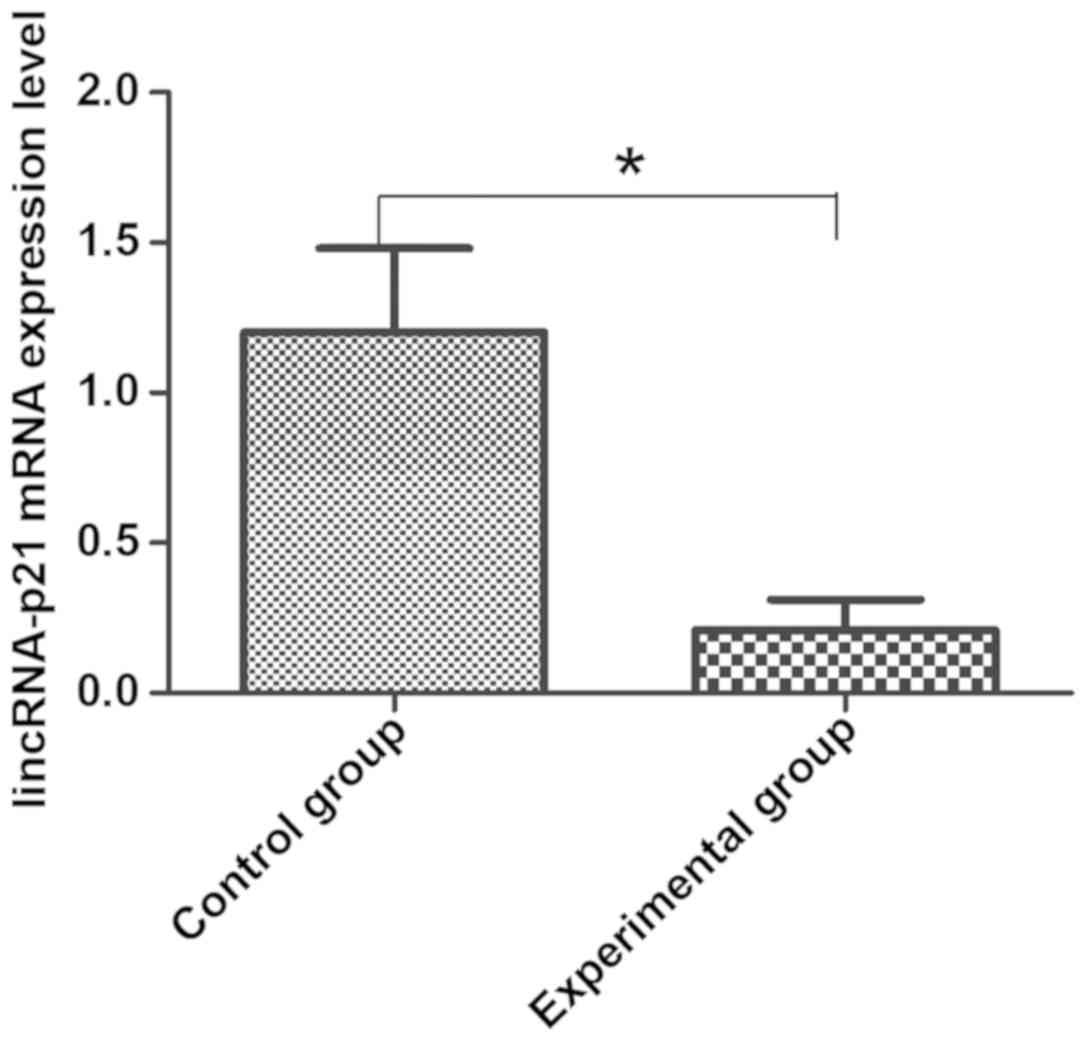
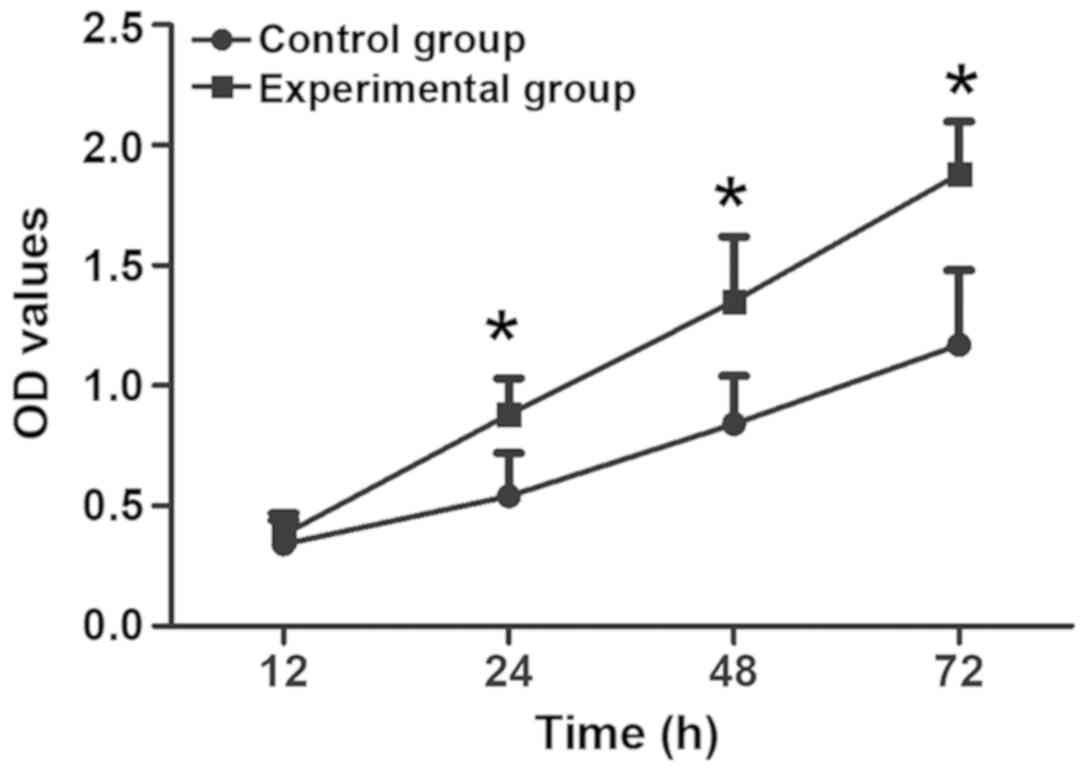
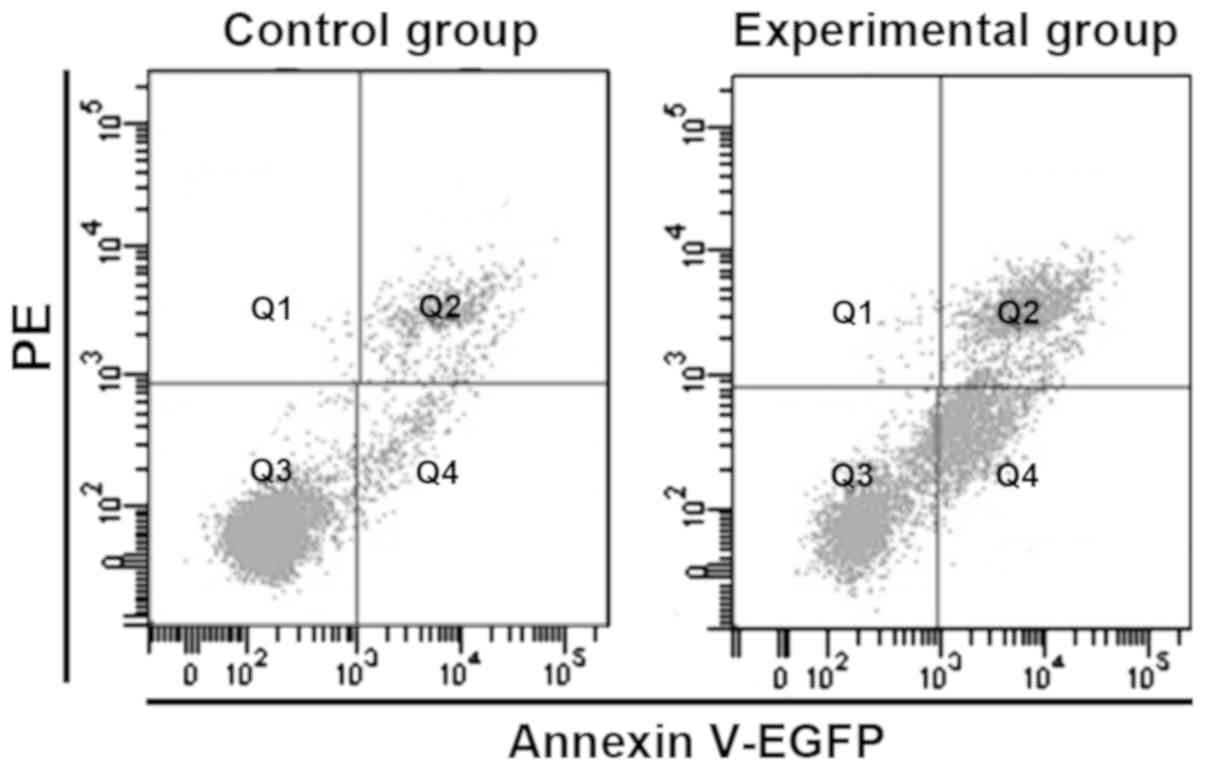
|
1
|
Sun T, Liu H and Ming L: Multiple roles of
autophagy in the sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 44:716–727. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pinter M, Weinmann A, Wörns MA, Hucke F,
Bota S, Marquardt JU, Duda DG, Jain RK, Galle PR, Trauner M, et al:
Use of inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system is associated
with longer survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
United European Gastroenterol J. 5:987–996. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sanduzzi Zamparelli M, Rocco A, Compare D
and Nardone G: The gut microbiota: A new potential driving force in
liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. United European
Gastroenterol J. 5:944–953. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
An C, Hu ZL, Liang P, Cheng ZG, Han ZY, Yu
J and Liu FY: Ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation vs.
surgical resection for thoracoabdominal wall implants from
hepatocellular carcinoma: Intermediate-term results. Int J
Hyperthermia. 21:1–10. 2017.
|
|
5
|
Chen X, Jiang W, Yue C, Zhang W, Tong C,
Dai D, Cheng B, Huang C and Lu L: Heparanase contributes to
trans-endothelial migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J
Cancer. 8:3309–3317. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen S, Liang H, Yang H, Zhou K, Xu L, Liu
J, Lai B, Song L, Luo H, Peng J, et al: LincRNa-p21: Function and
mechanism in cancer. Med Oncol. 34:982017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chillón I and Pyle AM: Inverted repeat Alu
elements in the human lincRNA-p21 adopt a conserved secondary
structure that regulates RNA function. Nucleic Acids Res.
44:9462–9471. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shen Y, Liu Y, Sun T and Yang W:
LincRNA-p21 knockdown enhances radiosensitivity of hypoxic tumor
cells by reducing autophagy through HIF-1/Akt/mTOR/P70S6K pathway.
Exp Cell Res. 358:188–198. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen Y, Wei G, Xia H, Yu H, Tang Q and Bi
F: Down regulation of lincRNA-p21 contributes to gastric cancer
development through Hippo-independent activation of YAP.
Oncotarget. 8:63813–63824. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang JY, Fang M, Boye A, Wu C, Wu JJ, Ma
Y, Hou S, Kan Y and Yang Y: Interaction of microRNA-21/145 and
Smad3 domain-specific phosphorylation in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 8:84958–84973. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Feng LH, Wang H, Dong H, Zhu YY and Cong
WM: The stromal morphological changes for differential diagnosis of
uninodular high-grade dysplastic nodule and well-differentiated
small hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:87329–87339. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ye JZ, Chen JZ, Li ZH, Bai T, Chen J, Zhu
SL, Li LQ and Wu FX: Efficacy of postoperative adjuvant
transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular
carcinoma patients with microvascular invasion. World J
Gastroenterol. 23:7415–7424. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sim HW and Knox J: Hepatocellular
carcinoma in the era of immunotherapy. Curr Probl Cancer. 42:40–48.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Honda H, Takamura M, Yamagiwa S, Genda T,
Horigome R, Kimura N, Setsu T, Tominaga K, Kamimura H, Matsuda Y,
et al: Overexpression of a disintegrin and metalloproteinase 21 is
associated with motility, metastasis, and poor prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep. 7:154852017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ding G, Peng Z, Shang J, Kang Y, Ning H
and Mao C: LincRNA-p21 inhibits invasion and metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma through miR-9/E-cadherin cascade signaling
pathway molecular mechanism. OncoTargets Ther. 10:3241–3247. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jia M, Jiang L, Wang YD, Huang JZ, Yu M
and Xue HZ: lincRNA-p21 inhibits invasion and metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma through Notch signaling-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Hepatol Res. 46:1137–1144. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu F, Guo Y, Chen B, Shi L, Dong P, Zhou M
and Zheng J: LincRNA-p21 Inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in
activated hepatic stellate cells via sponging microRNA-17-5p. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 41:1970–1980. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Castellano JJ, Navarro A, Viñolas N,
Marrades RM, Moises J, Cordeiro A, Saco A, Muñoz C, Fuster D,
Molins L, et al: LincRNA-p21 impacts prognosis in resected
non-small cell lung cancer patients through angiogenesis
regulation. J Thorac Oncol. 11:2173–2182. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|