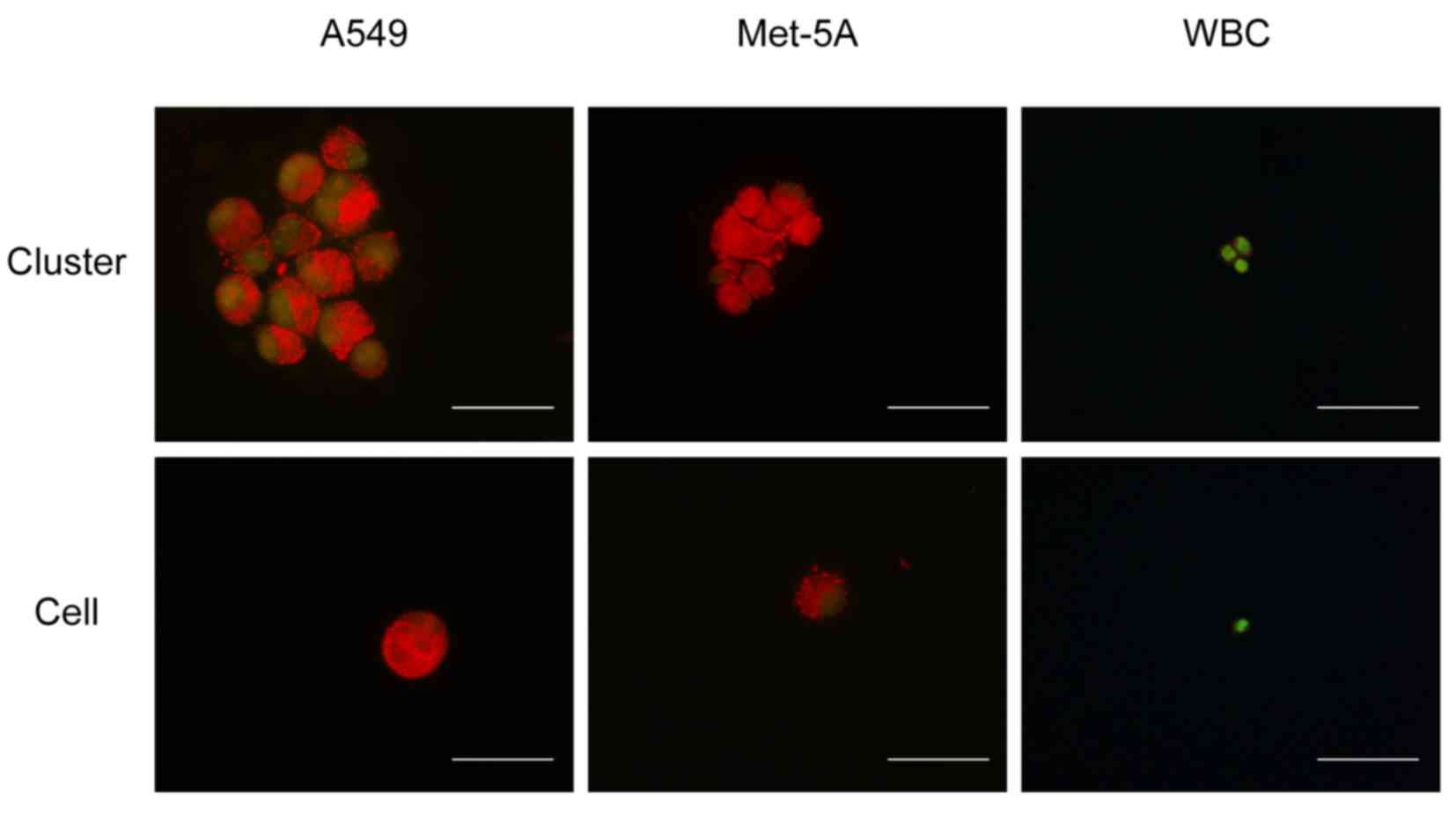
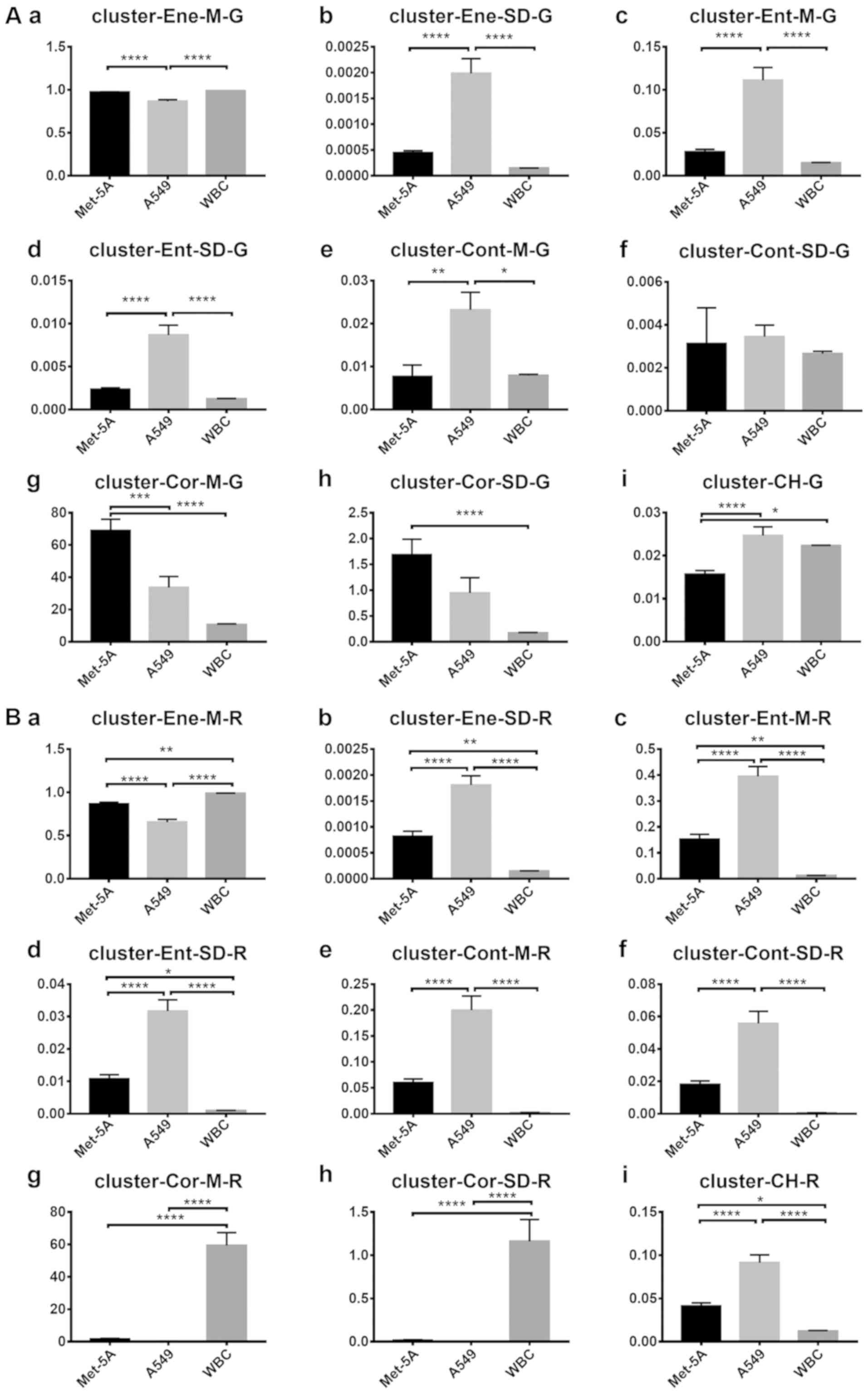
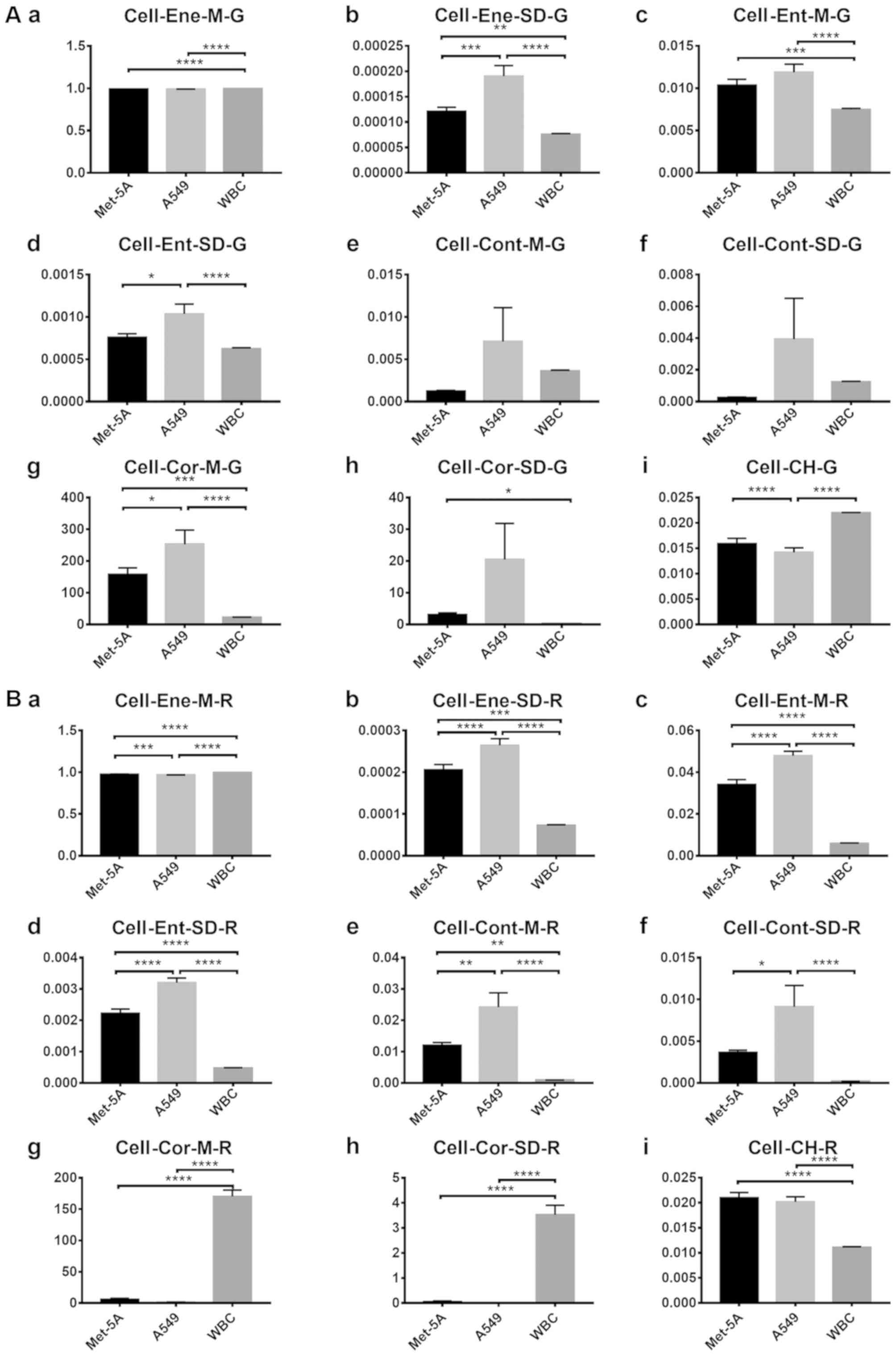
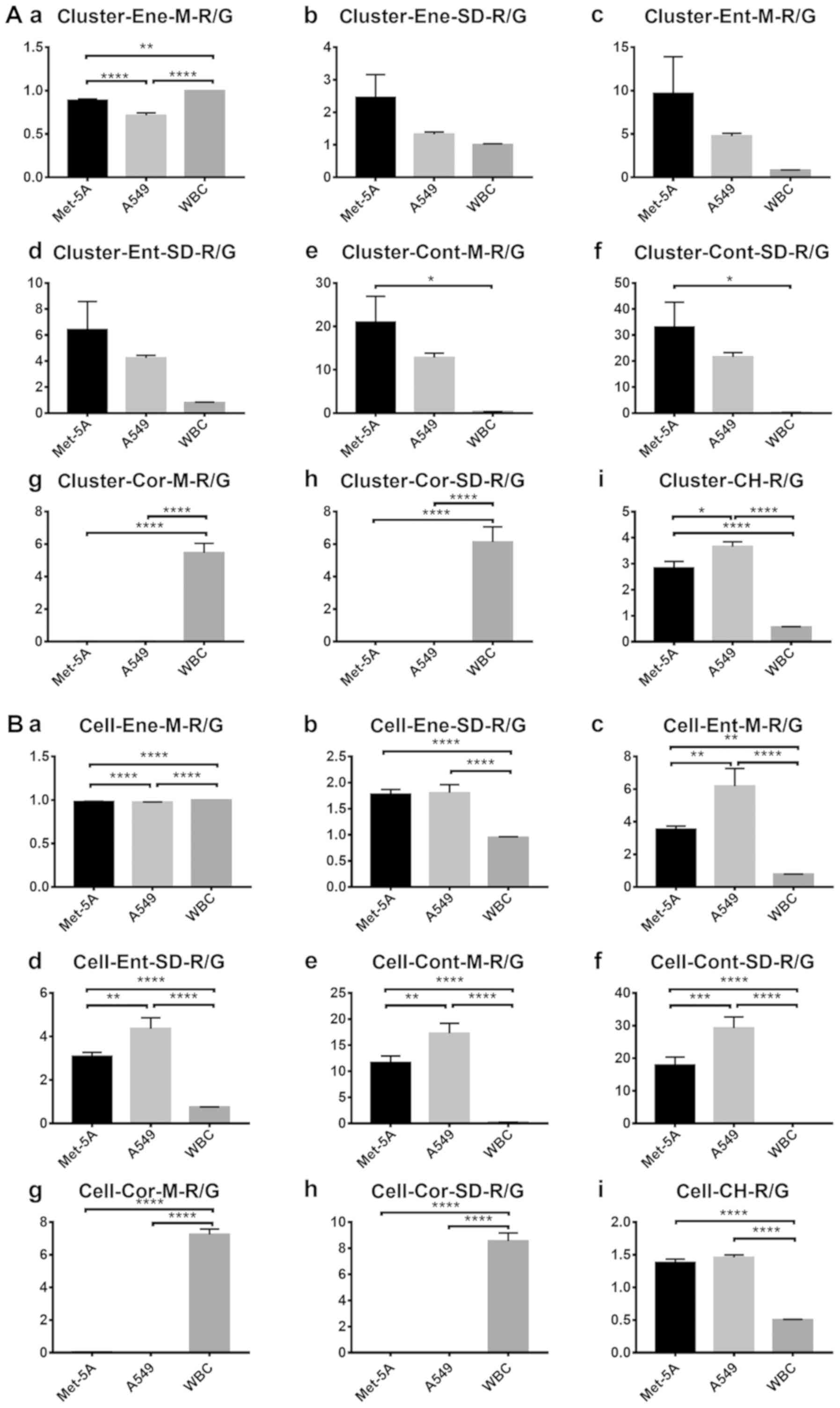
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Toufektzian L, Sepsas E, Drossos V,
Gkiozos I and Syrigos K: Pleural lavage cytology: Where do we
stand? Lung Cancer. 83:14–22. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tsuchido K, Yamada M, Satou T, Otsuki Y,
Shimizu S and Kobayashi H: Cytology of sclerosing epithelioid
fibrosarcoma in pleural effusion. Diagn Cytopathol. 38:748–753.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang CC and Michael CW: Cytomorphological
features of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma in serous effusions.
Cytopathology. 25:112–119. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Omori M, Kondo T, Yuminamochi T, Nakazawa
K, Ishii Y, Fukasawa H, Hashi A and Hirata S: Cytologic features of
ovarian granulosa cell tumors in pleural and ascitic fluids. Diagn
Cytopathol. 43:581–584. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kosmas K, Tsonou A, Mitropoulou G, Salemi
E, Kazi D and Theofanopoulou A: Malignant pleural effusion from
papillary thyroid carcinoma diagnosed by pleural effusion cytology:
A case report. Diagn Cytopathol. 46:204–207. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ferreiro L, Toubes ME and Valdes L:
Contribution of pleural fluid analysis to the diagnosis of pleural
effusion. Med Clin (Barc). 145:171–177. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Che J, Mach AJ, Go DE, Talati I, Ying Y,
Rao J, Kulkarni RP and Di Carlo D: Microfluidic purification and
concentration of malignant pleural effusions for improved molecular
and cytomorphological diagnostics. PLoS One. 8:e781942013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rashmi K, Shashikala P, Hiremath S and
Basavaraj HG: Cells in pleural fluid and their value in
differential diagnosis. J Cytology. 25:138–143. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Attanoos RL, Galateau-Salle F, Gibbs AR,
Muller S, Ghandour F and Dojcinov SD: Primary thymic epithelial
tumours of the pleura mimicking malignant mesothelioma.
Histopathology. 41:42–49. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wendel M, Bazhenova L, Boshuizen R,
Kolatkar A, Honnatti M, Cho EH, Marrinucci D, Sandhu A, Perricone
A, Thistlethwaite P, et al: Fluid biopsy for circulating tumor cell
identification in patients with early-and late-stage non-small cell
lung cancer: A glimpse into lung cancer biology. Phys Biol. Feb
9;0160052012.doi: 10.1088/1478-3967/9/1/016005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hsieh TC, Huang WW, Lai CL, Tsao SM and Su
CC: Diagnostic value of tumor markers in lung
adenocarcinoma-associated cytologically negative pleural effusions.
Cancer Cytopathol. 121:883–888. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bisht B, Handa U, Mohan H and Lehl SS:
Complementary value of DNA flow cytometry and image morphometry in
detection of malignant cells in effusion fluids. Malays J Pathol.
36:83–90. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ai T, Tabe Y, Takemura H, Kimura K,
Takahashi T, Yang H, Tsuchiya K, Konishi A, Uchihashi K, Horii T
and Ohsaka A: Novel flowcytometry-based approach of malignant cell
detection in body fluids using an automated hematology analyzer.
PLoS One. 13:e01908862018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Miédougé M, Rouzaud P, Salama G, Pujazon
MC, Vincent C, Mauduyt MA, Reyre J, Carles P and Serre G:
Evaluation of seven tumour markers in pleural fluid for the
diagnosis of malignant effusions. Br J Cancer. 81:1059–1065. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yanaihara N, Caplen N Bowman E, Seike M,
Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens RM, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, et
al: Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and
prognosis. Cancer Cell. 9:189–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hooper C, Lee YC and Maskell N; BTS
Pleural Guideline Group, : Investigation of a unilateral pleural
effusion in adults: British thoracic society pleural disease
guideline 2010. Thorax. 65:ii4–ii17. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Swiderek J, Morcos S, Donthireddy V,
Surapaneni R, Jackson-Thompson V, Schultz L, Kini S and Kvale P:
Prospective study to determine the volume of pleural fluid required
to diagnose malignancy. Chest. 137:68–73. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rooper LM, Ali SZ and Olson MT: A minimum
fluid volume of 75 ml is needed to ensure adequacy in a pleural
effusion: A retrospective analysis of 2540 Cases. Cancer
Cytopathol. 122:657–665. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Scholtens TM, Schreuder F, Ligthart ST,
Swennenhuis JF, Tibbe AGJ, Greve J and Terstappen LW: Cell Tracks
TDI: An image cytometer for cell characterization. Cytometry A.
79:203–213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yasuda K, Hattori A, Kim H, Terazono H,
Hayashi M, Takei H, Kaneko T and Nomura F: Non-destructive on-chip
imaging flow cell-sorting system for on-chip cellomics.
Microfluidics and Nanofluidics. 14:907–931. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Smith ZJ, Gao T, Chu K, Lane SM, Matthews
DL, Dwyre DM, Hood J, Tatsukawa K, Heifetz L and Wachsmann-Hogiu S:
Single-step preparation and image-based counting of minute volumes
of human blood. Lab Chip. 14:3029–3036. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao M, Wu A, Song J, Sun X and Dong N:
Automatic screening of cervical cells using block image processing.
Biomed Eng Online. 15:142016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Amado AM, Pazin WM, Ito AS, Kuzmin VA and
Borissevitch IE: Acridine orange interaction with DNA: Effect of
ionic strength. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 1861:900–909. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu M, Li R, Tang Y, Chang J, Han R, Zhang
S, Jiang N and Ma F: New applications of the acridine orange
fluorescence staining method: Screening for circulating tumor
cells. Oncol Lett. 13:2221–2229. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vona G Sabile A, Louha M, Sitruk V, Romana
S, Schütze K, Capron F, Franco D, Pazzagli M, Vekemans M, et al:
Isolation by size of epithelial tumor cells-A new method for the
immunomorphological and molecular characterization of circulating
tumor cells. Am J Pathol. 156:57–63. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mohamed H, Murray M, Turner JN and Caggana
M: Isolation of tumor cells using size and deformation. J
Chromatogr A. 1216:8289–8295. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang H, Li L, Ding Y Ye D, Wang Y, Cui S
and Liao L: Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on
bioinspired Au microflowers for ultra-trace cholesterol assay.
Biosens Bioelectron. 92:748–754. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fakhfouri A, Devendran C, Collins J, Ai Y
and Neild A: Virtual membrane for filtration of particles using
surface acoustic waves (SAW). Lab Chip. 16:3515–3523. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ren L, Chen Y, Li P, Mao Z, Huang PH, Rufo
J, Guo F, Wang L, McCoy JP, Levine SJ and Huang TJ: A
high-throughput acoustic cell sorter. Lab Chip. 15:3870–3879. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Adams JD, Kim U and Soh HT: Multitarget
magnetic activated cell sorter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:18165–18170. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Osman O, Toru S, Dumas-Bouchiat F, Dempsey
NM, Haddour N, Zanini LF, Buret F, Reyne G and Frenea-Robin M:
Microfluidic immunomagnetic cell separation using integrated
permanent micromagnets. Biomicrofluidics. 7:541152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sarioglu AF, Aceto N, Kojic N, Donaldson
MC, Zeinali M, Hamza B, Engstrom A, Zhu H, Sundaresan TK, Miyamoto
DT, et al: A microfluidic device for label-free, physical capture
of circulating tumor cell clusters. Nat Methods. 12:685–691. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Au SH, Edd J, Stoddard AE, Wong KHK,
Fachin F, Maheswaran S, Haber DA, Stott SL, Kapur R and Toner M:
Microfluidic isolation of circulating tumor cell clusters by size
and asymmetry. Sci Rep. 7:24332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|