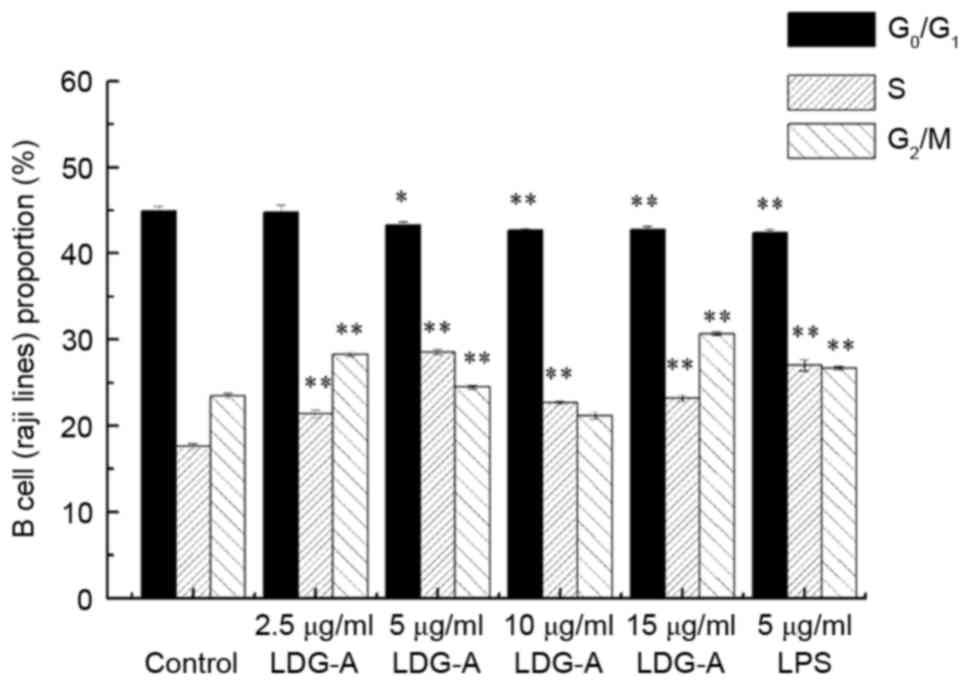
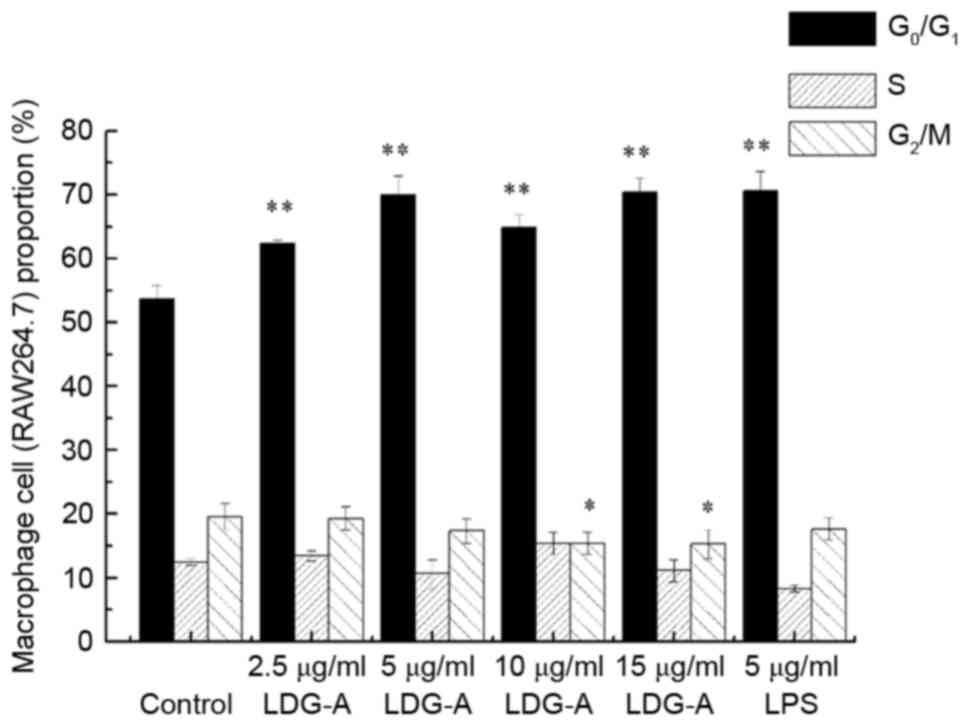
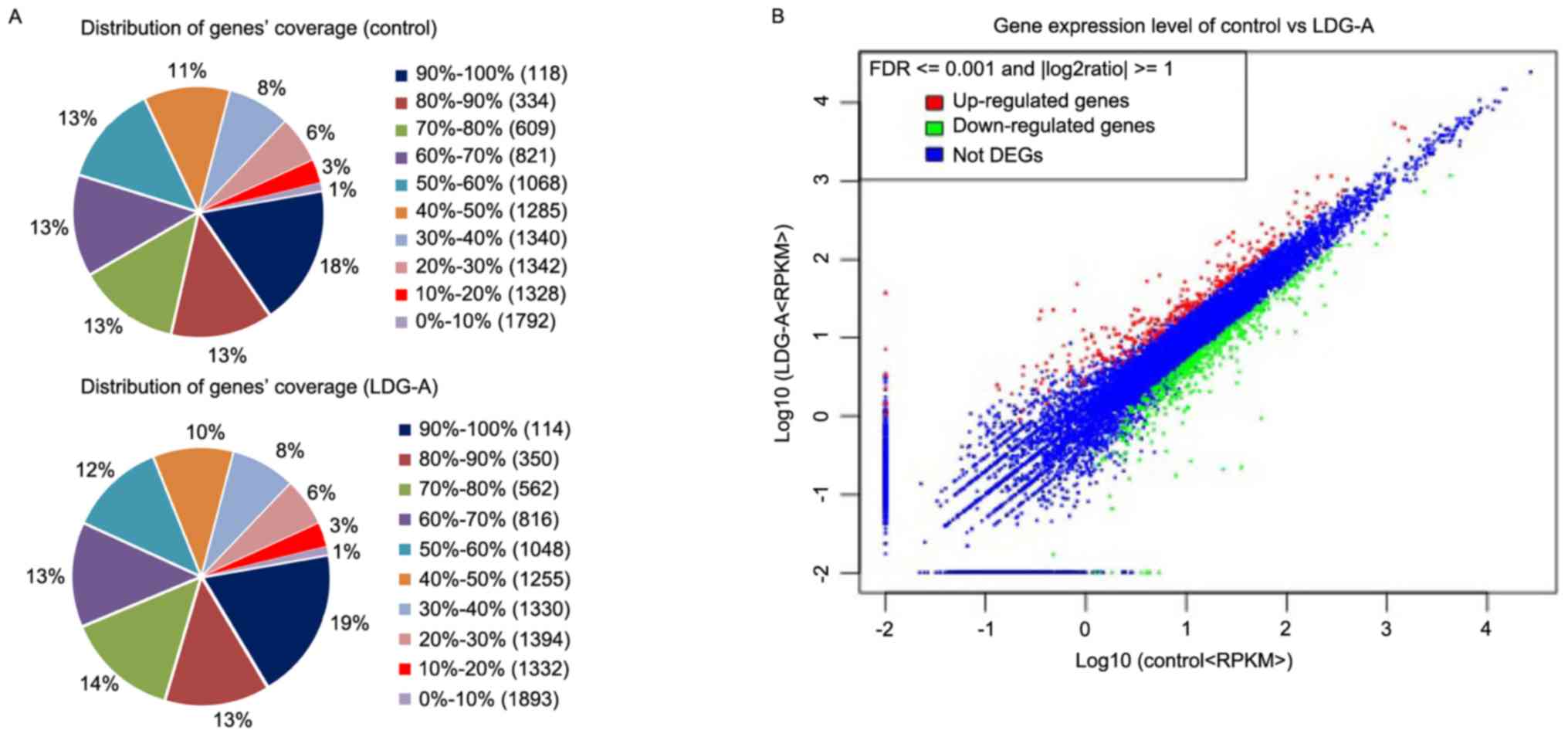
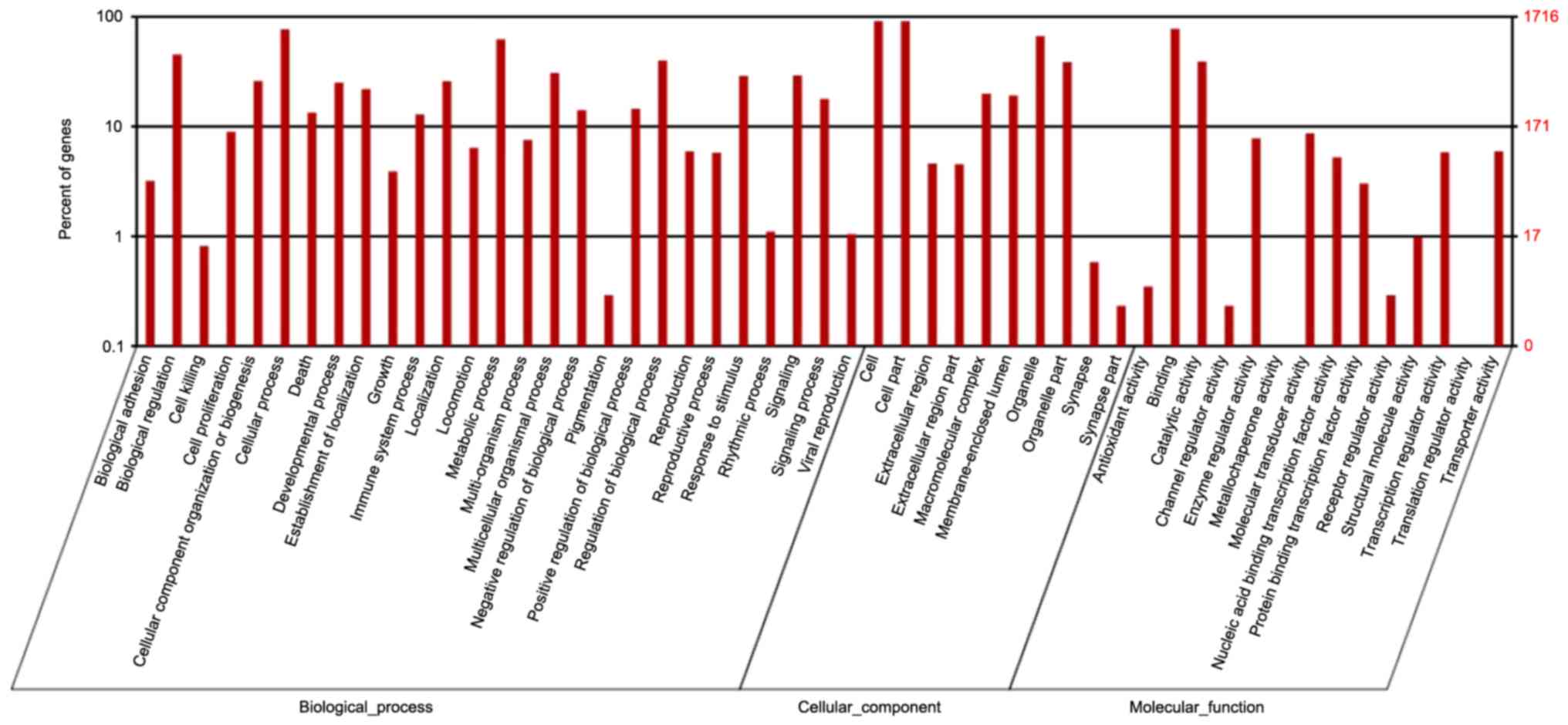
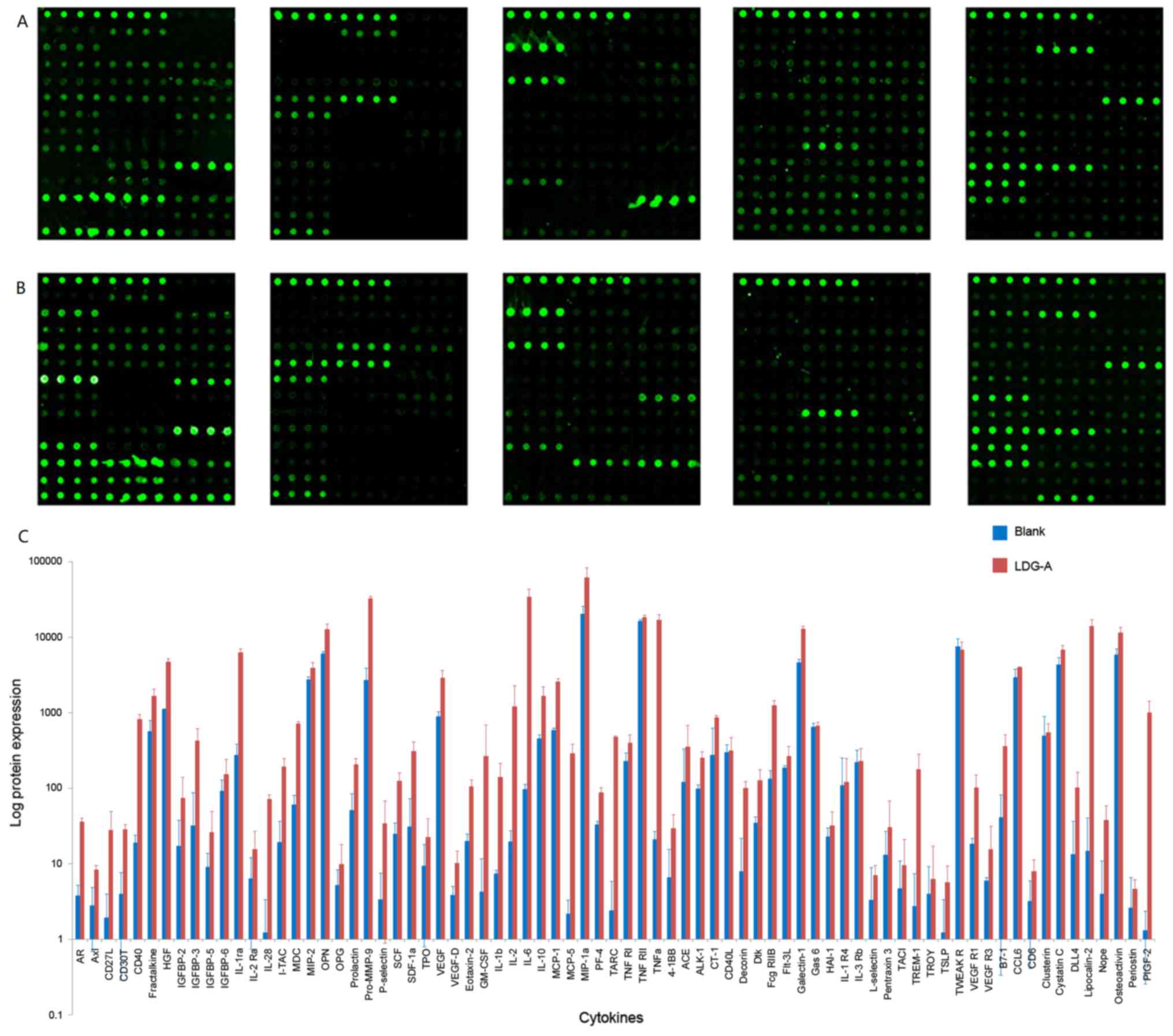
|
1
|
Song G and Du Q: Structure
characterization and antitumor activity of an α β-glucan
polysaccharide from auricularia polytricha. Food Res Int.
45:381–387. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Schepetkin I and Quinn M: Botanical
polysaccharides: Macrophage immunomodulation and therapeutic
potential. Int Immunopharmacol. 6:317–333. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhao Z, Li J, Wu X, Dai H, Gao X and Liu
M: Structures and immunological activities of two pectic
polysaccharides from the fruits of Ziziphus jujuba Mill. cv.
jinsixiaozao Hort. Food Res Int. 39:917–923. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lee K and Jeon Y: Macrophage activation by
polysaccharide isolated from astragalus membranaceus. Int
Immunopharmacol. 5:1225–1233. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Song JY, Han SK, Son EH, Pyo SN, Yun YS
and Yi SY: Induction of secretory and tumoricidal activities in
peritoneal macrophages by ginsan. Int Immunopharmacol. 2:857–865.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ma H, Liu G, Ding W, Wu Y, Cai L and Zhao
Y: Diabetes-induced alteration of F4/80+ macrophages: A study in
mice with streptozotocin-induced diabetes for a long term. J Mol
Med (Berl). 86:391–400. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Di Carlo E, Forni G, Lollini P, Colombo M,
Modesti A and Musiani P: The intriguing role of polymorphonuclear
neutrophils in antitumor reactions. Blood. 97:339–345. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen G and Goeddel D: TNF-R1 signaling: A
beautiful pathway. Science. 296:1634–1635. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng A, Wan F, Wang J, Jin Z and Xu X:
Macrophage immunomodulatory activity of polysaccharides isolated
from Glycyrrhiza uralensis fish. Int Immunopharmacol. 8:43–50.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chihara G, Maeda Y, Hamuro J, Sasaki T and
Fukuoka F: Inhibition of mouse sarcoma 180 by polysaccharides from
Lentinus edodes (Berk.) sing. Nature. 222:687–688. 1969. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kobayashi H, Yoshida R, Kanada Y, Fukuda
Y, Yagyu T, Inagaki K, Kondo T, Kurita N, Suzuki M and Terao T:
Suppressing effects of daily oral supplementation of beta-glucan
extracted from agaricus blazei Murill on spontaneous and peritoneal
disseminated metastasis in mouse model. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
131:527–538. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nakazato H, Koike A, Saji S, Ogawa N and
Sakamoto J: Efficacy of immunochemotherapy as adjuvant treatment
after curative resection of gastric cancer. Study Group of
Immunochemotherapy with PSK for gastric cancer. Lancet.
343:1122–1126. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shin JY, Song JY, Yun YS, Yang HO, Rhee DK
and Pyo S: Immunostimulating effects of acidic polysaccharides
extract of panax ginseng on macrophage function. Immunopharmacol
Immunotoxicol. 24:469–482. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ding X, Hou Y and Hou W: Structure feature
and antitumor activity of a novel polysaccharide isolated from
Lactarius deliciosus Gray. Carbohydr Polym. 89:397–402.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hou Y, Ding X, Hou W, Song B, Wang T, Wang
F and Zhong J: Immunostimulant activity of a novel polysaccharide
isolated from Lactarius deliciosus (L. ex Fr.) gray. Indian
J Pharm Sci. 75:393–399. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jianwei G, Jianzhong L, Bin L and
Zhensheng L: Isolation and purification of functional total RNA
from blue-grained wheat endosperm tissues containing high levels of
starches and flavonoids. Plant Mol Biol Rep. 19:185–186. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wagner GP, Kin K and Lynch VJ: Measurement
of mRNA abundance using RNA-seq data: RPKM measure is inconsistent
among samples. Theor Biosc. 131:281–285. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang Y, Meng Q, Jiang T, Wang H, Xie L
and Zhang R: A novel ferritin subunit involved in shell formation
from the pearl oyster (Pinctada fucata). Comp Biochem Physiol B
Biochem Mol Biol. 135:43–54. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Honarmand Ebrahimi K, Bill E, Hagedoorn P
and Hagen W: The catalytic center of ferritin regulates iron
storage via Fe(II)-Fe(III) displacement. Nat Chem Biol. 8:941–948.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Orton R, Sturm O, Vyshemirsky V, Calder M,
Gilbert D and Kolch W: Computational modelling of the
receptor-tyrosine-kinase-activated MAPK pathway. Biochem J.
392:249–261. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Herbst R: Review of epidermal growth
factor receptor biology. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 59 Suppl
2:S21–S26. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Nagashima T, Suzuki T, Kondo S, Kuroki Y,
Takahashi K, Ide K, Yumoto N, Hasegawa A, Toyoda T, Kojima T, et
al: Integrative genome-wide expression analysis bears evidence of
estrogen receptor-independent transcription in heregulin-stimulated
MCF-7 cells. PLoS One. 3:e18032008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|