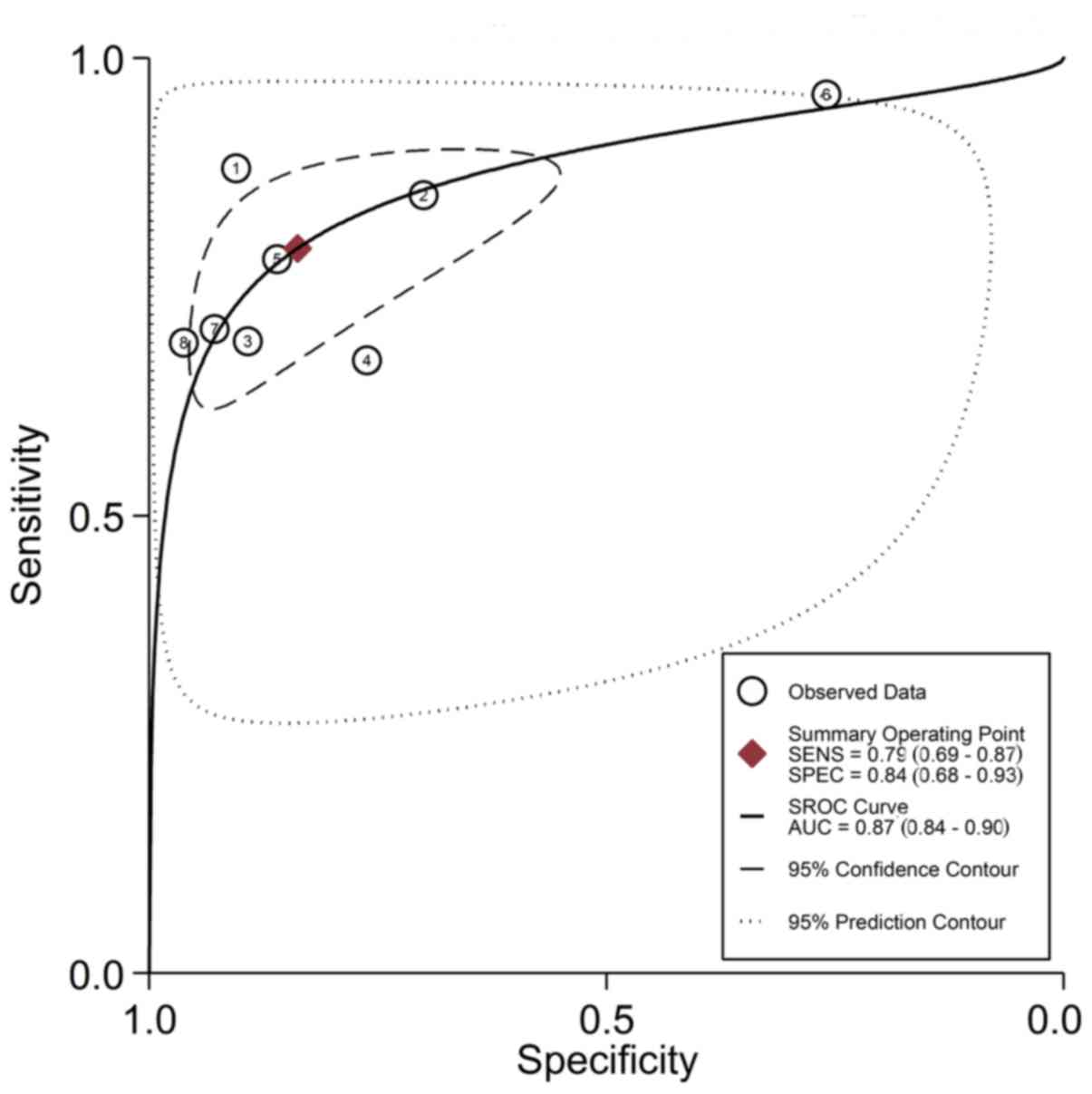
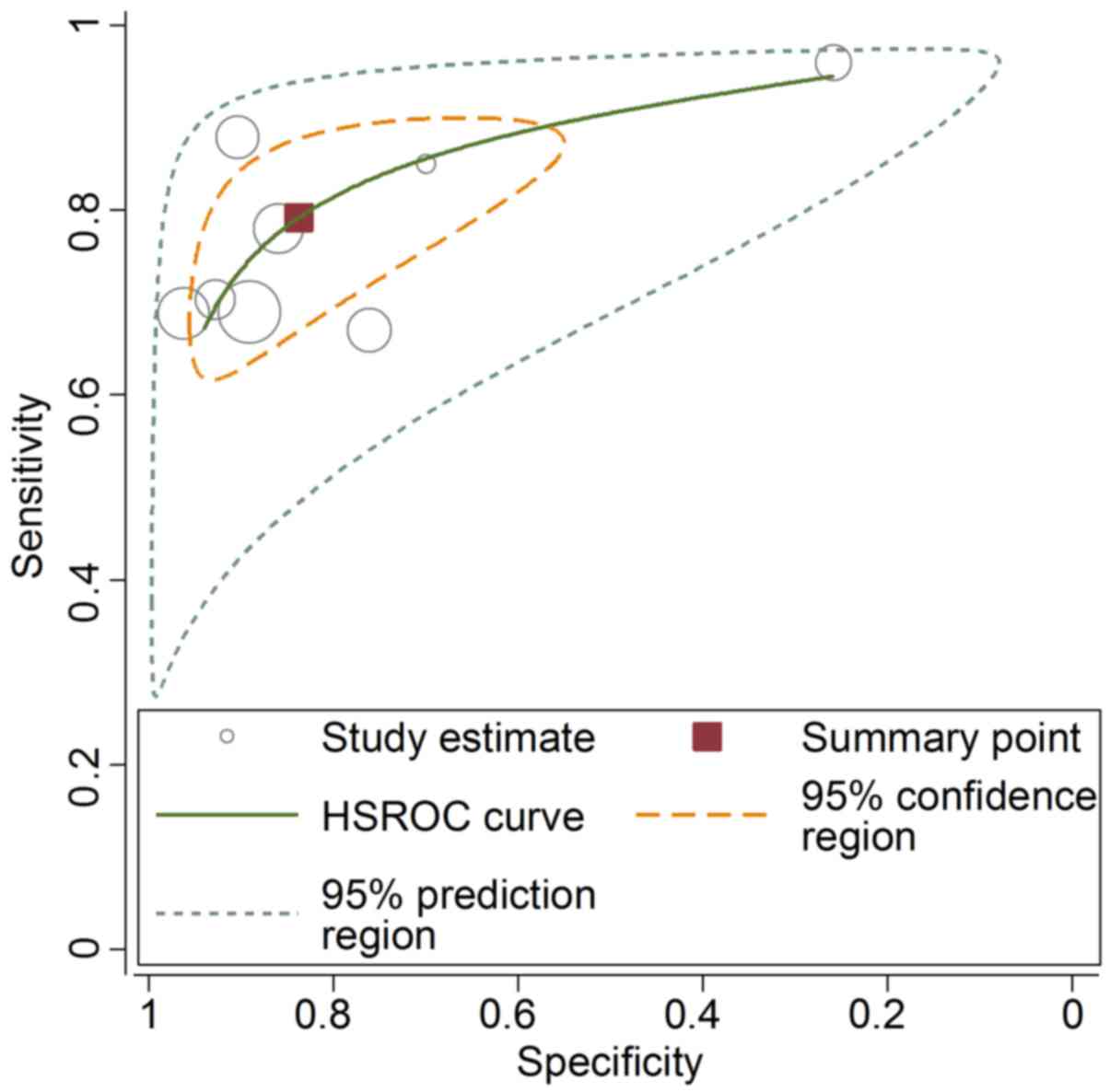
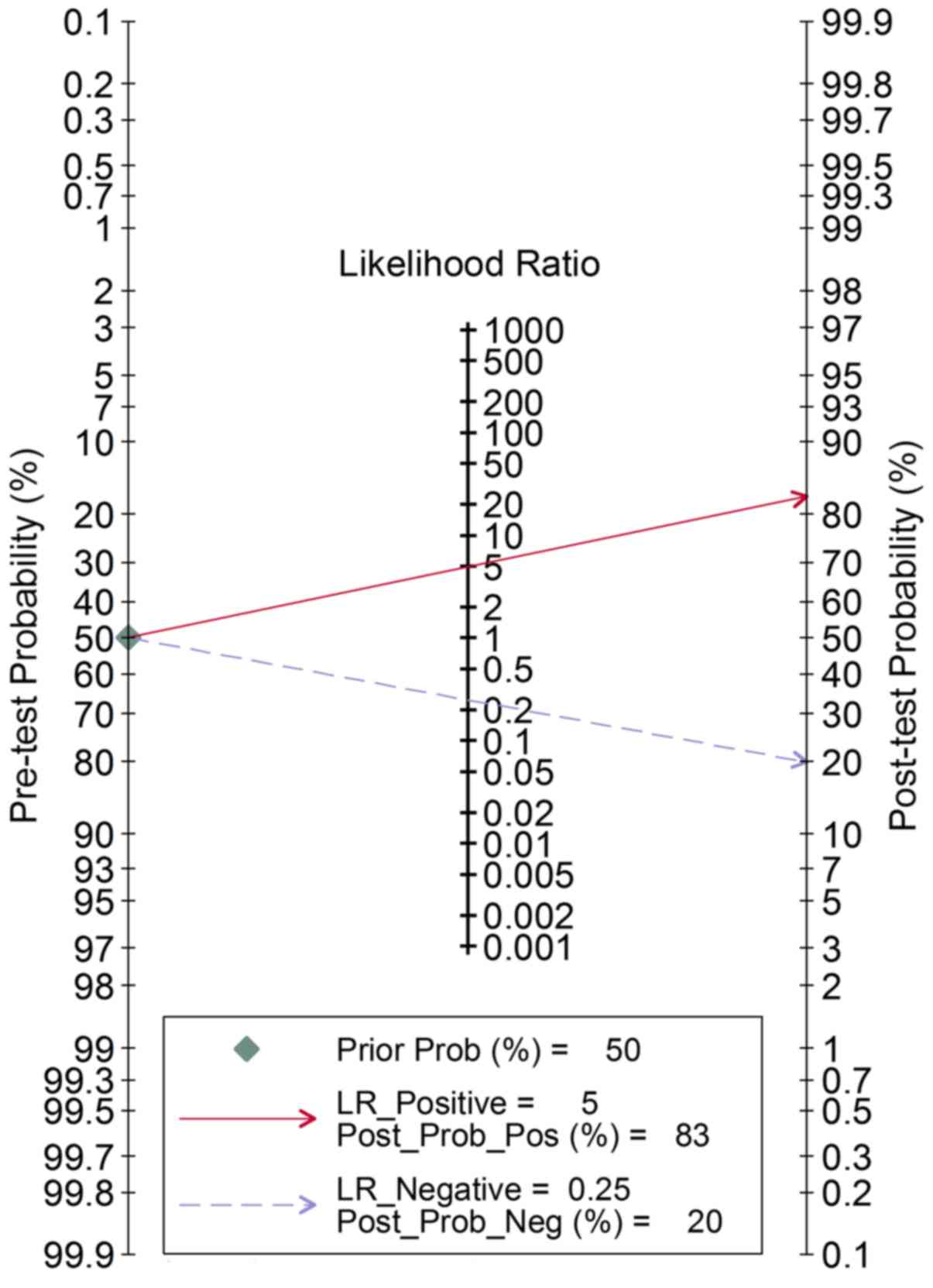
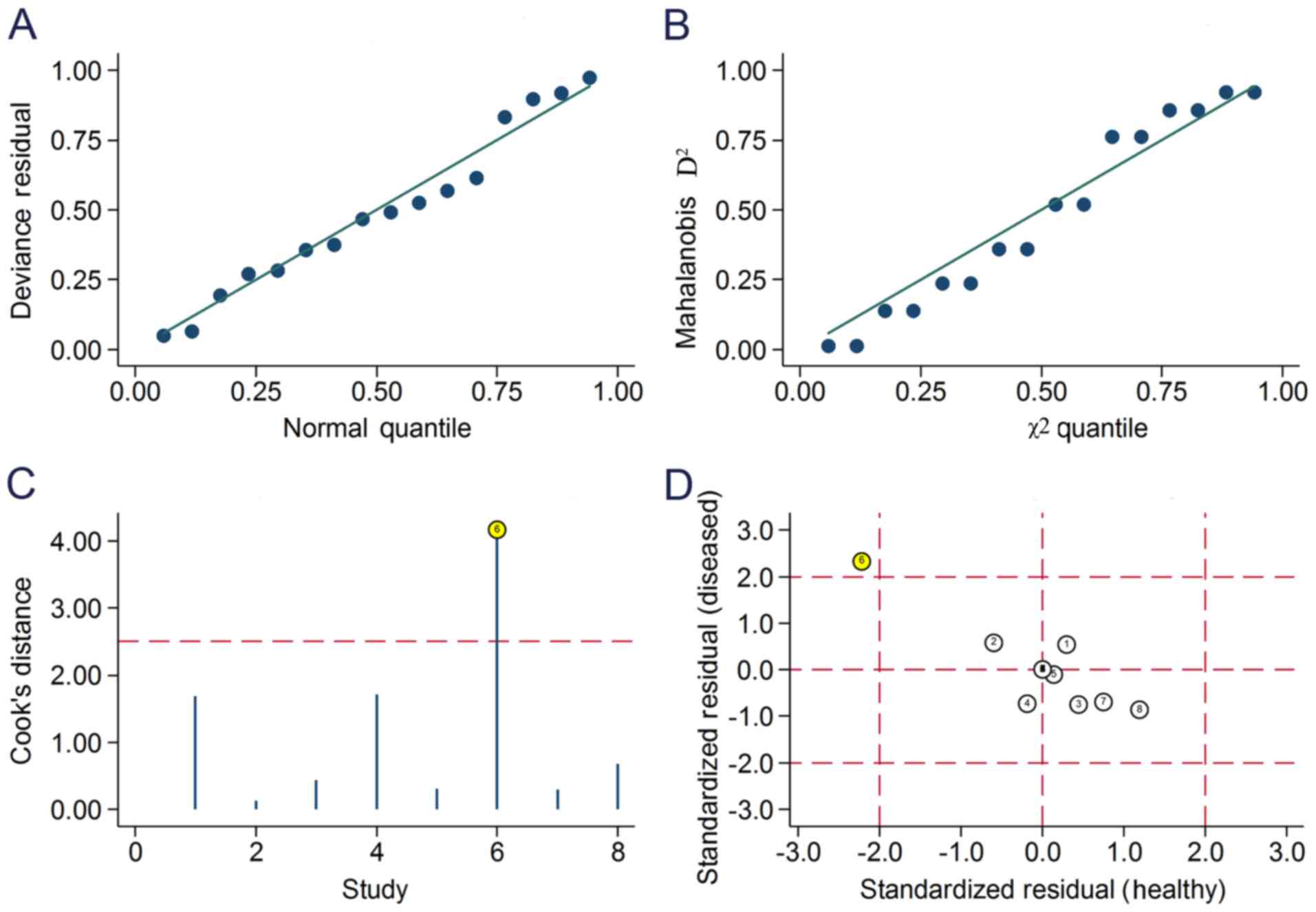
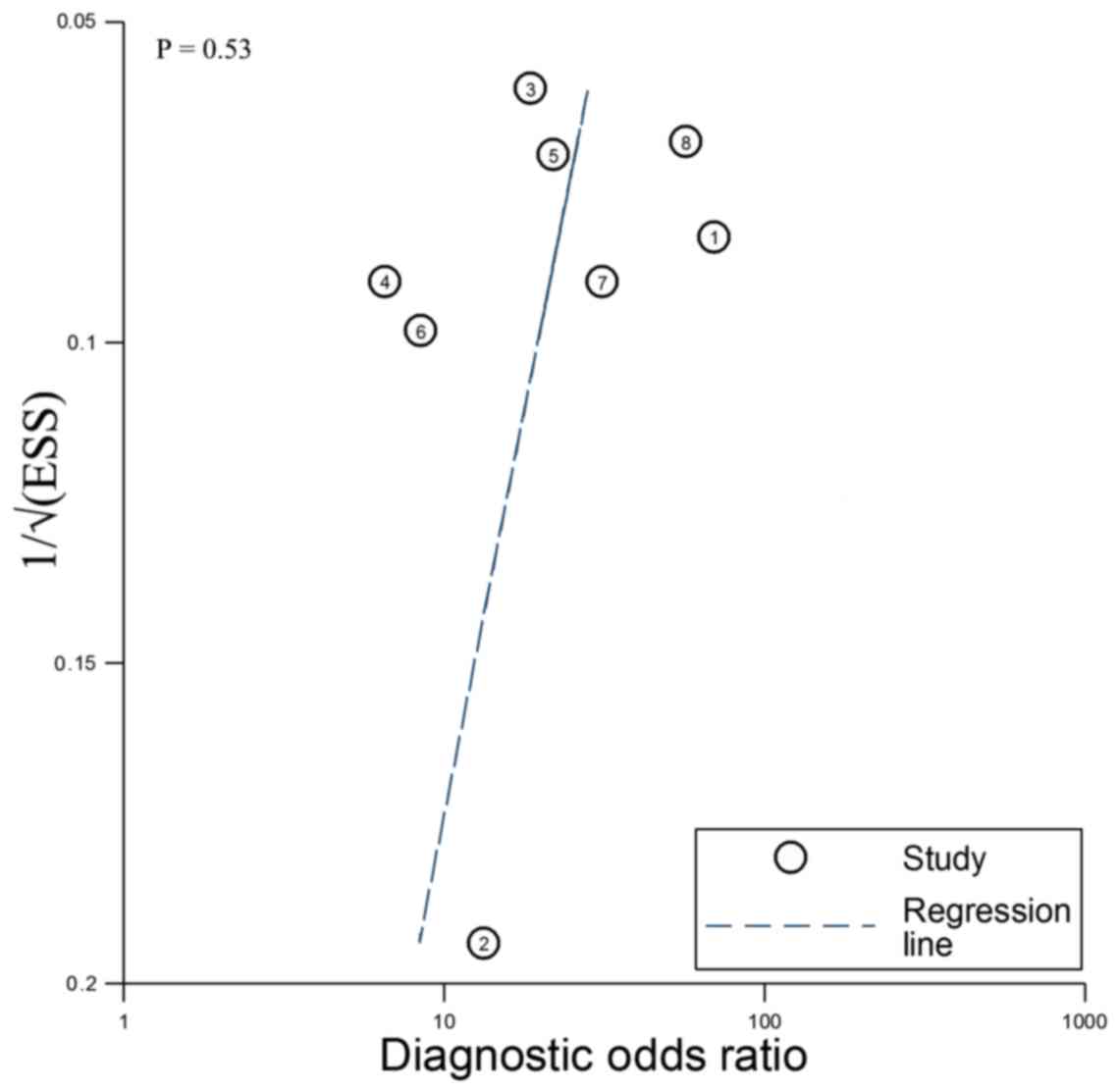
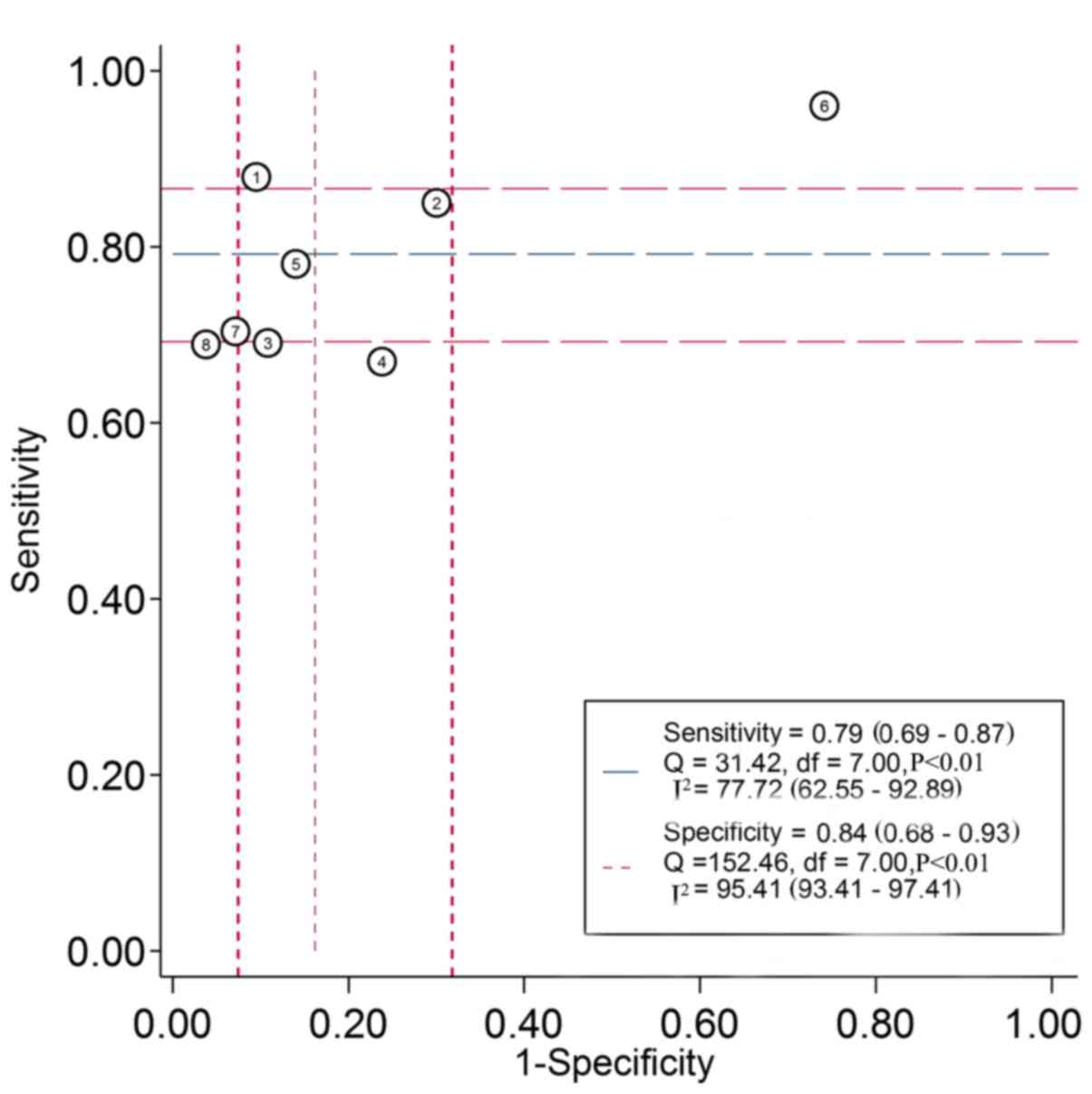
|
1
|
Bray F, Ren JS, Masuyer E and Ferlay J:
Global estimates of cancer prevalence for 27 sites in the adult
population in 2008. Int J Cancer. 132:1133–1145. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shin VY and Chu KM: MiRNA as potential
biomarkers and therapeutic targets for gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:10432–10439. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bushati N and Cohen SM: microRNA
functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 23:175–205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hainaut P and Plymoth A: Targeting the
hallmarks of cancer: Towards a rational approach to next-generation
cancer therapy. Curr Opin Oncol. 25:50–51. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Macfarlane LA and Murphy PR: MicroRNA:
Biogenesis, function and role in cancer. Curr Genomics. 11:537–561.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bartels CL and Tsongalis GJ: MicroRNAs:
Novel biomarkers for human cancer. Clin Chem. 55:623–631. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fabbri M: miRNAs as molecular biomarkers
of cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 10:435–444. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Madhavan D, Cuk K, Burwinkel B and Yang R:
Cancer diagnosis and prognosis decoded by blood-based circulating
microRNA signatures. Front Genet. 4:1162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Weiland M, Gao XH, Zhou L and Mi QS: Small
RNAs have a large impact: Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for
human diseases. RNA Biol. 9:850–859. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zen K and Zhang CY: Circulating microRNAs:
A novel class of biomarkers to diagnose and monitor human cancers.
Med Res Rev. 32:326–348. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Su K, Zhang T, Wang Y and Hao G:
Diagnostic and prognostic value of plasma microRNA-195 in patients
with non-small cell lung cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 14:2242016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Itesako T, Seki N, Yoshino H, Chiyomaru T,
Yamasaki T, Hidaka H, Yonezawa T, Nohata N, Kinoshita T, Nakagawa M
and Enokida H: The microRNA expression signature of bladder cancer
by deep sequencing: The functional significance of the miR-195/497
cluster. PLoS One. 9:e843112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Deng H, Guo Y, Song H, Xiao B, Sun W, Liu
Z, Yu X, Xia T, Cui L and Guo J: MicroRNA-195 and microRNA-378
mediate tumor growth suppression by epigenetical regulation in
gastric cancer. Gene. 518:351–359. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang F, Jiang C, Sun Q, Yan F, Wang L, Fu
Z, Liu T and Hu F: miR-195 is a key regulator of Raf1 in thyroid
cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 8:3021–3028. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang B, Tan Z and Song Y: Study on the
molecular regulatory mechanism of MicroRNA-195 in the invasion and
metastasis of colorectal carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Med.
8:3793–3800. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cai C, Chen QB, Han ZD, Zhang YQ, He HC,
Chen JH, Chen YR, Yang SB, Wu YD, Zeng YR, et al: miR-195 inhibits
tumor progression by targeting RPS6KB1 in human prostate cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 21:4922–4934. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Z, Wang H, Wang Z and Cai H: MiR-195
inhibits the proliferation of human cervical cancer cells by
directly targeting cyclin D1. Tumour Biol. 37:6457–6463. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang M, Zhang J, Tong L, Ma X and Qiu X:
MiR-195 is a key negative regulator of hepatocellular carcinoma
metastasis by targeting FGF2 and VEGFA. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:14110–14120. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Susluer Yilaz S, Avci Biray C, Dodurga Y,
Ozlem Dogan Sigva Z, Oktar N and Gunduz C: Downregulation of
miR-195 via cyclosporin A in human glioblastoma cells. J BUON.
20:1337–1340. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jia LF, Wei SB, Gong K, Gan YH and Yu GY:
Prognostic implications of micoRNA miR-195 expression in human
tongue squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e566342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fu MG, Li S, Yu TT, Qian LJ, Cao RS, Zhu
H, Xiao B, Jiao CH, Tang NN, Ma JJ, et al: Differential expression
of miR-195 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and miR-195
expression inhibits tumor cell proliferation and invasion by
targeting of Cdc42. FEBS Lett. 587:3471–3479. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Han K, Chen X, Bian N, Ma B, Yang T, Cai
C, Fan Q, Zhou Y and Zhao TB: MicroRNA profiling identifies MiR-195
suppresses osteosarcoma cell metastasis by targeting CCND1.
Oncotarget. 6:8875–8889. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhu Y, Wang EL, Li H, Zhong CC, Liu JN and
Duan GK: Clinical significance of serum miR-195 in the diagnosis of
breast cancer. J Tropical Med. 13:833–836. 2013.
|
|
25
|
Heneghan HM, Miller N, Kelly R, Newell J
and Kerin MJ: Systemic miRNA-195 differentiates breast cancer from
other malignancies and is a potential biomarker for detecting
noninvasive and early stage disease. Oncologist. 15:673–682. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Motawi TK, Shaker OG, El-Maraghy SA and
Senousy MA: Serum MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers for early
diagnosis of hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma in
Egyptian patients. PLoS One. 10:e01377062015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang IP, Tsai HL, Miao ZF, Huang CW, Kuo
CH, Wu JY, Wang WM, Juo SH and Wang JY: Development of a
deregulating microRNA panel for the detection of early relapse in
postoperative colorectal cancer patients. J Transl Med. 14:1082016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang WZ, Li Y and Tao CH: Value of
combined detection of multiple miRNA in diagnosis of early breast
carcinoma. J Hainan Med Univ. 22:1591–1593. 2016.
|
|
29
|
Zhao FL, Dou YC, Wang XF, Han DC, Lv ZG,
Ge SL and Zhang YK: Serum microRNA-195 is down-regulated in breast
cancer: A potential marker for the diagnosis of breast cancer. Mol
Biol Rep. 41:5913–5922. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Leeflang MM: Systematic reviews and
meta-analyses of diagnostic test accuracy. Clin Microbiol Infect.
20:105–113. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vamvakas EC: Meta-analyses of studies of
the diagnostic accuracy of laboratory tests: A review of the
concepts and methods. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 122:675–686.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rutter CM and Gatsonis CA: A hierarchical
regression approach to meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy
evaluations. Stat Med. 20:2865–2884. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Deeks JJ, Macaskill P and Irwig L: The
performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size
effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was
assessed. J Clin Epidemiol. 58:882–893. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hong Z, Zhang R and Qi H: Diagnostic and
prognostic relevance of serum miR-195 in pediatric acute myeloid
leukemia. Cancer Biomark. 21:269–275. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Paranjape T, Slack FJ and Weidhaas JB:
MicroRNAs: Tools for cancer diagnostics. Gut. 58:1546–1554. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lu J, Xie F, Geng L, Shen W, Sui C and
Yang J: Potential role of MicroRNA-210 as biomarker in human
cancers detection: A Meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int.
2015:3039872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lu D, Luo P, Wang Q, Ye Y and Wang B:
lncRNA PVT1 in cancer: A review and meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta.
474:1–7. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shuai P, Zhou Y, Gong B, Jiang Z, Yang C,
Yang H, Zhang D and Zhu S: Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 can serve as a
valuable biomarker for prognosis and lymph node metastasis in
various cancers: A meta-analysis. Springerplus. 5:17212016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|