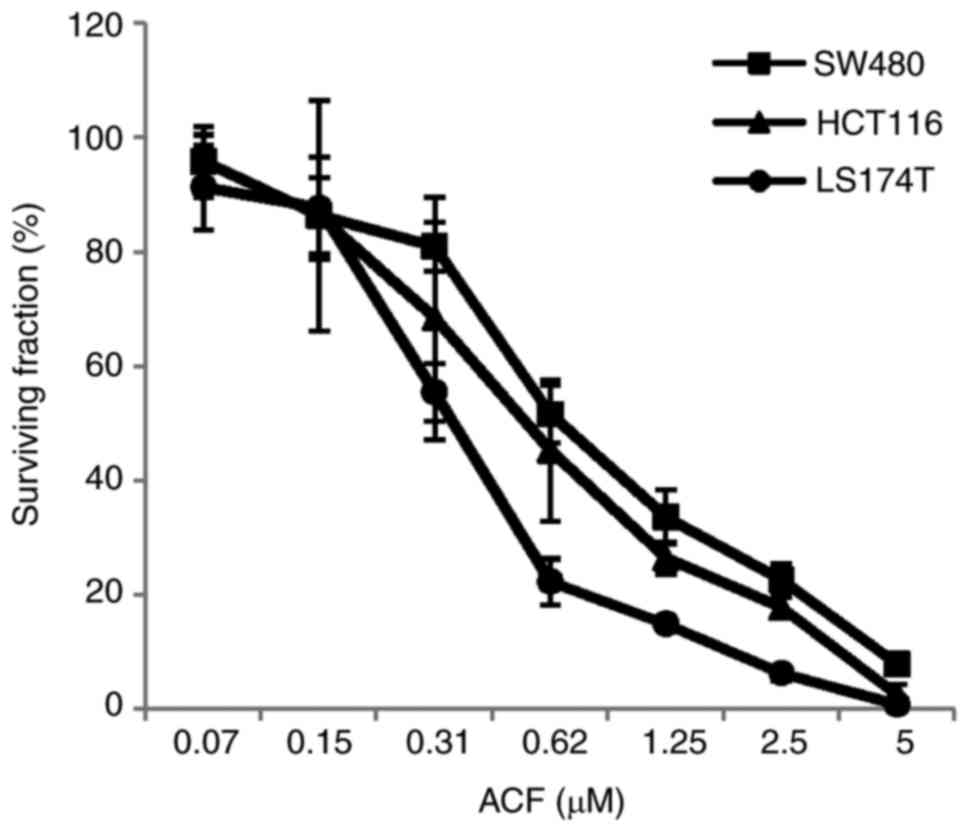
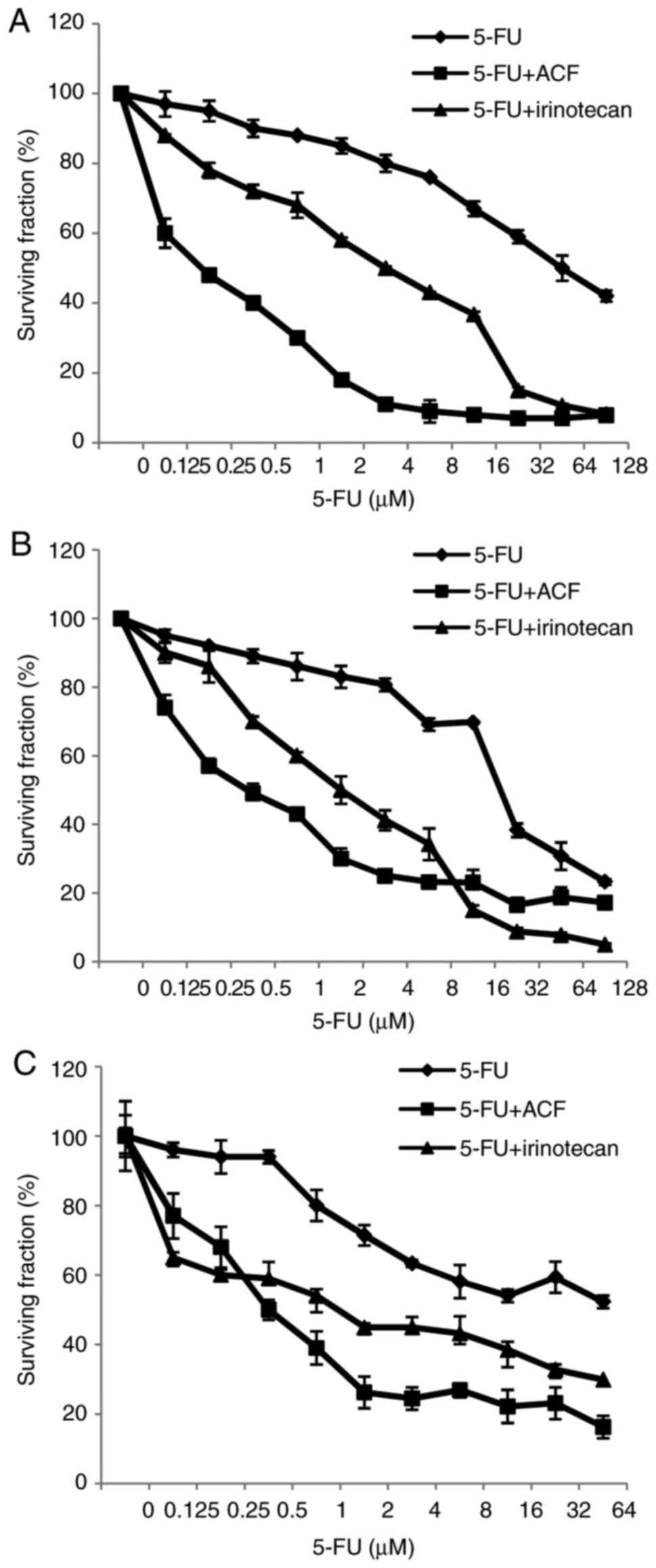
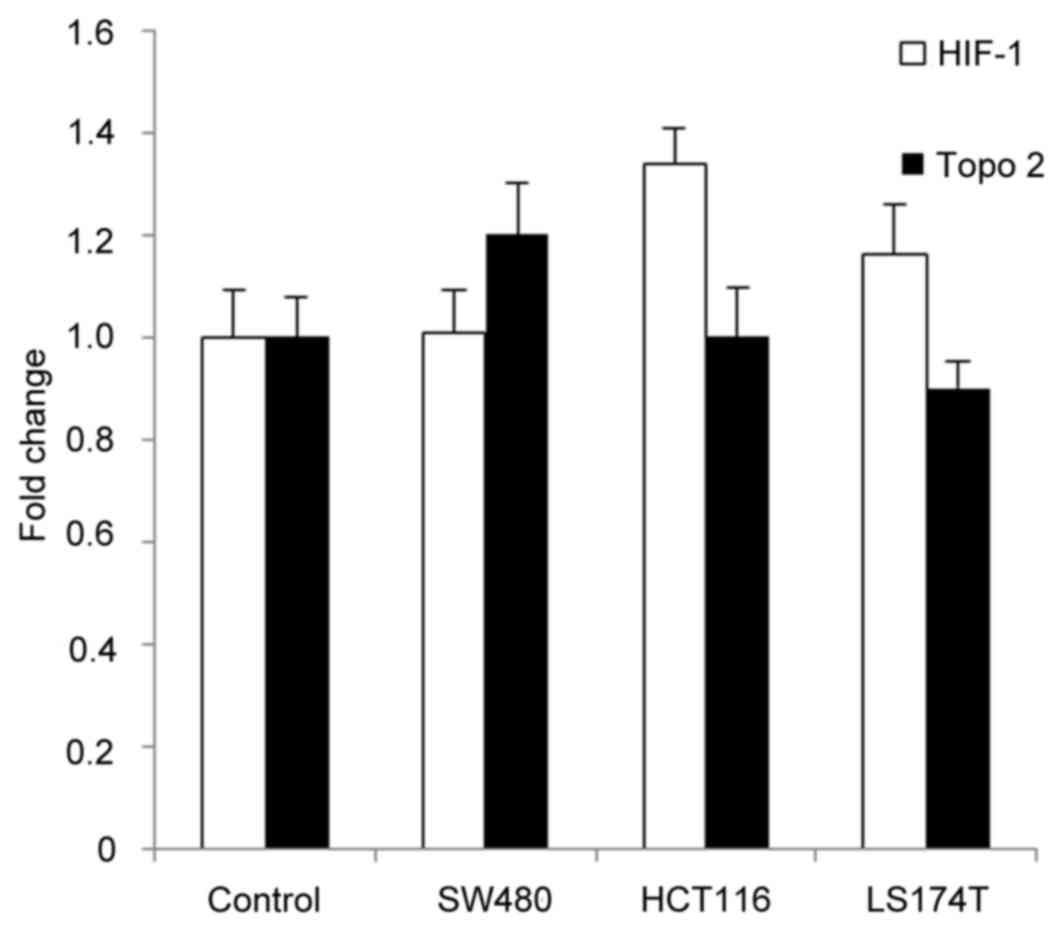
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2011: The impact of eliminating socioeconomic
and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:212–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Coppedè F, Lopomo A, Spisni R and Migliore
L: Genetic and epigenetic biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis and
treatment of colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 20:943–956.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Van Cutsem E and Oliveira J: ESMO
Guidelines Working Group: Advanced colorectal cancer: ESMO clinical
recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol.
20:61–63. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aschele C, Bergamo F and Lonardi S:
Chemotherapy for operable and advanced colorectal cancer. Cancer
Treat Rev. 35:509–516. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Prenen H, Vecchione L and Van Cutsem E:
Role of targeted agents in metastatic colorectal cancer. Target
Oncol. 8:83–96. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Longley DB, Harkin DP and Johnston PG:
5-fluorouracil: Mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat
Rev Cancer. 3:330–338. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Longley DB, Allen WL and Johnston PG: Drug
resistance, predictive markers and pharmacogenomics in colorectal
cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1766:184–196. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
de Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, Homerin
M, Hmissi A, Cassidy J, Boni C, Cortes-Funes H, Cervantes A, Freyer
G, et al: Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin
as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 18:2938–2947. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W,
Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, Berlin J, Baron A, Griffing S,
Holmgren E, et al: Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and
leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med.
350:2335–2342. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Peeters M, Price TJ, Cervantes A, Sobrero
AF, Ducreux M, Hotko Y, André T, Chan E, Lordick F, Punt CJ, et al:
Randomized phase III study of panitumumab with fluorouracil,
leucovorin, and irinotecan (FOLFIRI) compared with FOLFIRI alone as
second-line treatment in patients with metastatic colorectal
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 28:4706–4713. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wainwright M: Acridine-a neglected
antibacterial chromophore. J Antimicrob Chemother. 47:1–13. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim SG, Kim CW, Ahn ET, Lee KY, Hong EK,
Yoo BI and Han YB: Enhanced anti-tumour effects of acriflavine in
combination with guanosine in mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. 49:216–222.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee CJ, Yue CH, Lin YY, Wu JC and Liu JY:
Antitumor activity of acriflavine in human hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Anticancer Res. 34:3549–3556. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fan J, Yang X and Bi Z: Acriflavine
suppresses the growth of human osteosarcoma cells through apoptosis
and autophagy. Tumor Biol. 35:9571–9576. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yin T, He S, Shen G and Wang Y: HIF-1
Dimerization inhibitor acriflavine enhances antitumor activity of
sunitinib in breast cancer model. Oncol Res. 22:139–145. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Shay JE, Imtiyaz HZ, Sivanand S, Durham
AC, Skuli N, Hsu S, Mucaj V, Eisinger-Mathason TS, Krock BL,
Giannoukos DN and Simon MC: Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factors
limits tumor progression in a mouse model of colorectal cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 35:1067–1077. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mathé G, Pontiggia P, Orbach-Arbouys S,
Triana K, Ambetima N, Morette C, Hallard M and Blanquet D: AIDS
therapy with two, three or four agent combinations, applied in
short sequences, differing from each other by drug rotation. I.
First of two parts: A phase I trial equivalent, concerning five
virostatics: AZT, ddI, ddC, acriflavine and an ellipticine
analogue. Biomed Pharmacother. 50:220–227. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hassan S, Laryea D, Mahteme H, Felth J,
Fryknäs M, Fayad W, Linder S, Rickardson L, Gullbo J, Graf W, et
al: Novel activity of acriflavine against colorectal cancer tumor
cells. Cancer Sci. 102:2206–2213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Eftekhar E, Jaberie H and Naghibalhossaini
F: Carcinoembryonic antigen expression and resistance to radiation
and 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis and autophagy. Int J Mol Cell
Med. 5:80–89. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cao C, Yan TD, Black D and Morris DL: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of cytoreductive surgery with
perioperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy for peritoneal
carcinomatosis of colorectal origin. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:2152–2165.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma J, Zhang Y, Shen H, Kapesa L, Liu W,
Zeng M and Zeng S: Association between mismatch repair gene and
irinotecan-based chemotherapy in metastatic colon cancer. Tumor
Biol. 36:9599–9609. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Weijer R, Broekgaarden M, Krekorian M,
Alles LK, van Wijk AC, Mackaaij C, Verheij J, van der Wal AC, van
Gulik TM, Storm G and Heger M: Inhibition of hypoxia inducible
factor 1 and topoisomerase with acriflavine sensitizes perihilar
cholangiocarcinomas to photodynamic therapy. Oncotarget.
7:3341–3356. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lim MJ, Ahn JY, Han Y, Yu CH, Kim MH, Lee
SL, Lim DS and Song JY: Acriflavine enhances radiosensitivity of
colon cancer cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated
apoptosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:1214–1222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bunz F, Hwang PM, Torrance C, Waldman T,
Zhang Y, Dillehay L, Williams J, Lengauer C, Kinzler KW and
Vogelstein B: Disruption of p53 in human cancer cells alters the
responses to therapeutic agents. J Clin Invest. 104:263–269. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Longley DB, Boyer J, Allen WL, Latif T,
Ferguson PR, Maxwell PJ, McDermott U, Lynch M, Harkin DP and
Johnston PG: The role of thymidylate synthase induction in
modulating p53-regulated gene expression in response to
5-fluorouracil and antifolates. Cancer Res. 62:2644–2649.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pereira DM, Simões A, Gomes SE, Castro RE,
Carvalho T, Rodrigues CM and Borralho PM: MEK5/ERK5 signaling
inhibition increases colon cancer cell sensitivity to
5-fluorouracil through a p53-dependent mechanism. Oncotarget.
7:34322–34340. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sui X, Kong N, Wang X, Fang Y, Hu X, Xu Y,
Chen W, Wang K, Li D, Jin W, et al: JNK confers 5-fluorouracil
resistance in p53-deficient and mutant p53-expressing colon cancer
cells by inducing survival autophagy. Sci Rep. 4:46942014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Akasaka T, Tsujii M, Kondo J, Hayashi Y,
Ying J, Lu Y, Kato M, Yamada T, Yamamoto S, Inoue T, et al: 5-FU
resistance abrogates the amplified cytotoxic effects induced by
inhibiting checkpoint kinase 1 in p53-mutated colon cancer cells.
Int J Oncol. 46:63–70. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Seth P, Katayose D, Li Z, Kim M, Wersto R,
Craig C, Shanmugam N, Ohri E, Mudahar B, Rakkar AN, et al: A
recombinant adenovirus expressing wild type p53 induces apoptosis
in drug-resistant human breast cancer cells: A gene therapy
approach for drug-resistant cancers. Cancer Gene Ther. 4:383–390.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rodrigues NR, Rowan A, Smith M, Kerr IB,
Bodmer WF, Gannon JV and Lane DP: p53 mutations in colorectal
cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 87:7555–7559. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang H, Nan L, Yu D, Lindsey JR, Agrawal S
and Zhang R: Anti-tumor efficacy of a novel antisense anti-MDM2
mixed-backbone oligonucleotide in human colon cancer models:
p53-dependent and p53-independent mechanisms. Mol Med. 8:185–199.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hannun Y and Bell RM: Aminoacridines,
potent inhibitors of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 263:5124–5131.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim SG, Cho JY, Chung YS, Ahn ET, Lee KY
and Han YB: Suppression of xenobiotic-metabolizing enzyme
expression in rats by acriflavine, a protein kinase C inhibitor.
Effects on epoxide hydrolase, glutathione s-transferases, and
cytochromes P450. Drug Met Dispos. 26:66–72. 1998.
|
|
36
|
Lee K, Zhang H, Qian DZ, Rey S, Liu JO and
Semenza GL: Acriflavine inhibits HIF-1 dimerization, tumor growth,
and vascularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:17910–17915. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Waldner MJ and Neurath MF: The molecular
therapy of colorectal cancer. Mol Aspect Med. 31:171–178. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kuwai T, Kitadai Y, Tanaka S, Onogawa S,
Matsutani N, Kaio E, Ito M and Chayama K: Expression of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha is associated with tumor
vascularization in human colorectal carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
105:176–181. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|