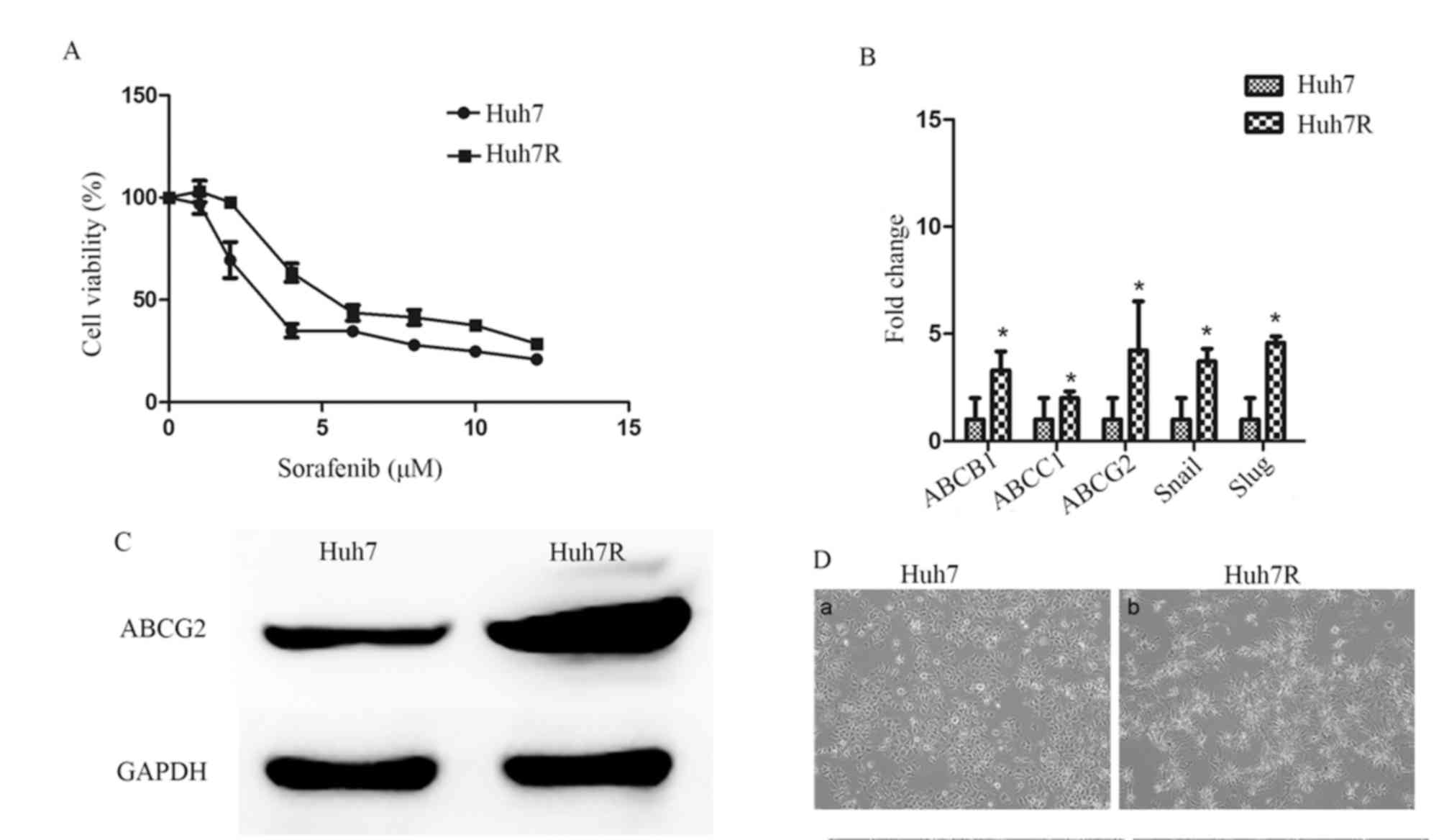
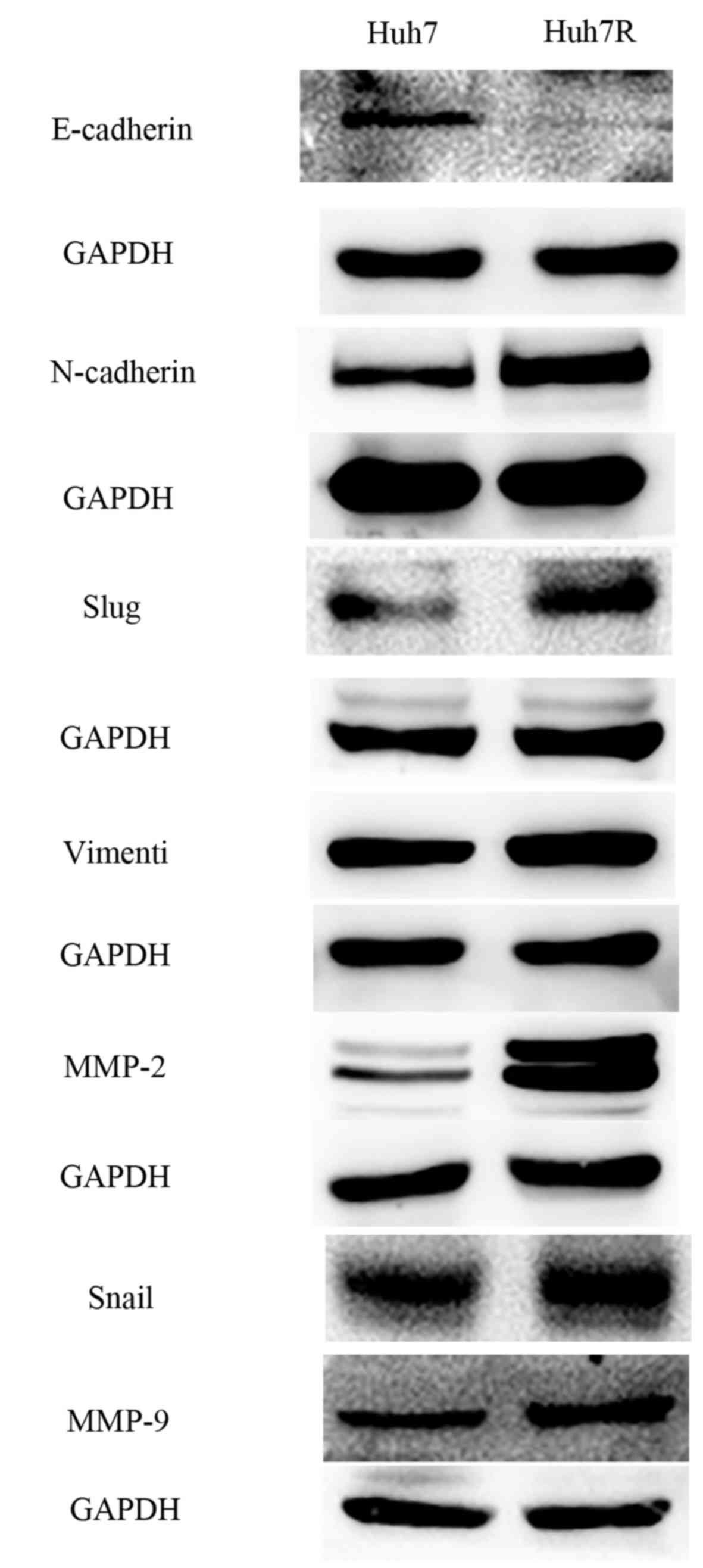
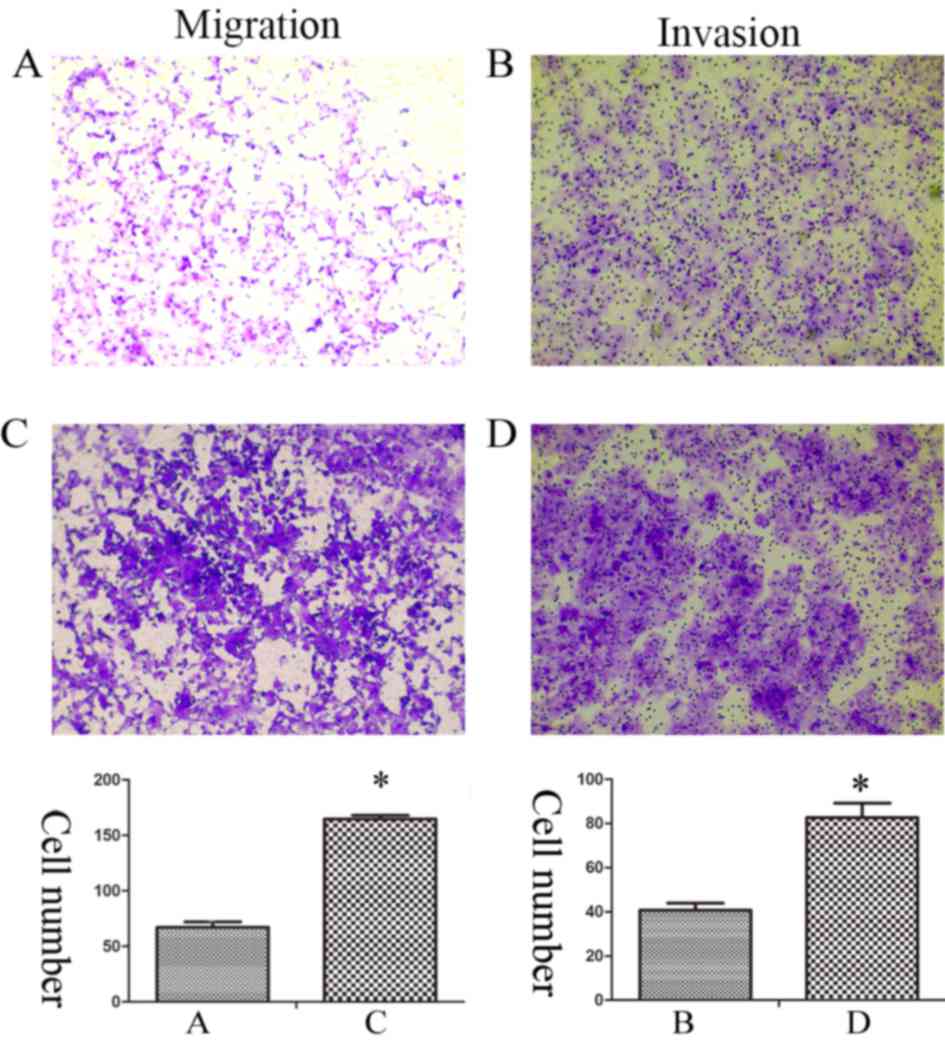
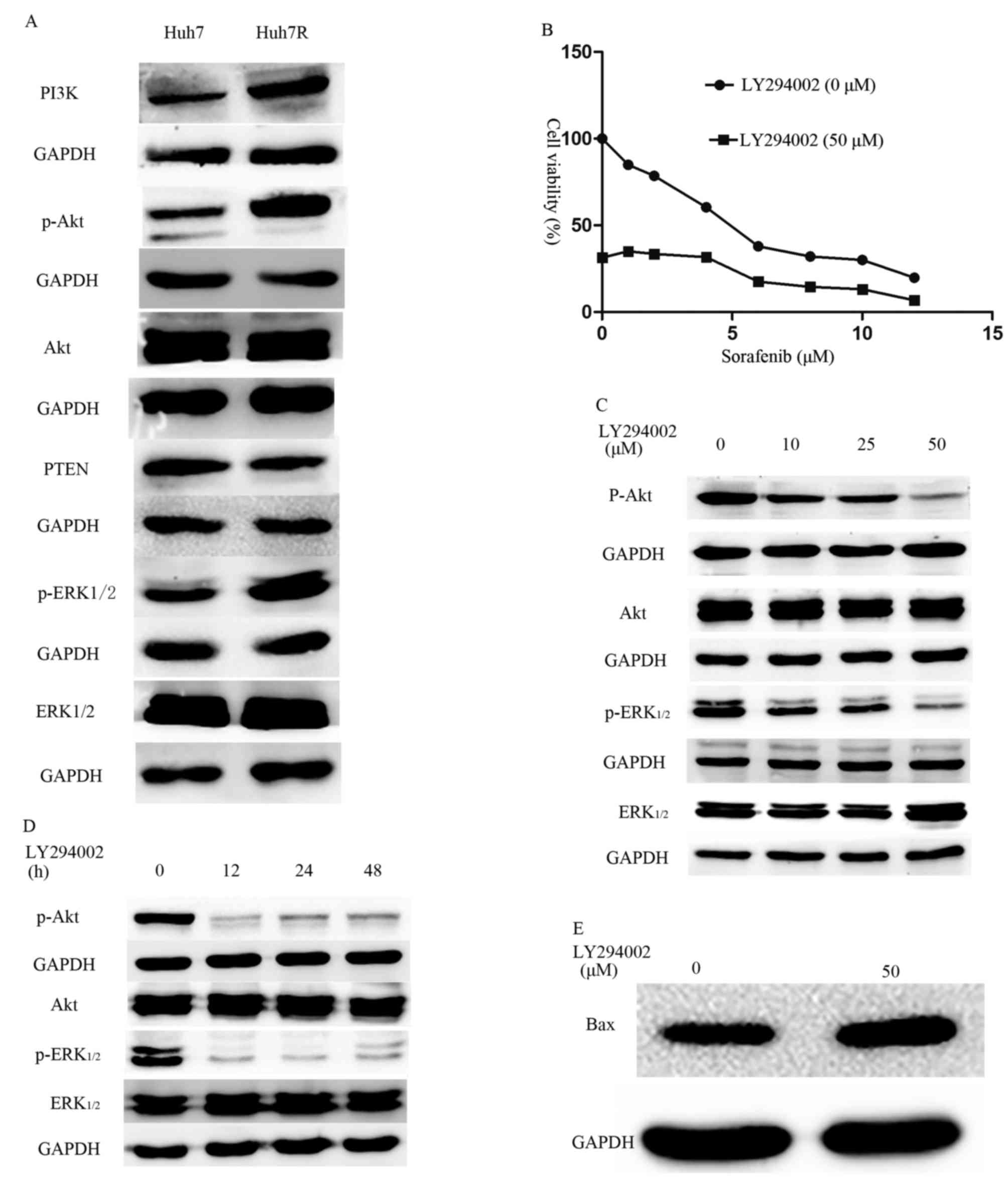
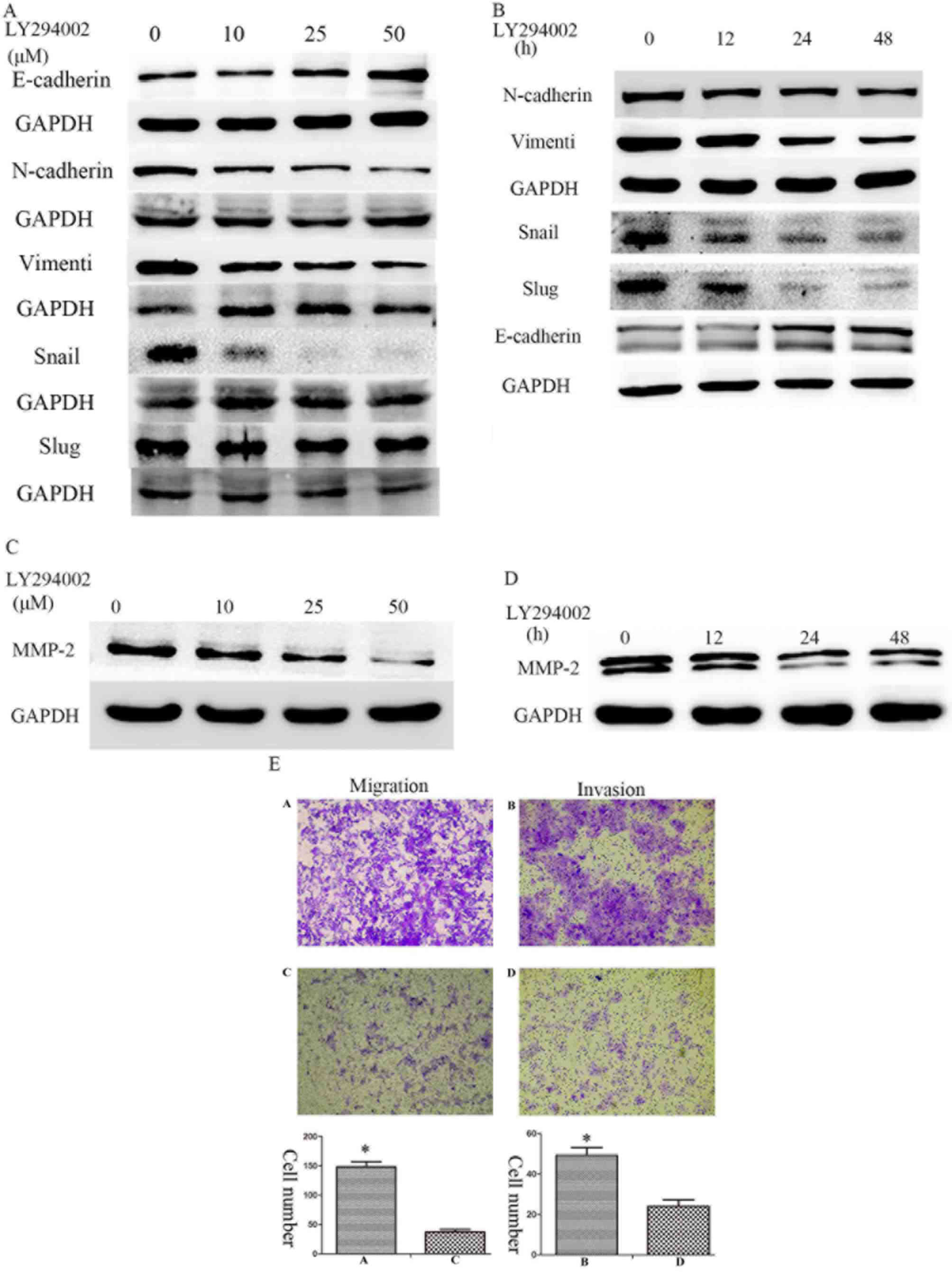
|
1
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, Zhang X, McNabola A,
Wilkie D, Wilhelm S, Lynch M and Carter C: Sorafenib blocks the
RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor
cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer
Res. 66:11851–11858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen S, Wang Y, Ruan W, Wang X and Pan C:
Reversing multidrug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
inhibiting extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated
protein kinase signaling pathway activity. Oncol Lett. 8:2333–2339.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S,
Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, et al: Efficacy and safety of
sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomised, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:25–34. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rimassa L and Santoro A: Sorafenib therapy
in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: The SHARP trial. Expert Rev
Anticancer Ther. 9:739–745. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen KF, Chen HL, Tai WT, Feng WC, Hsu CH,
Chen PJ and Cheng AL: Activation of phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway mediates acquired resistance to
sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
337:155–161. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ombrato L and Malanchi I: The EMT
universe: Space between cancer cell dissemination and metastasis
initiation. Crit Rev Oncog. 19:349–361. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang H, Xu L, Zhu X, Wang P, Chi H and
Meng Z: Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling
mediates sorafenib-induced invasion and metastasis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 32:1465–1472. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
van Malenstein H, Dekervel J, Verslype C,
Van Cutsem E, Windmolders P, Nevens F and van Pelt J: Long-term
exposure to sorafenib of liver cancer cells induces resistance with
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, increased invasion and risk
of rebound growth. Cancer Lett. 329:74–83. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chow AK, Ng L, Lam CS, Wong SK, Wan TM,
Cheng NS, Yau TC, Poon RT and Pang RW: The Enhanced metastatic
potential of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells with sorafenib
resistance. PLoS One. 8:e786752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mir N, Jayachandran A, Dhungel B, Shrestha
R and Steel JC: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition: A mediator of
sorafenib resistance in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 17:698–706. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu W, Yang Z and Lu N: A new role for the
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Cell Adh Migr. 9:317–324. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wen W, Ding J, Sun W, Fu J, Chen Y, Wu K,
Ning B, Han T, Huang L, Chen C, et al: Cyclin G1-mediated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt
signaling facilitates liver cancer progression. Hepatology.
55:1787–1798. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu YJ, Neoh CA, Tsao CY, Su JH and Li HH:
Sinulariolide suppresses human hepatocellular carcinoma cell
migration and invasion by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9
through MAPKs and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci.
16:16469–16482. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kunter I, Erdal E, Nart D, Yilmaz F,
Karademir S, Sagol O and Atabey N: Active form of AKT controls cell
proliferation and response to apoptosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 31:573–580. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dong J, Zhai B, Sun W, Hu F, Cheng H and
Xu J: Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/snail
signaling pathway contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal
transition-induced multi-drug resistance to sorafenib in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 12:e01850882017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang PF, Li KS, Shen YH, Gao PT, Dong ZR,
Cai JB, Zhang C, Huang XY, Tian MX, Hu ZQ, et al: Galectin-1
induces hepatocellular carcinoma EMT and sorafenib resistance by
activating FAK/PI3K/AKT signaling. Cell Death Dis. 7:e22012016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu Y, Huang J, Ma L, Shan J, Shen J, Yang
Z, Liu L, Luo Y, Yao C and Qian C: MicroRNA-122 confers sorafenib
resistance to hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting IGF-1R to
regulate RAS/RAF/ERK signaling pathways. Cancer Lett. 371:171–181.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen W, Wu J, Shi H, Wang Z, Zhang G, Gao
Y, Jiang C and Ding Y: Hepatic stellate cell coculture enables
sorafenib resistance in Huh7 cells through HGF/c-Met/Akt and
Jak2/Stat3 pathways. Biomed Res Int. 2014:7649812014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li QL, Gu FM, Wang Z, Jiang JH, Yao LQ,
Tan CJ, Huang XY, Ke AW, Dai Z, Fan J and Zhou J: Activation of
PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathway through a PDGFRβ-dependent feedback loop
is involved in rapamycin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.
PLoS One. 7:e333792012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu J, Zheng L, Chen J, Sun Y, Lin H, Jin
RA, Tang M, Liang X and Cai X: Increasing AR by HIF-2α inhibitor
(PT-2385) overcomes the side-effects of sorafenib by suppressing
hepatocellular carcinoma invasion via alteration of pSTAT3, pAKT
and pERK signals. Cell Death Dis. 8:e30952017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|