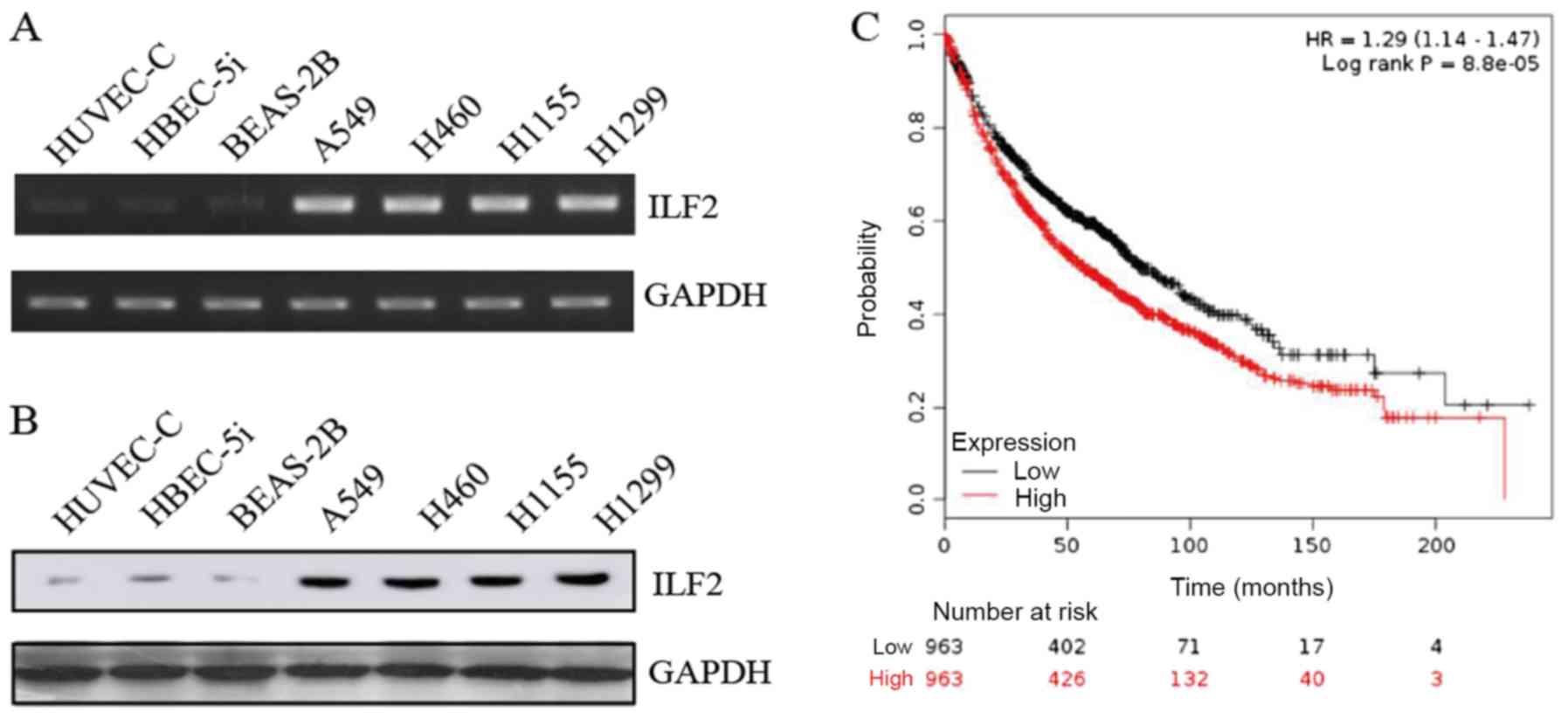
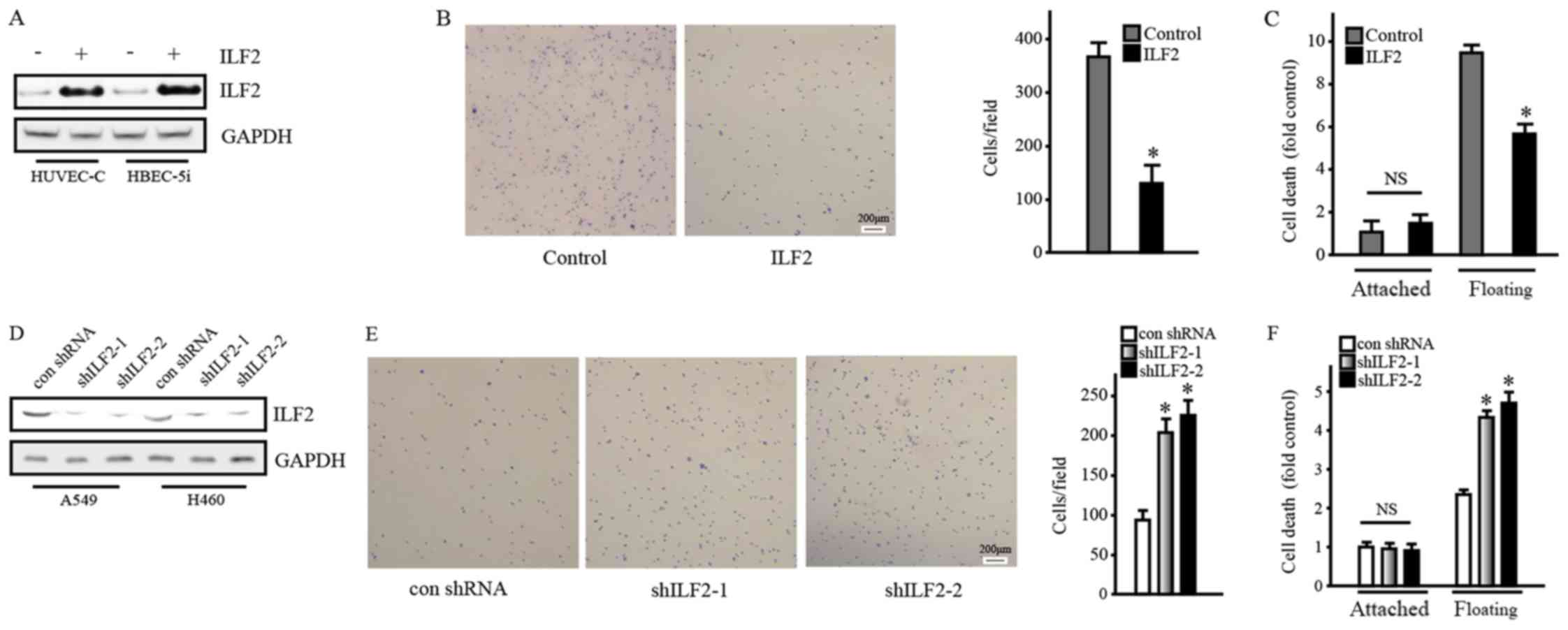
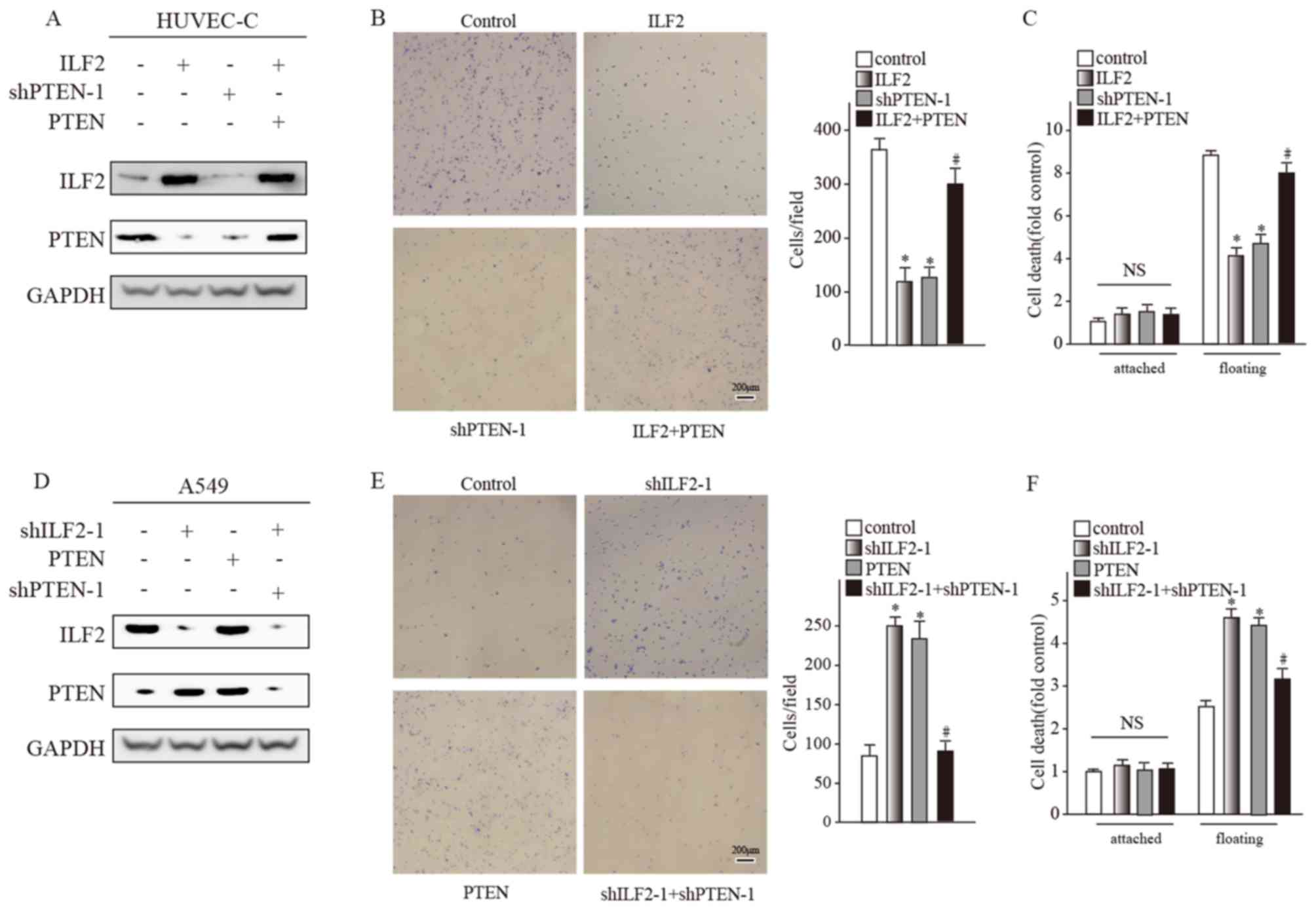
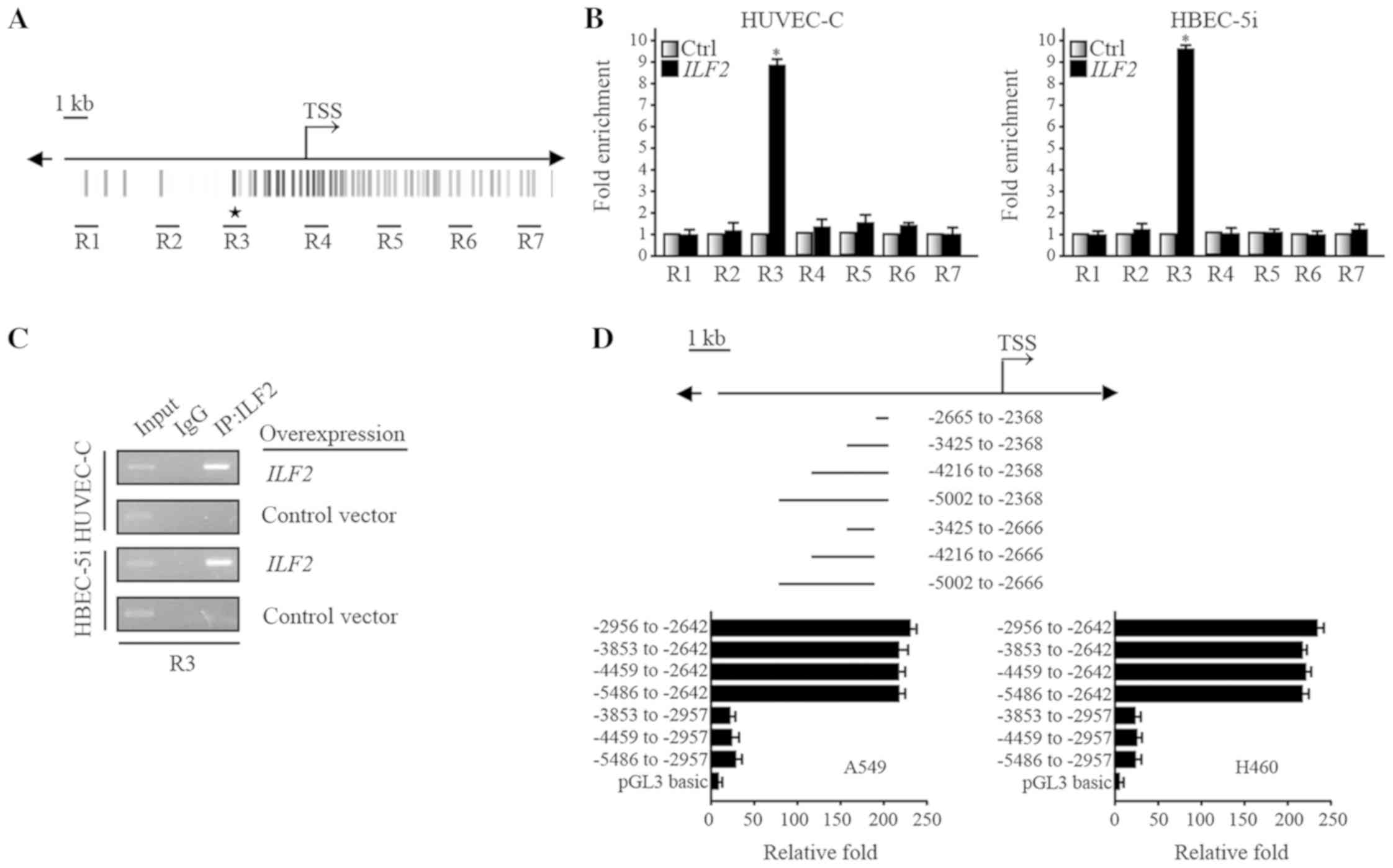
|
1
|
Fernandez LE, Gabri MR, Guthmann MD, Gomez
RE, Gold S, Fainboim L, Gomez DE and Alonso DF: NGcGM3 ganglioside:
A privileged target for cancer vaccines. Clin Dev Immunol.
2010:8143972010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ladanyi M and Pao W: Lung adenocarcinoma:
Guiding EGFR-targeted therapy and beyond. Mod Pathol. 21 (Suppl
2):S16–S22. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhan P, Wang J, Lv XJ, Wang Q, Qiu LX, Lin
XQ, Yu LK and Song Y: Prognostic value of vascular endothelial
growth factor expression in patients with lung cancer: A systematic
review with meta-analysis. J Thorac Oncol. 4:1094–1103. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wyllie AH: ‘Where, O death, is thy sting?’
A brief review of apoptosis biology. Mol Neurobiol. 42:4–9. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ruoslahti E and Reed JC: Anchorage
dependence, integrins, and apoptosis. Cell. 77:477–478. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cheng TL, Symons M and Jou TS: Regulation
of anoikis by Cdc42 and Rac1. Exp Cell Res. 295:497–511. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Frankel A, Rosen K, Filmus J and Kerbel
RS: Induction of anoikis and suppression of human ovarian tumor
growth in vivo by down-regulation of Bcl-X(L). Cancer Res.
61:4837–4841. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yamada KM and Araki M: Tumor suppressor
PTEN: Modulator of cell signaling, growth, migration and apoptosis.
J Cell Sci. 114:2375–2382. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhan M, Zhao H and Han ZC: Signalling
mechanisms of anoikis. Histol Histopathol. 19:973–983.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang Q, He X, Qiu X, Liu X, Sun G, Guo J,
Ding Z, Yang L, Ban N, Tao T and Wang D: Expression of NF45
correlates with malignant grade in gliomas and plays a pivotal role
in tumor growth. Tumour Biol. 35:10149–10157. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ni T, Mao G, Xue Q, Liu Y, Chen B, Cui X,
Lv L, Jia L, Wang Y and Ji L: Upregulated expression of ILF2 in
non-small cell lung cancer is associated with tumor cell
proliferation and poor prognosis. J Mol Histol. 46:325–335. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ni S, Zhu J, Zhang J, Zhang S, Li M, Ni R,
Liu J, Qiu H, Chen W, Wang H and Guo W: Expression and clinical
role of NF45 as a novel cell cycle protein in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma (ESCC). Tumour Biole. 36:747–756. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Haselmann V, Kurz A, Bertsch U, Hübner S,
Olempska-Müller M, Fritsch J, Häsler R, Pickl A, Fritsche H,
Annewanter F, et al: Nuclear death receptor TRAIL-R2 inhibits
maturation of let-7 and promotes proliferation of pancreatic and
other tumor cells. Gastroenterology. 146:278–290. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wan C, Gong C, Ji L, Liu X, Wang Y, Wang
L, Shao M, Yang L, Fan S, Xiao Y, et al: NF45 overexpression is
associated with poor prognosis and enhanced cell proliferation of
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 410:25–35.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee YY, McKinney KQ, Ghosh S, Iannitti DA,
Martinie JB, Caballes FR, Russo MW, Ahrens WA, Lundgren DH, Han DK,
et al: Subcellular tissue proteomics of hepatocellular carcinoma
for molecular signature discovery. J Proteome Res. 10:5070–5083.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li J, Yen C, Liaw D, Podsypanina K, Bose
S, Wang SI, Puc J, Miliaresis C, Rodgers L, McCombie R, et al:
PTEN, a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase gene mutated in human
brain, breast, and prostate cancer. Science. 275:1943–1947. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Datta SR, Brunet A and Greenberg ME:
Cellular survival: A play in three Akts. Genes Dev. 13:2905–2927.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sulis ML and Parsons R: PTEN: From
pathology to biology. Trends Cell Biol. 13:478–483. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tamura M, Gu J, Matsumoto K, Aota S,
Parsons R and Yamada KM: Inhibition of cell migration, spreading,
and focal adhesions by tumor suppressor PTEN. Science.
280:1614–1617. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhong H, Chiles K, Feldser D, Laughner E,
Hanrahan C, Georgescu MM, Simons JW and Semenza GL: Modulation of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression by the epidermal growth
factor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/AKT/FRAP pathway in human
prostate cancer cells: Implications for tumor angiogenesis and
therapeutics. Cancer Res. 60:1541–1545. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li X, Xu Z, Du W, Zhang Z, Wei Y, Wang H,
Zhu Z, Qin L, Wang L, Niu Q, et al: Aiolos promotes anchorage
independence by silencing p66Shc transcription in cancer cells.
Cancer Cell. 25:575–589. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu CY, Takemasa A, Liles WC, Goodman RB,
Jonas M, Rosen H, Chi E, Winn RK, Harlan JM and Chuang PI:
Broad-spectrum caspase inhibition paradoxically augments cell death
in TNF-alpha-stimulated neutrophils. Blood. 101:295–304. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu Z and Garrard WT: Long-range
interactions between three transcriptional enhancers, active Vkappa
gene promoters, and a 3′ boundary sequence spanning 46 kilobases.
Mol Cell Biol. 25:3220–3231. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Győrffy B, Surowiak P, Budczies J and
Lánczky A: Online survival analysis software to assess the
prognostic value of biomarkers using transcriptomic data in
non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 8:e822412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Di Cristofano A and Pandolfi PP: The
multiple roles of PTEN in tumor suppression. Cell. 100:387–390.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shi L, Qiu D, Zhao G, Corthesy B,
Lees-Miller S, Reeves WH and Kao PN: Dynamic binding of Ku80, Ku70
and NF90 to the IL-2 promoter in vivo in activated T-cells. Nucleic
Acids Res. 35:2302–2310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Reck M, Heigener DF, Mok T, Soria JC and
Rabe KF: Management of non-small-cell lung cancer: Recent
developments. Lancet. 382:709–719. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Goldstraw P, Ball D, Jett JR, Le Chevalier
T, Lim E, Nicholson AG and Shepherd FA: Non-small-cell lung cancer.
Lancet. 378:1727–1740. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tan WL, Jain A, Takano A, Newell EW, Iyer
NG, Lim WT, Tan EH, Zhai W, Hillmer AM, Tam WL and Tan DSW: Novel
therapeutic targets on the horizon for lung cancer. Lancet Oncol.
17:e347–e362. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Karmakar S, Mahajan MC, Schulz V, Boyapaty
G and Weissman SM: A multiprotein complex necessary for both
transcription and DNA replication at the β-globin locus. EMBO J.
29:3260–3271. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shamanna RA, Hoque M, Lewis-Antes A, Azzam
EI, Lagunoff D, Pe'ery T and Mathews MB: The NF90/NF45 complex
participates in DNA break repair via nonhomologous end joining. Mol
Cell Biol. 31:4832–4843. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Volk N and Shomron N: Versatility of
MicroRNA biogenesis. PLoS One. 6:e193912011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao G, Shi L, Qiu D, Hu H and Kao PN:
NF45/ILF2 tissue expression, promoter analysis, and interleukin-2
transactivating function. Exp Cell Res. 305:312–323. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shim C, Zhang W, Rhee CH and Lee JH:
Profiling of differentially expressed genes in human primary
cervical cancer by complementary DNA expression array. Clin Cancer
Res. 4:3045–3050. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chung FH, Lee HH and Lee HC: ToP: A
trend-of-disease- progression procedure works well for identifying
cancer genes from multi-state cohort gene expression data for human
colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 8:e656832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Overholtzer M, Mailleux AA, Mouneimne G,
Normand G, Schnitt SJ, King RW, Cibas ES and Brugge JS: A
nonapoptotic cell death process, entosis, that occurs by
cell-in-cell invasion. Cell. 131:966–979. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|