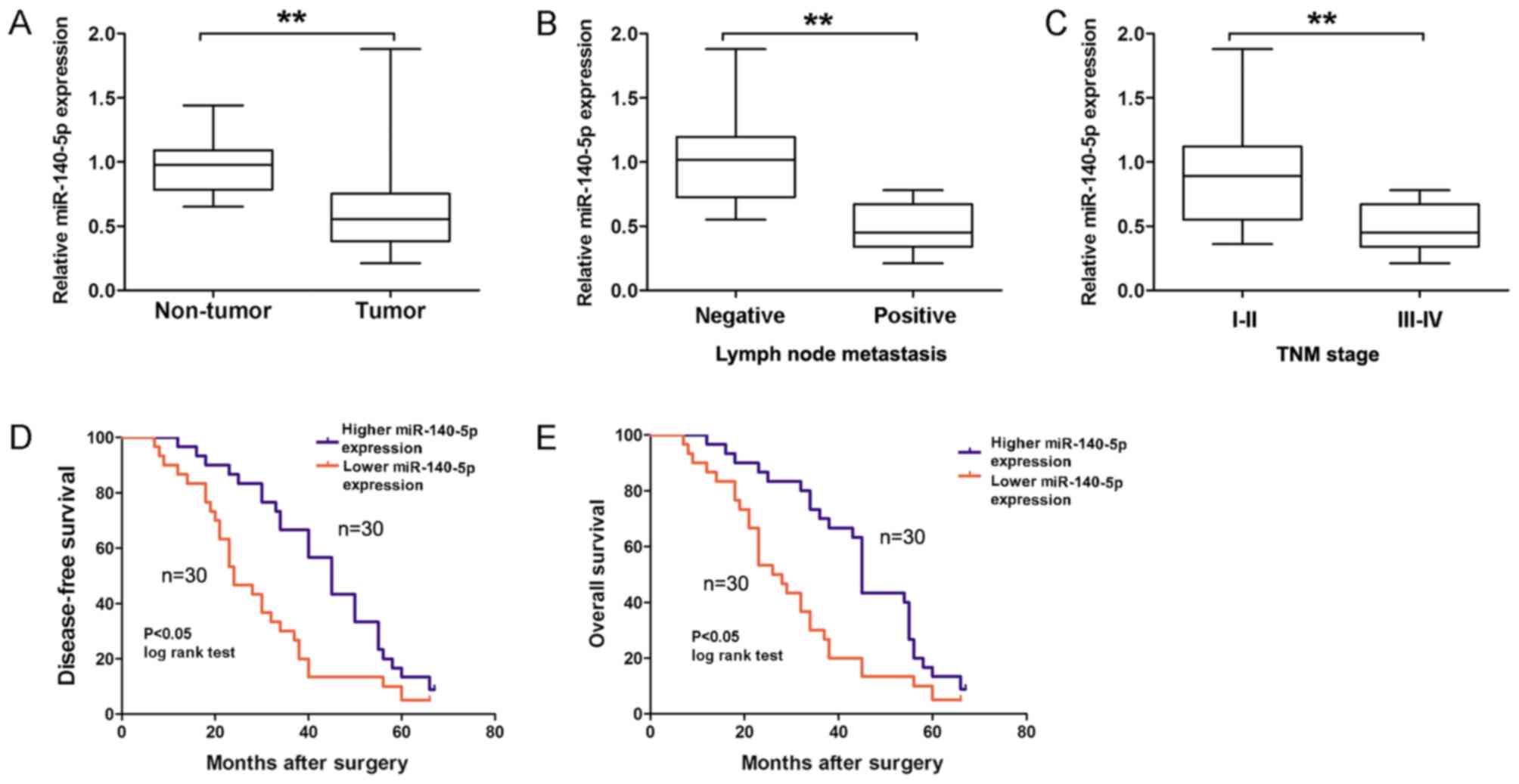
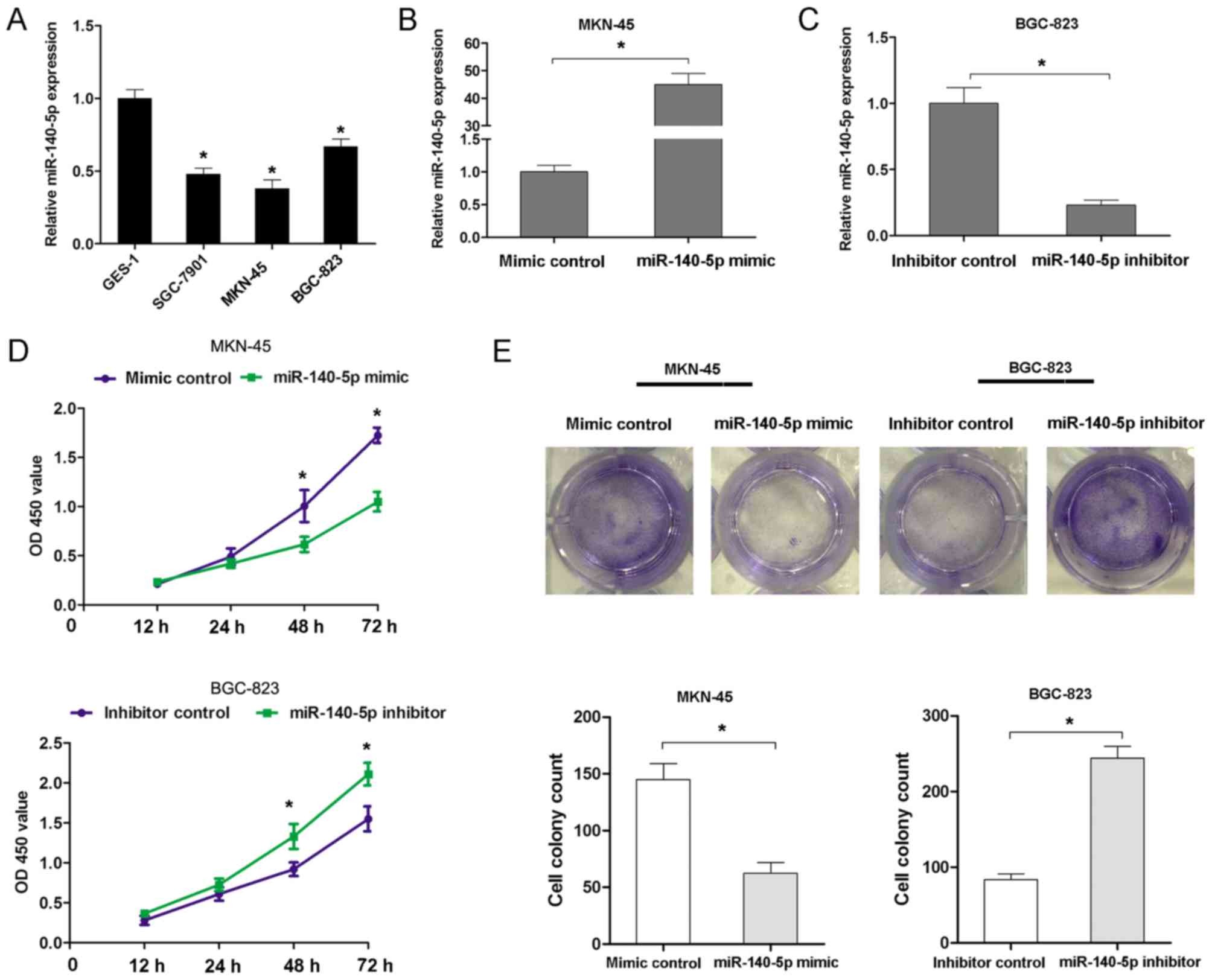
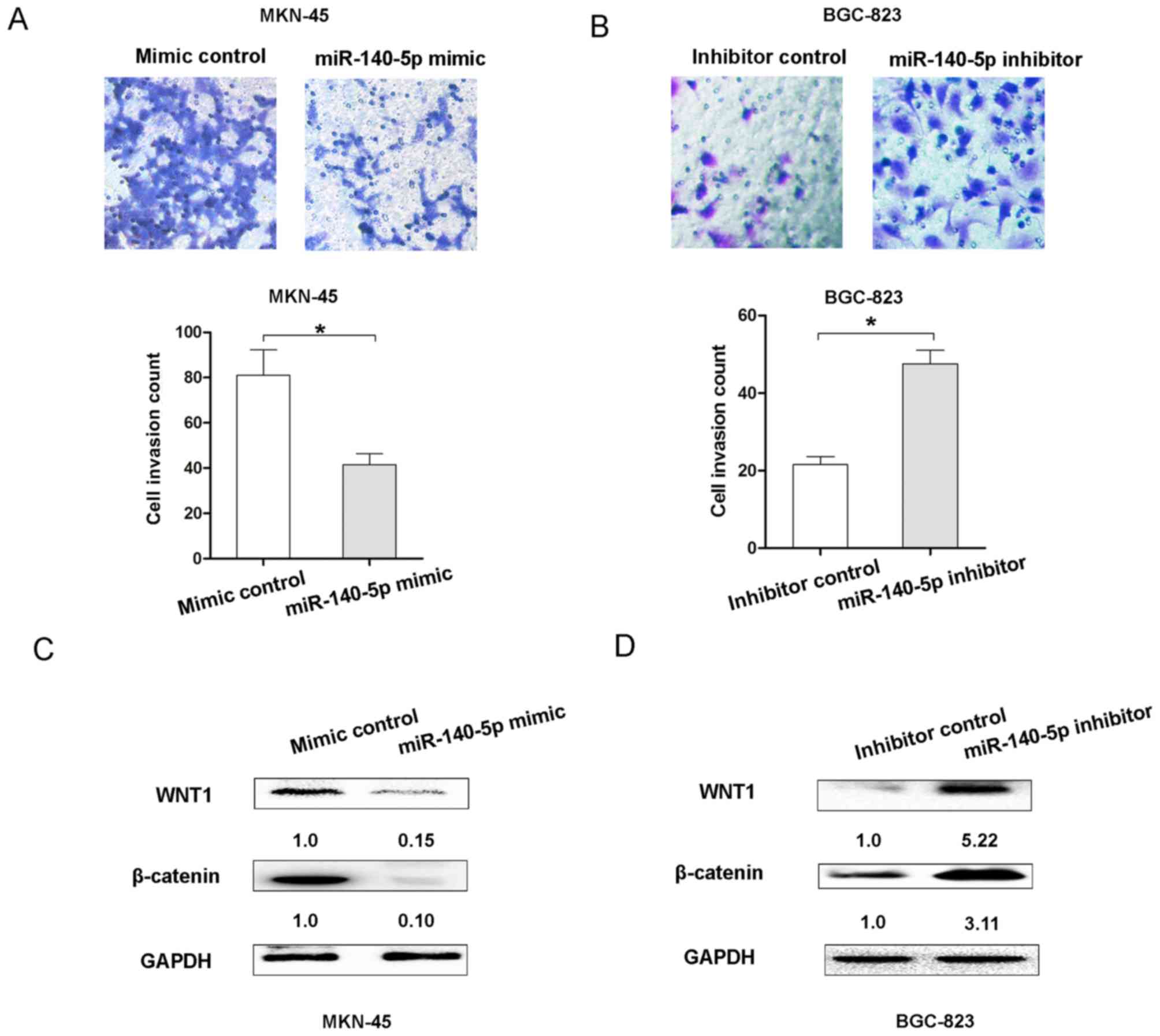
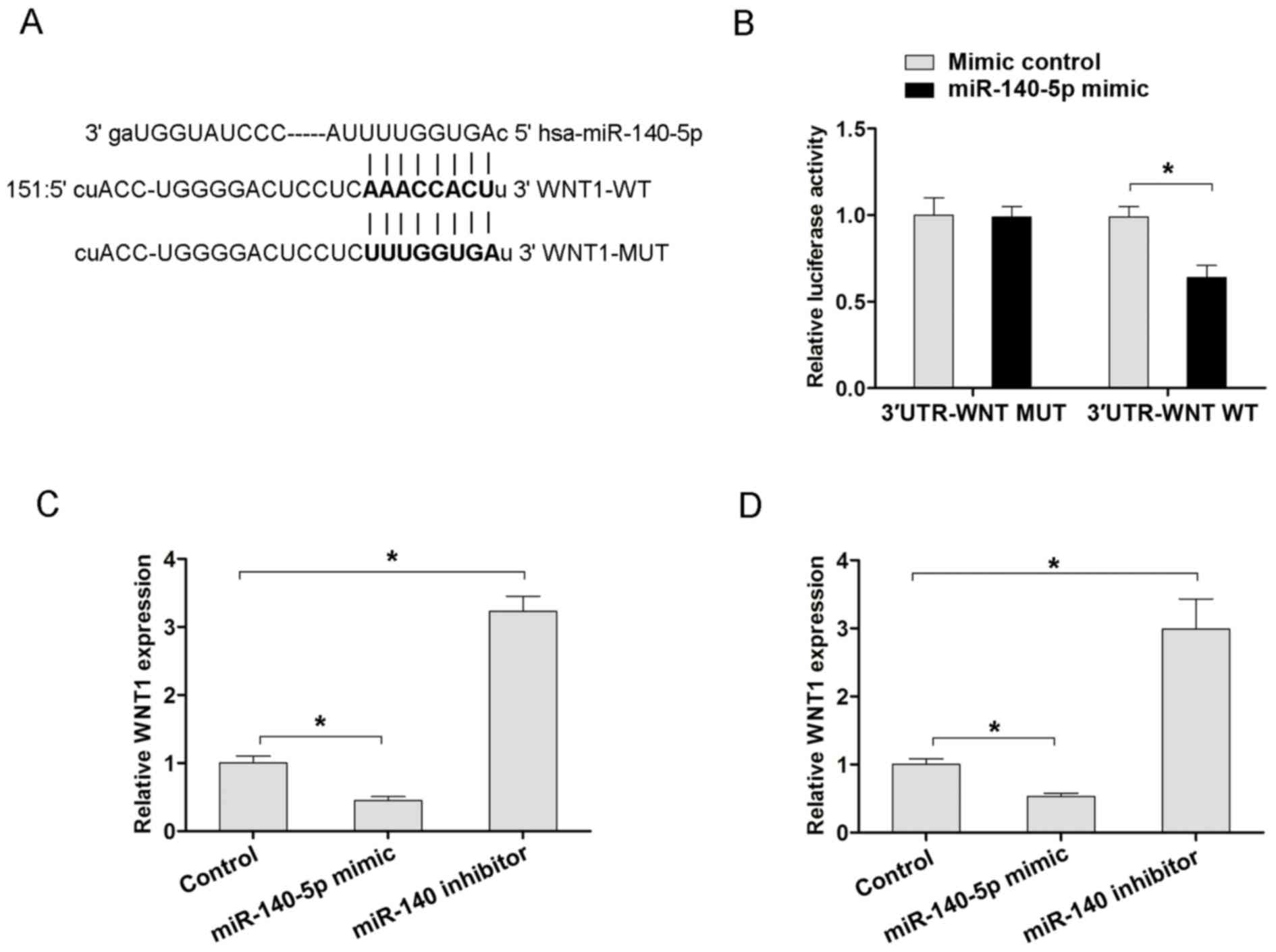
|
1
|
Leja M, You W, Camargo MC and Saito H:
Implementation of gastric cancer screening-the global experience.
Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 28:1093–1106. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carcas LP: Gastric cancer review. J
Carcinog. 13:142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rao M, Zhu Y, Cong X and Li Q: Knockdown
of CREB1 inhibits tumor growth of human gastric cancer in vitro and
in vivo. Oncol Rep. 37:3361–3368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xie M, Dart DA, Guo T, Xing XF, Cheng XJ,
Du H, Jiang WG, Wen XZ and Ji JF: MicroRNA-1 acts as a tumor
suppressor microRNA by inhibiting angiogenesis-related growth
factors in human gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 21:41–54. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jing P, Sa N, Liu X, Liu X and Xu W:
MicroR-140-5p suppresses tumor cell migration and invasion by
targeting ADAM10-mediated Notch1 signaling pathway in
hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Mol Pathol.
100:132–138. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wei R, Cao G, Deng Z, Su J and Cai L:
miR-140-5p attenuates chemotherapeutic drug-induced cell death by
regulating autophagy through inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate kinase 2
(IP3k2) in human osteosarcoma cells. Biosci Rep. 36:e003922016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fang Z, Yin S, Sun R, Zhang S, Fu M, Wu Y,
Zhang T, Khaliq J and Li Y: miR-140-5p suppresses the
proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer by
regulating YES1. Mol Cancer. 16:1392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Novák J and Fabian P: Comments on the TNM
classification of malignant tumours-7th edition. Klin Onkol.
24:149–150. 2011.(In Czech). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang T, Wu Y, Fang Z, Yan Q, Zhang S, Sun
R, Khaliq J and Li Y: Low expression of RBMS3 and SFRP1 are
associated with poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Am
J Cancer Res. 6:2679–2689. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang J, Chen X, Su L, Li P, Cai Q, Liu B,
Wu W and Zhu Z: MicroRNA-126 inhibits cell proliferation in gastric
cancer by targeting LAT-1. Biomed Pharmacother. 72:66–73. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xiang XJ, Deng J, Liu YW, Wan LY, Feng M,
Chen J and Xiong JP: MiR-1271 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion
and EMT in gastric cancer by targeting FOXQ1. Cell Physiol Biochem.
36:1382–1394. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang H, Fang F, Chang R and Yang L:
MicroRNA-140-5p suppresses tumor growth and metastasis by targeting
transforming growth factor β receptor 1 and fibroblast growth
factor 9 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 58:205–217. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li W and He F: Monocyte to macrophage
differentiation-associated (MMD) targeted by miR-140-5p regulates
tumor growth in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 450:844–850. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhai H, Fesler A, Ba Y, Wu S and Ju J:
Inhibition of colorectal cancer stem cell survival and invasive
potential by hsa-miR-140-5p mediated suppression of Smad2 and
autophagy. Oncotarget. 6:19735–19746. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang W, Zou C, Pan L, Xu Y, Qi W, Ma G,
Hou Y and Jiang P: MicroRNA-140-5p inhibits the progression of
colorectal cancer by targeting VEGFA. Cell Physiol Biochem.
37:1123–1133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu Y, Yan W, Liu X, Jia Y, Cao B, Yu Y, Lv
Y, Brock MV, Herman JG, Licchesi J, et al: DACT2 is frequently
methylated in human gastric cancer and methylation of DACT2
activated Wnt signaling. Am J Cancer Res. 4:710–724.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nunez F, Bravo S, Cruzat F, Montecino M
and De Ferrari GV: Wnt/β-catenin signaling enhances
cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2) transcriptional activity in gastric cancer
cells. PLoS One. 6:e185622011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yue H, Tang B, Zhao Y, Niu Y, Yin P, Yang
W, Zhang Z and Yu P: MIR-519d suppresses the gastric cancer
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Twist1 and inhibits
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 9:3654–3664.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu F, Li J, Guo N, Wang XH and Liao YQ:
MiRNA-27a promotes the proliferation and invasion of human gastric
cancer MGC803 cells by targeting SFRP1 via Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway. Am J Cancer Res. 7:405–416. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Peng Y, Zhang X, Ma Q, Yan R, Qin Y, Zhao
Y, Cheng Y, Yang M, Wang Q, Feng X, et al: MiRNA-194 activates the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in gastric cancer by targeting the
negative Wnt regulator, SUFU. Cancer Lett. 385:117–127. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shan Y, Ying R, Jia Z, Kong W, Wu Y, Zheng
S and Jin H: LINC00052 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation
and metastasis via activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Oncol Res. 25:1589–1599. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|