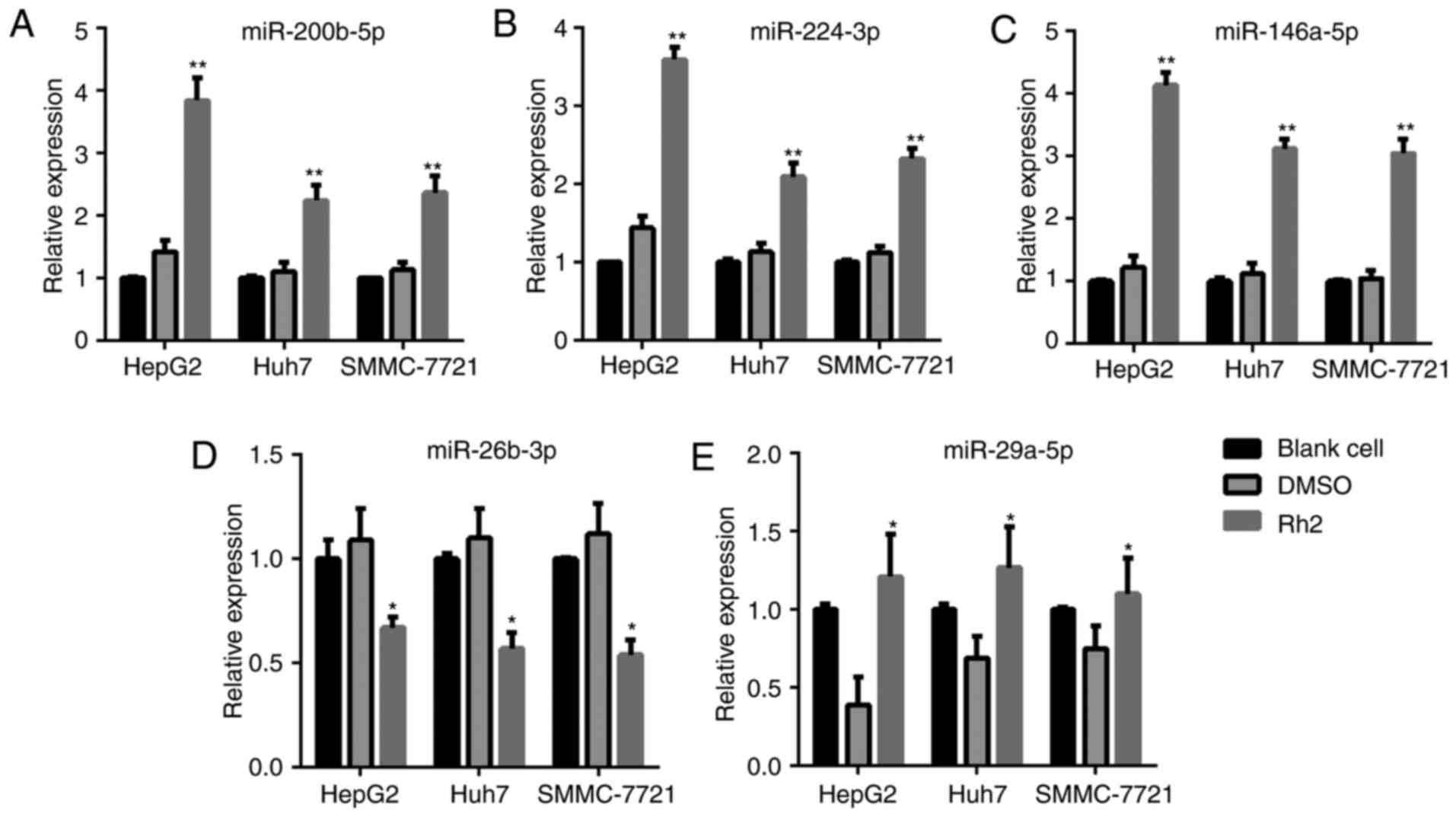
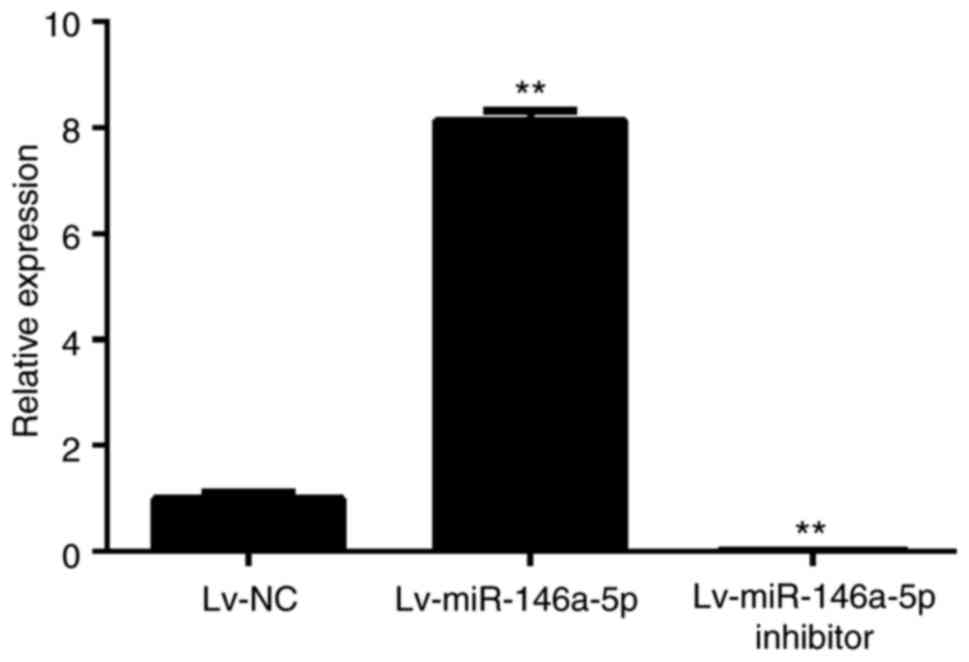
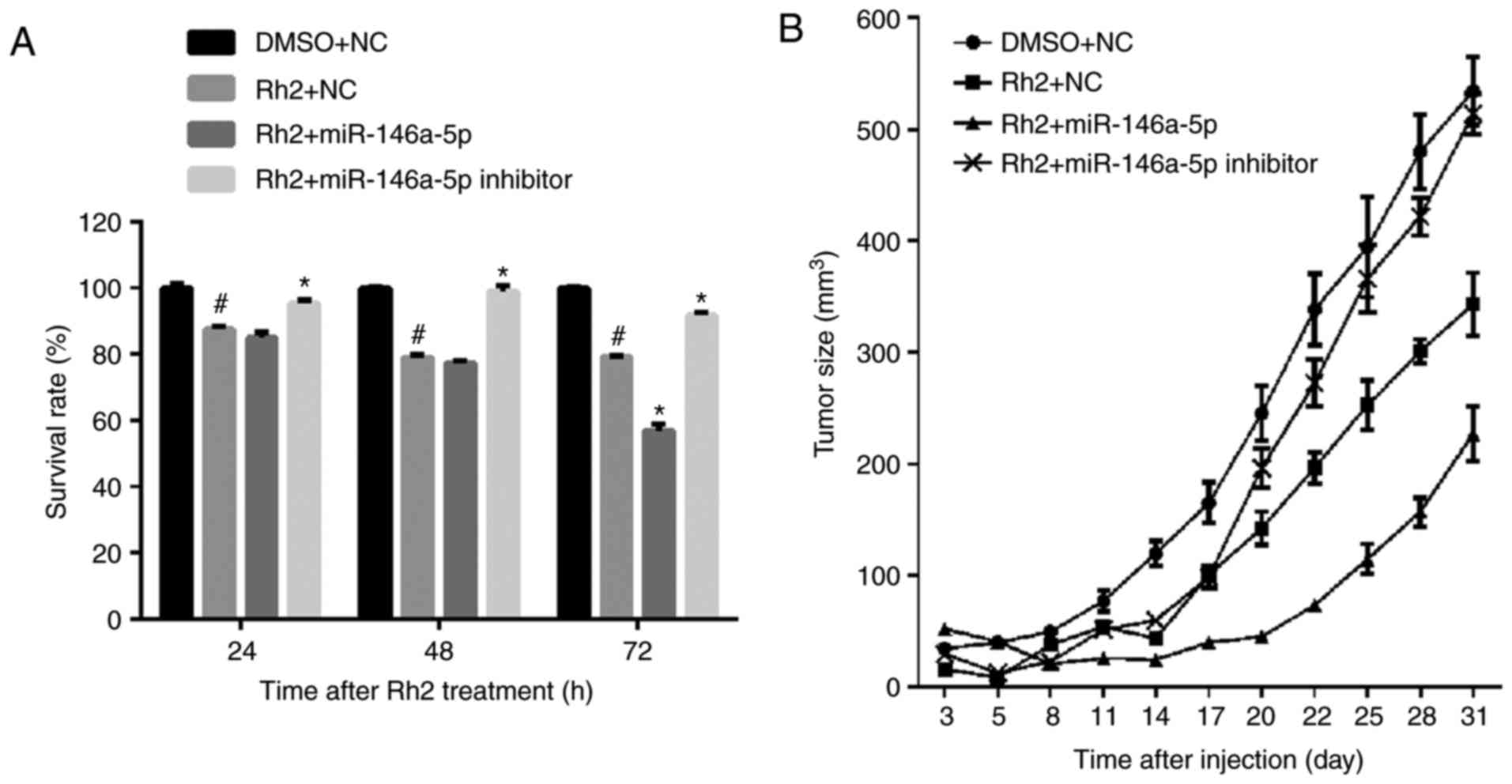
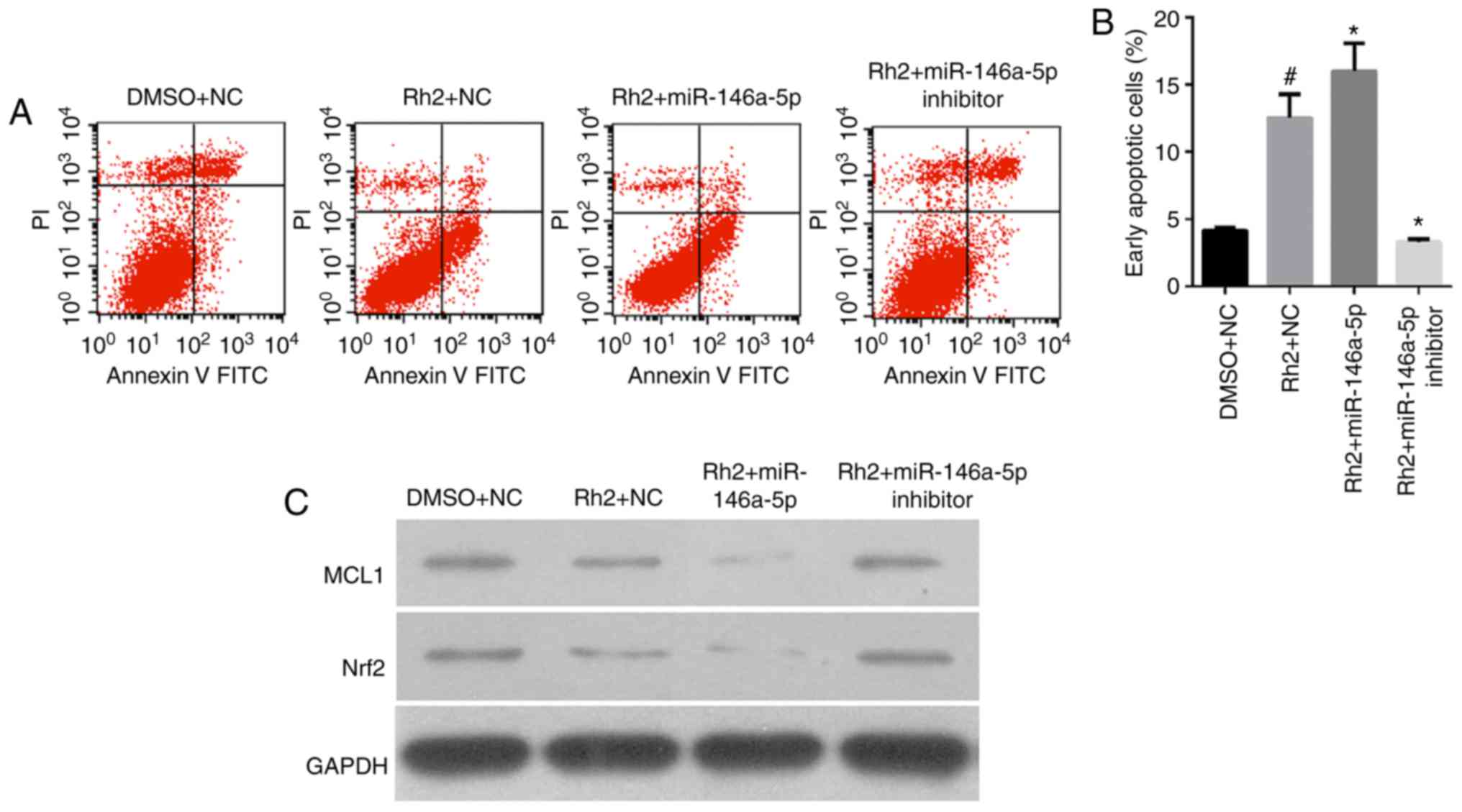
|
1
|
Oh M, Choi YH, Choi S, Chung H, Kim K, Kim
SI, Kim DK and Kim ND: Anti-proliferating effects of ginsenoside
Rh2 on MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 14:869–875.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nakata H, Kikuchi Y, Tode T, Hirata J,
Kita T, Ishii K, Kudoh K, Nagata I and Shinomiya N: Inhibitory
effects of ginsenoside Rh2 on tumor growth in nude mice bearing
human ovarian cancer cells. Jpn J Cancer Res. 89:733–740. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xie X, Eberding A, Madera C, Fazli L, Jia
W, Goldenberg L, Gleave M and Guns ES: Rh2 synergistically enhances
paclitaxel or mitoxantrone in prostate cancer models. J Urol.
175:1926–1931. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xia T, Wang YN, Zhou CX, Wu LM, Liu Y,
Zeng QH, Zhang XL, Yao JH, Wang M and Fang JP: Ginsenoside Rh2 and
Rg3 inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis by increasing
mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in human leukemia Jurkat
cells. Mol Med Rep. 15:3591–3598. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang J, Yuan D, Xing T, Su H, Zhang S, Wen
J, Bai Q and Dang D: Ginsenoside Rh2 inhibiting HCT116 colon cancer
cell proliferation through blocking PDZ-binding kinase/T-LAK
cell-originated protein kinase. J Ginseng Res. 40:400–408. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang Z, Zhao T, Liu H and Zhang L:
Ginsenoside Rh2 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma through β-catenin
and autophagy. Sci Rep. 6:193832016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guan N, Huo X, Zhang Z, Zhang S, Luo J and
Guo W: Ginsenoside Rh2 inhibits metastasis of glioblastoma
multiforme through Akt-regulated MMP13. Tumour Biol. 36:6789–6795.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li S, Gao Y, Ma W, Cheng T and Liu Y:
Ginsenoside Rh2 inhibits invasiveness of glioblastoma through
modulation of VEGF-A. Tumour Biol. 2015.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
9
|
Li S, Gao Y, Ma W, Guo W, Zhou G, Cheng T
and Liu Y: EGFR signaling-dependent inhibition of glioblastoma
growth by ginsenoside Rh2. Tumour Biol. 35:5593–5598. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang J, Peng K, Wang L, Wen B, Zhou L,
Luo T, Su M, Li J and Luo Z: Ginsenoside Rh2 inhibits proliferation
and induces apoptosis in human leukemia cells via TNF-α signaling
pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 48:750–755. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Han S, Jeong AJ, Yang H, Kang Bin K, Lee
H, Yi EH, Kim BH, Cho CH, Chung JW, Sung SH and Ye SK: Ginsenoside
20(S)-Rh2 exerts anti-cancer activity through targeting
IL-6-induced JAK2/STAT3 pathway in human colorectal cancer cells. J
Ethnopharmacol. 194:83–90. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Alvarez-Garcia I and Miska EA: MicroRNA
functions in animal development and human disease. Development.
132:4653–4662. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Joshi P, Middleton J, Jeon YJ and Garofalo
M: MicroRNAs in lung cancer. World J Methodol. 4:59–72. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wen X, Zhang HD, Zhao L, Yao YF, Zhao JH
and Tang JH: Ginsenoside Rh2 differentially mediates microRNA
expression to prevent chemoresistance of breast cancer. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 16:1105–1109. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
An IS, An S, Kwon KJ, Kim YJ and Bae S:
Ginsenoside Rh2 mediates changes in the microRNA expression profile
of human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Oncol Rep.
29:523–528. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu N, Wu GC, Hu R, Li M and Feng H:
Ginsenoside Rh2 inhibits glioma cell proliferation by targeting
microRNA-128. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 32:345–353. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo H and Xia B: Collapsin response
mediator protein 4 isoforms (CRMP4a and CRMP4b) have opposite
effects on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in gastric
cancer. BMC Cancer. 16:5652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lv Q, Rong N, Liu LJ, Xu XL, Liu JT, Jin
FX and Wang CM: Antitumoral activity of (20R)- and
(20S)-Ginsenoside Rh2 on transplanted hepatocellular carcinoma in
mice. Planta Med. 82:705–711. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
López-Terrada D, Cheung SW, Finegold MJ
and Knowles BB: Hep G2 is a hepatoblastoma-derived cell line. Hum
Pathol. 40:1512–1515. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Qiu GH, Xie X, Xu F, Shi X, Wang Y and
Deng L: Distinctive pharmacological differences between liver
cancer cell lines HepG2 and Hep3B. Cytotechnology. 67:1–12. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Moi P, Chan K, Asunis I, Cao A and Kan YW:
Isolation of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a NF-E2-like basic
leucine zipper transcriptional activator that binds to the tandem
NF-E2/AP1 repeat of the beta-globin locus control region. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 91:9926–9930. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Milkovic L, Zarkovic N and Saso L:
Controversy about pharmacological modulation of Nrf2 for cancer
therapy. Redox Biol. 12:727–732. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zu Y, Yang Y, Zhu J, Bo X, Hou S, Zhang B,
Qiu J and Zheng J: MiR-146a suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma by
downregulating TRAF6. Am J Cancer Res. 6:2502–2513. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|