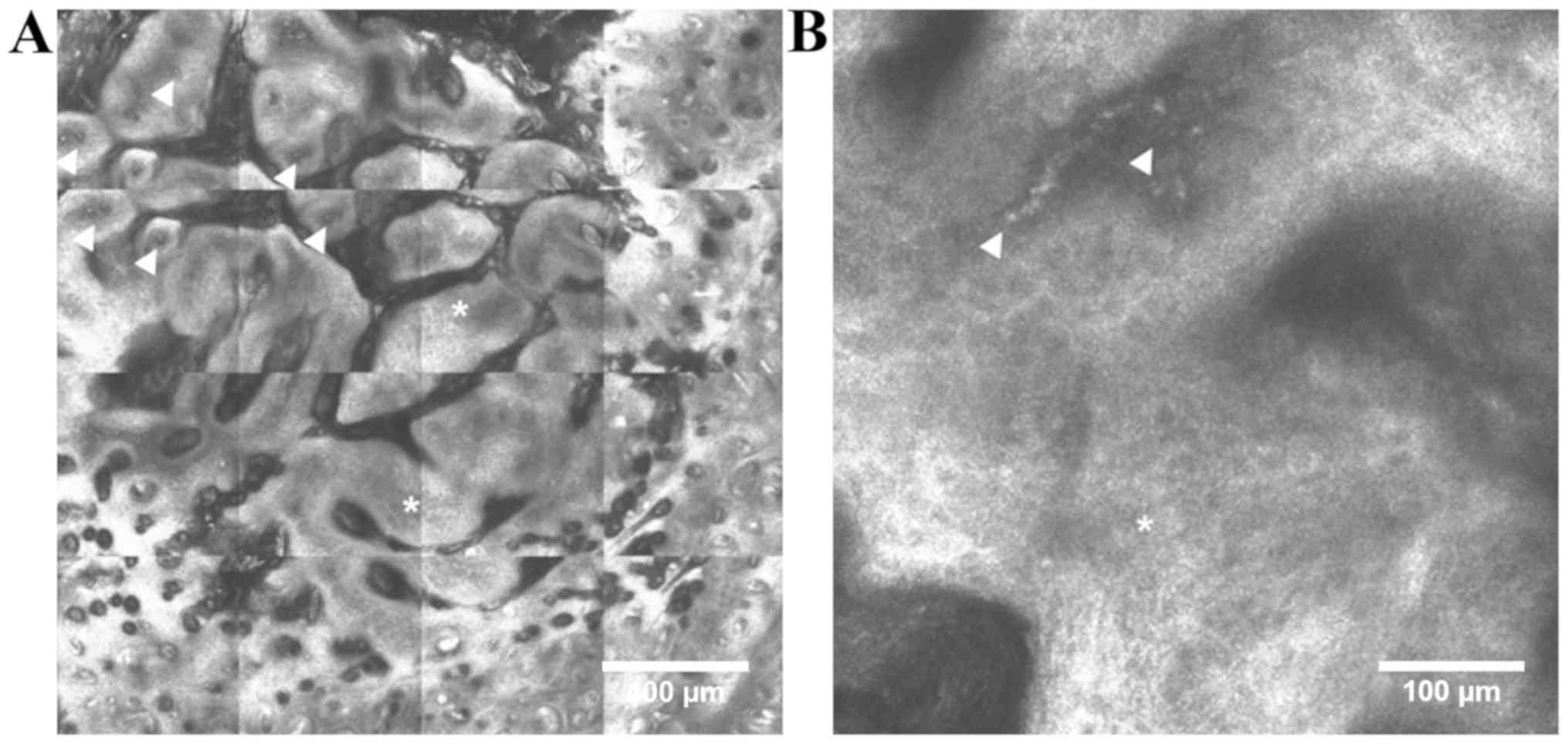
|
1
|
Diaconeasa A, Boda D, Neagu M, Constantin
C, Căruntu C, Vlădău L and Guţu D: The role of confocal microscopy
in the dermato-oncology practice. J Med Life. 4:63–74.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Aghassi D, González E, Anderson RR,
Rajadhyaksha M and González S: Elucidating the pulsed-dye laser
treatment of sebaceous hyperplasia in vivo with real-time confocal
scanning laser microscopy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 43:49–53. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
González S, Swindells K, Rajadhyaksha M
and Torres A: Changing paradigms in dermatology: Confocal
microscopy in clinical and surgical dermatology. Clin Dermatol.
21:359–369. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rajadhyaksha M, González S, Zavislan JM,
Anderson RR and Webb RH: In vivo confocal scanning laser microscopy
of human skin II: Advances in instrumentation and comparison with
histology. J Invest Dermatol. 113:293–303. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
González S, Sackstein R, Anderson RR and
Rajadhyaksha M: Real-time evidence of in vivo leukocyte trafficking
in human skin by reflectance confocal microscopy. J Invest
Dermatol. 117:384–386. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Peppelman M, Wolberink EA, Gerritsen MJ,
van de Kerkhof PC and van Erp PE: Application of leukotriene B4 and
reflectance confocal microscopy as a noninvasive in vivo model to
study the dynamics of skin inflammation. Skin Res Technol.
21:232–240. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Batani A, Brănișteanu DE, Ilie MA, Boda D,
Ianosi S, Ianosi G and Caruntu C: Assessment of dermal papillary
and microvascular parameters in psoriasis vulgaris using in vivo
reflectance confocal microscopy. Exp Ther Med. 15:1241–1246.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Căruntu C, Boda D, Căruntu A, Rotaru M,
Baderca F and Zurac S: In vivo imaging techniques for psoriatic
lesions. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 55 (Suppl 3):1191–1196.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ghiţă MA, Căruntu C, Rosca AE, Căruntu A,
Moraru L, Constantin C, Neagu M and Boda D: Real-time investigation
of skin blood flow changes induced by topical capsaicin. Acta
Dermatovenerol Croat. 25:223–227. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Căruntu C and Boda D: Evaluation through
in vivo reflectance confocal microscopy of the cutaneous neurogenic
inflammatory reaction induced by capsaicin in human subjects. J
Biomed Opt. 17:0850032012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Okabe M, Ikawa M, Kominami K, Nakanishi T
and Nishimune Y: ‘Green mice’ as a source of ubiquitous green
cells. FEBS Lett. 407:313–319. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Meyer LE, Otberg N, Sterry W and Lademann
J: In vivo confocal scanning laser microscopy: Comparison of the
reflectance and fluorescence mode by imaging human skin. J Biomed
Opt. 11:0440122006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Skvara H, Plut U, Schmid JA and Jonak C:
Combining in vivo reflectance with fluorescence confocal microscopy
provides additive information on skin morphology. Dermatol Pract
Concept. 2:3–12. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rajadhyaksha M, Grossman M, Esterowitz D,
Webb RH and Anderson RR: In vivo confocal scanning laser microscopy
of human skin: Melanin provides strong contrast. J Invest Dermatol.
104:946–952. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pellacani G, Guitera P, Longo C, Avramidis
M, Seidenari S and Menzies S: The impact of in vivo reflectance
confocal microscopy for the diagnostic accuracy of melanoma and
equivocal melanocytic lesions. J Invest Dermatol. 127:2759–2765.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guida S, Longo C, Casari A, Ciardo S,
Manfredini M, Reggiani C, Pellacani G and Farnetani F: Update on
the use of confocal microscopy in melanoma and non-melanoma skin
cancer. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 150:547–563. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pellacani G, De Pace B, Reggiani C,
Cesinaro AM, Argenziano G, Zalaudek I, Soyer HP and Longo C:
Distinct melanoma types based on reflectance confocal microscopy.
Exp Dermatol. 23:414–418. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Serban ED, Farnetani F, Pellacani G and
Constantin MM: Role of in vivo reflectance confocal microscopy in
the analysis of melanocytic lesions. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat.
26:64–67. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
González S, Sánchez V, González-Rodríguez
A, Parrado C and Ullrich M: Confocal microscopy patterns in
nonmelanoma skin cancer and clinical applications. Actas
Dermosifiliogr. 105:446–458. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Białek-Galas K, Wielowieyska-Szybińska D,
Dyduch G and Wojas-Pelc A: The use of reflectance confocal
microscopy in selected inflammatory skin diseases. Pol J Pathol.
66:103–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Constantin MM, Bucur S, Serban DE, Caruntu
C, Orzan OA and Constantin T: Dermoscopic and laser confocal
features of an exogenous ochronosis case. G Ital Dermatol Venereol.
Jun 29–2018.(Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lange-Asschenfeldt S, Bob A, Terhorst D,
Ulrich M, Fluhr J, Mendez G, Roewert-Huber HJ, Stockfleth E and
Lange-Asschenfeldt B: Applicability of confocal laser scanning
microscopy for evaluation and monitoring of cutaneous wound
healing. J Biomed Opt. 17:0760162012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Altintas AA, Altintas MA, Ipaktchi K,
Guggenheim M, Theodorou P, Amini P and Spilker G: Assessment of
microcirculatory influence on cellular morphology in human burn
wound healing using reflectance-mode-confocal microscopy. Wound
Repair Regen. 17:498–504. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Altintas AA, Guggenheim M, Oezcelik A,
Gehl B, Aust MC and Altintas MA: Local burn versus local cold
induced acute effects on in vivo microcirculation and
histomorphology of the human skin. Microsc Res Tech. 74:963–969.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Longo C, Ragazzi M, Rajadhyaksha M, Nehal
K, Bennassar A, Pellacani G and Malvehy Guilera J: In vivo and ex
vivo confocal microscopy for dermatologic and Mohs surgeons.
Dermatol Clin. 34:497–504. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bennàssar A, Vilata A, Puig S and Malvehy
J: Ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy for fast evaluation of
tumour margins during Mohs surgery. Br J Dermatol. 170:360–365.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Miller DL and Weinstock MA: Nonmelanoma
skin cancer in the United States: Incidence. J Am Acad Dermatol.
30:774–778. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lomas A, Leonardi-Bee J and Bath-Hextall
F: A systematic review of worldwide incidence of nonmelanoma skin
cancer. Br J Dermatol. 166:1069–1080. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen CS, Sierra H, Cordova M and
Rajadhyaksha M: Confocal microscopy-guided laser ablation for
superficial and early nodular Basal cell carcinoma: A promising
surgical alternative for superficial skin cancers. JAMA Dermatol.
150:994–998. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lupu M, Caruntu C, Ghita MA, Voiculescu V,
Voiculescu S, Rosca AE, Caruntu A, Moraru L, Popa IM, Calenic B, et
al: Gene expression and proteome analysis as sources of biomarkers
in basal cell carcinoma. Dis Markers. 2016:98312372016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ghita MA, Caruntu C, Rosca AE, Kaleshi H,
Caruntu A, Moraru L, Docea AO, Zurac S, Boda D, Neagu M, et al:
Reflectance confocal microscopy and dermoscopy for in vivo,
non-invasive skin imaging of superficial basal cell carcinoma.
Oncol Lett. 11:3019–3024. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Longo C, Lallas A, Kyrgidis A, Rabinovitz
H, Moscarella E, Ciardo S, Zalaudek I, Oliviero M, Losi A, Gonzalez
S, et al: Classifying distinct basal cell carcinoma subtype by
means of dermatoscopy and reflectance confocal microscopy. J Am
Acad Dermatol. 71:716–724. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Căruntu C, Boda D, Guţu DE and Căruntu A:
In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy of basal cell carcinoma
with cystic degeneration. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 55:1437–1441.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Peppelman M, Wolberink EA, Blokx WA, van
de Kerkhof PC, van Erp PE and Gerritsen MJ: In vivo diagnosis of
basal cell carcinoma subtype by reflectance confocal microscopy.
Dermatology. 227:255–262. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nori S, Rius-Díaz F, Cuevas J, Goldgeier
M, Jaen P, Torres A and González S: Sensitivity and specificity of
reflectance-mode confocal microscopy for in vivo diagnosis of basal
cell carcinoma: A multicenter study. J Am Acad Dermatol.
51:923–930. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
González S and Tannous Z: Real-time, in
vivo confocal reflectance microscopy of basal cell carcinoma. J Am
Acad Dermatol. 47:869–874. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Stephens A, Fraga-Braghiroli N, Oliviero
M, Rabinovitz H and Scope A: Spoke wheel-like structures in
superficial basal cell carcinoma: A correlation between dermoscopy,
histopathology, and reflective confocal microscopy. J Am Acad
Dermatol. 69:e219–e221. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ulrich M, Roewert-Huber J, González S,
Rius-Diaz F, Stockfleth E and Kanitakis J: Peritumoral clefting in
basal cell carcinoma: Correlation of in vivo reflectance confocal
microscopy and routine histology. J Cutan Pathol. 38:190–195. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Que SK, Fraga-Braghiroli N, Grant-Kels JM,
Rabinovitz HS, Oliviero M and Scope A: Through the looking glass:
Basics and principles of reflectance confocal microscopy. J Am Acad
Dermatol. 73:276–284. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lupu M, Caruntu C, Solomon I, Popa A,
Lisievici C, Draghici C, Papagheorghe L, Voiculescu VM and
Giurcaneanu C: The use of in vivo reflectance confocal microscopy
and dermoscopy in the preoperative determination of basal cell
carcinoma histopathological subtypes. DermatoVenerol. 62:7–13.
2017.
|
|
41
|
Segura S, Puig S, Carrera C, Palou J and
Malvehy J: Dendritic cells in pigmented basal cell carcinoma: A
relevant finding by reflectance-mode confocal microscopy. Arch
Dermatol. 143:883–886. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pan ZY, Lin JR, Cheng TT, Wu JQ and Wu WY:
In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy of basal cell carcinoma:
Feasibility of preoperative mapping of cancer margins. Dermatol
Surg. 38:1945–1950. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Webber SA, Wurm EMT, Douglas NC, Lambie D,
Longo C, Pellacani G and Soyer HP: Effectiveness and limitations of
reflectance confocal microscopy in detecting persistence of basal
cell carcinomas: A preliminary study. Australas J Dermatol.
52:179–185. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ahlgrimm-Siess V, Horn M, Koller S, Ludwig
R, Gerger A and Hofmann-Wellenhof R: Monitoring efficacy of
cryotherapy for superficial basal cell carcinomas with in vivo
reflectance confocal microscopy: A preliminary study. J Dermatol
Sci. 53:60–64. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Voiculescu V, Calenic B, Ghita M, Lupu M,
Caruntu A, Moraru L, Voiculescu S, Ion A, Greabu M, Ishkitiev N, et
al: From normal skin to squamous cell carcinoma: A quest for novel
biomarkers. Dis Markers. 2016:45174922016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Boda D, Neagu M, Constantin C, Voinescu
RN, Caruntu C, Zurac S, Spandidos DA, Drakoulis N, Tsoukalas D and
Tsatsakis AM: HPV strain distribution in patients with genital
warts in a female population sample. Oncol Lett. 12:1779–1782.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Boda D, Docea AO, Calina D, Ilie MA,
Caruntu C, Zurac S, Neagu M, Constantin C, Branisteanu DE,
Voiculescu V, et al: Human papilloma virus: Apprehending the link
with carcinogenesis and unveiling new research avenues (Review).
Int J Oncol. 52:637–655. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Georgescu SR, Sârbu MI, Matei C, Ilie MA,
Caruntu C, Constantin C, Neagu M and Tampa M: Capsaicin: Friend or
foe in skin cancer and other related malignancies? Nutrients.
9:13652017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Lupu M, Caruntu A, Caruntu C, Papagheorghe
LML, Ilie MA, Voiculescu V, Boda D, Constantin C, Tanase C, Sifaki
M, et al: Neuroendocrine factors: The missing link in non-melanoma
skin cancer (Review). Oncol Rep. 38:1327–1340. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Solomon I, Voiculescu VM, Caruntu C, Lupu
M, Popa A, Ilie MA, Albulescu R, Caruntu A, Tanase C, Constantin C,
et al: Neuroendocrine factors and head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma: An affair to remember. Dis Markers. 2018:97878312018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tampa M, Caruntu C, Mitran M, Mitran C,
Sarbu I, Rusu LC, Matei C, Constantin C, Neagu M and Georgescu SR:
Markers of oral lichen planus malignant transformation. Dis
Markers. 2018:19595062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
González S and Ahlgrimm-Siess V:
Reflectance confocal microscopy in dermatology: Fundamentals and
clinical applications. Aula Médica. p1112012.
|
|
53
|
Rossi R, Mori M and Lotti T: Actinic
keratosis. Int J Dermatol. 46:895–904. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wolff K and Johnson RA: Fitzpatrick's
Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology. 6th. McGraw-Hill;
New York, NY: pp. 267–270. 2009
|
|
55
|
Aghassi D, Anderson RR and González S:
Confocal laser microscopic imaging of actinic keratoses in vivo: A
preliminary report. J Am Acad Dermatol. 43:42–48. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Peppelman M, Nguyen KP, Hoogedoorn L, van
Erp PE and Gerritsen MJ: Reflectance confocal microscopy:
Non-invasive distinction between actinic keratosis and squamous
cell carcinoma. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 29:1302–1309. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Rishpon A, Kim N, Scope A, Porges L,
Oliviero MC, Braun RP, Marghoob AA, Fox CA and Rabinovitz HS:
Reflectance confocal microscopy criteria for squamous cell
carcinomas and actinic keratoses. Arch Dermatol. 145:766–772. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Branzan AL, Landthaler M and Szeimies RM:
In vivo confocal scanning laser microscopy in dermatology. Lasers
Med Sci. 22:73–82. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chung VQ, Dwyer PJ, Nehal KS, Rajadhyaksha
M, Menaker GM, Charles C and Jiang SB: Use of ex vivo confocal
scanning laser microscopy during Mohs surgery for nonmelanoma skin
cancers. Dermatol Surg. 30:1470–1478. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lupu M, Caruntu A, Caruntu C, Boda D,
Moraru L, Voiculescu V and Bastian A: Non-invasive imaging of
actinic cheilitis and squamous cell carcinoma of the lip. Mol Clin
Oncol. 8:640–646. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Clark AL, Gillenwater AM, Collier TG,
Alizadeh-Naderi R, El-Naggar AK and Richards-Kortum RR: Confocal
microscopy for real-time detection of oral cavity neoplasia. Clin
Cancer Res. 9:4714–4721. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zurac S, Neagu M, Constantin C, Cioplea M,
Nedelcu R, Bastian A, Popp C, Nichita L, Andrei R, Tebeica T, et
al: Variations in the expression of TIMP1, TIMP2 and TIMP3 in
cutaneous melanoma with regression and their possible function as
prognostic predictors. Oncol Lett. 11:3354–3360. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Neagu M, Constantin C and Zurac S: Immune
parameters in the prognosis and therapy monitoring of cutaneous
melanoma patients: Experience, role, and limitations. BioMed Res
Int. 2013:1079402013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Neagu M, Constantin C, Manda G and
Margaritescu I: Biomarkers of metastatic melanoma. Biomarkers Med.
3:71–89. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Neagu M, Constantin C and Tanase C:
Immune-related biomarkers for diagnosis/prognosis and therapy
monitoring of cutaneous melanoma. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 10:897–919.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Surcel M, Constantin C, Caruntu C, Zurac S
and Neagu M: Inflammatory cytokine pattern is sex-dependent in
mouse cutaneous melanoma experimental model. J Immunol Res.
2017:92121342017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Caruntu C, Mirica A, Rosca A, Mirica R,
Caruntu A, Tampa M, Matei C, Constantin C, Neagu M, Badarau A, et
al: The role of estrogens and estrogen receptors in melanoma
development and progression. Acta Endo Buc. 12:234–241. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Caruntu C, Boda D, Constantin C, Caruntu A
and Neagu M: Catecholamines increase in vitro proliferation of
murine B16F10 melanoma cells. Acta Endo Buc. 10:545–558. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Neagu M, Constantin C, Dumitrascu GR, Lupu
AR, Caruntu C, Boda D and Zurac S: Inflammation markers in
cutaneous melanoma - edgy biomarkers for prognosis. Discoveries
(Craiova). 3:e382015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Ene CD, Anghel AE, Neagu M and Nicolae I:
25-OH vitamin D and interleukin-8: Emerging biomarkers in cutaneous
melanoma development and progression. Mediators Inflamm.
2015:9048762015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Solovastru LG, Vâta D, Statescu L,
Constantin MM and Andrese E: Skin cancer between myth and reality,
yet ethically constrained. Rev Rom Bioet. 12:47–52. 2014.
|
|
72
|
Rigel DS, Friedman RJ, Kopf AW and Polsky
D: ABCDE - an evolving concept in the early detection of melanoma.
Arch Dermatol. 141:1032–1034. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Grob JJ and Bonerandi JJ: The ‘ugly
duckling’ sign: Identification of the common characteristics of
nevi in an individual as a basis for melanoma screening. Arch
Dermatol. 134:103–104. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Hansen C, Wilkinson D, Hansen M and
Argenziano G: How good are skin cancer clinics at melanoma
detection? Number needed to treat variability across a national
clinic group in Australia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 61:599–604. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Sidhu S, Bodger O, Williams N and Roberts
DL: The number of benign moles excised for each malignant melanoma:
The number needed to treat. Clin Exp Dermatol. 37:6–9. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Goodson AG, Florell SR, Hyde M, Bowen GM
and Grossman D: Comparative analysis of total body and
dermatoscopic photographic monitoring of nevi in similar patient
populations at risk for cutaneous melanoma. Dermatol Surg.
36:1087–1098. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Moloney FJ, Guitera P, Coates E, Haass NK,
Ho K, Khoury R, O'Connell RL, Raudonikis L, Schmid H, Mann GJ, et
al: Detection of primary melanoma in individuals at extreme high
risk: A prospective 5-year follow-up study. JAMA Dermatol.
150:819–827. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
March J, Hand M and Grossman D: Practical
application of new technologies for melanoma diagnosis: Part I.
Noninvasive approaches. J Am Acad Dermatol. 72:929–942. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ulrich M and Lange-Asschenfeldt S: In vivo
confocal microscopy in dermatology: From research to clinical
application. J Biomed Opt. 18:0612122013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Carrera C, Puig S and Malvehy J: In vivo
confocal reflectance microscopy in melanoma. Dermatol Ther
(Heidelb). 25:410–422. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Longo C, Farnetani F, Ciardo S, Cesinaro
AM, Moscarella E, Ponti G, Zalaudek I, Argenziano G and Pellacani
G: Is confocal microscopy a valuable tool in diagnosing nodular
lesions? A study of 140 cases. Br J Dermatol. 169:58–67. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Gerger A, Koller S, Weger W, Richtig E,
Kerl H, Samonigg H, Krippl P and Smolle J: Sensitivity and
specificity of confocal laser-scanning microscopy for in vivo
diagnosis of malignant skin tumors. Cancer. 107:193–200. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Sokołowska-Wojdyło M, Olek-Hrab K and
Ruckemann-Dziurdzińska K: Primary cutaneous lymphomas: Diagnosis
and treatment. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 32:368–383. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Ion A, Popa IM, Papagheorghe LML,
Lisievici C, Lupu M, Voiculescu V, Caruntu C and Boda D: Proteomic
approaches to biomarker discovery in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Dis
Markers. 2016:96024722016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Fabbrocini G, Mazzella C, Cantelli M,
Baldo A, Russo D, De Rosa G and Monfrecola G: Reflectance confocal
microscopy as new diagnostic tool in folliculotropic mycosis
fungoides. Skin Appendage Disord. 4:118–121. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Mancebo SE, Cordova M, Myskowski PL,
Flores ES, Busam K, Jawed SI, Skripnik A, Rajadhyaksha M and
Querfeld C: Reflectance confocal microscopy features of mycosis
fungoides and Sézary syndrome: Correlation with histopathologic and
T-cell receptor rearrangement studies. J Cutan Pathol. 43:505–515.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Li W, Dai H, Li Z and Xu AE: Reflectance
confocal microscopy for the characterization of mycosis fungoides
and correlation with histology: A pilot study. Skin Res Technol.
19:352–355. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Lange-Asschenfeldt S, Babilli J, Beyer M,
Ríus-Diaz F, González S, Stockfleth E and Ulrich M: Consistency and
distribution of reflectance confocal microscopy features for
diagnosis of cutaneous T cell lymphoma. J Biomed Opt.
17:0160012012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Koller S, Gerger A, Ahlgrimm-Siess V,
Weger W, Smolle J and Hofmann-Wellenhof R: In vivo reflectance
confocal microscopy of erythematosquamous skin diseases. Exp
Dermatol. 18:536–540. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Agero AL, Gill M, Ardigo M, Myskowski P,
Halpern AC and González S: In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy
of mycosis fungoides: A preliminary study. J Am Acad Dermatol.
57:435–441. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Ardigò M, Donadio C, Vega H, Cota C,
Moscarella E and Agozzino M: Concordance between in vivo
reflectance confocal microscopy and optical histology of
lymphomatoid papulosis. Skin Res Technol. 19:308–313. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Ardigò M, El Shabrawi-Caelen L and Tosti
A: In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy assessment of the
therapeutic follow-up of cutaneous T-cell lymphomas causing scalp
alopecia. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 27:248–251. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
de Vries E, Trakatelli M, Kalabalikis D,
Ferrandiz L, Ruiz-de-Casas A, Moreno-Ramirez D, Sotiriadis D,
Ioannides D, Aquilina S, Apap C, et al EPIDERM Group, : Known and
potential new risk factors for skin cancer in European populations:
A multicentre case-control study. Br J Dermatol. 167 (Suppl
2):1–13. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Maru GB, Gandhi K, Ramchandani A and Kumar
G: The role of inflammation in skin cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol.
816:437–469. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Neagu M, Caruntu C, Constantin C, Boda D,
Zurac S, Spandidos DA and Tsatsakis AM: Chemically induced skin
carcinogenesis: Updates in experimental models (Review). Oncol Rep.
35:2516–2528. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Abel EL, Angel JM, Kiguchi K and
DiGiovanni J: Multi-stage chemical carcinogenesis in mouse skin:
Fundamentals and applications. Nat Protoc. 4:1350–1362. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Hashemi P, Pulitzer MP, Scope A,
Kovalyshyn I, Halpern AC and Marghoob AA: Langerhans cells and
melanocytes share similar morphologic features under in vivo
reflectance confocal microscopy: A challenge for melanoma
diagnosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 66:452–462. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Li Y, Gonzalez S, Terwey TH, Wolchok J, Li
Y, Aranda I, Toledo-Crow R and Halpern AC: Dual mode reflectance
and fluorescence confocal laser scanning microscopy for in vivo
imaging melanoma progression in murine skin. J Invest Dermatol.
125:798–804. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Izatt JA, Kulkarni MD, Hsing-Wen W,
Kobayashi K and Sivak MV: Optical coherence tomography and
microscopy in gastrointestinal tissues. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum
Electron. 2:1017–1028. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Ono I, Sakemoto A, Ogino J, Kamiya T,
Yamashita T and Jimbow K: The real-time, three-dimensional analyses
of benign and malignant skin tumors by confocal laser scanning
microscopy. J Dermatol Sci. 43:135–141. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Skvara H, Kittler H, Schmid JA, Plut U and
Jonak C: In vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy: Indocyanine
green enhances the contrast of epidermal and dermal structures. J
Biomed Opt. 16:0960102011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|