|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lordick F, Allum W, Carneiro F, Mitry E,
Tabernero J, Tan P, Van Cutsem E, van de Velde C and Cervantes A:
Unmet needs and challenges in gastric cancer: The way forward.
Cancer Treat Rev. 40:692–700. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lordick F, Lorenzen S, Yamada Y and Ilson
D: Optimal chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer: Is there a
global consensus? Gastric Cancer. 17:213–225. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Amable L: Cisplatin resistance and
opportunities for precision medicine. Pharmacol Res. 106:27–36.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Basourakos SP, Li L, Aparicio AM, Corn PG,
Kim J and Thompson TC: Combination platinum-based and DNA damage
response-targeting cancer therapy: Evolution and future directions.
Curr Med Chem. 24:1586–1606. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Crosby ME, Kulshreshtha R, Ivan M and
Glazer PM: MicroRNA regulation of DNA repair gene expression in
hypoxic stress. Cancer Res. 69:1221–1229. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xie QH, He XX, Chang Y, Sun SZ, Jiang X,
Li PY and Lin JS: MiR-192 inhibits nucleotide excision repair by
targeting ERCC3 and ERCC4 in HepG2.2.15 cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 410:440–445. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xiang Y, Ma N, Wang D, Zhang Y, Zhou J, Wu
G, Zhao R, Huang H, Wang X, Qiao Y, et al: MiR-152 and miR-185
co-contribute to ovarian cancer cells cisplatin sensitivity by
targeting DNMT1 directly: A novel epigenetic therapy independent of
decitabine. Oncogene. 33:378–386. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shang Y, Zhang Z, Liu Z, Feng B, Ren G, Li
K, Zhou L, Sun Y, Li M, Zhou J, et al: miR-508-5p regulates
multidrug resistance of gastric cancer by targeting ABCB1 and
ZNRD1. Oncogene. 33:3267–3276. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fang L, Li H, Wang L, Hu J, Jin T, Wang J
and Yang BB: MicroRNA-17-5p promotes chemotherapeutic drug
resistance and tumor metastasis of colorectal cancer by repressing
PTEN expression. Oncotarget. 5:2974–2987. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
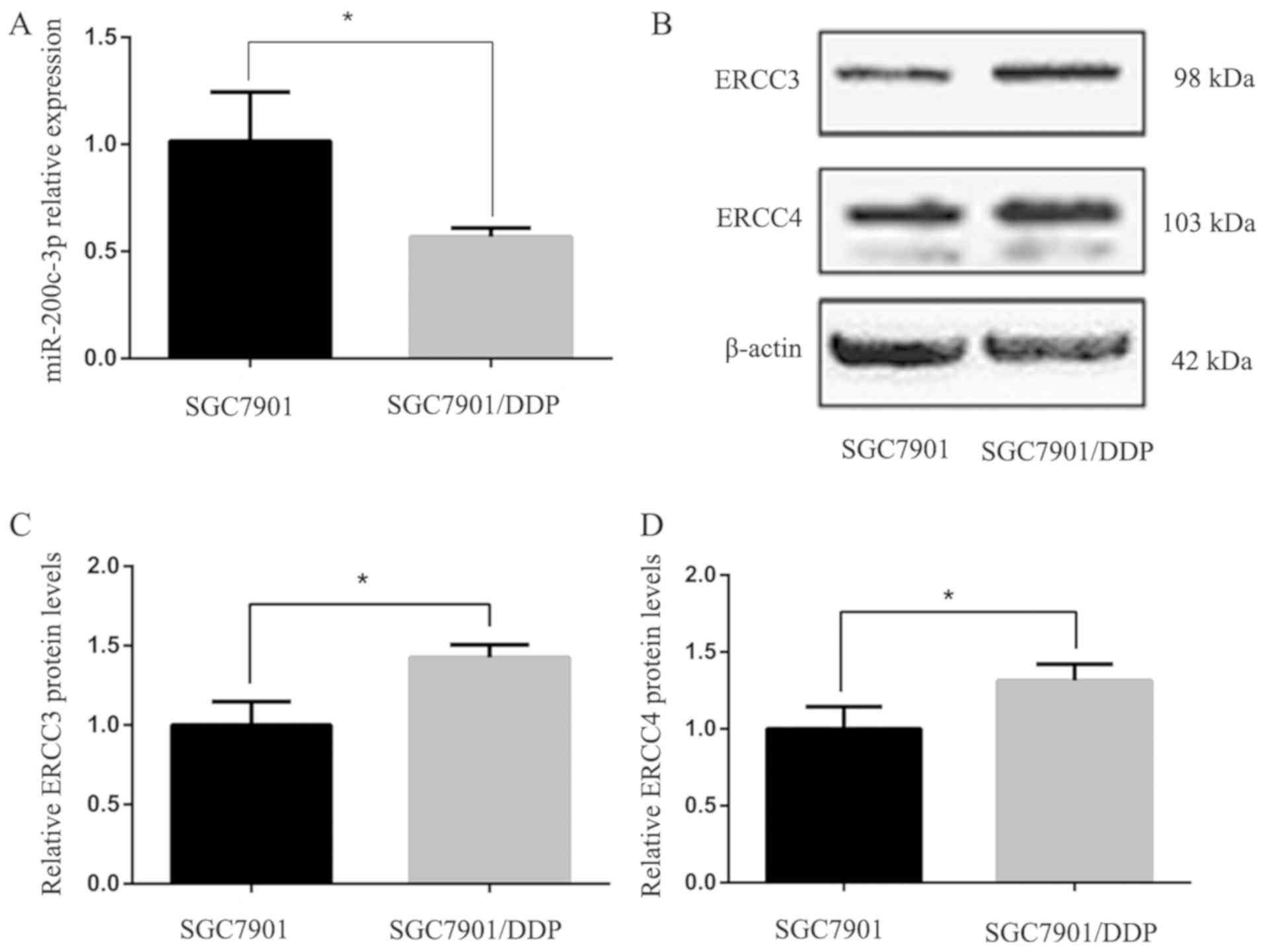
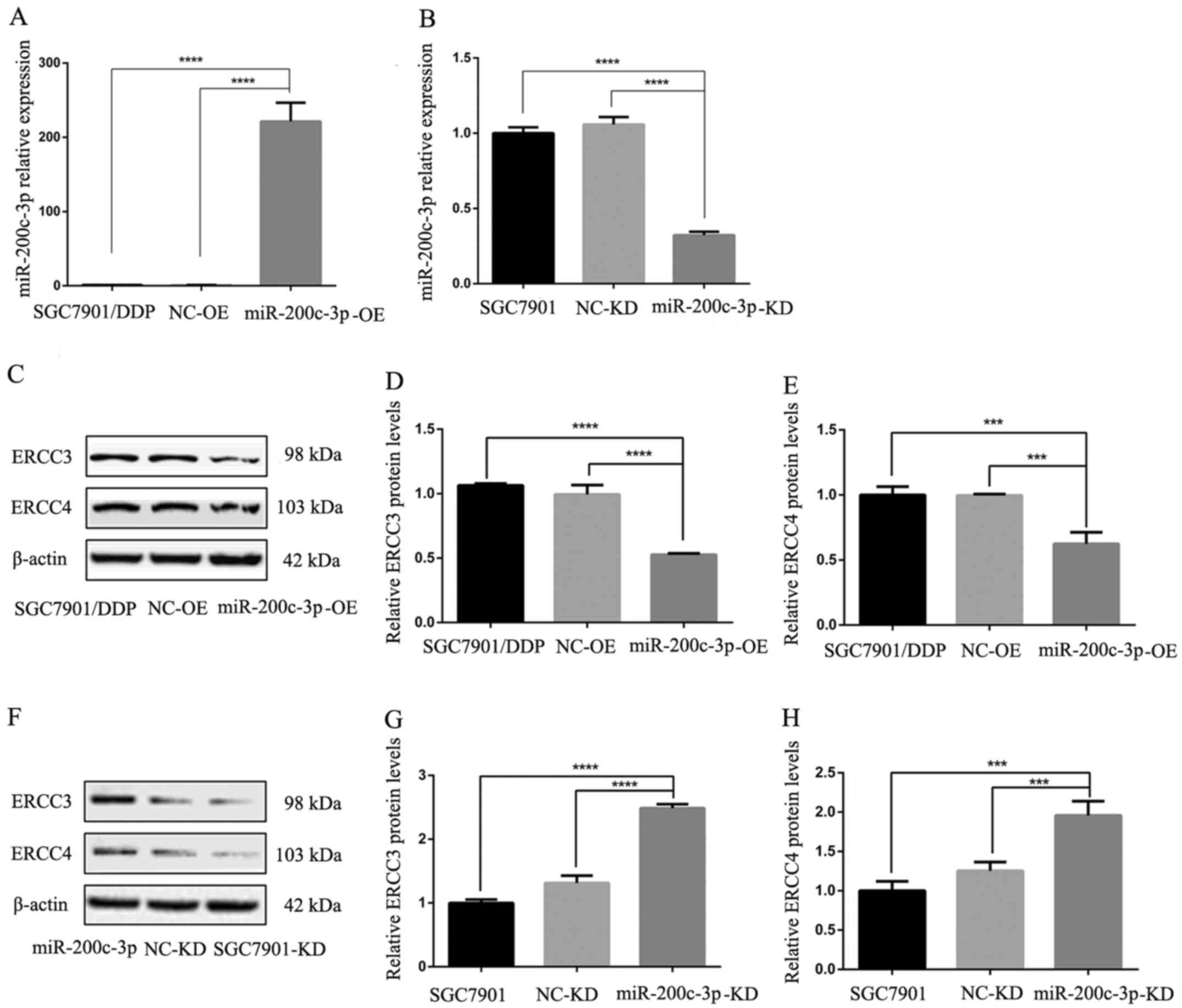
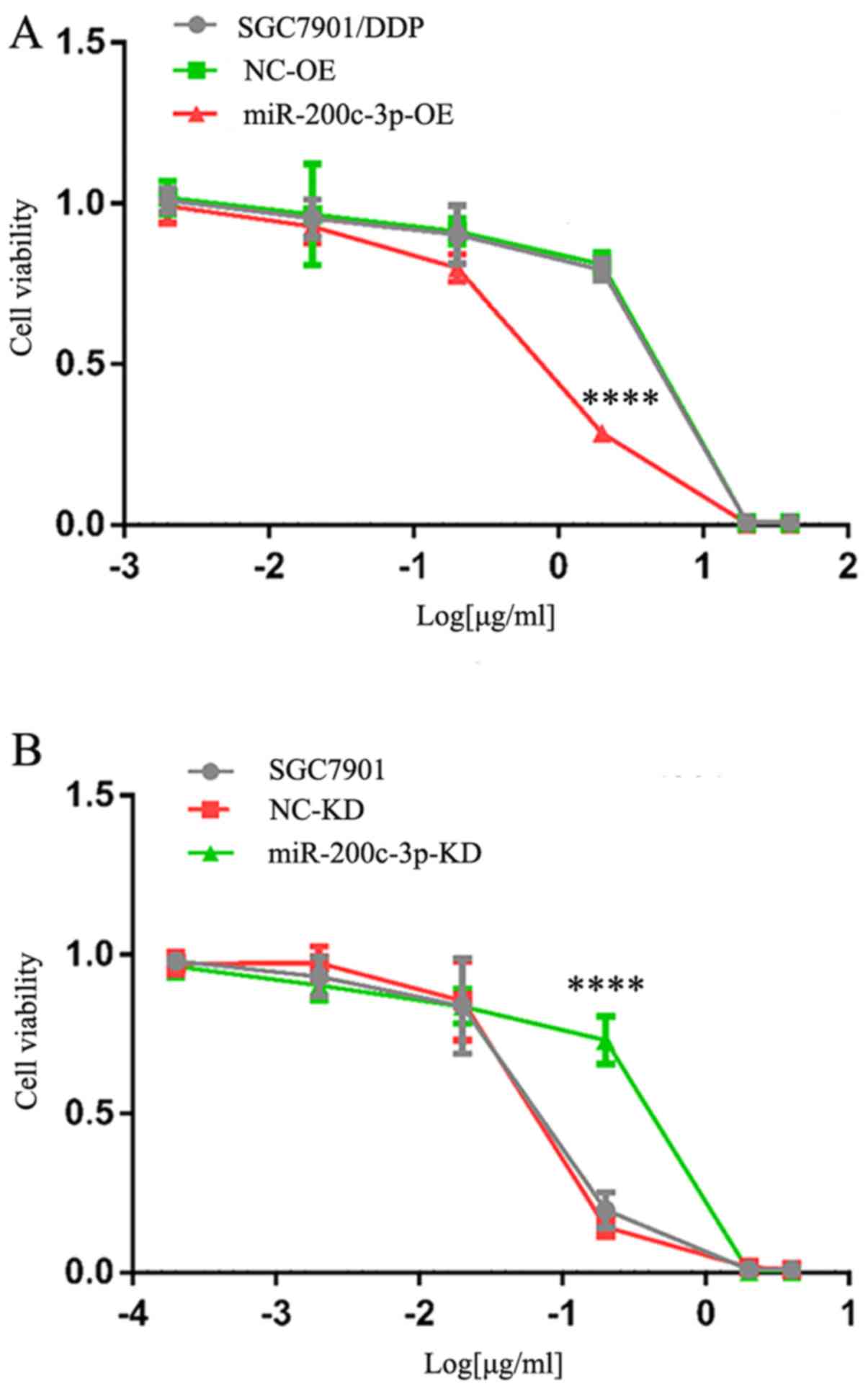
Chen Y, Zuo J, Liu Y, Gao H and Liu W:
Inhibitory effects of miRNA-200c on chemotherapy-resistance and
cell proliferation of gastric cancer SGC7901/DDP cells. Chin J
Cancer. 29:1006–1011. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hatano K, Kumar B, Zhang Y, Coulter JB,
Hedayati M, Mears B, Ni X, Kudrolli TA, Chowdhury WH, Rodriguez R,
et al: A functional screen identifies miRNAs that inhibit DNA
repair and sensitize prostate cancer cells to ionizing radiation.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43:4075–4086. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu RL, Dong Y, Deng YZ, Wang WJ and Li
WD: Tumor suppressor miR-145 reverses drug resistance by directly
targeting DNA damage-related gene RAD18 in colorectal cancer.
Tumour Biol. 36:5011–5019. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu J, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Sato N,
Kayashima T, Fujita H, Nakata K and Tanaka M: MicroRNA,
hsa-miR-200c, is an independent prognostic factor in pancreatic
cancer and its upregulation inhibits pancreatic cancer invasion but
increases cell proliferation. Mol Cancer. 9:1692010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li RH, Chen M, Liu J, Shao CC, Guo CP, Wei
XL, Li YC, Huang WH and Zhang GJ: Long noncoding RNA ATB promotes
the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by upregulating the
miR-200c/Twist1 axe and predicts poor prognosis in breast cancer.
Cell Death Dis. 9:11712018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cao W and Sun J: MicroRNA-200c promotes
tumor cell proliferation and migration by directly targeting
dachshund family transcription factor 1 by the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Anticancer Drugs.
30:218–224. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen ML, Liang LS and Wang XK: miR-200c
inhibits invasion and migration in human colon cancer cells
SW480/620 by targeting ZEB1. Clin Exp Metastasis. 29:457–469. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Adam L, Zhong M, Choi W, Qi W, Nicoloso M,
Arora A, Calin G, Wang H, Siefker-Radtke A, McConkey D, et al:
miR-200 expression regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
in bladder cancer cells and reverses resistance to epidermal growth
factor receptor therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 15:5060–5072. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang HL, Ruan L, Zheng LM, Whyte D, Tzeng
CM and Zhou XW: Association between class III β-tubulin expression
and response to paclitaxel/vinorebine-based chemotherapy for
non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Lung Cancer. 77:9–15.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
He W, Zhang D, Jiang J, Liu P and Wu C:
The relationships between the chemosensitivity of human gastric
cancer to paclitaxel and the expressions of class III β-tubulin,
MAPT, and survivin. Med Oncol. 31:9502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Duran GE, Wang YC, Moisan F, Francisco EB
and Sikic BI: Decreased levels of baseline and drug-induced tubulin
polymerisation are hallmarks of resistance to taxanes in ovarian
cancer cells and are associated with epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Br J Cancer. 116:1318–1328. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cochrane DR, Spoelstra NS, Howe EN,
Nordeen SK and Richer JK: MicroRNA-200c mitigates invasiveness and
restores sensitivity to microtubule-targeting chemotherapeutic
agents. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:1055–1066. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou X, Men X, Zhao R, Han J, Fan Z, Wang
Y, Lv Y, Zuo J, Zhao L, Sang M, et al: miR-200c inhibits
TGF-β-induced-EMT to restore trastuzumab sensitivity by targeting
ZEB1 and ZEB2 in gastric cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 25:68–76. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu Y, Xiao Y, Ding X, Zhuo Y, Ren P, Zhou
C and Zhou J: A miR-200b/200c/429-binding site polymorphism in the
3′ untranslated region of the AP-2α gene is associated with
cisplatin resistance. PLoS One. 6:e290432011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hamano R, Miyata H, Yamasaki M, Kurokawa
Y, Hara J, Moon JH, Nakajima K, Takiguchi S, Fujiwara Y, Mori M and
Doki Y: Overexpression of miR-200c induces chemoresistance in
esophageal cancers mediated through activation of the Akt signaling
pathway. Clin Cancer Res. 17:3029–3038. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jiang T, Dong P, Li L, Ma X, Xu P, Zhu H,
Wang Y, Yang B, Liu K, Liu J, et al: MicroRNA-200c regulates
cisplatin resistance by targeting ZEB2 in human gastric cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 38:151–158. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chang L, Guo F, Wang Y, Lv Y, Huo B, Wang
L and Liu W: MicroRNA-200c regulates the sensitivity of
chemotherapy of gastric cancer SGC7901/DDP cells by directly
targeting RhoE. Pathol Oncol Res. 20:93–98. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li M, Gu K, Liu W, Xie X and Huang X:
MicroRNA-200c as a prognostic and sensitivity marker for platinum
chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 8:51190–51199.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hwang JR, Moncollin V, Vermeulen W, Seroz
T, van Vuuren H, Hoeijmakers JH and Egly JM: A 3′->5′ XPB
helicase defect in repair/transcription factor TFIIH of xeroderma
pigmentosum group B affects both DNA repair and transcription. J
Biol Chem. 271:15898–15904. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lankoff A, Sochacki J, Spoof L, Meriluoto
J, Wojcik A, Wegierek A and Verschaeve L: Nucleotide excision
repair impairment by nodularin in CHO cell lines due to ERCC1/XPF
inactivation. Toxicol Lett. 179:101–107. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
McDaniel LD and Schultz RA: XPF/ERCC4 and
ERCC1: Their products and biological roles. Adv Exp Med Biol.
637:65–82. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Andressoo JO, Weeda G, de Wit J, Mitchell
JR, Beems RB, van Steeg H, van der Horst GT and Hoeijmakers JH: An
Xpb mouse model for combined xeroderma pigmentosum and cockayne
syndrome reveals progeroid features upon further attenuation of DNA
repair. Mol Cell Biol. 29:1276–1290. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Poterszman A, Lamour V, Egly JM, Moras D,
Thierry JC and Poch O: A eukaryotic XPB/ERCC3-like helicase in
Mycobacterium leprae? Trends Biochem Sci. 22:418–419. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Friedberg EC: How nucleotide excision
repair protects against cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 1:22–33. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ning J, Jiao Y, Xie X, Deng X, Zhang Y,
Yang Y, Zhao C, Wang H and Gu K: miR-138-5p modulates the
expression of excision repair cross-complementing proteins ERCC1
and ERCC4 and regulates the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to
cisplatin. Oncol Rep. 41:1131–1139. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|