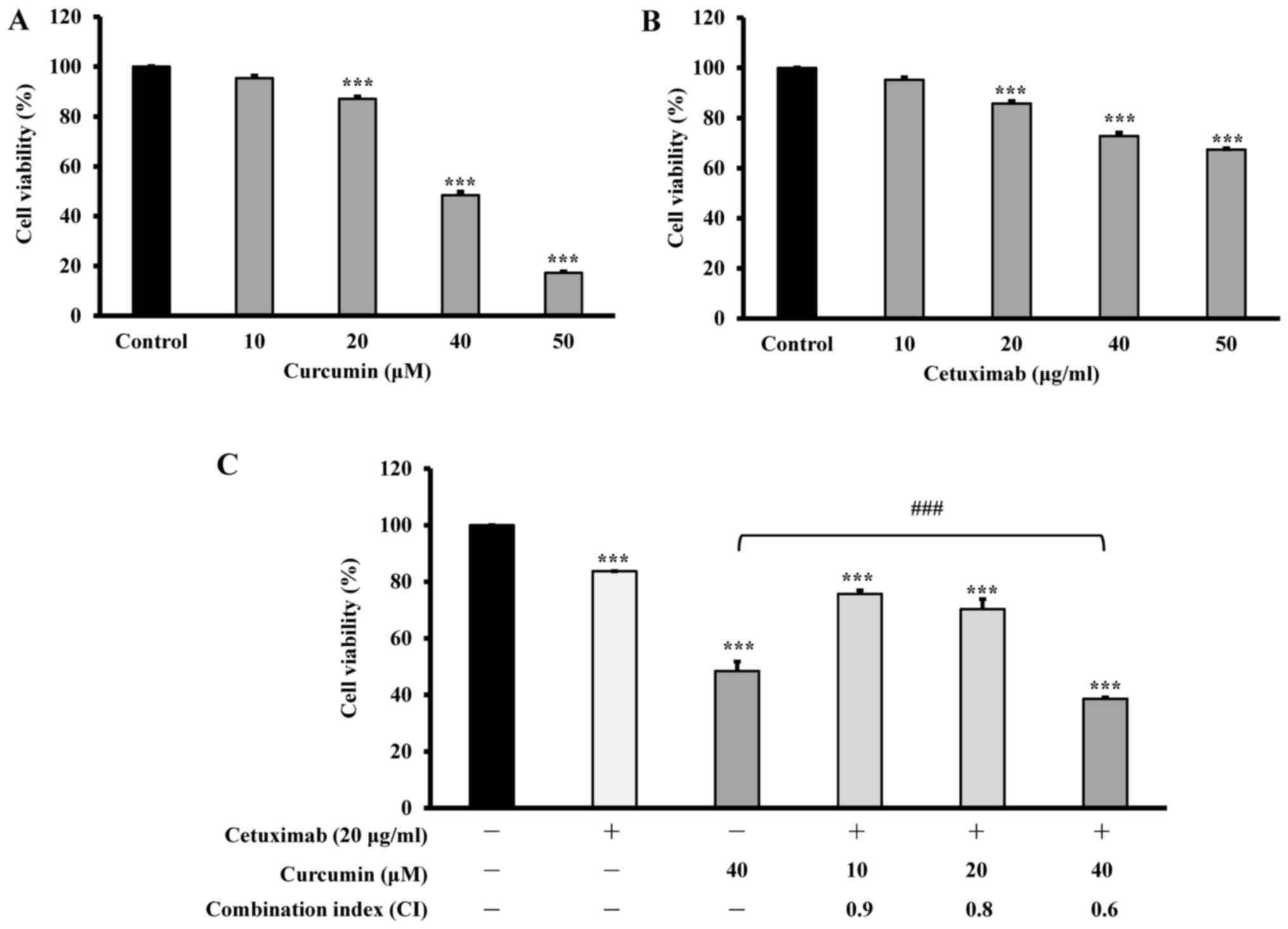
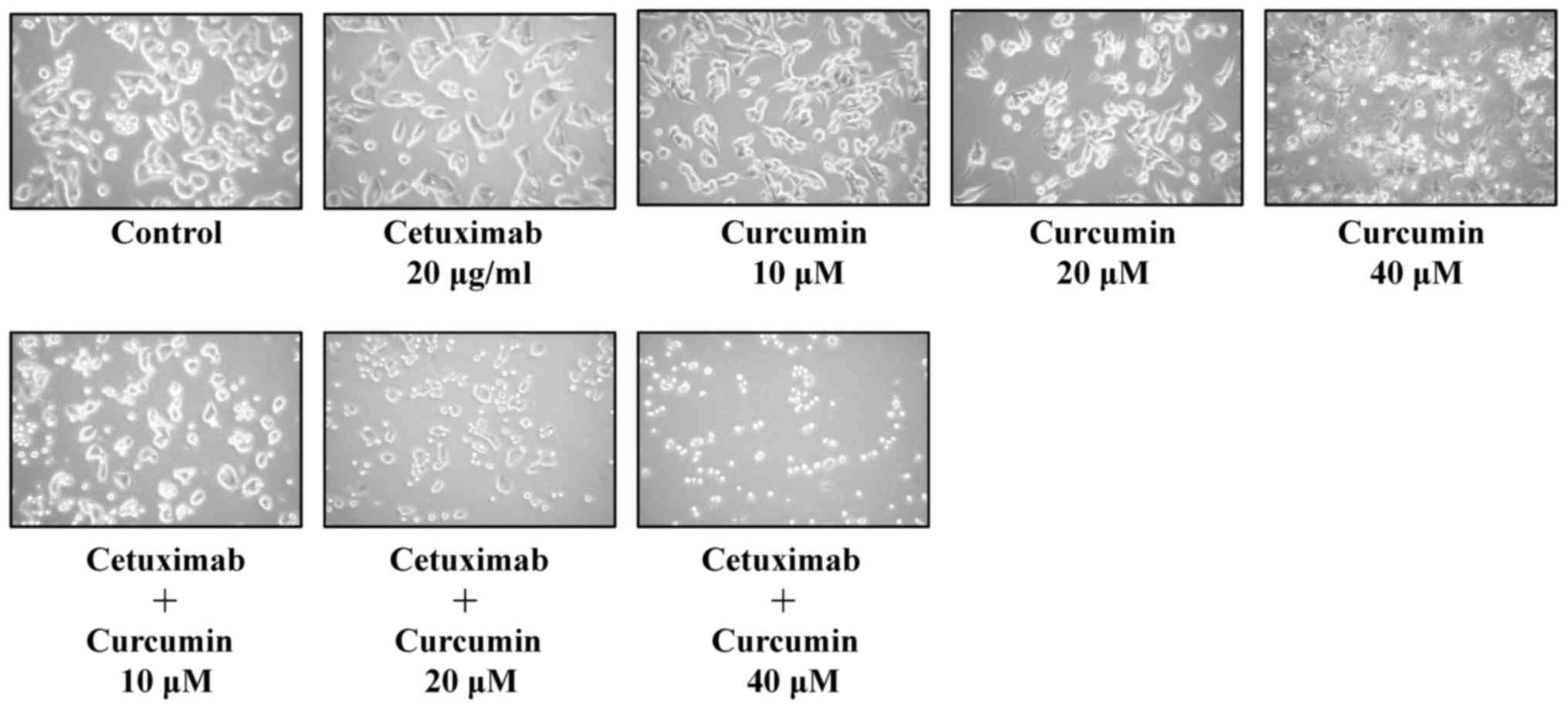
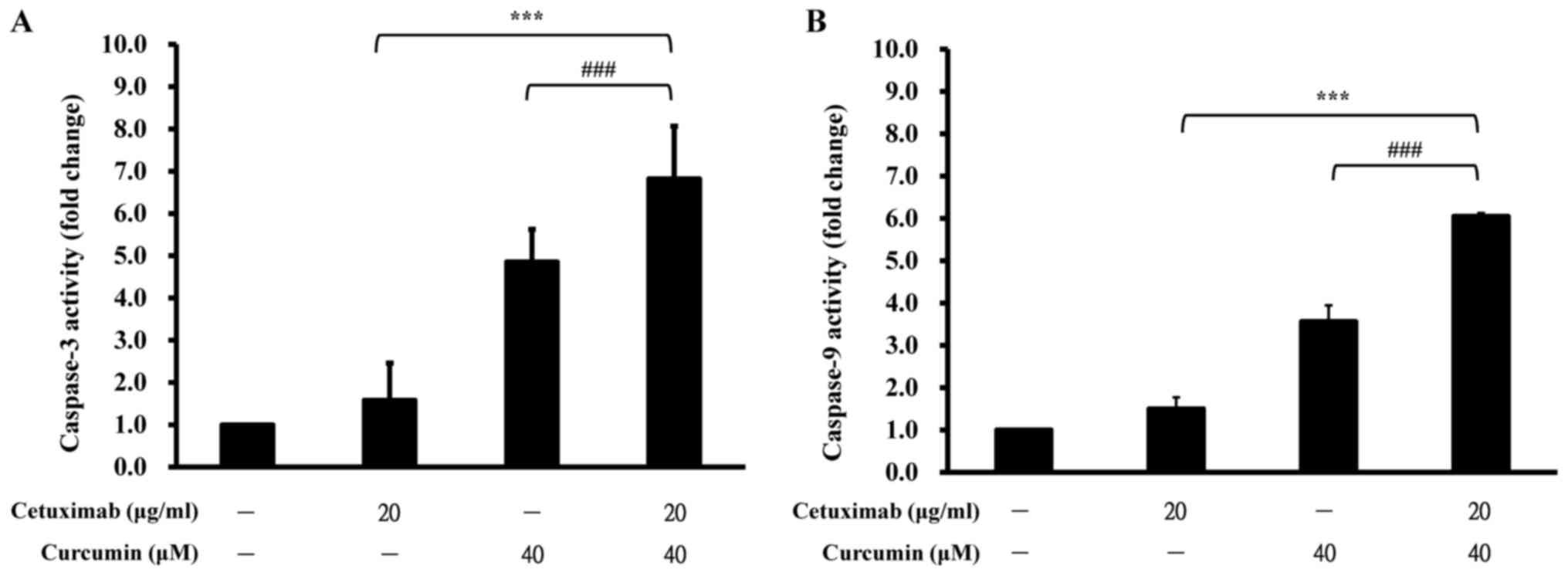
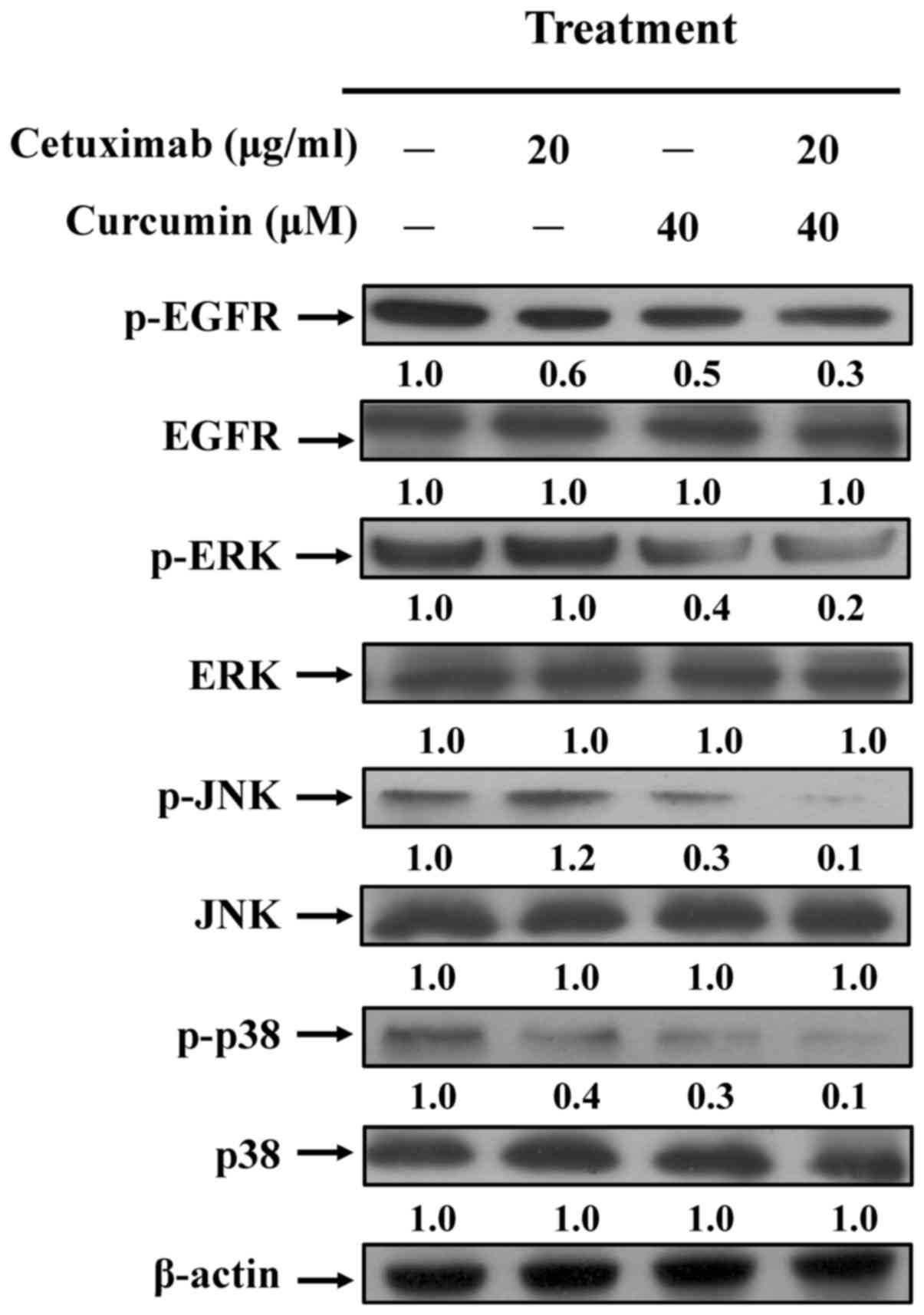
|
1
|
Horn D, Hess J, Freier K, Hoffmann J and
Freudlsperger C: Targeting EGFR-PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling enhances
radiosensitivity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 19:795–805. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Prince A, Aguirre-Ghizo J, Genden E,
Posner M and Sikora A: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: New
translational therapies. Mt Sinai J Med. 77:684–699. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mendelsohn J and Baselga J: Epidermal
growth factor receptor targeting in cancer. Semin Oncol.
33:369–385. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Todd R and Wong DT: Epidermal growth
factor receptor (EGFR) biology and human oral cancer. Histol
Histopathol. 14:491–500. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pickhard A, Siegl M, Baumann A, Huhn M,
Wirth M, Reiter R, Rudelius M, Piontek G and Brockhoff G: The
response of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to cetuximab
treatment depends on Aurora kinase A polymorphism. Oncotarget.
5:5428–5438. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin MC, Huang MJ, Liu CH, Yang TL and
Huang MC: GALNT2 enhances migration and invasion of oral squamous
cell carcinoma by regulating EGFR glycosylation and activity. Oral
Oncol. 50:478–484. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cassell A and Grandis JR: Investigational
EGFR-targeted therapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 19:709–722. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hoch MA, Cousins K, Nartey R, Riley K and
Hartranft M: Two cases of combination therapy with cetuximab,
paclitaxel, and cisplatin for advanced head and neck cancer. J
Oncol Pharm Pract 1078155217722406. 2017.
|
|
9
|
Liebig H, Günther G, Kolb M, Mozet C,
Boehm A, Dietz A and Wichmann G: Reduced proliferation and colony
formation of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) after
dual targeting of EGFR and hedgehog pathways. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 79:411–420. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Moon C, Chae YK and Lee J: Targeting
epidermal growth factor receptor in head and neck cancer: Lessons
learned from cetuximab. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 235:907–920. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Astsaturov I, Cohen RB and Harari P:
EGFR-targeting monoclonal antibodies in head and neck cancer. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 6:691–710. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dai W, Li Y, Zhou Q, Xu Z, Sun C, Tan X
and Lu L: Cetuximab inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma invasion
and metastasis via degradation of epidermal growth factor receptor.
J Oral Pathol Med. 43:250–257. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Psyrri A, Seiwert TY and Jimeno A:
Molecular pathways in head and neck cancer: EGFR, PI3K, and more.
Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 246–255. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Astsaturov I, Cohen RB and Harari P:
EGFR-targeting monoclonal antibodies in head and neck cancer. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 7:650–665. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Burgy M, Barthélémy P, Lefevre F,
Dupret-Bories A, Truntzer P, Korenbaum C, Flesch H, Bronner G and
Borel C: Cetuximab-carboplatin-5-fluorouracil regimen in elderly
patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous-cell
carcinoma: A French retrospective survey. Oncology. 93:11–17. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guigay J, Even C, Mayache-Badis L, Debbah
M, Saada-Bouzid E, Tao Y, Deschamps F, Janot F, Lezghed N and
Michel C: Long-term response in patient with recurrent
oropharyngeal carcinoma treated with cetuximab, docetaxel and
cisplatin (TPEx) as first-line treatment followed by cetuximab
maintenance. Oral Oncol. 68:114–118. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Unlu A, Nayir E, Kalenderoglu Dogukan M,
Kirca O and Ozdogan M: Curcumin (Turmeric) and cancer. J BUON.
21:1050–1060. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
He Y, Yue Y, Zheng X, Zhang K, Chen S and
Du Z: Curcumin, inflammation, and chronic diseases: How are they
linked? Molecules. 20:9183–9213. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang J and Jiang YF: Natural compounds as
anticancer agents: Experimental evidence. World J Exp Med. 2:45–57.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen ZF and Liang H: Progresses in TCM
metal-based antitumour agents. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
10:412–423. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Devi Pandima K, Rajavel T, Daglia M,
Nabavi SF, Bishayee A and Nabavi SM: Targeting miRNAs by
polyphenols: Novel therapeutic strategy for cancer. Semin Cancer
Biol. 46:146–157. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Owen HC, Appiah S, Hasan N, Ghali L,
Elayat G and Bell C: Phytochemical modulation of apoptosis and
autophagy: Strategies to overcome chemoresistance in leukemic stem
cells in the bone marrow microenvironment. Int Rev Neurobiol.
135:249–278. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Karimian MS, Pirro M, Johnston TP, Majeed
M and Sahebkar A: Curcumin and endothelial function: Evidence and
mechanisms of protective effects. Curr Pharm Des. 23:2462–2473.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jha A, Mohapatra PP, AlHarbi SA and Jahan
N: Curcumin: Not so spicy after all. Mini Rev Med Chem.
17:1425–1434. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Peng SF, Lee CY, Hour MJ, Tsai SC, Kuo DH,
Chen FA, Shieh PC and Yang JS: Curcumin-loaded nanoparticles
enhance apoptotic cell death of U2OS human osteosarcoma cells
through the Akt-Bad signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 44:238–246.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Borges GÁ, Rêgo DF, Assad DX, Coletta RD,
De Luca Canto G and Guerra EN: In vivo and in vitro effects of
curcumin on head and neck carcinoma: A systematic review. J Oral
Pathol Med. 46:3–20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vander Broek R, Snow GE, Chen Z and Van
Waes C: Chemoprevention of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
through inhibition of NF-kB signaling. Oral Oncol. 50:930–941.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Agrawal DK and Mishra PK: Curcumin and its
analogues: Potential anticancer agents. Med Res Rev. 30:818–860.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin JK: Molecular targets of curcumin. Adv
Exp Med Biol. 595:227–243. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fetoni AR, Paciello F, Mezzogori D, Rolesi
R, Eramo SL, Paludetti G and Troiani D: Molecular targets for
anticancer redox chemotherapy and cisplatin-induced ototoxicity:
The role of curcumin on pSTAT3 and Nrf-2 signalling. Br J Cancer.
113:1434–1444. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sivanantham B, Sethuraman S and Krishnan
UM: Combinatorial effects of curcumin with an anti-neoplastic agent
on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through the regulation of
EGFR-ERK1/2 and apoptotic signaling pathways. ACS Comb Sci.
18:22–35. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gosepath EM, Eckstein N, Hamacher A,
Servan K, von Jonquieres G, Lage H, Györffy B, Royer HD and Kassack
MU: Acquired cisplatin resistance in the head-neck cancer cell line
Cal27 is associated with decreased DKK1 expression and can
partially be reversed by overexpression of DKK1. Int J Cancer.
123:2013–2019. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chang PY, Peng SF, Lee CY, Lu CC, Tsai SC,
Shieh TM, Wu TS, Tu MG, Chen MY and Yang JS: Curcumin-loaded
nanoparticles induce apoptotic cell death through regulation of the
function of MDR1 and reactive oxygen species in cisplatin-resistant
CAR human oral cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 43:1141–1150. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee MR, Lin C, Lu CC, Kuo SC, Tsao JW,
Juan YN, Chiu HY, Lee FY, Yang JS and Tsai FJ: YC-1 induces
G0/G1 phase arrest and mitochondria-dependent
apoptosis in cisplatin-resistant human oral cancer CAR cells.
Biomedicine (Taipei). 7:122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lu CC, Yang JS, Chiang JH, Hour MJ, Lin
KL, Lee TH and Chung JG: Cell death caused by quinazolinone HMJ-38
challenge in oral carcinoma CAL 27 cells: Dissections of
endoplasmic reticulum stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and tumor
xenografts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1840:2310–2320. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu Y, Xin Y, Diao Y, Lu C, Fu J, Luo L and
Yin Z: Synergistic effects of apigenin and paclitaxel on apoptosis
of cancer cells. PLoS One. 6:e291692011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lu CC, Huang BR, Liao PJ and Yen GC:
Ursolic acid triggers nonprogrammed death (necrosis) in human
glioblastoma multiforme DBTRG-05MG cells through MPT pore opening
and ATP decline. Mol Nutr Food Res. 58:2146–2156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chiang JH, Yang JS, Lu CC, Hour MJ, Chang
SJ, Lee TH and Chung JG: Newly synthesized quinazolinone HMJ-38
suppresses angiogenetic responses and triggers human umbilical vein
endothelial cell apoptosis through p53-modulated Fas/death receptor
signaling. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 269:150–162. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ma YS, Weng SW, Lin MW, Lu CC, Chiang JH,
Yang JS, Lai KC, Lin JP, Tang NY, Lin JG and Chung JG: Antitumor
effects of emodin on LS1034 human colon cancer cells in vitro and
in vivo: Roles of apoptotic cell death and LS1034 tumor xenografts
model. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:1271–1278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huang WW, Chiu YJ, Fan MJ, Lu HF, Yeh HF,
Li KH, Chen PY, Chung JG and Yang JS: Kaempferol induced apoptosis
via endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondria-dependent pathway
in human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells. Mol Nutr Food Res.
54:1585–1595. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Grossi V, Peserico A, Tezil T and Simone
C: p38alpha MAPK pathway: A key factor in colorectal cancer therapy
and chemoresistance. World J Gastroenterol. 20:9744–9758. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nibu KI, Hayashi R, Asakage T, Ojiri H,
Kimata Y, Kodaira T, Nagao T, Nakashima T, Fujii T, Fujii H, et al:
Japanese clinical practice guideline for head and neck cancer.
Auris Nasus Larynx. 44:375–380. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Brockstein BE and Vokes EE: Oral
chemotherapy in head and neck cancer. Drugs. 58 Suppl 3:S91–S97.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Köberle B, Tomicic MT, Usanova S and Kaina
B: Cisplatin resistance: Preclinical findings and clinical
implications. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1806:172–182. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Carlsson L, Bratman SV, Siu LL and
Spreafico A: The cisplatin total dose and concomitant radiation in
locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer: Any recent evidence
for dose efficacy? Curr Treat Options Oncol. 18:392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang C, Liu XQ, Hou JS, Wang JN and Huang
HZ: Molecular mechanisms of chemoresistance in oral cancer. Chin J
Dent Res. 19:25–33. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Dasari S and Tchounwou PB: Cisplatin in
cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol.
740:364–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Brozovic A: The relationship between
platinum drug resistance and epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Arch Toxicol. 91:605–619. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Alorabi M, Shonka NA and Ganti AK: EGFR
monoclonal antibodies in locally advanced head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma: What is their current role? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
99:170–179. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kuroda H, Takeno M, Murakami S, Miyazawa
N, Kaneko T and Ishigatsubo Y: Inhibition of heme oxygenase-1 with
an epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor and cisplatin
decreases proliferation of lung cancer A549 cells. Lung Cancer.
67:31–36. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Seo Y, Ishii Y, Ochiai H, Fukuda K,
Akimoto S, Hayashida T, Okabayashi K, Tsuruta M, Hasegawa H and
Kitagawa Y: Cetuximab-mediated ADCC activity is correlated with the
cell surface expression level of EGFR but not with the KRAS/BRAF
mutational status in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 31:2115–2122.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kondo N, Tsukuda M, Sakakibara A,
Takahashi H, Hyakusoku H, Komatsu M, Niho T, Nakazaki K and Toth G:
Combined molecular targeted drug therapy for EGFR and HER-2 in head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Int J Oncol.
40:1805–1812. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ji JL, Huang XF and Zhu HL: Curcumin and
its formulations: Potential anti-cancer agents. Anticancer Agents
Med Chem. 12:210–218. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Shehzad A, Wahid F and Lee YS: Curcumin in
cancer chemoprevention: Molecular targets, pharmacokinetics,
bioavailability, and clinical trials. Arch Pharm (Weinheim).
343:489–499. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Qadir MI, Naqvi ST and Muhammad SA:
Curcumin: A polyphenol with molecular targets for cancer control.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 17:2735–2739. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Weisberg S, Leibel R and Tortoriello DV:
Proteasome inhibitors, including curcumin, improve pancreatic
β-cell function and insulin sensitivity in diabetic mice. Nutr
Diabetes. 6:e2052016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Lee JY, Lee YM, Chang GC, Yu SL, Hsieh WY,
Chen JJ, Chen HW and Yang PC: Curcumin induces EGFR degradation in
lung adenocarcinoma and modulates p38 activation in intestine: The
versatile adjuvant for gefitinib therapy. PLoS One. 6:e237562011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Son DJ, Hong JE, Ban JO, Park JH, Lee HL,
Gu SM, Hwang JY, Jung MH, Lee DW, Han SB and Hong JT: Synergistic
inhibitory effects of cetuximab and cisplatin on human colon cancer
cell growth via inhibition of the ERK-dependent EGF receptor
signaling pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2015:3975632015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li X, Lu Y, Pan T and Fan Z: Roles of
autophagy in cetuximab-mediated cancer therapy against EGFR.
Autophagy. 6:1066–1077. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Douglass BJ and Clouatre DL: Beyond yellow
curry: Assessing commercial curcumin absorption technologies. J Am
Coll Nutr. 34:347–358. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Chang LC, Hsieh MT, Yang JS, Lu CC, Tsai
FJ, Tsao JW, Chiu YJ, Kuo SC and Lee KH: Effect of
bis(hydroxymethyl) alkanoate curcuminoid derivative MTH-3 on cell
cycle arrest, apoptotic and autophagic pathway in triple-negative
breast adenocarcinoma MDA-MB-231 cells: An in vitro study. Int J
Oncol. 52:67–76. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hsieh MT, Chang LC, Hung HY, Lin HY, Shih
MH, Tsai CH, Kuo SC and Lee KH: New bis(hydroxymethyl) alkanoate
curcuminoid derivatives exhibit activity against triple-negative
breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Med Chem. 131:141–151.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|