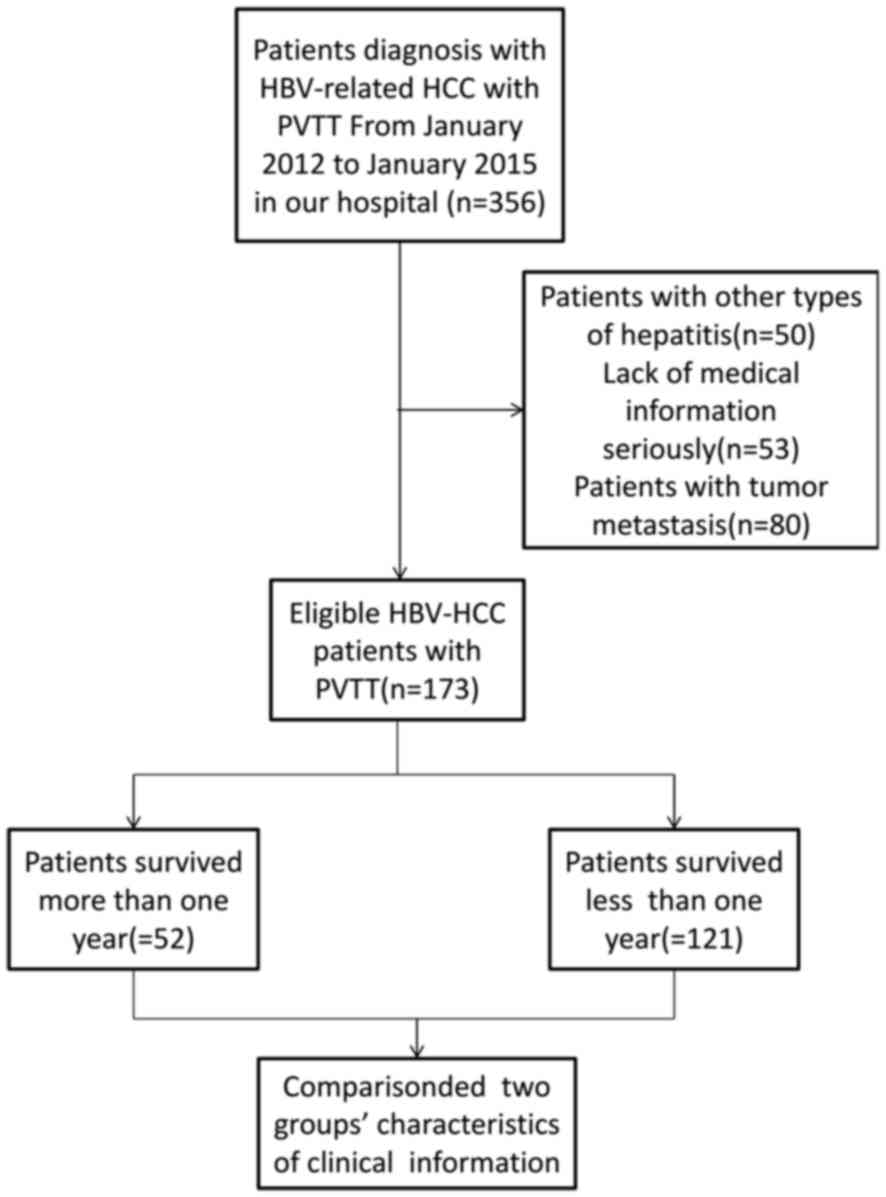
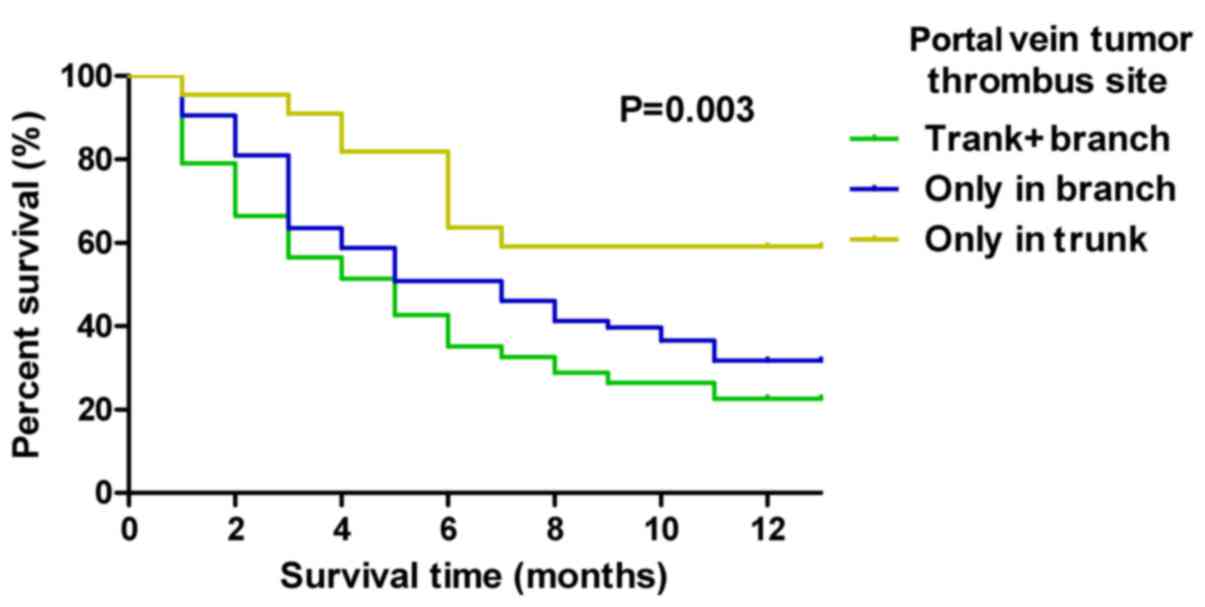
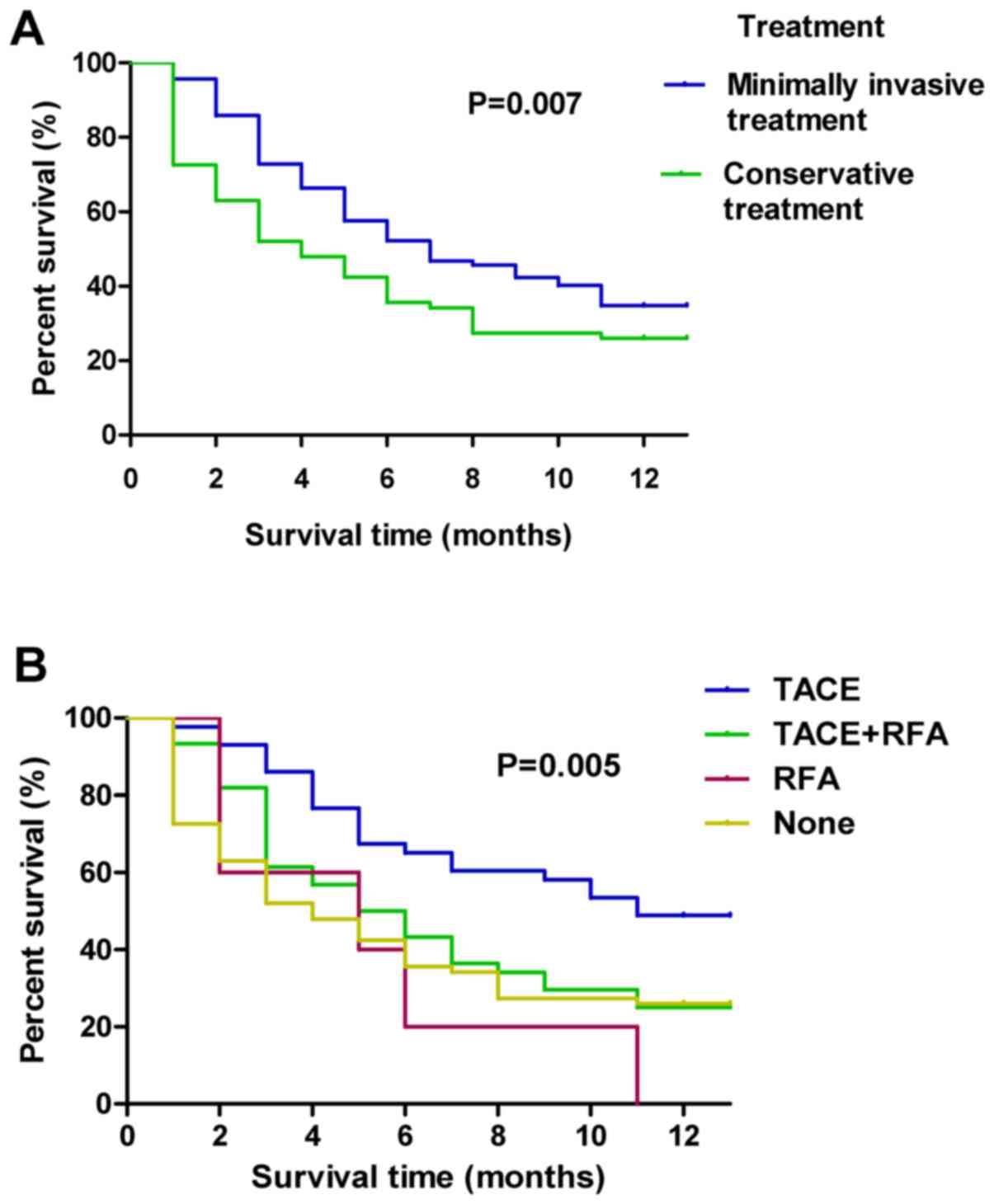
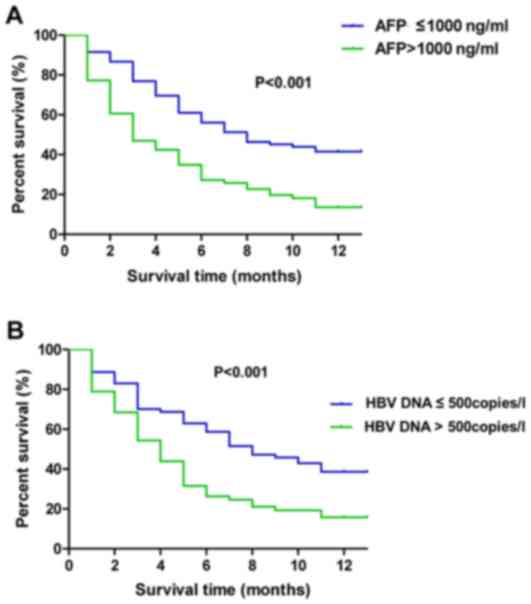
|
1
|
Taketomi A: Clinical trials of
antiangiogenic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin
Oncol. 21:213–218. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Facciorusso A, Di Maso M and Muscatiello
N: Drug-eluting beads versus conventional chemoembolization for the
treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A
meta-analysis. Dig Liver Dis. 48:571–577. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang ZM, Lai EC, Zhang C, Yu HW, Liu Z,
Wan BJ, Liu LM, Tian ZH, Deng H, Sun QH and Chen XP: The strategies
for treating primary hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein
tumor thrombus. Int J Surg. 20:8–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bucci L, Garuti F, Lenzi B, Pecorelli A,
Farinati F, Giannini EG, Granito A, Ciccarese F, Rapaccini GL, Di
Marco M, et al: The evolutionary scenario of hepatocellular
carcinoma in Italy: An update. Liver Int. 37:259–270. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ramirez AG, Munoz E, Holden AE, Adeigbe RT
and Suarez L: Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in Texas
Latinos, 1995-2010: An update. PLoS One. 9:e993652014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nakazawa T, Adachi S, Kitano M, Isobe Y,
Kokubu S, Hidaka H, Ono K, Okuwaki Y, Watanabe M, Shibuya A, et al:
Potential prognostic benefits of radiotherapy as an initial
treatment for patients with unresectable advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma with invasion to intrahepatic large vessels. Oncology.
73:90–97. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tanaka Y, Nakazawa T, Komori S, Hidaka H,
Okuwaki Y, Takada J, Watanabe M, Shibuya A, Minamino T, Yamamoto H,
et al: Radiotherapy for patients with unresectable advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma with invasion to intrahepatic large
vessels: Efficacy and outcomes. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
29:352–357. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stippel DL, Wahba R, Bruns CJ, Bunck A,
Baues C and Persigehl T: Image-guided, minimally invasive surgery
and other local therapeutic procedures for primary liver tumors.
Chirug. 2018.(In German).
|
|
10
|
Bruix J and Sherman M; American
Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, . Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shen A, Tang C, Wang Y, Chen Y, Yan X,
Zhang C, Liu R, Wei X, Zhu Y, Zhang H and Wu Z: A systematic review
of sorafenib in Child-Pugh A patients with unresectable
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Gastroenterol. 47:871–880. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cheah YL and Chow PKH: Liver
transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: An appraisal of
current controversies. Liver Cancer. 1:183–189. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Malinchoc M, Kamath PS, Gordon FD, Peine
CJ, Rank J and ter Borg PC: A model to predict poor survival in
patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts.
Hepatology. 31:864–871. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Eguchi S, Kanematsu T, Arii S, Omata M,
Kudo M, Sakamoto M, Takayasu K, Makuuchi M, Matsuyama Y and Monden
M; Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan, . Recurrence-free survival
more than 10 years after liver resection for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Br J Surg. 98:552–557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zou Z, Yuan Z, Zhang Q, Long Z, Chen J,
Tang Z, Zhu Y, Chen S, Xu J, Yan M, et al: Aurora kinase A
inhibition-induced autophagy triggers drug resistance in breast
cancer cells. Autophagy. 8:1798–1810. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gao J, Zou Z, Gao J, Zhang H, Lin Z, Zhang
Y, Luo X, Liu C, Xie J and Cai C: Increased expression of HMGB3: A
novel independent prognostic marker of worse outcome in patients
with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:345–352. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tandon P and Garcia-Tsao G: Prognostic
indicators in hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review of 72
studies. Liver Int. 29:502–510. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang TT, Zhao XQ, Liu Z, Mao ZY and Bai
L: Factors affecting the recurrence and survival of hepatocellular
carcinoma after hepatectomy: A retrospective study of 601 Chinese
patients. Clin Transl Oncol. 18:831–840. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schöniger-Hekele M, Müller C, Kutilek M,
Oesterreicher C, Ferenci P and Gangl A: Hepatocellular carcinoma in
Central Europe: Prognostic features and survival. Gut. 48:103–109.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Llovet JM, Bustamante J, Castells A,
Vilana R, Ayuso Mdel C, Sala M, Brú C, Rodés J and Bruix J: Natural
history of untreated nonsurgical hepatocellular carcinoma:
Rationale for the design and evaluation of therapeutic trials.
Hepatology. 29:62–67. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kokudo T, Hasegawa K, Matsuyama Y,
Takayama T, Izumi N, Kadoya M, Kudo M, Ku Y, Sakamoto M, Nakashima
O, et al: Survival benefit of liver resection for hepatocellular
carcinoma associated with portal vein invasion. J Hepatol.
65:938–943. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang M, Lin Q, Wang H, Chen J, Bai M,
Wang L, Zhu K, Jiang Z, Guan S, Li Z, et al: Survival benefit of
chemoembolization plus Iodine125 seed implantation in unresectable
hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma with PVTT: A
retrospective matched cohort study. Eur Radiol. 26:3428–3436. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lu XJ, Dong J, Ji LJ, Luo JH, Cao HM, Xiao
LX, Zhou J and Ling CQ: Safety and efficacy of TACE and gamma knife
on hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion. Gut.
65:715–716. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Riaz A, Ryu RK, Kulik LM, Mulcahy MF,
Lewandowski RJ, Minocha J, Ibrahim SM, Sato KT, Baker T, Miller FH,
et al: Alpha-fetoprotein response after locoregional therapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma: Oncologic marker of radiologic response,
progression, and survival. J Clin Oncol. 27:5734–5742. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chan SL, Mo FK, Johnson PJ, Hui EP, Ma BB,
Ho WM, Lam KC, Chan AT, Mok TS and Yeo W: New utility of an old
marker: Serial alpha-fetoprotein measurement in predicting
radiologic response and survival of patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma undergoing systemic chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol.
27:446–452. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee MH, Kim SU, Kim DY, Ahn SH, Choi EH,
Lee KH, Lee DY, Seong J, Han KH, Chon CY and Park JY: Early
on-treatment predictions of clinical outcomes using
alpha-fetoprotein and des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin responses in
patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 27:313–322. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nobuoka D, Kato Y, Gotohda N, Takahashi S,
Nakagohri T, Konishi M, Kinoshita T and Nakatsura T: Postoperative
serum alpha-fetoprotein level is a useful predictor of recurrence
after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
24:521–528. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bujold A, Massey CA, Kim JJ, Brierley J,
Cho C, Wong RK, Dinniwell RE, Kassam Z, Ringash J, Cummings B, et
al: Sequential phase I and II trials of stereotactic body
radiotherapy for locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin
Oncol. 31:1631–1639. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kubo S, Hirohashi K, Tanaka H, Tsukamoto
T, Shuto T, Yamamoto T, Ikebe T, Wakasa K, Nishiguchi S and
Kinoshita H: Effect of viral status on recurrence after liver
resection for patients with hepatitis B virus-related
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer-Am Cancer Soc. 88:1016–1024.
2000.
|
|
30
|
Ohkubo K, Kato Y, Ichikawa T, Kajiya Y,
Takeda Y, Higashi S, Hamasaki K, Nakao K, Nakata K and Eguchi K:
Viral load is a significant prognostic factor for hepatitis B
virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 94:2663–2668.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hirooka M, Koizumi Y, Kisaka Y, Abe M,
Murakami H, Matsuura B, Hiasa Y and Onji M: Mass reduction by
radiofrequency ablation before hepatic arterial infusion
chemotherapy improved prognosis for patients with huge
hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein thrombus. AJR Am J
Roentgenol. 194:W221–W226. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lai JC, Covinsky KE, Dodge JL, Boscardin
WJ, Segev DL, Roberts JP and Feng S: Development of a novel frailty
index to predict mortality in patients with end-stage liver
disease. Hepatology. 66:564–574. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Benko T, Gallinat A, Minor T, Saner FH,
Sotiropoulos GC, Paul A and Hoyer DP: The postoperative model for
end stage liver disease score as a predictor of short-term outcome
after transplantation of extended criteria donor livers. Eur J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 29:716–722. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|