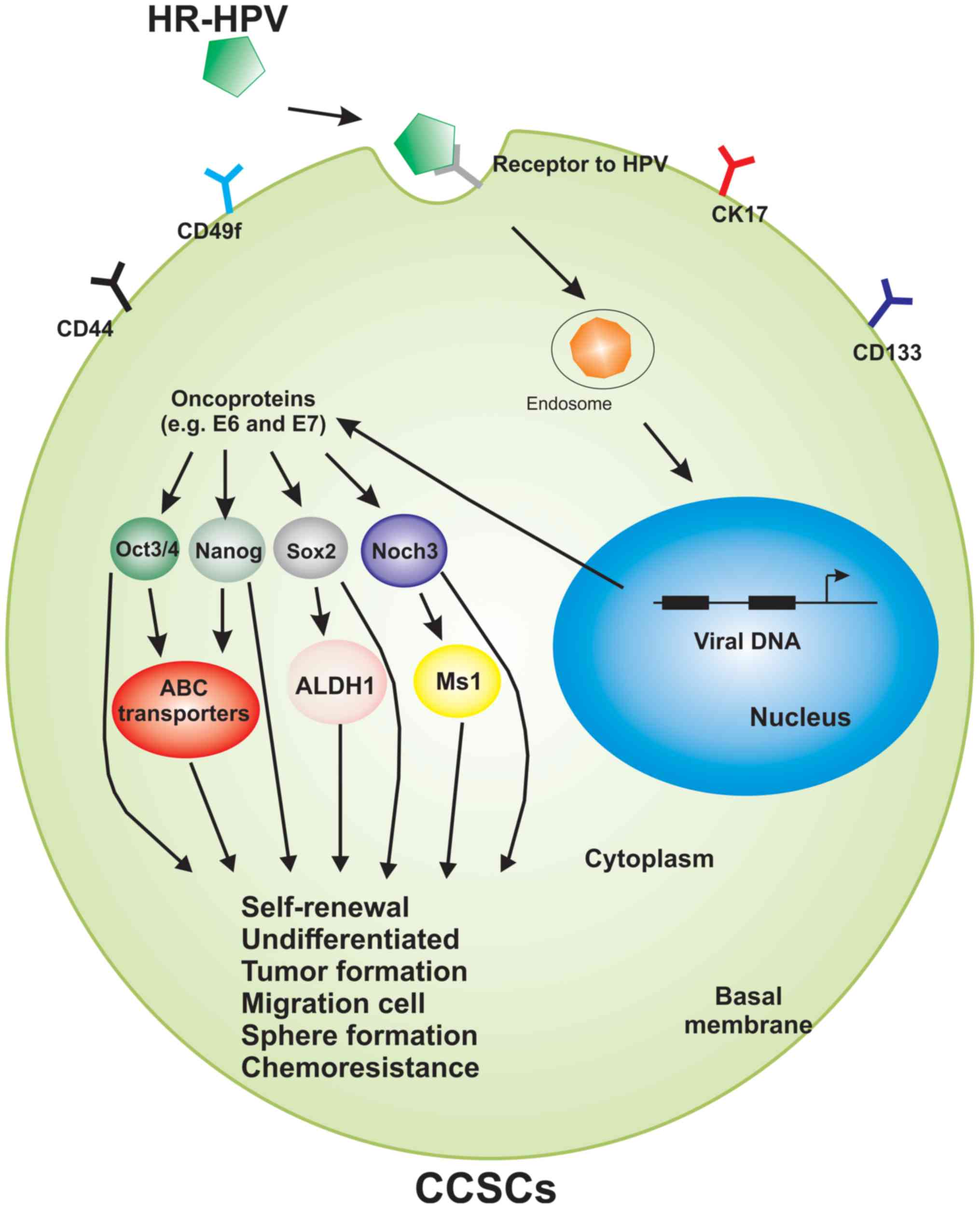
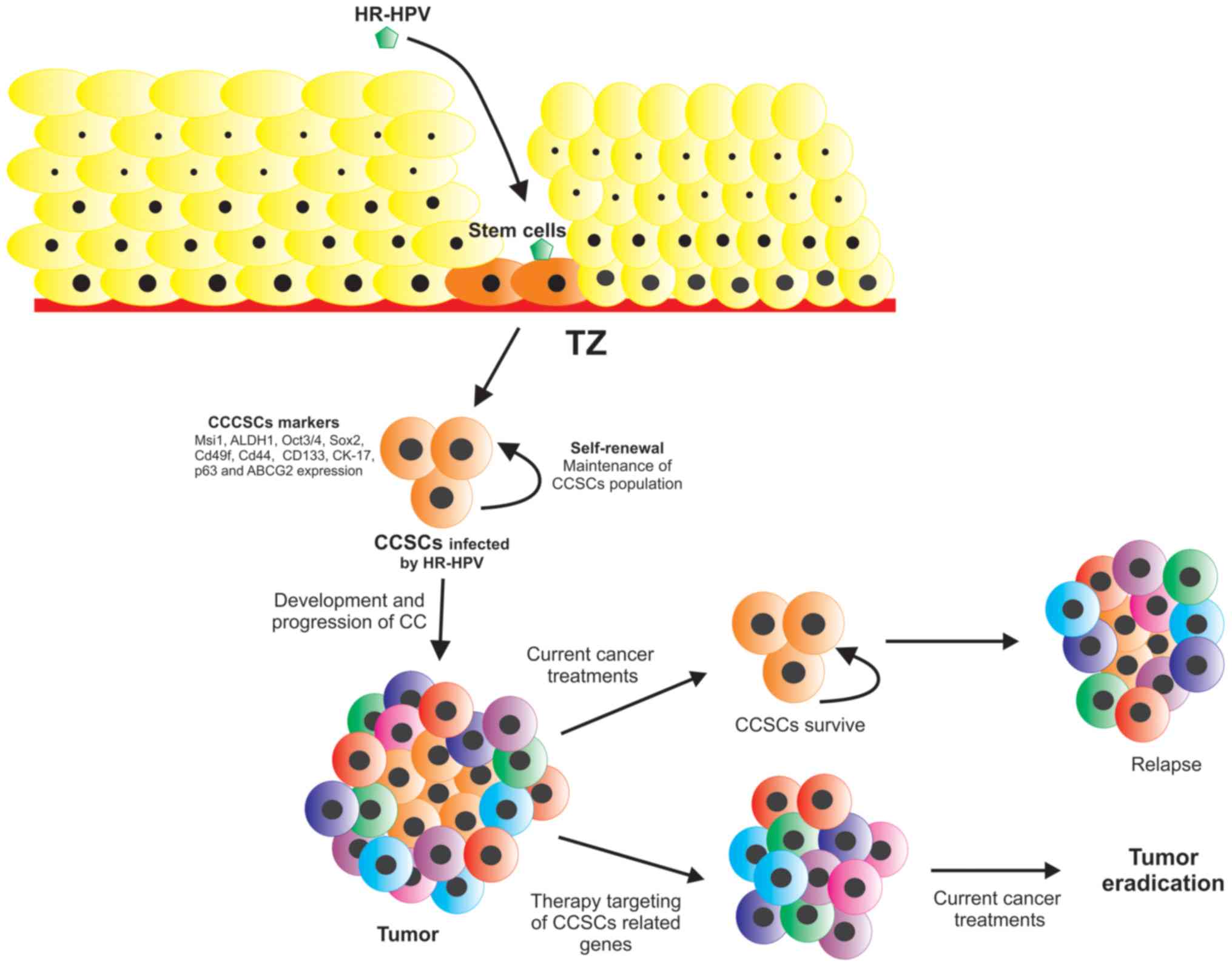
|
1
|
Globocan 2012, . http://globocan.iarc.frOct. 2017
|
|
2
|
Paavonen J: Human papillomavirus infection
and the development of cervical cancer and related genital
neoplasias. Int J Infect Dis. 11 (Suppl 2):S3–S9. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Senapati R, Nayak B, Kar SK and Dwibedi B:
HPV genotypes co-infections associated with cervical carcinoma:
Special focus on phylogenetically related and non-vaccine targeted
genotypes. PLoS One. 12:e01878442017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Badaracco G, Savarese A, Micheli A, Rizzo
C, Paolini F, Carosi M, Cutillo G, Vizza E, Arcangeli G and Venuti
A: Persistence of HPV after radio-chemotherapy in locally advanced
cervical cancer. Oncol Rep. 23:1093–1099. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF and
Weissman IL: Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature.
414:105–111. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Herfs M, Yamamoto Y, Laury A, Wang X,
Nucci MR, McLaughlin-Drubin ME, Münger K, Feldman S, McKeon FD,
Xian W and Crum CP: A discrete population of squamocolumnar
junction cells implicated in the pathogenesis of cervical cancer.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:10516–10521. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Herfs M, Vargas SO, Yamamoto Y, Howitt BE,
Nucci MR, Hornick JL, Mckeon FD, Xian W and Crum CP: A novel
blueprint for ‘top down’ differentiation defines the cervical
squamocolumnar junction during development, reproductive life, and
neoplasia. J Pathol. 229:460–468. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu H, Wang YJ, Bian L, Fang ZH, Zhang QY
and Cheng JX: CD44+/CD24+ cervical cancer cells resist radiotherapy
and exhibit properties of cancer stem cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 20:1745–1754. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
López J, Poitevin A, Mendoza-Martínez V,
Pérez-Plasencia C and García-Carrancá A: Cancer-initiating cells
derived from established cervical cell lines exhibit stem-cell
markers and increased radioresistance. BMC Cancer. 12:482012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ortiz-Sánchez E, Santiago-López L,
Cruz-Domínguez VB, Toledo-Guzmán ME, Hernández-Cueto D,
Muñiz-Hernández S, Garrido E, De León DC and García-Carrancá A:
Characterization of cervical cancer stem cell-like cells:
Phenotyping, stemness, and human papilloma virus co-receptor
expression. Oncotarget. 7:31943–31954. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dobbin ZC and Landen CN: Isolation and
characterization of potential cancer stem cells from solid human
tumors-potential applications. Curr Protoc Pharmacol. 63:Unit
14.28. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
McLaughlin-Drubin ME, Meyers J and Munger
K: Cancer associated human papillomaviruses. Curr Opin Virol.
2:459–466. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Organista-Nava J, Gómez-Gómez Y,
Ocadiz-Delgado R, García-Villa E, Bonilla-Delgado J,
Lagunas-Martínez A, Tapia JS, Lambert PF, García-Carrancá A and
Gariglio P: The HPV16 E7 oncoprotein increases the expression of
Oct3/4 and stemness-related genes and augments cell self-renewal.
Virology. 499:230–242. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang R and Rofstad EK: Cancer stem cells
(CSCs), cervical CSCs and targeted therapies. Oncotarget.
8:35351–35367. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hou T, Zhang W, Tong C, Kazobinka G, Huang
X, Huang Y and Zhang Y: Putative stem cell markers in cervical
squamous cell carcinoma are correlated with poor clinical outcome.
BMC Cancer. 15:7852015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Martens JE, Arends J, Van Der Linden PJ,
De Boer BA and Helmerhorst TJ: Cytokeratin 17 and p63 are markers
of the HPV target cell, the cervical stem cell. Anticancer Res.
24:771–776. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ikeda K, Tate G, Suzuki T and Mitsuya T:
Coordinate expression of cytokeratin 8 and cytokeratin 17
immunohistochemical staining in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
and cervical squamous cell carcinoma: An immunohistochemical
analysis and review of the literature. Gynecol Oncol. 108:598–602.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Aksoy P, Gottschalk EY and Meneses PI: HPV
entry into cells. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 772:13–22. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
López J, Ruíz G, Organista-Nava J,
Gariglio P and García-Carrancá A: Human papillomavirus infections
and cancer stem cells of tumors from the uterine cervix. Open Virol
J. 6:232–240. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Olivero C, Lanfredini S, Borgogna C,
Gariglio M and Patel GK: HPV-induced field cancerisation:
Transformation of adult tissue stem cell into cancer stem cell.
Front Microbiol. 9:5462018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kareta MS, Gorges LL, Hafeez S, Benayoun
BA, Marro S, Zmoos AF, Cecchini MJ, Spacek D, Batista LF, O'Brien
M, et al: Inhibition of pluripotency networks by the Rb tumor
suppressor restricts reprogramming and tumorigenesis. Cell Stem
Cell. 16:39–50. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lin T, Chao C, Saito S, Mazur SJ, Murphy
ME, Appella E and Xu Y: p53 induces differentiation of mouse
embryonic stem cells by suppressing Nanog expression. Nat Cell
Biol. 7:165–171. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tyagi A, Vishnoi K, Mahata S, Verma G,
Srivastava Y, Masaldan S, Roy BG, Bharti AC and Das BC: Cervical
cancer stem cells selectively overexpress HPV oncoprotein E6 that
controls stemness and self-renewal through upregulation of HES1.
Clin Cancer Res. 22:4170–4184. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xi R, Pan S, Chen X, Hui B, Zhang L, Fu S,
Li X, Zhang X, Gong T, Guo J, et al: HPV16 E6-E7 induces cancer
stem-like cells phenotypes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
through the activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in vitro and
in vivo. Oncotarget. 7:57050–57065. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu K, Lin B, Zhao M, Yang X, Chen M, Gao
A, Liu F, Que J and Lan X: The multiple roles for Sox2 in stem cell
maintenance and tumorigenesis. Cell Signal. 25:1264–1271. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang YD, Cai N, Wu XL, Cao HZ, Xie LL and
Zheng PS: OCT4 promotes tumorigenesis and inhibits apoptosis of
cervical cancer cells by miR-125b/BAK1 pathway. Cell Death Dis.
4:e7602013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ding Y, Yu AQ, Wang XL, Guo XR, Yuan YH
and Li DS: Forced expression of Nanog with mRNA synthesized in
vitro to evaluate the malignancy of HeLa cells through
acquiring cancer stem cell phenotypes. Oncol Rep. 35:2643–2650.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jeong JY, Kang H, Kim TH, Kim G, Heo JH,
Kwon AY, Kim S, Jung SG and An HJ: MicroRNA-136 inhibits cancer
stem cell activity and enhances the anti-tumor effect of paclitaxel
against chemoresistant ovarian cancer cells by targeting Notch3.
Cancer Lett. 386:168–178. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu XF, Yang WT, Xu R, Liu JT and Zheng
PS: Cervical cancer cells with positive Sox2 expression exhibit the
properties of cancer stem cells. PLoS One. 9:e870922014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang L, Zhang X, Zhang M, Zhang J, Sheng
Y, Sun X, Chen Q and Wang LX: Increased Nanog expression promotes
tumor development and Cisplatin resistance in human esophageal
cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 30:943–952. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jia Q, Zhang X, Deng T and Gao J: Positive
correlation of Oct4 and ABCG2 to chemotherapeutic resistance in
CD90(+)CD133(+) liver cancer stem cells. Cell Reprogram.
15:143–150. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pastò A, Serafin V, Pilotto G, Lago C,
Bellio C, Trusolino L, Bertotti A, Hoey T, Plateroti M, Esposito G,
et al: NOTCH3 signaling regulates MUSASHI-1 expression in
metastatic colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Res. 74:2106–2118. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Feng D, Peng C, Li C, Zhou Y, Li M, Ling
B, Wei H and Tian Z: Identification and characterization of cancer
stem-like cells from primary carcinoma of the cervix uteri. Oncol
Rep. 22:1129–1134. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Grasso C, Anaka M, Hofmann O, Sompallae R,
Broadley K, Hide W, Berridge MV, Cebon J, Behren A and McConnell
MJ: Iterative sorting reveals CD133+ and CD133-melanoma cells as
phenotypically distinct populations. BMC Cancer. 16:7262016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang P, Gao Q, Suo Z, Munthe E, Solberg S,
Ma L, Wang M, Westerdaal NA, Kvalheim G and Gaudernack G:
Identification and characterization of cells with cancer stem cell
properties in human primary lung cancer cell lines. PLoS One.
8:e570202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Muraro MG, Mele V, Däster S, Han J,
Heberer M, Cesare Spagnoli G and Iezzi G: CD133+, CD166+CD44+, and
CD24+CD44+ phenotypes fail to reliably identify cell populations
with cancer stem cell functional features in established human
colorectal cancer cell lines. Stem Cells Transl Med. 1:592–603.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zakaria N, Yusoff NM, Zakaria Z, Lim MN,
Baharuddin PJN, Fakiruddin KS and Yahaya B: Human non-small cell
lung cancer expresses putative cancer stem cell markers and
exhibits the transcriptomic profile of multipotent cells. BMC
Cancer. 15:842015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen HY, Lin LT, Wang ML, Tsai KL, Huang
PI, Yang YP, Lee YY, Chen YW, Lo WL, Lan YT, et al: Musashi-1
promotes chemoresistant granule formation by PKR/eIF2α signalling
cascade in refractory glioblastoma. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis
Dis. 1864:1850–1861. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Okano H, Imai T and Okabe M: Musashi: A
translational regulator of cell fate. J Cell Sci. 115:1355–1359.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Singh S, Brocker C, Koppaka V, Chen Y,
Jackson BC, Matsumoto A, Thompson DC and Vasiliou V: Aldehyde
dehydrogenases in cellular responses to oxidative/electrophilic
stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 56:89–101. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ueda K, Ogasawara S, Akiba J, Nakayama M,
Todoroki K, Ueda K, Sanada S, Suekane S, Noguchi M, Matsuoka K and
Yano H: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 identifies cells with cancer stem
cell-like properties in a human renal cell carcinoma cell line.
PLoS One. 8:e754632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rao QX, Yao TT, Zhang BZ, Lin RC, Chen ZL,
Zhou H, Wang LJ, Lu HW, Chen Q, Di N and Lin ZQ: Expression and
functional role of ALDH1 in cervical carcinoma cells. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 13:1325–1331. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xie Q, Liang J, Rao Q, Xie X, Li R, Liu Y,
Zhou H, Han J, Yao T and Lin Z: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 expression
predicts chemoresistance and poor clinical outcomes in patients
with locally advanced cervical cancer treated with neoadjuvant
chemotherapy prior to radical hysterectomy. Ann Surg Oncol.
23:163–170. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yao T, Wu Z, Liu Y, Rao Q and Lin Z:
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 (ALDH1) positivity correlates with poor
prognosis in cervical cancer. J Int Med Res. 42:1038–1042. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yao T, Lu R, Li Y, Peng Y, Ding M, Xie X
and Lin Z: ALDH1 might influence the metastatic capability of HeLa
cells. Tumor Biol. 36:7045–7051. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Nichols J, Zevnik B, Anastassiadis K, Niwa
H, Klewe-Nebenius D, Chambers I, Schöler H and Smith A: Formation
of pluripotent stem cells in the mammalian embryo depends on the
POU transcription factor Oct4. Cell. 95:379–391. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Loh YH, Wu Q, Chew JL, Vega VB, Zhang W,
Chen X, Bourque G, George J, Leong B, Liu J, et al: The Oct4 and
Nanog transcription network regulates pluripotency in mouse
embryonic stem cells. Nat Genet. 38:431–440. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yin X, Zhang BH, Zheng SS, Gao DM, Qiu SJ,
Wu WZ and Ren ZG: Coexpression of gene Oct4 and Nanog initiates
stem cell characteristics in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of Stat3/Snail
signaling. J Hematol Oncol. 8:232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Beier D, Hau P, Proescholdt M, Lohmeier A,
Wischhusen J, Oefner PJ, Aigner L, Brawanski A, Bogdahn U and Beier
CP: CD133(+) and CD133(−) glioblastoma-derived cancer stem cells
show differential growth characteristics and molecular profiles.
Cancer Res. 67:4010–4015. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li SW, Wu XL, Dong CL, Xie XY, Wu JF and
Zhang X: The differential expression of OCT4 isoforms in cervical
carcinoma. PLoS One. 10:e01180332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Shen L, Huang X, Xie X, Su J, Yuan J and
Chen X: High expression of SOX2 and OCT4 indicates radiation
resistance and an independent negative prognosis in cervical
squamous cell carcinoma. J Histochem Cytochem. 62:499–509. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yang Y, Wang Y, Yin C and Li X: Clinical
significance of the stem cell gene Oct-4 in cervical cancer. Tumor
Biol. 35:5339–5345. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Liu H, Wang H, Li C, Zhang T, Meng X,
Zhang Y and Qian H: Spheres from cervical cancer cells display
stemness and cancer drug resistance. Oncol Lett. 12:2184–2188.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Villodre ES, Kipper FC, Pereira MB and
Lenz G: Roles of OCT4 in tumorigenesis, cancer therapy resistance
and prognosis. Cancer Treat Rev. 51:1–9. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kim BW, Cho H, Choi CH, Ylaya K, Chung JY,
Kim JH and Hewitt SM: Clinical significance of OCT4 and SOX2
protein expression in cervical cancer. BMC Cancer. 15:10152015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Boumahdi S, Driessens G, Lapouge G, Rorive
S, Nassar D, Le Mercier M, Delatte B, Caauwe A, Lenglez S, Nkusi E,
et al: SOX2 controls tumour initiation and cancer stem-cell
functions in squamous-cell carcinoma. Nature. 511:246–250. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wilbertz T, Wagner P, Petersen K, Stiedl
AC, Scheble VJ, Maier S, Reischl M, Mikut R, Altorki NK, Moch H, et
al: SOX2 gene amplification and protein overexpression are
associated with better outcome in squamous cell lung cancer. Mod
Pathol. 24:944–953. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Stewart CJ and Crook M: SOX2 expression in
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 3 (CIN3) and superficially
invasive (stage IA1) squamous carcinoma of the cervix. Int J
Gynecol Pathol. 35:566–573. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kaufhold S, Garbán H and Bonavida B: Yin
Yang 1 is associated with cancer stem cell transcription factors
(SOX2, OCT4, BMI1) and clinical implication. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
35:842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Krebsbach PH and Villa-Diaz LG: The role
of integrin α6 (CD49f) in stem cells: More than a conserved
biomarker. Stem Cells and Dev. 26:1090–1099. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Chang JY, Wang C, Jin C, Yang C, Huang Y,
Liu J, McKeehan WL, D'Souza RN and Wang F: Self-renewal and
multilineage differentiation of mouse dental epithelial stem cells.
Stem Cell Res. 11:990–1002. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Villanueva-Toledo J, Ponciano-Gómez A,
Ortiz-Sánchez E and Garrido E: Side populations from
cervical-cancer-derived cell lines have stem-cell-like properties.
Mol Biol Rep. 41:1993–2004. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ammothumkandy A, Maliekal TT, Bose MV,
Rajkumar T, Shirley S, Thejaswini B, Giri VG and Krishna S: CD66
and CD49f expressing cells are associated with distinct neoplastic
phenotypes and progression in human cervical cancer. Eur J Cancer.
60:166–178. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Castelli G, Pelosi E and Testa U: Liver
cancer: Molecular characterization, clonal evolution and cancer
stem cells. Cancers (Basel). 9(pii): E1272017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Xiao S, Zhou Y, Jiang J, Yuan L and Xue M:
CD44 affects the expression level of FOS-like antigen 1 in cervical
cancer tissues. Mol Med Rep. 9:1667–1674. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yin AH, Miraglia S, Zanjani ED,
Almeida-Porada G, Ogawa M, Leary AG, Olweus J, Kearney J and Buck
DW: AC133, a novel marker for human hematopoietic stem and
progenitor cells. Blood. 90:5002–5012. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Jang JW, Song Y, Kim SH, Kim J and Seo HR:
Potential mechanisms of CD133 in cancer stem cells. Life Sci.
184:25–29. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, Squire JA,
Bayani J, Hide T, Henkelman RM, Cusimano MD and Dirks PB:
Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature.
432:396–401. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Javed S, Sharma BK, Sood S, Sharma S,
Bagga R, Bhattacharyya S, Rayat CS, Dhaliwal L and Srinivasan R:
Significance of CD133 positive cells in four novel HPV-16 positive
cervical cancer-derived cell lines and biopsies of invasive
cervical cancer. BMC Cancer. 18:3572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
McGowan KM and Coulombe PA: Onset of
keratin 17 expression coincides with the definition of major
epithelial lineages during skin development. J Cell Biol.
143:469–486. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Carrilho C, Alberto M, Buane L and David
L: Keratins 8, 10, 13, and 17 are useful markers in the diagnosis
of human cervix carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 35:546–551. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wu L, Han L, Zhou C, Wei W, Chen X, Yi H,
Wu X, Bai X, Guo S, Yu Y, et al: TGF-β1-induced CK17 enhances
cancer stem cell-like properties rather than EMT in promoting
cervical cancer metastasis via the ERK1/2-MZF1 signaling pathway.
FEBS J. 284:3000–3017. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Thomas C and Tampé R: Multifaceted
structures and mechanisms of ABC transport systems in health and
disease. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 51:116–128. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Begicevic RR and Falasca M: ABC
transporters in cancer stem cells: Beyond chemoresistance. Int J
Mol Sci. 18(pii): E23622017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Shukla S, Ohnuma S and Ambudkar SV:
Improving cancer chemotherapy with modulators of ABC drug
transporters. Curr Drug Targets. 12:621–630. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Noguchi K, Katayama K and Sugimoto Y:
Human ABC transporter ABCG2/BCRP expression in chemoresistance:
Basic and clinical perspectives for molecular cancer therapeutics.
Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 7:53–64. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Dębska S, Owecka A, Czernek U,
Szydłowska-Pazera K, Habib M and Potemski P: Transmembrane
transporters ABCC-structure, function and role in multidrug
resistance of cancer cells. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online).
65:552–561. 2011.(In Polish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Kim JK, Jeon HY and Kim H: The molecular
mechanisms underlying the therapeutic resistance of cancer stem
cells. Arch Pharm Res. 38:389–401. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Tyagi A, Vishnoi K, Kaur H, Srivastava Y,
Roy BG, Das BC and Bharti AC: Cervical cancer stem cells manifest
radioresistance: Association with upregulated AP-1 activity. Sci
Rep. 7:47812017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Wei ZT, Yu XW, He JX, Liu Y and Zhang SL:
Characteristics of primary side population cervical cancer cells.
Oncol Lett. 14:3536–3544. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhang Y, Liu L, Li F, Wu T, Jiang H, Jiang
X, Du X and Wang Y: Salinomycin exerts anticancer effects on PC-3
cells and PC-3-derived cancer stem cells in vitro and in vivo.
Biomed Res Int. 2017:41016532017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Sordillo PP and Helson L: Curcumin and
cancer stem cells: Curcumin has asymmetrical effects on cancer and
normal stem cells. Anticancer Res. 35:599–614. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Li Y and Zhang T: Targeting cancer stem
cells by curcumin and clinical applications. Cancer Lett.
346:197–205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Liu CM, Peng CY, Liao YW, Lu MY, Tsai ML,
Yeh JC, Yu CH and Yu CC: Sulforaphane targets cancer stemness and
tumor initiating properties in oral squamous cell carcinomas via
miR-200c induction. J Formos Med Assoc. 116:41–48. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Wang X, Li Y, Dai Y, Liu Q, Ning S, Liu J,
Shen Z, Zhu D, Jiang F and Li Z: Sulforaphane improves chemotherapy
efficacy by targeting cancer stem cell-like properties via the
miR-124/IL-6R/STAT3 axis. Sci Rep. 6:367962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Naujokat C and Steinhart R: Salinomycin as
a drug for targeting human cancer stem cells. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2012:9506582012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|