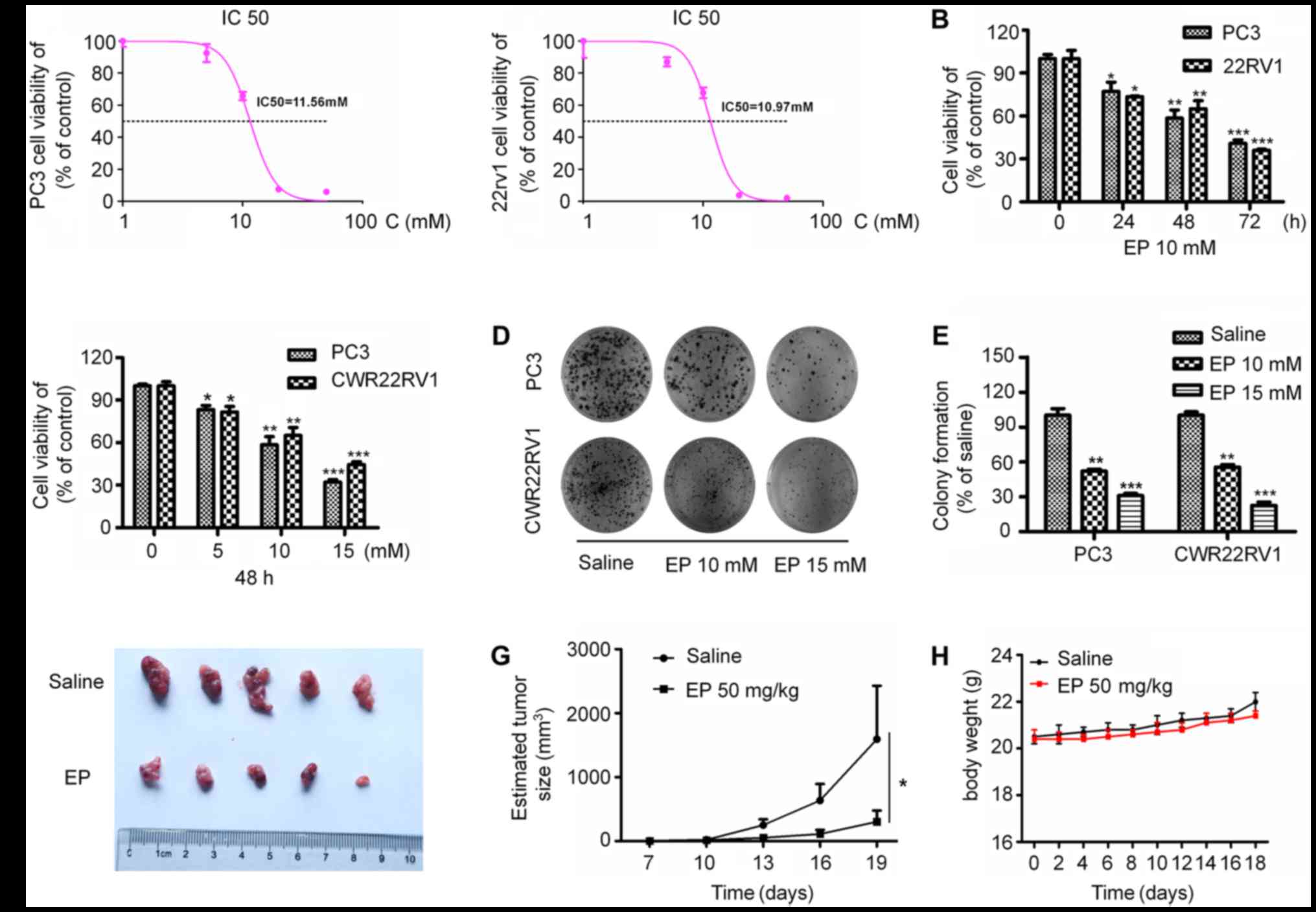
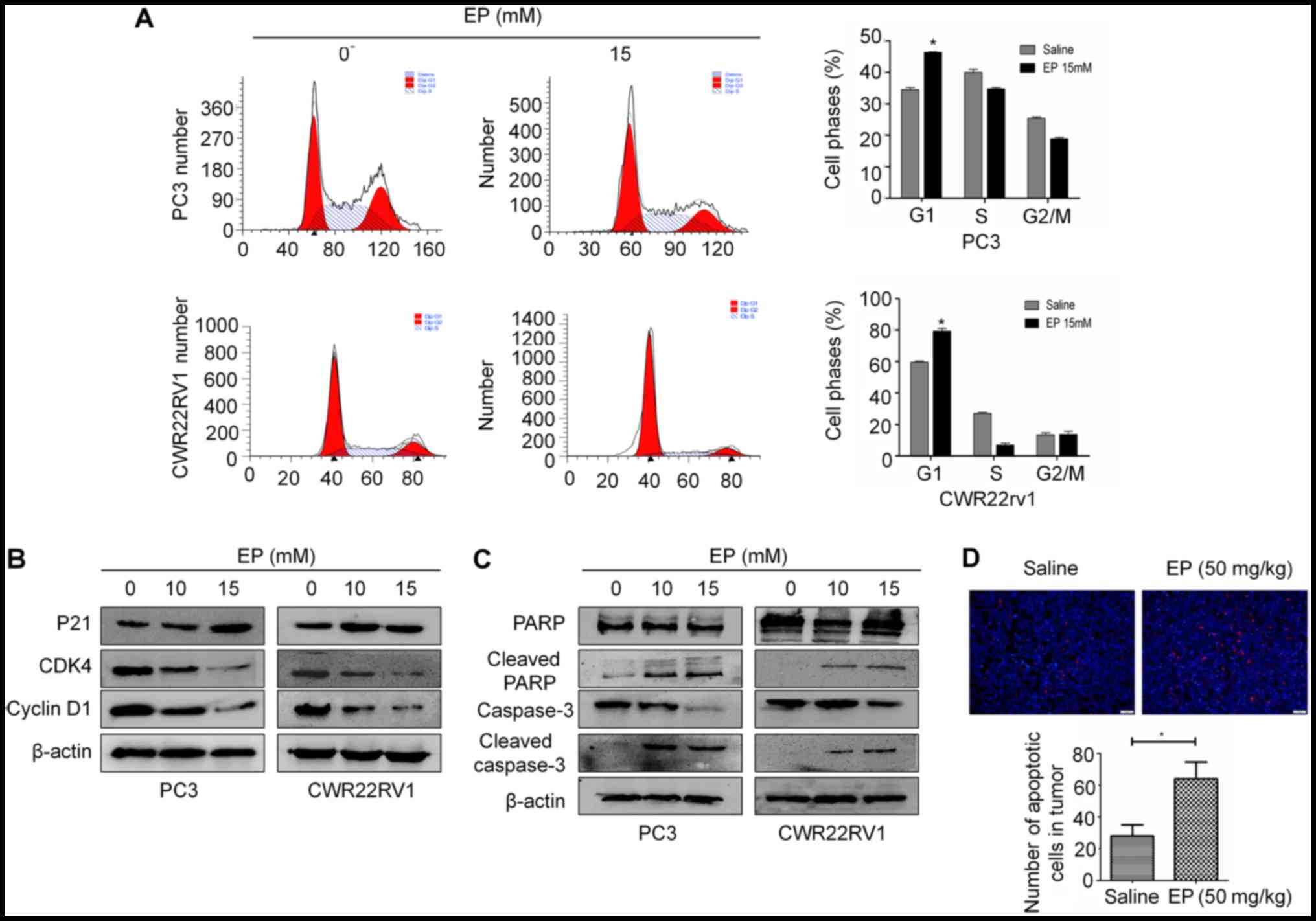
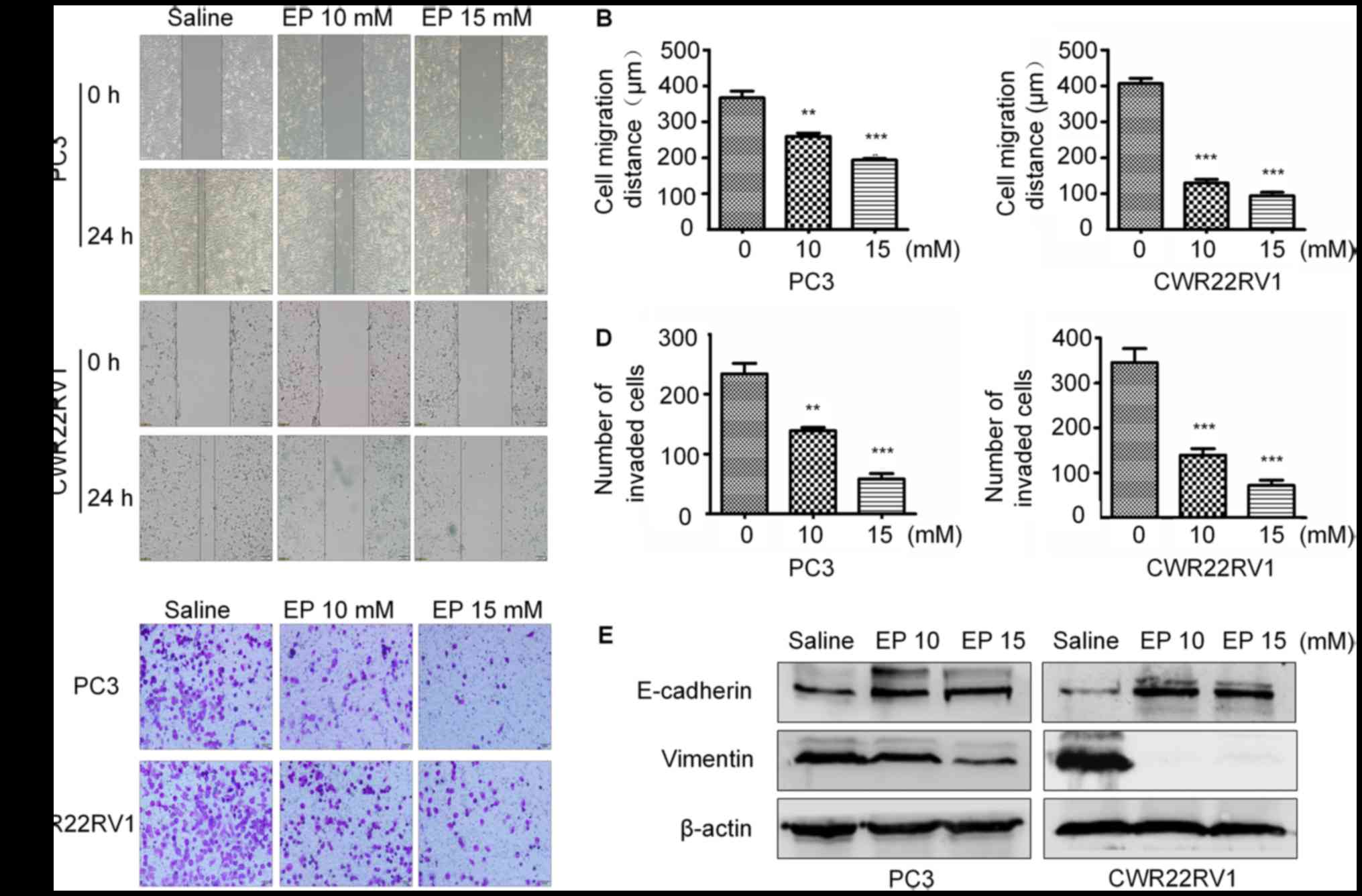
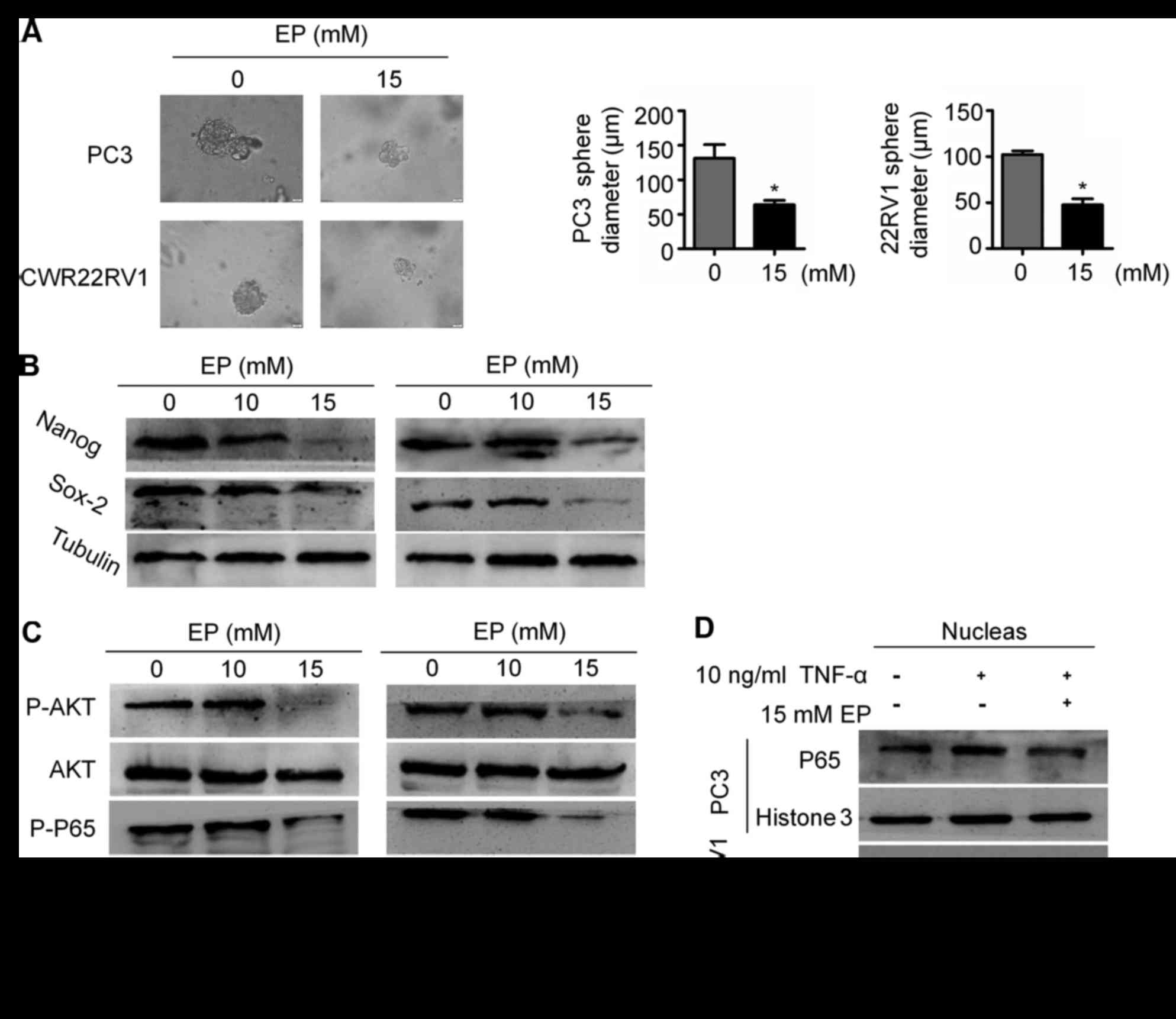
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shafi AA, Yen AE and Weigel NL: Androgen
receptors in hormone-dependent and castration-resistant prostate
cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 140:223–238. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Loriot Y, Bianchini D, Ileana E, Sandhu S,
Patrikidou A, Pezaro C, Albiges L, Attard G, Fizazi K, De Bono JS
and Massard C: Antitumour activity of abiraterone acetate against
metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer progressing after
docetaxel and enzalutamide (MDV3100). Ann Oncol. 24:1807–1812.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schrader AJ, Boegemann M, Ohlmann CH,
Schnoeller TJ, Krabbe LM, Hajili T, Jentzmik F, Stoeckle M,
Schrader M, Herrmann E and Cronauer MV: Enzalutamide in
castration-resistant prostate cancer patients progressing after
docetaxel and abiraterone. Eur Urol. 65:30–36. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chaffer CL, Juan San BP, Lim E and
Weinberg RA: Emt, cell plasticity and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 35:645–654. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang D, Plukker J and Coppes RP: Cancer
stem cells with increased metastatic potential as a therapeutic
target for esophageal cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 44:60–66. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jaworska D, Król W and Szliszka E:
Prostate cancer stem cells: Research advances. Int J Mol Sci.
16:27433–27449. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bitting RL, Schaeffer D, Somarelli JA,
Garcia-Blanco MA and Armstrong AJ: The role of epithelial
plasticity in prostate cancer dissemination and treatment
resistance. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 33:441–468. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen X, Li Q, Liu X, Liu C, Liu R, Rycaj
K, Zhang D, Liu B, Jeter C, Calhoun-Davis T, et al: Defining a
population of stem-like human prostate cancer cells that can
generate and propagate castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 22:4505–4516. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen W, Lian J, Ye JJ, Mo QF, Qin J, Hong
GL, Chen LW, Zhi SC, Zhao GJ and Lu ZQ: Ethyl pyruvate reverses
development of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia during
sepsis-induced immunosuppression. Int Immunopharmacol. 52:61–69.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fink MP: Ethyl pyruvate: A novel
anti-inflammatory agent. J Intern Med. 261:349–362. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pellegrini L, Xue J, Larson D, Pastorino
S, Jube S, Forest KH, Saad-Jube ZS, Napolitano A, Pagano I, Negi
VS, et al: HMGB1 targeting by ethyl pyruvate suppresses malignant
phenotype of human mesothelioma. Oncotarget. 8:22649–22661. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Birkenmeier G, Hemdan NY, Kurz S, Bigl M,
Pieroh P, Debebe T, Buchold M, Thieme R, Wichmann G and Dehghani F:
Ethyl pyruvate combats human leukemia cells but spares normal blood
cells. PLoS One. 11:e01615712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liang X, Chavez AR, Schapiro NE, Loughran
P, Thorne SH, Amoscato AA, Zeh HJ, Beer-Stolz D, Lotze MT and de
Vera ME: Ethyl pyruvate administration inhibits hepatic tumor
growth. J Leukoc Biol. 86:599–607. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li ML, Wang XF, Tan ZJ, Dong P, Gu J, Lu
JH, Wu XS, Zhang L, Ding QC, Wu WG, et al: Ethyl pyruvate
administration suppresses growth and invasion of gallbladder cancer
cells via downregulation of HMGB1-RAGE axis. Int J Immunopathol
Pharmacol. 25:955–965. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Park SY, Yi EY, Jung M, Lee YM and Kim YJ:
Ethyl pyruvate, an anti-inflammatory agent, inhibits tumor
angiogenesis through inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Cancer Lett. 303:150–154. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cheng P, Dai W, Wang F, Lu J, Shen M, Chen
K, Li J, Zhang Y, Wang C, Yang J, et al: Ethyl pyruvate inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma via
regulation of the HMGB1-RAGE and AKT pathways. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 443:1162–1168. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lv D, Wu H, Xing R, Shu F, Lei B, Lei C,
Zhou X, Wan B, Yang Y, Zhong L, et al: HnRNP-L mediates bladder
cancer progression by inhibiting apoptotic signaling and enhancing
MAPK signaling pathways. Oncotarget. 8:13586–13599. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhong D, Zhang HJ, Jiang YD, Wu P, Qi H,
Cai C, Zheng SB and Dang Q: Saikosaponin-d: A potential
chemotherapeutics in castration resistant prostate cancer by
suppressing cancer metastases and cancer stem cell phenotypes.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 474:722–729. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ye X and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity: A central regulator of cancer
progression. Trends Cell Biol. 25:675–686. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Karlsson MC, Gonzalez SF, Welin J and Fuxe
J: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis through
the lymphatic system. Mol Oncol. 11:781–791. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lessard L, Karakiewicz PI, Bellon-Gagnon
P, Alam-Fahmy M, Ismail HA, Mes-Masson AM and Saad F: Nuclear
localization of nuclear factor-kappaB p65 in primary prostate
tumors is highly predictive of pelvic lymph node metastases. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:5741–5745. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ismail HA, Lessard L, Mes-Masson AM and
Saad F: Expression of NF-kappaB in prostate cancer lymph node
metastases. Prostate. 58:308–313. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Min C, Eddy SF, Sherr DH and Sonenshein
GE: NF-kappaB and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of cancer. J
Cell Biochem. 104:733–744. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rajasekhar VK, Studer L, Gerald W, Socci
ND and Scher HI: Tumour-initiating stem-like cells in human
prostate cancer exhibit increased NF-κB signalling. Nat Commun.
2:1622011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakazawa M and Kyprianou N:
Epithelial-mesenchymal-transition regulators in prostate cancer:
Androgens and beyond. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 166:84–90. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li P, Yang R and Gao WQ: Contributions of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells to the
development of castration resistance of prostate cancer. Mol
Cancer. 13:552014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun Y, Wang BE, Leong KG, Yue P, Li L,
Jhunjhunwala S, Chen D, Seo K, Modrusan Z, Gao WQ, et al: Androgen
deprivation causes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the
prostate: Implications for androgen-deprivation therapy. Cancer
Res. 72:527–536. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Figiel S, Vasseur C, Bruyere F, Rozet F,
Maheo K and Fromont G: Clinical significance of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in prostate cancer. Hum
Pathol. 61:26–32. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shiota M, Yokomizo A, Tada Y, Inokuchi J,
Kashiwagi E, Masubuchi D, Eto M, Uchiumi T and Naito S: Castration
resistance of prostate cancer cells caused by castration-induced
oxidative stress through Twist1 and androgen receptor
overexpression. Oncogene. 29:237–250. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu K, Gore C, Yang L, Fazli L, Gleave M,
Pong RC, Xiao G, Zhang L, Yun EJ, Tseng SF, et al: Slug, a unique
androgen-regulated transcription factor, coordinates androgen
receptor to facilitate castration resistance in prostate cancer.
Mol Endocrinol. 26:1496–1507. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ni J, Cozzi P, Hao J, Duan W, Graham P,
Kearsley J and Li Y: Cancer stem cells in prostate cancer
chemoresistance. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 14:225–240. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yun EJ, Zhou J, Lin CJ, Hernandez E, Fazli
L, Gleave M and Hsieh JT: Targeting cancer stem cells in
castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 22:670–679.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang X, Kruithof-de Julio M, Economides
KD, Walker D, Yu H, Halili MV, Hu YP, Price SM, Abate-Shen C and
Shen MM: A luminal epithelial stem cell that is a cell of origin
for prostate cancer. Nature. 461:495–500. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jeter CR, Liu B, Liu X, Chen X, Liu C,
Calhoun-Davis T, Repass J, Zaehres H, Shen JJ and Tang DG: NANOG
promotes cancer stem cell characteristics and prostate cancer
resistance to androgen deprivation. Oncogene. 30:3833–3845. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jeter CR, Badeaux M, Choy G, Chandra D,
Patrawala L, Liu C, Calhoun-Davis T, Zaehres H, Daley GQ and Tang
DG: Functional evidence that the self-renewal gene NANOG regulates
human tumor development. Stem Cells. 27:993–1005. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rybak AP and Tang D: SOX2 plays a critical
role in EGFR-mediated self-renewal of human prostate cancer
stem-like cells. Cell Signal. 25:2734–2742. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kregel S, Kiriluk KJ, Rosen AM, Cai Y,
Reyes EE, Otto KB, Tom W, Paner GP, Szmulewitz RZ and Griend Vander
DJ: Sox2 is an androgen receptor-repressed gene that promotes
castration-resistant prostate cancer. PLoS One. 8:e537012013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Taniguchi K and Karin M: NF-κB,
inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat Rev Immunol.
18:309–324. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kotiyal S and Bhattacharya S: Breast
cancer stem cells, emt and therapeutic targets. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 453:112–116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ozes ON, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Pfeffer SR,
Pfeffer LM and Donner DB: NF-kappaB activation by tumour necrosis
factor requires the Akt serine-threonine kinase. Nature. 401:82–85.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Han Y, Englert JA, Yang R, Delude RL and
Fink MP: Ethyl pyruvate inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent
signaling by directly targeting p65. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
312:1097–1105. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lee SO, Lou W, Nadiminty N, Lin X and Gao
AC: Requirement for NF-(kappa)B in interleukin-4-induced androgen
receptor activation in prostate cancer cells. Prostate. 64:160–167.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Penning TM: Mechanisms of drug resistance
that target the androgen axis in castration resistant prostate
cancer (CRPC). J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 153:105–113. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bennett-Guerrero E, Swaminathan M, Grigore
AM, Roach GW, Aberle LG, Johnston JM and Fink MP: A phase II
multicenter double-blind placebo-controlled study of ethyl pyruvate
in high-risk patients undergoing cardiac surgery with
cardiopulmonary bypass. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 23:324–329.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|