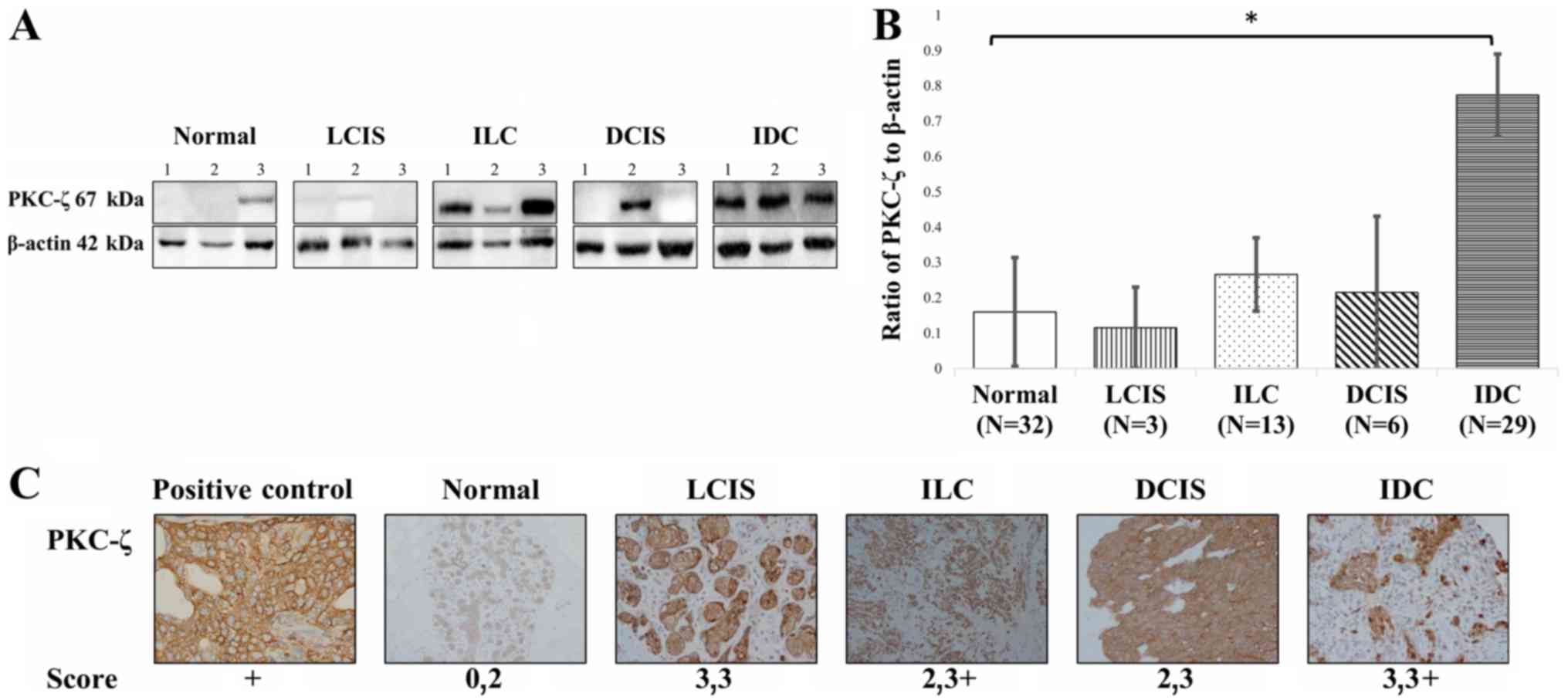
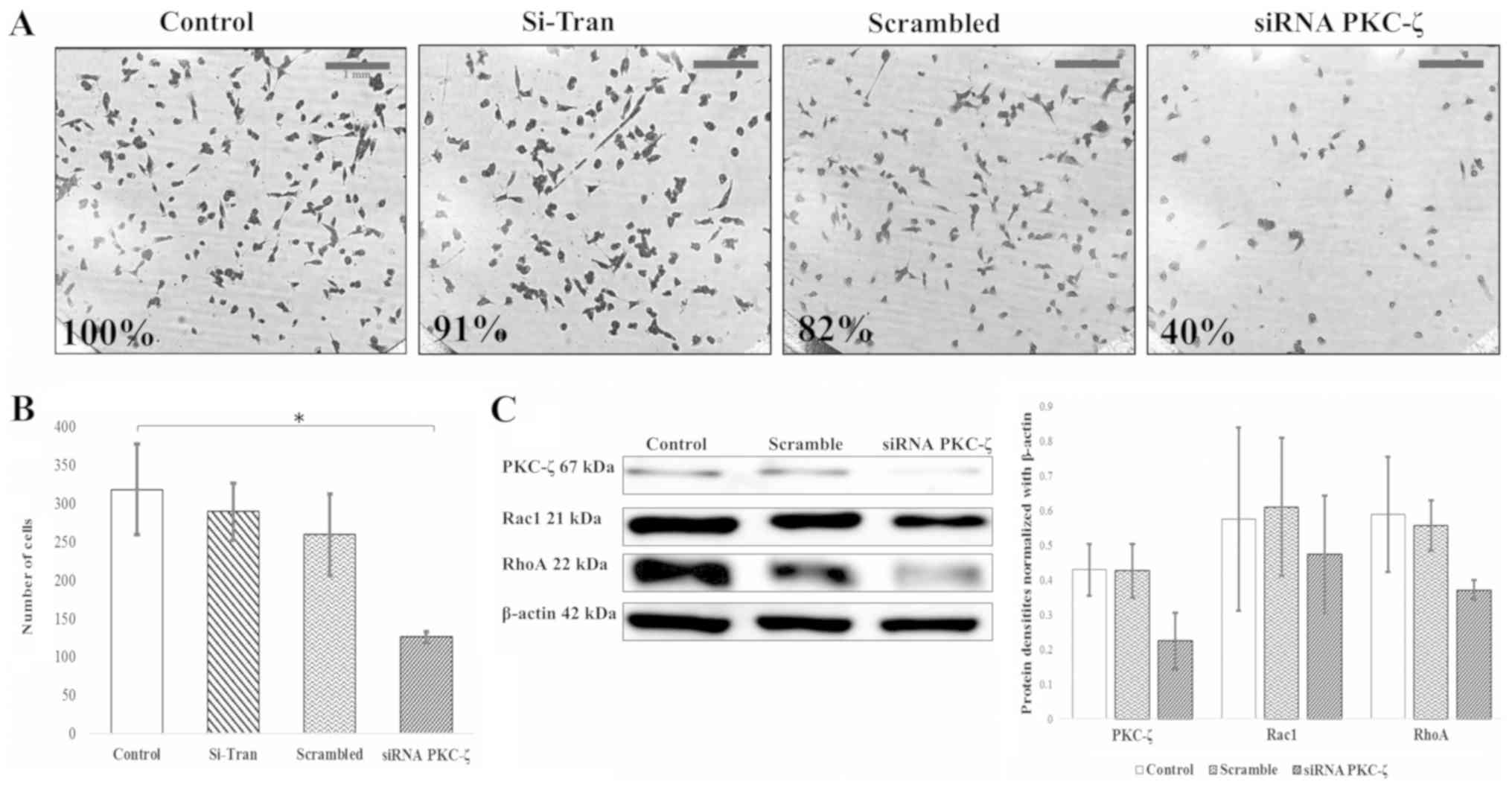
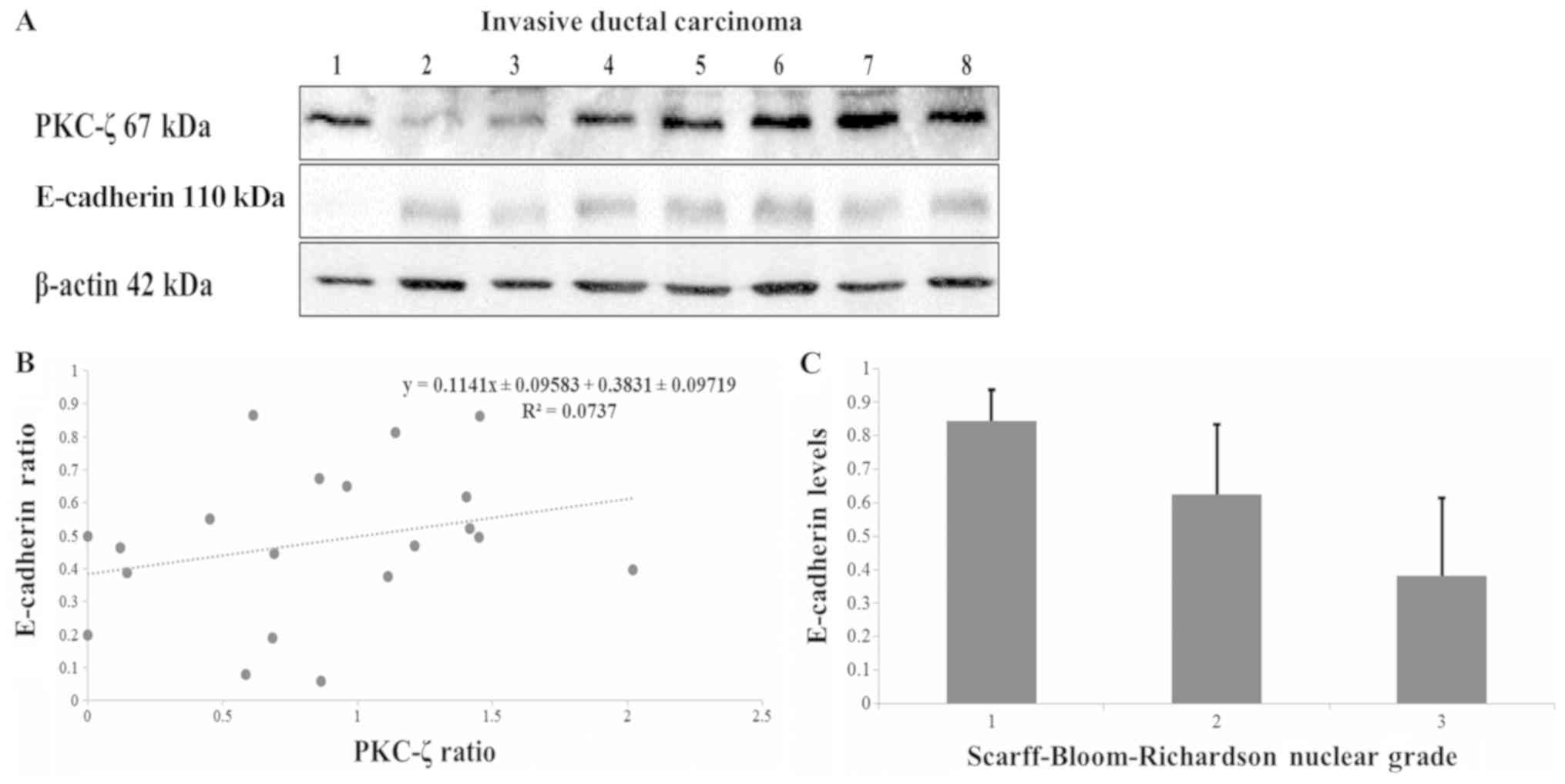
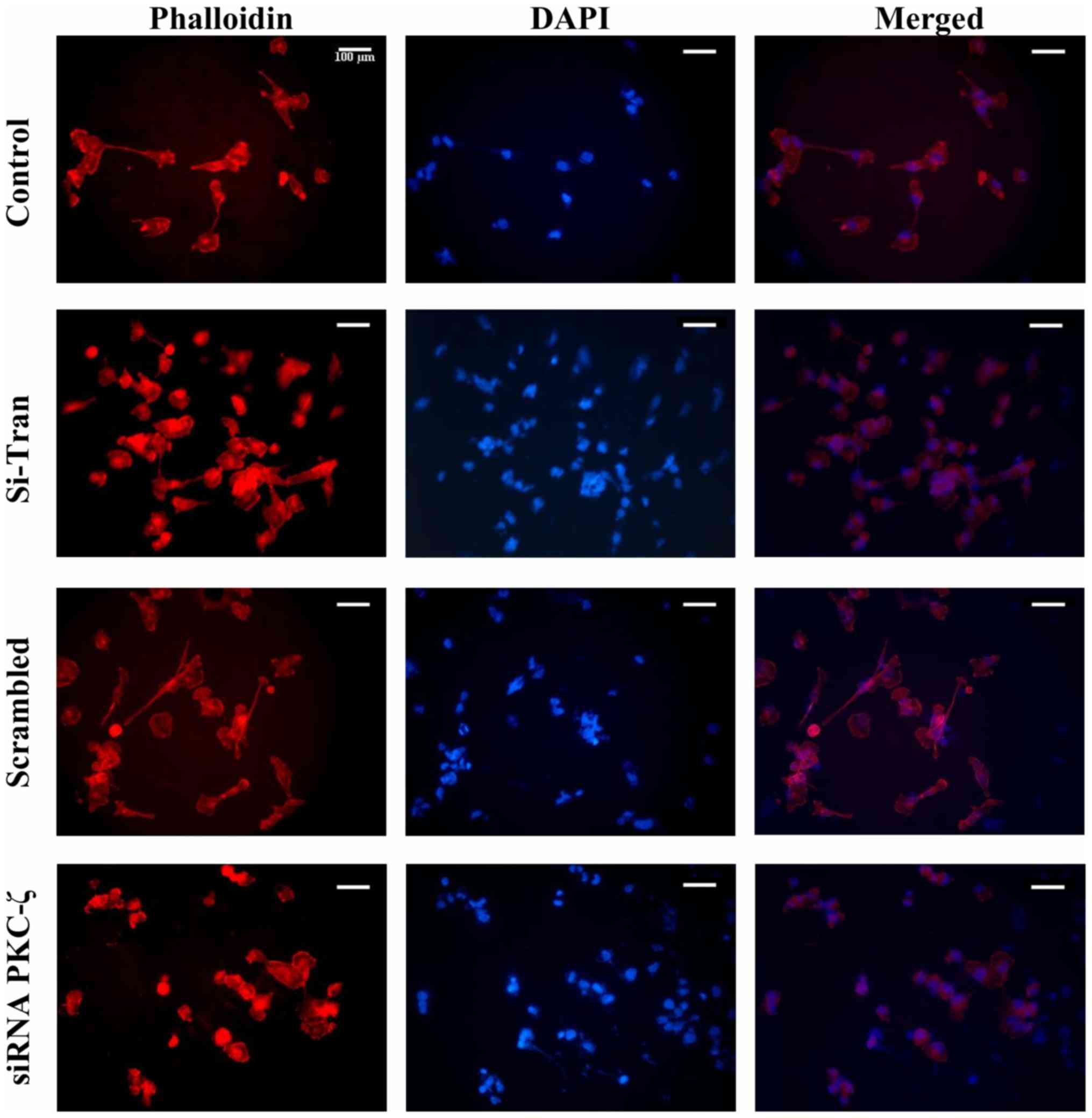
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kuhn E: Quick Guide for Most Commonly Used
Breast Cancer Statements. Susan G. Komen. 10–11. 2015.
|
|
3
|
COSMIC: Catalogue of somatic mutations in
cancer. 2016.
|
|
4
|
Ruibal A, Núñez MI, del Rio M, Arias J,
Martínez MI, Rabadán J and Tejerina A: Clinical-biological
differences between invasive ductal carcinomas and breast lobular
carcinomas. Preliminary results. Rev Esp Med Nucl. 18:84–87.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hoesel B and Schmid JA: The complexity of
NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer. 12:862013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Paul A, Danley M, Saha B, Tawfik O and
Paul S: PKCζ promotes breast cancer invasion by regulating
expression of E-Cadherin and Zonula Occludens-1 (ZO-1) via
NFκB-p65. Sci Rep. 5:125202015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chua HL, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Clare SE,
Morimiya A, Badve S and Nakshatri H: NF-kappaB represses E-cadherin
expression and enhances epithelial to mesenchymal transition of
mammary epithelial cells: Potential involvement of ZEB-1 and ZEB-2.
Oncogene. 26:711–724. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Singhai R, Patil VW, Jaiswal SR, Patil SD,
Tayade MB and Patil AV: E-Cadherin as a diagnostic biomarker in
breast cancer. N Am J Med Sci. 3:227–233. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hirai T and Chida K: Protein kinase Czeta
(PKCzeta): Activation mechanisms and cellular functions. J Biochem.
133:1–7. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Islam SMA, Patel R and Acevedo-Duncan M:
Protein Kinase C-ζ stimulates colorectal cancer cell carcinogenesis
via PKC-ζ/Rac1/Pak1/β-Catenin signaling cascade. Biochim Biophys
Acta Mol Cell Res. 1865:650–664. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu J, Liu S, Fan Z, Zhang L, Tian Y and
Yang R: A novel and selective inhibitor of PKC ζ potently inhibits
human breast cancer metastasis in vitro and in mice. Tumour Biol.
83:8391–8401. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lin YM, Su CC, Su WW, Hwang JM, Hsu HH,
Tsai CH, Wang YC, Tsai FJ, Huang CY, Liu JY and Chen LM: Expression
of protein kinase C isoforms in cancerous breast tissue and
adjacent normal breast tissue. Chin J Physiol. 55:55–61. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schöndorf T, Kurbacher CM, Becker M, Warm
M, Kolhagen H and Göhring UJ: Heterogeneity of proteinkinase C
activity and PKC-zeta expression in clinical breast carcinomas.
Clin Exp Med. 1:1–8. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim SW, Roh J and Park CS:
Immunohistochemistry for pathologists: Protocols, pitfalls, and
Tips. J Pathol Transl Med. 50:411–418. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
GraphPad Software: GraphPad QuickCalcs.
Linear regression calculator. 2018.
|
|
16
|
Social science statistics: Chi-square test
calculator-up to 5×5 contingency table. 2018.
|
|
17
|
Yin WJ, Lu JS, Di GH, Lin YP, Zhou LH, Liu
GY, Wu J, Shen KW, Han QX, Shen ZZ and Shao ZM: Clinicopathological
features of the triple-negative tumors in Chinese breast cancer
patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 115:325–333. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hugo HJ, Gunasinghe NPAD, Hollier BG,
Tanaka T, Blick T, Toh A, Hill P, Gilles C, Waltham M and Thompson
EW: Epithelial requirement for in vitro proliferation and xenograft
growth and metastasis of MDA-MB-468 human breast cancer cells:
Oncogenic rather than tumor-suppressive role of E-cadherin. Breast
Cancer Res. 19:862017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Onder TT, Gupta PB, Mani SA, Yang J,
Lander ES and Weinberg RA: Loss of E-cadherin promotes metastasis
via multiple downstream transcriptional pathways. Cancer Res.
68:3645–3654. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lauffenburger DA: Cell motility. Making
connections count. Nature. 383:390–391. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Raftopoulou M and Hall A: Cell migration:
Rho GTPases lead the way. Dev Biol. 265:23–32. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lawson CD and Ridley AJ: Rho GTPase
signaling complexes in cell migration and invasion. J Cell Biol.
217:447–457. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Small JV, Stradal T, Vignal E and Rottner
K: The lamellipodium: Where motility begins. Trends Cell Biol.
12:112–120. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nobes CD and Hall A: Rho GTPases control
polarity, protrusion, and adhesion during cell movement. J Cell
Biol. 144:1235–1244. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|