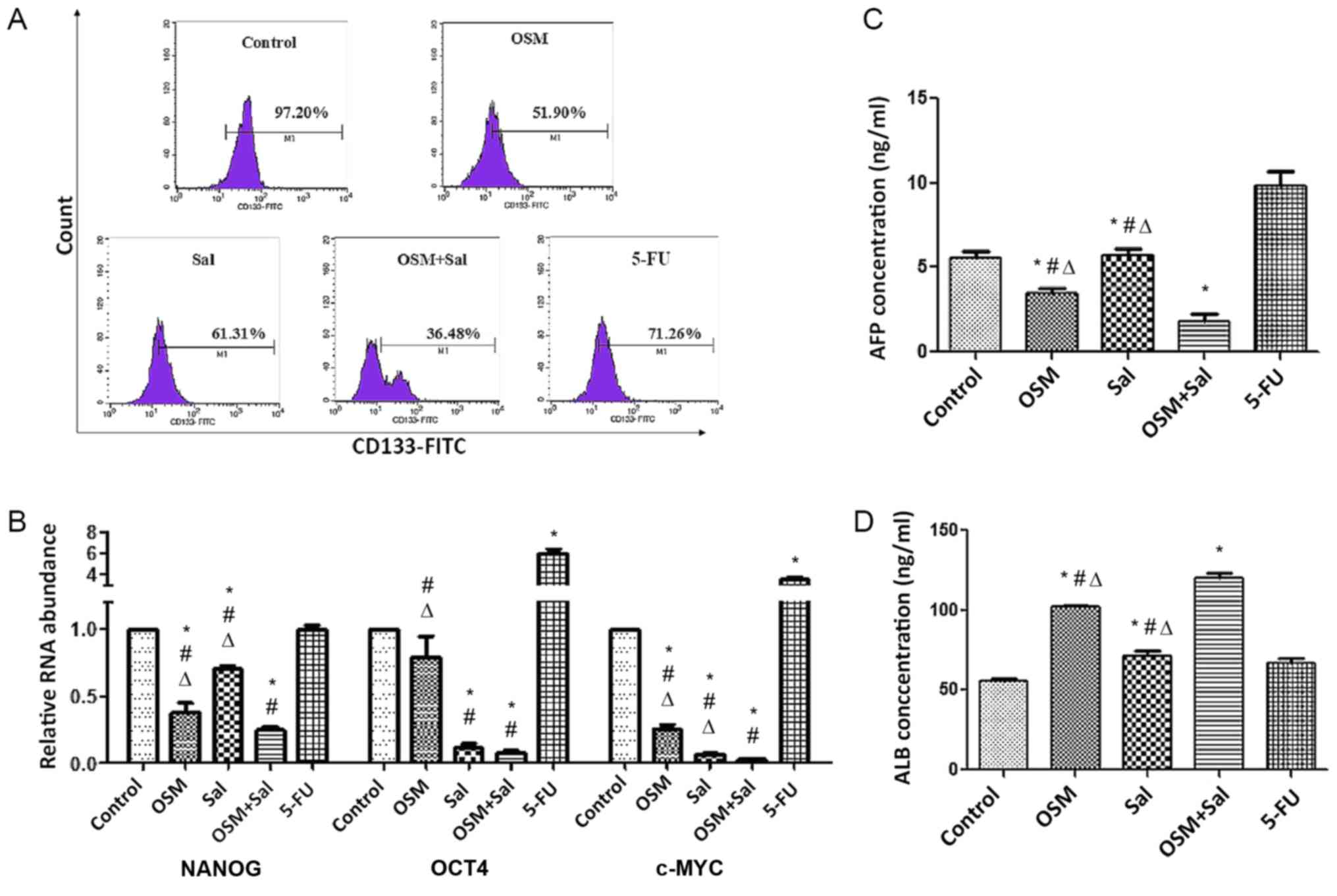
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jordan CT, Guzman ML and Noble M: Cancer
stem cells. N Engl J Med. 355:1253–1261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Naujokat C and Steinhart R: Salinomycin as
a drug for targeting human cancer stem cells. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2012:9506582012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bexell D, Gunnarsson S, Siesjö P, Bengzon
J and Darabi A: CD133+ and nestin+ tumor-initiating cells dominate
in N29 and N32 experimental gliomas. Int J Cancer. 125:15–22. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, Tao K,
Kuperwasser C, Weinberg RA and Lander ES: Identification of
selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput
screening. Cell. 138:645–659. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhi QM, Chen XH, Ji J, Zhang JN, Li JF,
Cai Q, Liu BY, Gu QL, Zhu ZG and Yu YY: Salinomycin can effectively
kill ALDH(high) stem-like cells on gastric cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 65:509–515. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dong TT, Zhou HM, Wang LL, Feng B, Lv B
and Zheng MH: Salinomycin selectively targets ‘CD133+’
cell subpopulations and decreases malignant traits in colorectal
cancerlines. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:1797–1804. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim KY, Yu SN, Lee SY, Chun SS, Choi YL,
Park YM, Song CS, Chatterjee B and Ahn SC: Salinomycin-induced
apoptosis of human prostate cancer cells due to accumulated
reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial membrane depolarization.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 413:80–86. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
He L, Wang F, Dai WQ, Wu D, Lin CL, Wu SM,
Cheng P, Zhang Y, Shen M, Wang CF, et al: Mechanism of action of
salinomycin of growth and migration in pancreatic cancer cell line.
Pancreatology. 13:72–78. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang F, He L, Dai WQ, Xu YP, Wu D, Lin CL,
Wu SM, Cheng P, Zhang Y, Shen M, et al: Salinomycin inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis of human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 7:e506382012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Park SY, Gönen M, Kim HJ, Michor F and
Polyak K: Cellular and genetic diversity in the progression of in
situ human breast carcinomas to aninvasive phenotype. J Clin
Invest. 120:636–644. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yamashita T, Honda M, Nio K, Nakamoto Y,
Yamashita T, Takamura H, Tani T, Zen Y and Kaneko S: Oncostatin m
renders epithelial cell adhesion molecule-positive liver cancer
stem cells sensitive to 5-Fluorouracil by inducing hepatocytic.
Cancer Res. 70:4687–4697. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zheng H, Pomyen Y, Hernandez MO, Li C,
Livak F, Tang W, Dang H, Greten TF, Davis JL, Zhao Y, et al: Single
cell analysis reveals cancer stem cell heterogeneity in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 68:127–140. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun J, Luo Q, Liu L, Yang X, Zhu S and
Song G: Salinomycin attenuates liver cancer stem cell motility by
enhancing cell stiffness and increasing F-actin formation via the
FAK-ERK1/2 signalling pathway. Toxicology. 384:1–10. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tanaka M and Miyajima A: Oncostatin M, a
multifunctional cytokine. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 149:39–52.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nakamura K, Nonaka H, Saito H, Tanaka M
and Miyajima A: Hepatocyte proliferation and tissue remodeling is
impaired after liver injury in oncostatin M receptor knockout mice.
Hepatology. 39:635–644. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Larrea E, Aldabe R, Gonzalez I, Segura V,
Sarobe P, Echeverria I and Prieto J: Oncostatin M enhances the
antiviral effects of type I interferon and activates
immunostimulatory functions in liver epithelial cells. J Virol.
83:3298–3311. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lepiller Q, Abbas W, Kumar A, Tripathy MK
and Herbein G: HCMV activates the IL-6-JAK-STAT3 axis in HepG2
cells and primary human hepatocytes. PLoS One. 8:e595912013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ajani JA, Song S, Hochster HS and
Steinberg IB: Cancer stem cells: The promise and the potential.
Semin Oncol. 42 Suppl:3–17. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ma S, Chan KW, Hu L, Lee TK, Wo JY, Ng IO,
Zheng BJ and Guan XY: Identification and characterization of
tumorigenic liver cancer stem/progenitor cells. Gastroenterology.
132:2542–2556. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma S, Lee TK, Zheng BJ, Chan KW and Guan
XY: CD133+ HCC cancer stem cells confer chemmoresistance by
preferential expression of the Akt/PKB survival pathway. Oncogen.
27:1749–1758. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lan X, Wu YZ, Wang Y, Wu FR, Zang CB, Tang
C, Cao S and Li SL: CD133 silencing inhibits stemness properties
and enhances chemoradiosensitivity in CD133-positive liver cancer
stem cells. Int J Mol Med. 31:315–324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kong N, Zhang XM, Wang HT, Mu XP, Han HZ
and Yan WQ: Inhibition of growth and induction of differentiation
of SMMC-7221 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by oncostatin M.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:747–752. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee S and Schmitt CA: Chemotherapy
response and resistance. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 13:90–96. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kaplan F and Teksen F: Apoptotic effects
of salinomycin on human ovarian cancer cell line (ovcar-3). Tumor
Biol. 37:3897–3903. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Arafat K, Iratni R, Takahashi T, Parekh K,
Al Dhaheri Y, Adrian TE and Attoub S: Inhibitory effects of
salinomycin on cell survival, colony growth, migration, and
invasion of human non-small cell lung cancer a549 and lnm35:
Involvment of nag-1. PLoS One. 8:e669312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu D, Zhang Y, Huang J, Fan Z, Shi F and
Wang S: Salinomycin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of
human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell and suppresses tumor growth in
vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 443:712–717. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang C, Tian Y, Song F, Fu C, Han B and
Wang Y: Salinomycin inhibits the growth of colorectal carcinoma by
targeting tumor stem cells. Oncol Rep. 34:2469–2476. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee KD, Kuo TK, Whang-Peng J, Chung YF,
Lin CT, Chou SH, Chen JR, Chen YP and Lee OK: In vitro hepatic
differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Hepatology.
40:1275–1284. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xue TC, Jia QA, Bu Y, Chen RX, Cui JF,
Tang ZY and Ye SL: CXCR7 correlates with the differentiation of
hepatocellular carcinoma and suppresses HNF4α expression through
the ERK pathway. Oncol Rep. 32:2387–2396. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mitani M, Yamanishi T, Miyazaki Y and
Otake N: Salinomycin effects on mitochondrial ion translocation and
respiration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 9:655–660. 1976.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Managò A, Leanza L, Carraretto L, Sassi N,
Grancara S, Quintana-Cabrera R, Trimarco V, Toninello A, Scorrano
L, Trentin L, et al: Early effects of the antineoplastic agent
salinomycin on mitochondrial function. Cell Death Dis. 6:e19302015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Klose J, Stankov MV, Kleine M, Ramackers
W, Panayotova-Dimitrova D, Jäger MD, Klempnauer J, Winkler M,
Bektas H, Behrens GM and Vondran FW: Inhibition of autophagic flux
by salinomycin results in anti-cancer effect in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 9:e959702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fu YZ, Yan YY, He M, Xiao QH, Yao WF, Zhao
L, Wu HZ, Yu ZJ, Zhou MY, Lv MT, et al: Salinomycin induces
selective cytotoxicity to MCF-7 mammosphere cells through targeting
the Hedgehog signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 35:912–922. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhu LQ, Zhen YF, Zhang Y, Guo ZX, Dai J
and Wang XD: Salinomycin activates AMP-activated protein
kinase-dependent autophagy in cultured osteoblastoma cells: A
negative regulator against cell apoptosis. PLos One. 8:e841752013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang Y, Zuo Y, Guan Z, Lu W, Xu Z, Zhang
H, Yang Y, Yang M, Zhu H and Chen X: Salinomycin radiosensitizes
human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line CNE-2 to radiation. Tumour
Bio. 37:305–311. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Mao J, Fan S, Ma W, Fan P, Wang B, Zhang
J, Wang H, Tang B, Zhang Q, Yu X, et al: Roles of Wnt/β-catenin
signaling in the gastric cancer stem cells proliferation and
salinomycin treatment. Cell Death Dis. 5:e10392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|