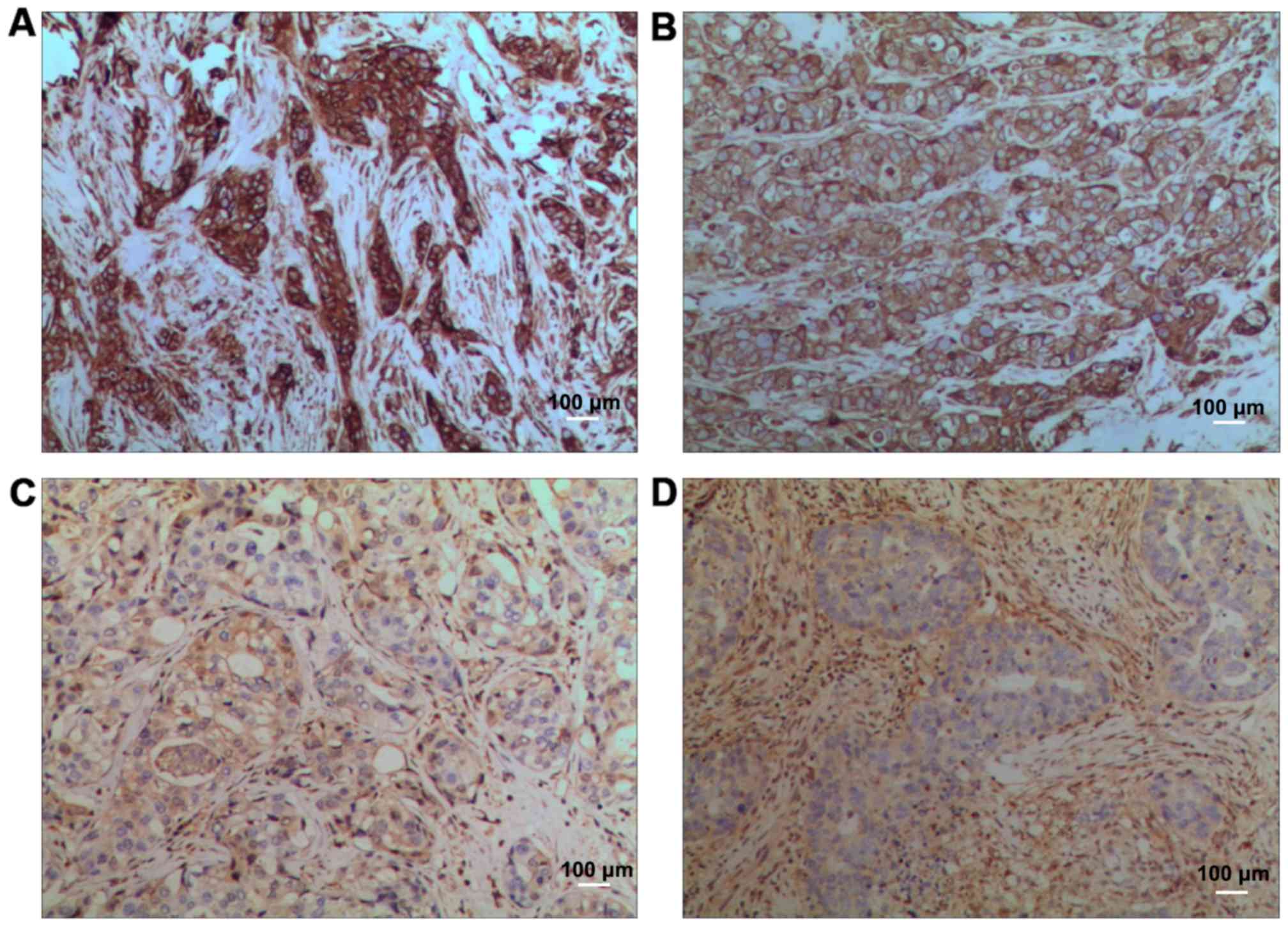
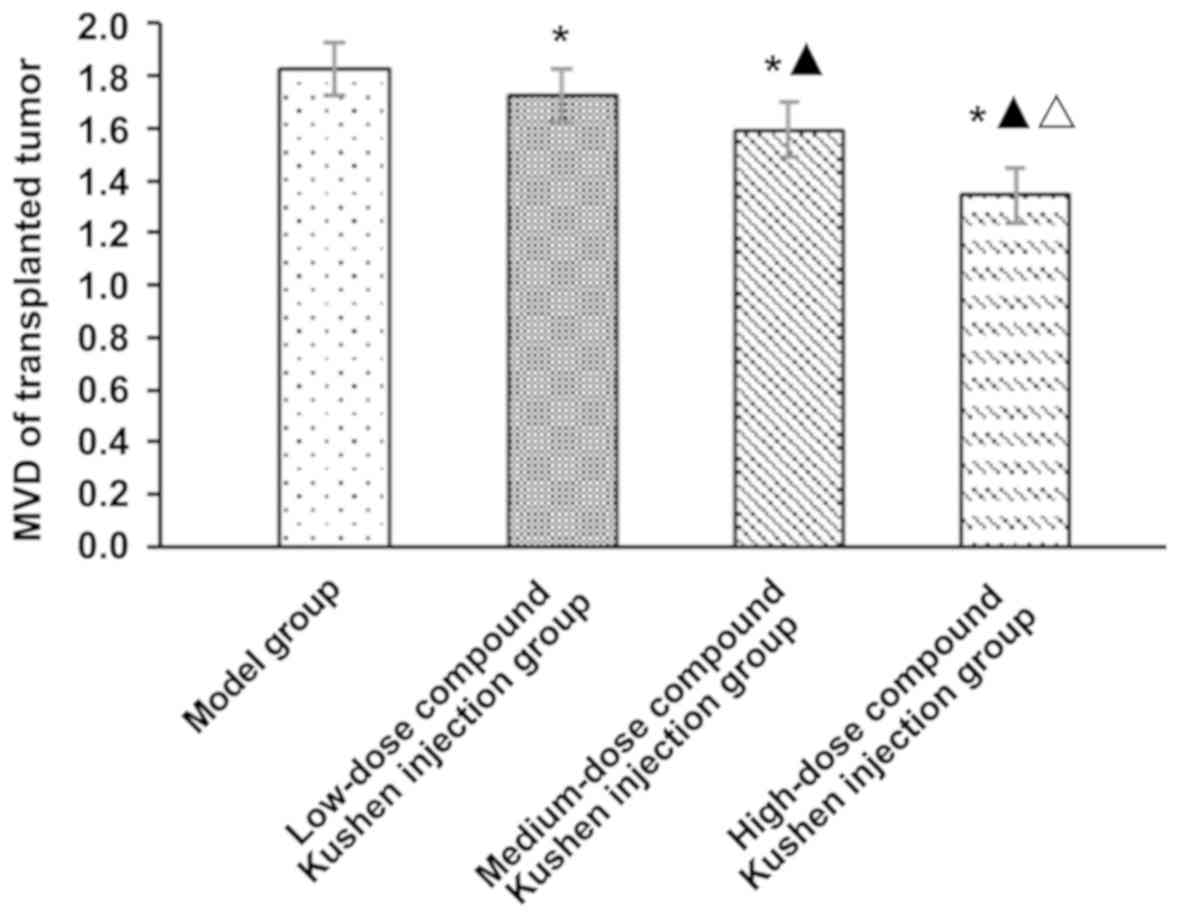
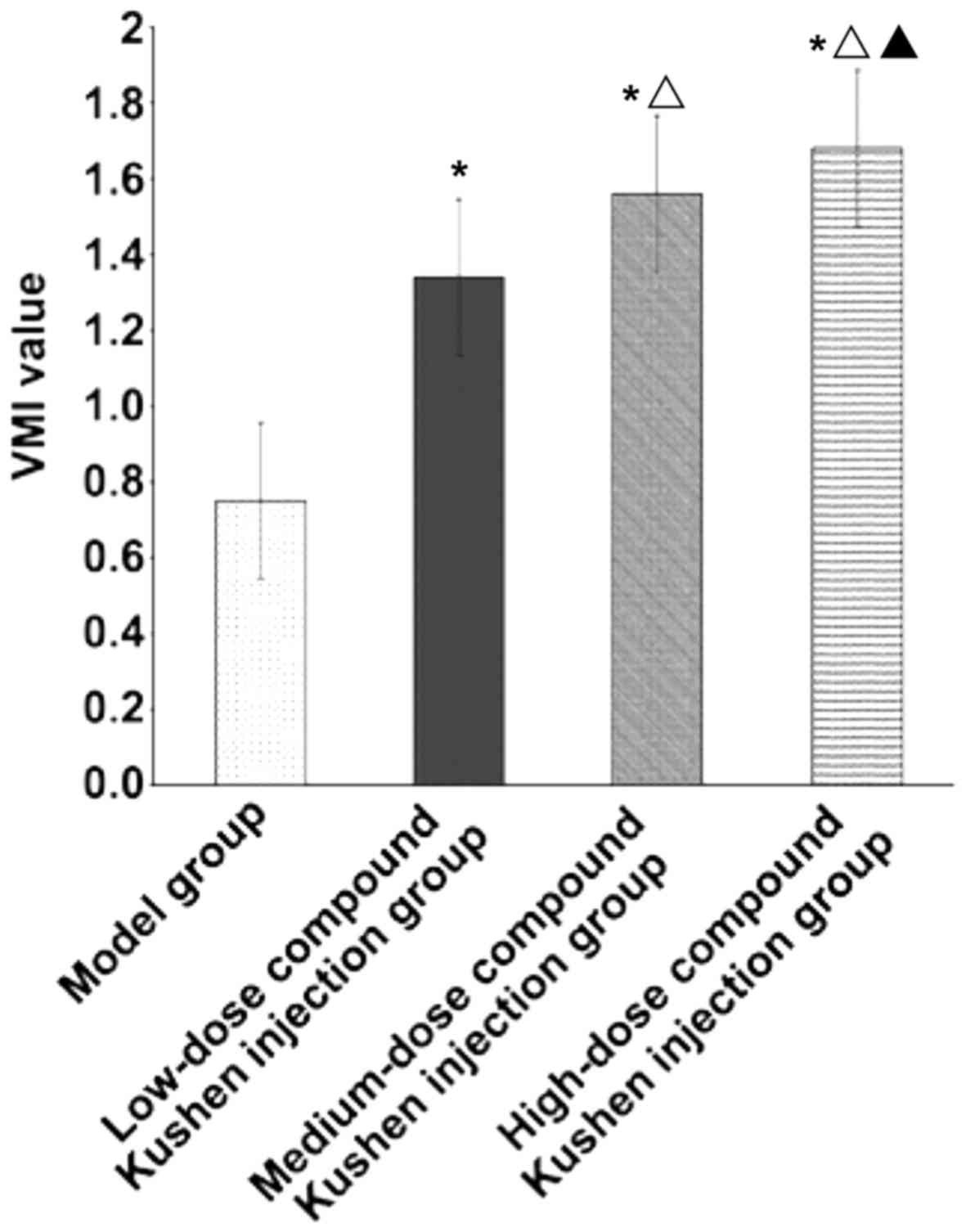
|
1
|
Yu L, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Lu F and Fan Y:
Efficacy and safety of Compound Kushen Injection on patients with
advanced colon cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled
trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017:71025142017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang W, You RL, Qin WJ, Hai LN, Fang MJ,
Huang GH, Kang RX, Li MH, Qiao YF, Li JW, et al: Anti-tumor
activities of active ingredients in Compound Kushen injection. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 36:676–679. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li J, Wu M, Tian Q, Xie G, Hu Y, Meng Q
and Zhang M: The clinical value of Fufangkushen injection in the
treatment of stomach cancer: A meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Ther. 10
Suppl 1:42–45. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yanju B, Yang L, Hua B, Hou W, Shi Z, Li
W, Li C, Chen C, Liu R, Qin Y, et al: A systematic review and
meta-analysis on the use of traditional Chinese medicine compound
Kushen injection for bone cancer pain. Support Care Cancer.
22:825–836. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
López-Terrada D, Cheung SW, Finegold MJ
and Knowles BB: Hep G2 is a hepatoblastoma-derived cell line. Hum
Pathol. 40:1512–1515. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhao Z, Liao H and Ju Y: Effect of
compound Kushen injection on T-cell subgroups and natural killer
cells in patients with locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
treated with concomitant radiochemotherapy. J Tradit Chin Med.
36:14–18. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cao YG, Jing S, Li L, Gao JQ, Shen ZY, Liu
Y, Xing Y, Wu ML, Wang Y, Xu CQ, et al: Antiarrhythmic effects and
ionic mechanisms of oxymatrine from Sophora flavescens.
Phytother Res. 24:1844–1849. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang S, Lian X, Sun M, Luo L and Guo L:
Efficacy of compound Kushen injection plus radiotherapy on
non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
J Cancer Res Ther. 12:1298–1306. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Malhotra J, Jabbour SK and Aisner J:
Erratum to current state of immunotherapy for non-small cell lung
cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 6:6122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guo YM, Huang YX, Shen HH, Sang XX, Ma X,
Zhao YL and Xiao XH: Efficacy of Compound Kushen injection in
relieving cancer-related pain: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015:8407422015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Olaso E and Vidal-Vanaclocha F: Use of
tumor-activated hepatic stellate cell as a target for the
preclinical testing of anti-angiogenic drugs against hepatic tumor
development. Methods Mol Med. 85:79–86. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Browder T, Butterfield CE, Kräling BM, Shi
B, Marshall B, O'Reilly MS and Folkman J: Antiangiogenic scheduling
of chemotherapy improves efficacy against experimental
drug-resistant cancer. Cancer Res. 60:1878–1886. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhao Z, Fan H, Higgins T, Qi J, Haines D,
Trivett A, Oppenheim JJ, Wei H, Li J, Lin H, et al: Fufang Kushen
injection inhibits sarcoma growth and tumor-induced hyperalgesia
via TRPV1 signaling pathways. Cancer Lett. 355:232–241. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee CN, Cheng WF, Chen CA, Chu JS, Hsieh
CY and Hsieh FJ: Angiogenesis of endometrial carcinomas assessed by
measurement of intratumoral blood flow, microvessel density, and
vascular endothelial growth factor levels. Obstet Gynecol.
96:615–621. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Carmeliet P: VEGF as a key mediator of
angiogenesis in cancer. Oncology. 69 Suppl 3:4–10. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|