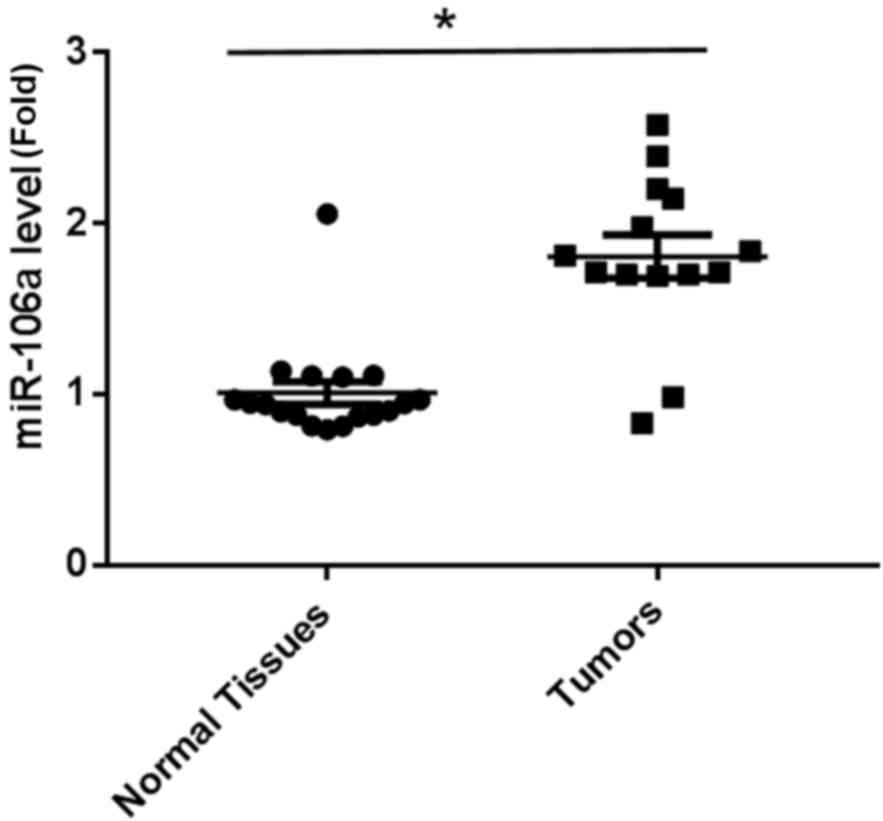
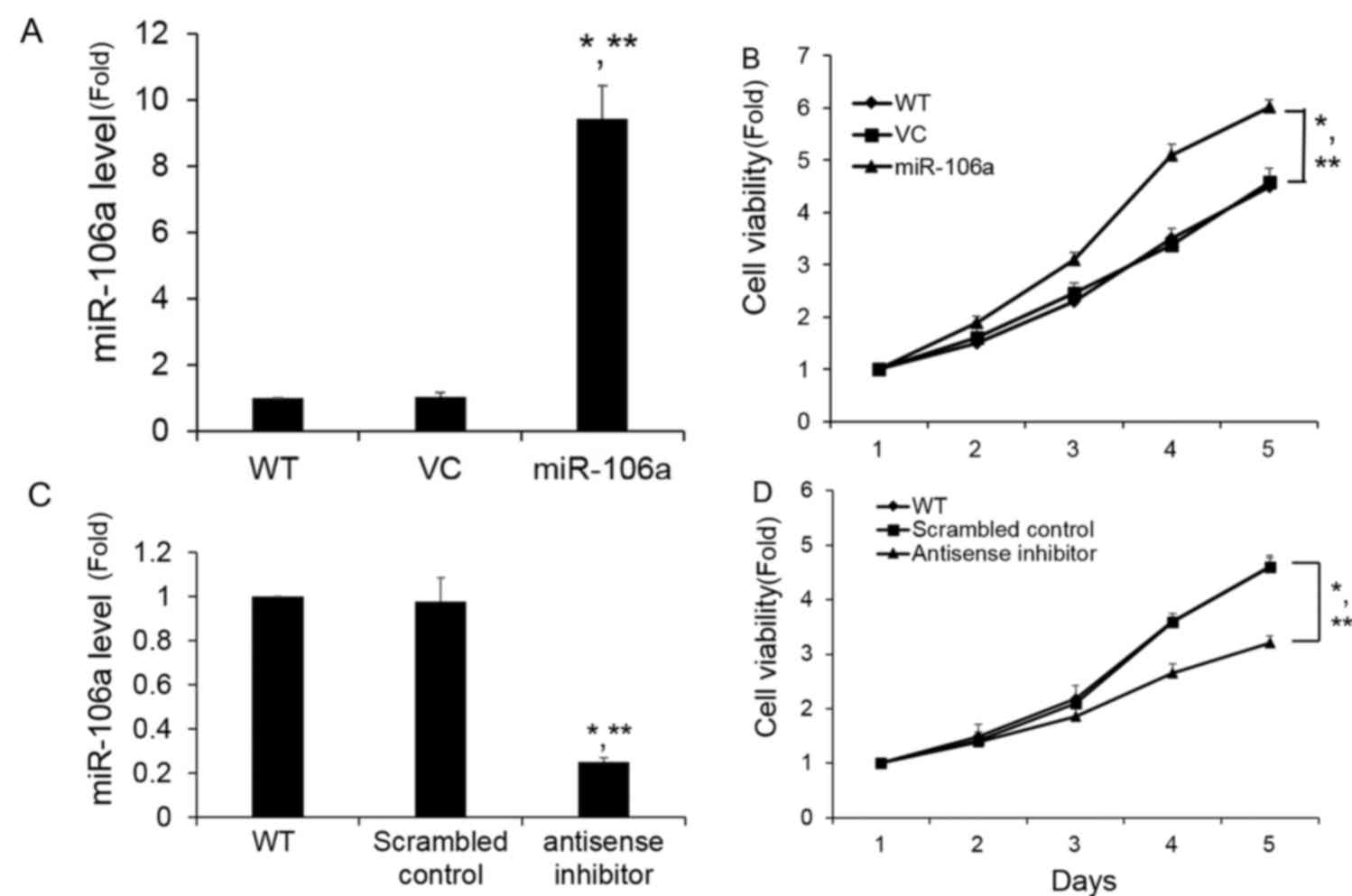
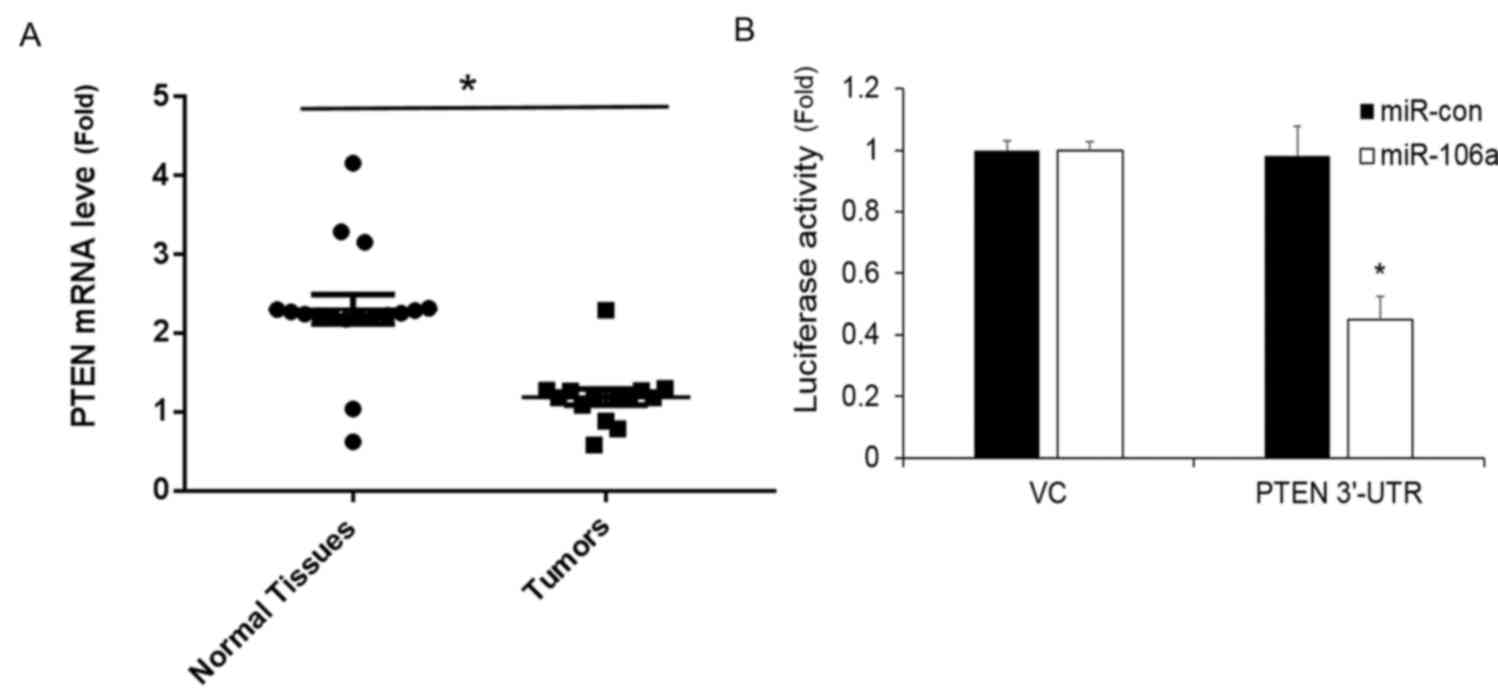
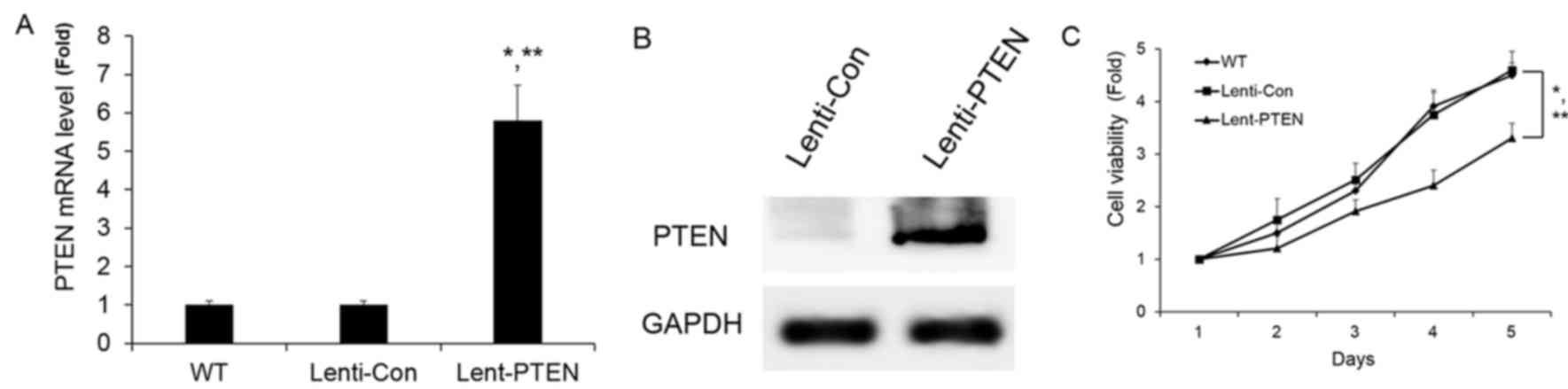
|
1
|
Delongchamps Barry N: Prostate cancer:
Review in 2014. Diagn Interv Imaging. 95:739–742. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lesko LJ and Atkinson AJ Jr: Use of
biomarkers and surrogate endpoints in drug development and
regulatory decision making: Criteria, validation, strategies. Annu
Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 41:347–366. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Madu CO and Lu Y: Novel diagnostic
biomarkers for prostate cancer. J Cancer. 1:150–177. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jackson BL, Grabowska A and Ratan HL:
MicroRNA in prostate cancer: Functional importance and potential as
circulating biomarkers. BMC Cancer. 14:9302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Coppola V, De Maria R and Bonci D:
MicroRNAs and prostate cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 17:F1–F17.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tay Y, Zhang J, Thomson AM, Lim B and
Rigoutsos I: MicroRNAs to Nanog, Oct4 and Sox2 coding regions
modulate embryonic stem cell differentiation. Nature.
455:1124–1128. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ahmad J, Hasnain SE, Siddiqui MA, Ahamed
M, Musarrat J and Al-Khedhairy AA: MicroRNA in carcinogenesis &
cancer diagnostics: a new paradigm. Indian J Med Res. 137:680–694.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li Y, Sun Z, Liu B, Shan Y, Zhao L and Jia
L: Tumor-suppressive miR-26a and miR-26b inhibit cell
aggressiveness by regulating FUT4 in colorectal cancer. Cell Death
Dis. 8:e28922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li J, Yen C, Liaw D, Podsypanina K, Bose
S, Wang SI, Puc J, Miliaresis C, Rodgers L, McCombie R, et al:
PTEN, a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase gene mutated in human
brain, breast, and prostate cancer. Science. 275:1943–1947. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Steck PA, Pershouse MA, Jasser SA, Yung
WK, Lin H, Ligon AH, Langford LA, Baumgard ML, Hattier T, Davis T,
et al: Identification of a candidate tumour suppressor gene, MMAC1,
at chromosome 10q23.3 that is mutated in multiple advanced cancers.
Nat Genet. 15:356–362. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Miao Y, Zheng W, Li N, Su Z, Zhao L, Zhou
H and Jia L: MicroRNA-130b targets PTEN to mediate drug resistance
and proliferation of breast cancer cells via the PI3K/Akt signaling
pathway. Sci Rep. 7:419422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu ZL, Wang H, Liu J and Wang ZX:
MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) expression promotes growth, metastasis, and
chemo- or radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells by
targeting PTEN. Mol Cell Biochem. 372:35–45. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu W, Yang J, Feng X, Wang H, Ye S, Yang
P, Tan W, Wei G and Zhou Y: MicroRNA-32 (miR-32) regulates
phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) expression and promotes
growth, migration, and invasion in colorectal carcinoma cells. Mol
Cancer. 12:302013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Alimirah F, Chen J, Basrawala Z, Xin H and
Choubey D: DU-145 and PC-3 human prostate cancer cell lines express
androgen receptor: Implications for the androgen receptor functions
and regulation. FEBS Lett. 580:2294–2300. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Reid G, Pel ME, Kirschner MB, Cheng YY,
Mugridge N, Weiss J, Williams M, Wright C, Edelman JJ, Vallely MP,
et al: Restoring expression of miR-16: a novel approach to therapy
for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Ann Oncol. 24:3128–3135. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thomson DW, Bracken CP, Szubert JM and
Goodall GJ: On measuring miRNAs after transient transfection of
mimics or antisense inhibitors. PLoS One. 8:e552142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xie X, Liu HT, Mei J, Ding FB, Xiao HB, Hu
FQ, Hu R and Wang MS: miR-106a promotes growth and metastasis of
non-small cell lung cancer by targeting PTEN. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:3827–3834. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Amir S, Ma AH, Shi XB, Xue L, Kung HJ and
White Devere RW: Oncomir miR-125b suppresses p14(ARF) to modulate
p53-dependent and p53-independent apoptosis in prostate cancer.
PLoS One. 8:e610642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lu Z, Liu M, Stribinskis V, Klinge CM,
Ramos KS, Colburn NH and Li Y: MicroRNA-21 promotes cell
transformation by targeting the programmed cell death 4 gene.
Oncogene. 27:4373–4379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang CH, Yue J, Fan M and Pfeffer LM: IFN
induces miR-21 through a signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3-dependent pathway as a suppressive negative
feedback on IFN-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 70:8108–8116. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Spahn M, Kneitz S, Scholz CJ, Stenger N,
Rüdiger T, Ströbel P, Riedmiller H and Kneitz B: Expression of
microRNA-221 is progressively reduced in aggressive prostate cancer
and metastasis and predicts clinical recurrence. Int J Cancer.
127:394–403. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li P, Xu Q, Zhang D, Li X, Han L, Lei J,
Duan W, Ma Q, Wu Z and Wang Z: Upregulated miR-106a plays an
oncogenic role in pancreatic cancer. FEBS Lett. 588:705–712. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li X, Lin G, Wu B, Zhou X and Zhou K:
Overexpression of PTEN induces cell growth arrest and apoptosis in
human breast cancer ZR-75-1 cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 39:745–750. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Qin Y, Huo Z, Song X, Chen X, Tian X and
Wang X: mir-106a regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis of
colon cancer cells through targeting the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling
pathway. Oncol Lett. 15:3197–3201. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yu YX, Wang Y and Liu H: Overexpression of
PTEN suppresses non-small-cell lung carcinoma metastasis through
inhibition of integrin alphaVbeta6 signaling. Am J Transl Res.
9:3304–3314. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
de la Rosa J, Weber J, Rad R, Bradley A
and Cadinanos J: Disentangling PTEN-cooperating tumor suppressor
gene networks in cancer. Mol Cell Oncol. 4:e13255502017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li S, Shen Y, Wang M and Yang J, Lv M, Li
P, Chen Z and Yang J: Loss of PTEN expression in breast cancer:
Association with clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis.
Oncotarget. 8:32043–32054. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Carver BS, Tran J, Gopalan A, Chen Z,
Shaikh S, Carracedo A, Alimonti A, Nardella C, Varmeh S, Scardino
PT, et al: Aberrant ERG expression cooperates with loss of PTEN to
promote cancer progression in the prostate. Nat Genet. 41:619–624.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xiao J, Hu CP, He BX, Chen X, Lu XX, Xie
MX, Li W, He SY, You SJ and Chen Q: PTEN expression is a prognostic
marker for patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic
review and meta-analysis of the literature. Oncotarget.
7:57832–57840. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|