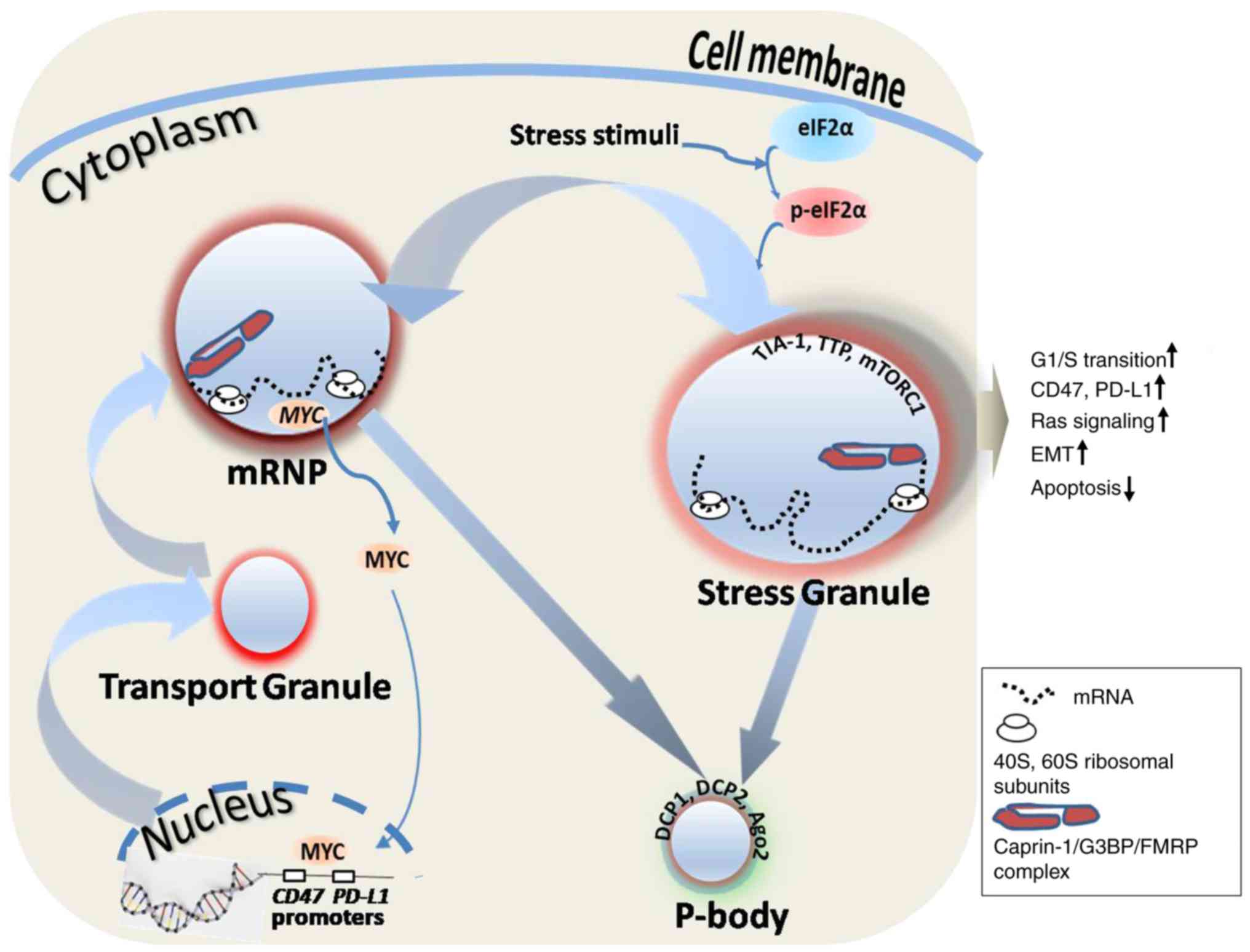
|
1
|
Gerstberger S, Hafner M and Tuschl T: A
census of human RNA-binding proteins. Nat Rev Genet. 15:829–845.
2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gerstberger S, Hafner M, Ascano M and
Tuschl T: Evolutionary conservation and expression of human
RNA-binding proteins and their role in human genetic disease. Adv
Exp Med Biol. 825:1–55. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mori T, Ngouv H, Hayashida M, Akutsu T and
Nacher JC: ncRNA-disease association prediction based on sequence
information and tripartite network. BMC Syst Biol. 12 (Suppl
1):S372018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hudson WH and Ortlund EA: The structure,
function and evolution of proteins that bind DNA and RNA. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 15:749–760. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Keene JD: RNA regulons: Coordination of
post-transcriptional events. Nat Rev Genet. 8:533–543. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nishida K, Kuwano Y, Nishikawa T, Masuda K
and Rokutan K: RNA binding proteins and genome integrity. Int J Mol
Sci. 18:E13412017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kai M: Roles of RNA-binding proteins in
DNA damage response. Int J Mol Sci. 17:3102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Harvey R, Dezi V, Pizzinga M and Willis
AE: Post-transcriptional control of gene expression following
stress: The role of RNA-binding proteins. Biochem Soc Trans.
45:1007–1014. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sheinberger J and Shav-Tal Y: mRNPs meet
stress granules. FEBS Lett. 591:2534–2542. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Maziuk B, Balance HI and Wolozin B:
Dysregulation of RNA binding protein aggregation in
neurodegenerative disorders. Front Mol Neurosci. 10:892017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Geuens T, Bouhy D and Timmerman V: The
hnRNP family: Insights into their role in health and disease. Hum
Genet. 135:851–867. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wurth L and Gebauer F: RNA-binding
proteins, multifaceted translational regulators in cancer. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1849:881–886. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pereira B, Billaud M and Almeida R:
RNA-binding proteins in cancer: Old players and new actors. Trends
Cancer. 3:506–528. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Paronetto MP, Cappellari M, Busa R,
Pedrotti S, Vitali R, Comstock C, Hyslop T, Knudsen KE and Sette C:
Alternative splicing of the cyclin D1 proto-oncogene is regulated
by the RNA-binding protein Sam68. Cancer Res. 70:229–239. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hsieh AC and Ruggero D: Targeting
eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) in cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 16:4914–4920. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Abdelmohsen K and Gorospe M:
Posttranscriptional regulation of cancer traits by HuR. Wiley
Interdiscip Rev RNA. 1:214–229. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang B, David MD and Schrader JW: Absence
of caprin-1 results in defects in cellular proliferation. J
Immunol. 175:4274–4282. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Solomon S, Xu Y, Wang B, David MD,
Schubert P, Kennedy D and Schrader JW: Distinct structural features
of caprin-1 mediate its interaction with G3BP-1 and its induction
of phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor
2alpha, entry to cytoplasmic stress granules, and selective
interaction with a subset of mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 27:2324–2342.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Reich J and Papoulas O: Caprin controls
follicle stem cell fate in the Drosophila ovary. PLoS One.
7:e353652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qiu YQ, Yang CW, Lee YZ, Yang RB, Lee CH,
Hsu HY, Chang CC and Lee SJ: Targeting a ribonucleoprotein complex
containing the caprin-1 protein and the c-Myc mRNA suppresses tumor
growth in mice: An identification of a novel oncotarget.
Oncotarget. 6:2148–2163. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Grill B, Wilson GM, Zhang KX, Wang B,
Doyonnas R, Quadroni M and Schrader JW: Activation/division of
lymphocytes results in increased levels of cytoplasmic
activation/proliferation-associated protein-1: Prototype of a new
family of proteins. J Immunol. 172:2389–2400. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gong B, Hu H, Chen J, Cao S, Yu J, Xue J,
Chen F, Cai Y, He H and Zhang L: Caprin-1 is a novel microRNA-223
target for regulating the proliferation and invasion of human
breast cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 67:629–636. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sabile AA, Arlt MJ, Muff R, Husmann K,
Hess D, Bertz J, Langsam B, Aemisegger C, Ziegler U, Born W and
Fuchs B: Caprin-1, a novel Cyr61-interacting protein, promotes
osteosarcoma tumor growth and lung metastasis in mice. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1832:1173–1182. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xiao H, Zeng J, Li H, Chen K, Yu G, Hu J,
Tang K, Zhou H, Huang Q, Li A, et al: MiR-1 downregulation
correlates with poor survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
where it interferes with cell cycle regulation and metastasis.
Oncotarget. 6:13201–13215. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Teng Y, Ren Y, Hu X, Mu J, Samykutty A,
Zhuang X, Deng Z, Kumar A, Zhang L, Merchant ML, et al:
MVP-mediated exosomal sorting of miR-193a promotes colon cancer
progression. Nat Commun. 8:144482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Matsumura I, Tanaka H and Kanakura Y: E2F1
and c-Myc in cell growth and death. Cell Cycle. 2:333–338. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pardee AB: G1 events and regulation of
cell proliferation. Science. 246:603–608. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang L, Gui H, Tang XJ, Yang ZS, Zou DD,
Lu JT, Yan LD, Dai LJ, Luo J and Wang B: Expression and
tumor-Promoting effects of caprin-1 in human glioma. Glioma.
1:136–141. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Casey SC, Tong L, Li Y, Do R, Walz S,
Fitzgerald KN, Gouw AM, Baylot V, Gütgemann I, Eilers M and Felsher
DW: MYC regulates the antitumor immune response through CD47 and
PD-L1. Science. 352:227–231. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
El Fatimy R, Tremblay S, Dury AY, Solomon
S, De Koninck P, Schrader JW and Khandjian EW: Fragile X mental
retardation protein interacts with the RNA-binding protein caprin1
in neuronal ribonucleoprotein complexes [corrected]. PLoS One.
7:e393382012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Katoh H, Okamoto T, Fukuhara T, Kambara H,
Morita E, Mori Y, Kamitani W and Matsuura Y: Japanese encephalitis
virus core protein inhibits stress granule formation through an
interaction with Caprin-1 and facilitates viral propagation. J
Virol. 87:489–502. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jin P, Zarnescu DC, Ceman S, Nakamoto M,
Mowrey J, Jongens TA, Nelson DL, Moses K and Warren ST: Biochemical
and genetic interaction between the fragile X mental retardation
protein and the microRNA pathway. Nat Neurosci. 7:113–117. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu Y, Zhu J, Huang X and Du Z: Crystal
structure of a dimerization domain of human Caprin-1: Insights into
the assembly of an evolutionarily conserved ribonucleoprotein
complex consisting of Caprin-1, FMRP and G3BP1. Acta Crystallogr D
Struct Biol. 72:718–727. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mingle LA, Okuhama NN, Shi J, Singer RH,
Condeelis J and Liu G: Localization of all seven messenger RNAs for
the actin-polymerization nucleator Arp2/3 complex in the
protrusions of fibroblasts. J Cell Sci. 118:2425–2433. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Carson JH and Barbarese E: Systems
analysis of RNA trafficking in neural cells. Biol Cell. 97:51–62.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Copsey AC, Cooper S, Parker R, Lineham E,
Lapworth C, Jallad D, Sweet S and Morley SJ: The helicase, DDX3X,
interacts with poly(A)-binding protein 1 (PABP1) and caprin-1 at
the leading edge of migrating fibroblasts and is required for
efficient cell spreading. Biochem J. 474:3109–3120. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Thomas MG, Loschi M, Desbats MA and
Boccaccio GL: RNA granules: The good, the bad and the ugly. Cell
Signal. 23:324–334. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kedersha N, Ivanov P and Anderson P:
Stress granules and cell signaling: More than just a passing phase?
Trends Biochem Sci. 38:494–506. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gilks N, Kedersha N, Ayodele M, Shen L,
Stoecklin G, Dember LM and Anderson P: Stress granule assembly is
mediated by prion-like aggregation of TIA-1. Mol Biol Cell.
15:5383–5398. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tourriere H, Chebli K, Zekri L, Courselaud
B, Blanchard JM, Bertrand E and Tazi J: The RasGAP-associated
endoribonuclease G3BP assembles stress granules. J Cell Biol.
160:823–831. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kedersha N, Cho MR, Li W, Yacono PW, Chen
S, Gilks N, Golan DE and Anderson P: Dynamic shuttling of TIA-1
accompanies the recruitment of mRNA to mammalian stress granules. J
Cell Biol. 151:1257–1268. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mazroui R, Huot ME, Tremblay S, Filion C,
Labelle Y and Khandjian EW: Trapping of messenger RNA by fragile X
mental retardation protein into cytoplasmic granules induces
translation repression. Hum Mol Genet. 11:3007–3017. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Stoecklin G, Stubbs T, Kedersha N, Wax S,
Rigby WF, Blackwell TK and Anderson P: MK2-induced
tristetraprolin:14-3-3 complexes prevent stress granule association
and ARE-mRNA decay. EMBO J. 23:1313–1324. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Buchan JR and Parker R: Eukaryotic stress
granules: The ins and outs of translation. Mol Cell. 36:932–941.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gupta N, Badeaux M, Liu Y, Naxerova K,
Sgroi D, Munn LL, Jain RK and Garkavtsev I: Stress
granule-associated protein G3BP2 regulates breast tumor initiation.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:1033–1038. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Anderson P, Kedersha N and Ivanov P:
Stress granules, P-bodies and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1849:861–870. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Adjibade P, St-Sauveur VG, Quevillon
Huberdeau M, Fournier MJ, Savard A, Coudert L, Khandjian EW and
Mazroui R: Sorafenib, a multikinase inhibitor, induces formation of
stress granules in hepatocarcinoma cells. Oncotarget.
6:43927–43943. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Vilas-Boas Fde A, da Silva AM, de Sousa
LP, Lima KM, Vago JP, Bittencourt LF, Dantas AE, Gomes DA, Vilela
MC, Teixeira MM and Barcelos LS: Impairment of stress granule
assembly via inhibition of the eIF2alpha phosphorylation sensitizes
glioma cells to chemotherapeutic agents. J Neurooncol. 127:253–260.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Somasekharan SP, El-Naggar A, Leprivier G,
Cheng H, Hajee S, Grunewald TG, Zhang F, Ng T, Delattre O,
Evdokimova V, et al: YB-1 regulates stress granule formation and
tumor progression by translationally activating G3BP1. J Cell Biol.
208:913–929. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Leprivier G, Rotblat B, Khan D, Jan E and
Sorensen PH: Stress-mediated translational control in cancer cells.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1849:845–860. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Szaflarski W, Fay MM, Kedersha N, Zabel M,
Anderson P and Ivanov P: Vinca alkaloid drugs promote
stress-induced translational repression and stress granule
formation. Oncotarget. 7:30307–30322. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Fournier MJ, Coudert L, Mellaoui S,
Adjibade P, Gareau C, Côté MF, Sonenberg N, Gaudreault RC and
Mazroui R: Inactivation of the mTORC1-eukaryotic translation
initiation factor 4E pathway alters stress granule formation. Mol
Cell Biol. 33:2285–2301. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tan N, Dai L, Liu X, Pan G, Chen H, Huang
J and Xu Q: Upregulation of caprin1 expression is associated with
poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract.
213:1563–1567. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Campanile C, Arlt MJ, Kramer SD, Honer M,
Gvozdenovic A, Brennecke P, Fischer CR, Sabile AA, Müller A,
Ametamey SM, et al: Characterization of different osteosarcoma
phenotypes by PET imaging in preclinical animal models. J Nucl Med.
54:1362–1368. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kedracka-Krok S, Jankowska U, Elas M, Sowa
U, Swakon J, Cierniak A, Olko P, Romanowska-Dixon B and Urbanska K:
Proteomic analysis of proton beam irradiated human melanoma cells.
PLoS One. 9:e846212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Min L, Ruan Y, Shen Z, Jia D, Wang X, Zhao
J, Sun Y and Gu J: Overexpression of Ras-GTPase-activating protein
SH3 domain-binding protein 1 correlates with poor prognosis in
gastric cancer patients. Histopathology. 67:677–688. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang H, Zhang SH, He HW, Zhang CX, Yu DK
and Shao RG: Downregulation of G3BPs inhibits the growth, migration
and invasion of human lung carcinoma H1299 cells by suppressing the
Src/FAK-associated signaling pathway. Cancer Gene Ther. 20:622–629.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Taniuchi K, Nishimori I and Hollingsworth
MA: The N-terminal domain of G3BP enhances cell motility and
invasion by posttranscriptional regulation of BART. Mol Cancer Res.
9:856–866. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhang H, Zhang S, He H, Zhao W, Chen J and
Shao RG: GAP161 targets and downregulates G3BP to suppress cell
growth and potentiate cisplaitin-mediated cytotoxicity to colon
carcinoma HCT116 cells. Cancer Sci. 103:1848–1856. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|