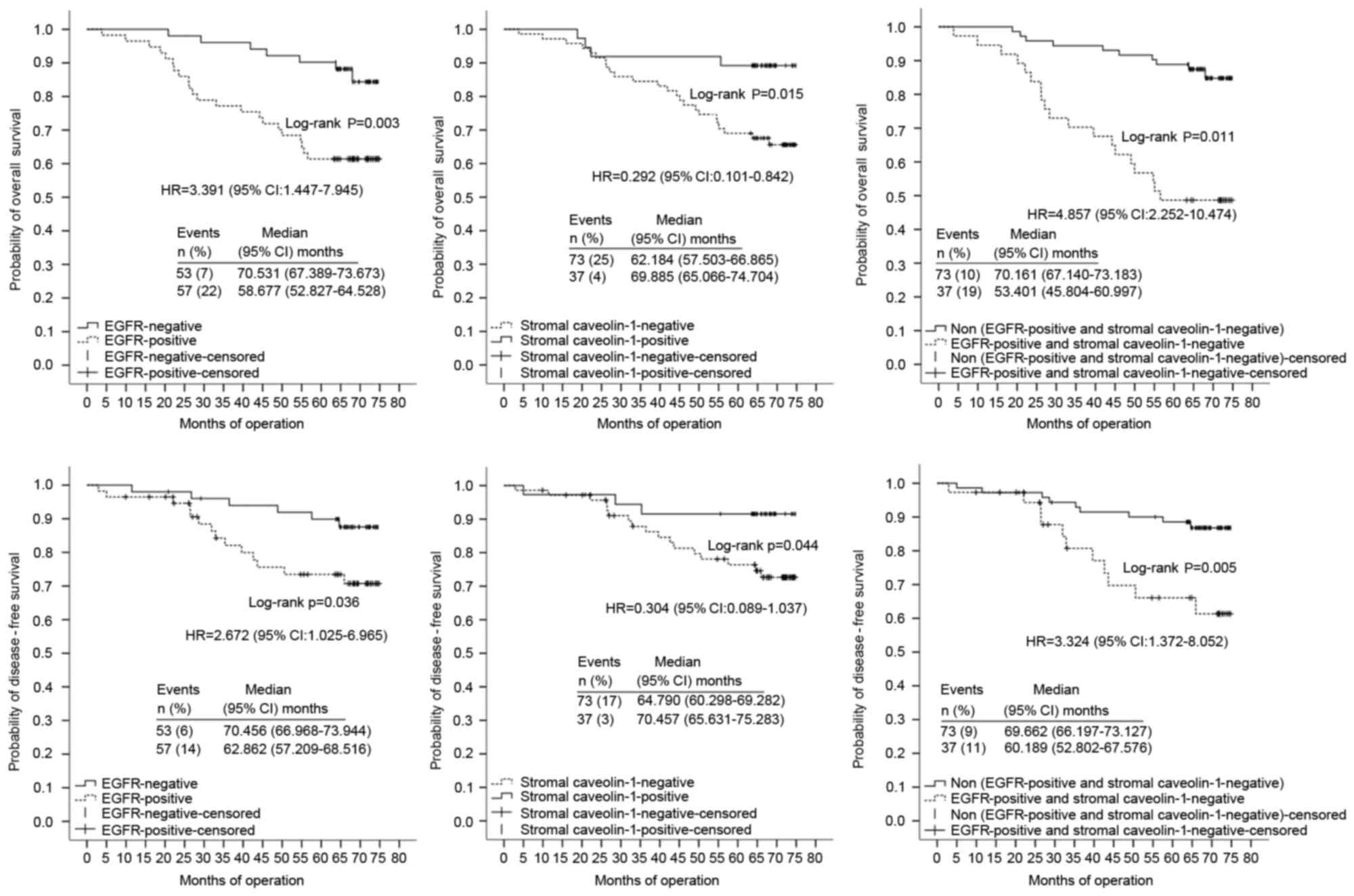
|
1
|
Liedtke C, Kersting C, Bürger H, Kiesel L
and Wülfing P: Caveolin-1 expression in benign and malignant
lesions of the breast. World J Surg Oncol. 5:1102007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Engelman JA, Zhang XL, Galbiati F and
Lisanti MP: Chromosomal localization, genomic organization, and
developmental expression of the murine caveolin gene family (Cav-1,
−2 and −3). Cav-1 and Cav-2 genes map to a known tumor suppressor
locus (6-A2/7q31). FEBS Lett. 429:330–336. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Engelman JA, Zhang XL and Lisanti MP:
Genes encoding human caveolin-1 and −2 are co-localized to the
D7S522 locus (7q31.1), a known fragile site (FRA7G) that is
frequently deleted in human cancers. FEBS Lett. 436:403–410. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Okamoto T, Schlegel A, Scherer PE and
Lisanti MP: Caveolins, a family of scaffolding proteins for
organizing ‘preassembled signaling complexes’ at the plasma
membrane. J Biol Chem. 273:5419–5422. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hnasko R and Lisanti MP: The biology of
caveolae: Lessons from caveolin knockout mice and implications for
human disease. Mol Interv. 3:445–464. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Engelman JA, Zhang X, Galbiati F, Volonte
D, Sotgia F, Pestell RG, Minetti C, Scherer PE, Okamoto T and
Lisanti MP: Molecular genetics of the caveolin gene family:
Implications for human cancers, diabetes, Alzheimer disease, and
muscular dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 63:1578–1587. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang W, Razani B, Altschuler Y, Bouzahzah
B, Mostov KE, Pestell RG and Lisanti MP: Caveolin-1 inhibits
epidermal growth factor-stimulated lamellipod extension and cell
migration in metastatic mammary adenocarcinoma cells (MTLn3).
Transformation suppressor effects of adenovirus-mediated gene
delivery of caveolin-1. J Biol Chem. 275:20717–20725. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Smart EJ, Graf GA, McNiven MA, Sessa WC,
Engelman JA, Scherer PE, Okamoto T and Lisanti MP: Caveolins,
liquid-ordered domains, and signal transduction. Mol Cell Biol.
19:7289–7304. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Koleske AJ, Baltimore D and Lisanti MP:
Reduction of caveolin and caveolae in oncogenically transformed
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:1381–1385. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Quest AF, Gutierrez-Pajares JL and Torres
VA: Caveolin-1: An ambiguous partner in cell signalling and cancer.
J Cell Mol Med. 12:1130–1150. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sloan EK, Ciocca DR, Pouliot N, Natoli A,
Restall C, Henderson MA, Fanelli MA, Cuello-Carrión FD, Gago FE and
Anderson RL: Stromal cell expression of caveolin-1 predicts outcome
in breast cancer. Am J Pathol. 174:2035–2043. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
El-Gendi SM, Mostafa MF and El-Gendi AM:
Stromal caveolin-1 expression in breast carcinoma. Correlation with
early tumor recurrence and clinical outcome. Pathol Oncol Res.
18:459–469. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Witkiewicz AK, Dasgupta A, Sotgia F,
Mercier I, Pestell RG, Sabel M, Kleer CG, Brody JR and Lisanti MP:
An absence of stromal caveolin-1 expression predicts early tumor
recurrence and poor clinical outcome in human breast cancers. Am J
Pathol. 174:2023–2034. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Couet J, Sargiacomo M and Lisanti MP:
Interaction of a receptor tyrosine kinase, EGF-R, with caveolins.
Caveolin binding negatively regulates tyrosine and serine/threonine
kinase activities. J Biol Chem. 272:30429–30438. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lajoie P, Partridge EA, Guay G, Goetz JG,
Pawling J, Lagana A, Joshi B, Dennis JW and Nabi IR: Plasma
membrane domain organization regulates EGFR signaling in tumor
cells. J Cell Biol. 179:341–356. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Park WY, Park JS, Cho KA, Kim DI, Ko YG,
Seo JS and Park SC: Up-regulation of caveolin attenuates epidermal
growth factor signaling in senescent cells. J Biol Chem.
275:20847–20852. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Savage K, Lambros MB, Robertson D, Jones
RL, Jones C, Mackay A, James M, Hornick JL, Pereira EM, Milanezi F,
et al: Caveolin 1 is overexpressed and amplified in a subset of
basal-like and metaplastic breast carcinomas: A morphologic,
ultrastructural, immunohistochemical, and in situ hybridization
analysis. Clin Cancer Res. 13:90–101. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Agelaki S, Spiliotaki M, Markomanolaki H,
Kallergi G, Mavroudis D, Georgoulias V and Stournaras C: Caveolin-1
regulates EGFR signaling in MCF-7 breast cancer cells and enhances
gefitinib-induced tumor cell inhibition. Cancer Biol Ther.
8:1470–1477. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ferrero JM, Ramaioli A, Largillier R,
Formento JL, Francoual M, Ettore F, Namer M and Milano G: Epidermal
growth factor receptor expression in 780 breast cancer patients: A
reappraisal of the prognostic value based on an eight-year median
follow-up. Ann Oncol. 12:841–846. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jorge SE, Kobayashi SS and Costa DB:
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in lung cancer:
Preclinical and clinical data. Braz J Med Biol Res. 47:929–939.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA and
Settleman J: Gefitinib-sensitizing EGFR mutations in lung cancer
activate anti-apoptotic pathways. Science. 305:1163–1167. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Salomon DS, Brandt R, Ciardiello F and
Normanno N: Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their
receptors in human malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
19:183–232. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R,
Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat
SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, et al: Activating mutations in the
epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of
non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med.
350:2129–2139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee JC, Vivanco I, Beroukhim R, Huang JH,
Feng WL, DeBiasi RM, Yoshimoto K, King JC, Nghiemphu P, Yuza Y, et
al: Epidermal growth factor receptor activation in glioblastoma
through novel missense mutations in the extracellular domain. PLoS
Med. 3:e4852006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lafky JM, Wilken JA, Baron AT and Maihle
NJ: Clinical implications of the ErbB/epidermal growth factor (EGF)
receptor family and its ligands in ovarian cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1785:232–265. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Koenders PG, Beex LV, Kienhuis CB,
Kloppenborg PW and Benraad TJ: Epidermal growth factor receptor and
prognosis in human breast cancer: A prospective study. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 25:21–27. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mineo C, Gill GN and Anderson RG:
Regulated migration of epidermal growth factor receptor from
caveolae. J Biol Chem. 274:30636–30643. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hoop CL, Sivanandam VN, Kodali R, Srnec MN
and van der Wel PC: Structural characterization of the caveolin
scaffolding domain in association with cholesterol-rich membranes.
Biochemistry. 51:90–99. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American Joint
Committee on Cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cohen AW, Razani B, Wang XB, Combs TP,
Williams TM, Scherer PE and Lisanti MP: Caveolin-1-deficient mice
show insulin resistance and defective insulin receptor protein
expression in adipose tissue. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
285:C222–C235. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee SW, Reimer CL, Oh P, Campbell DB and
Schnitzer JE: Tumor cell growth inhibition by caveolin
re-expression in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 16:1391–1397.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|