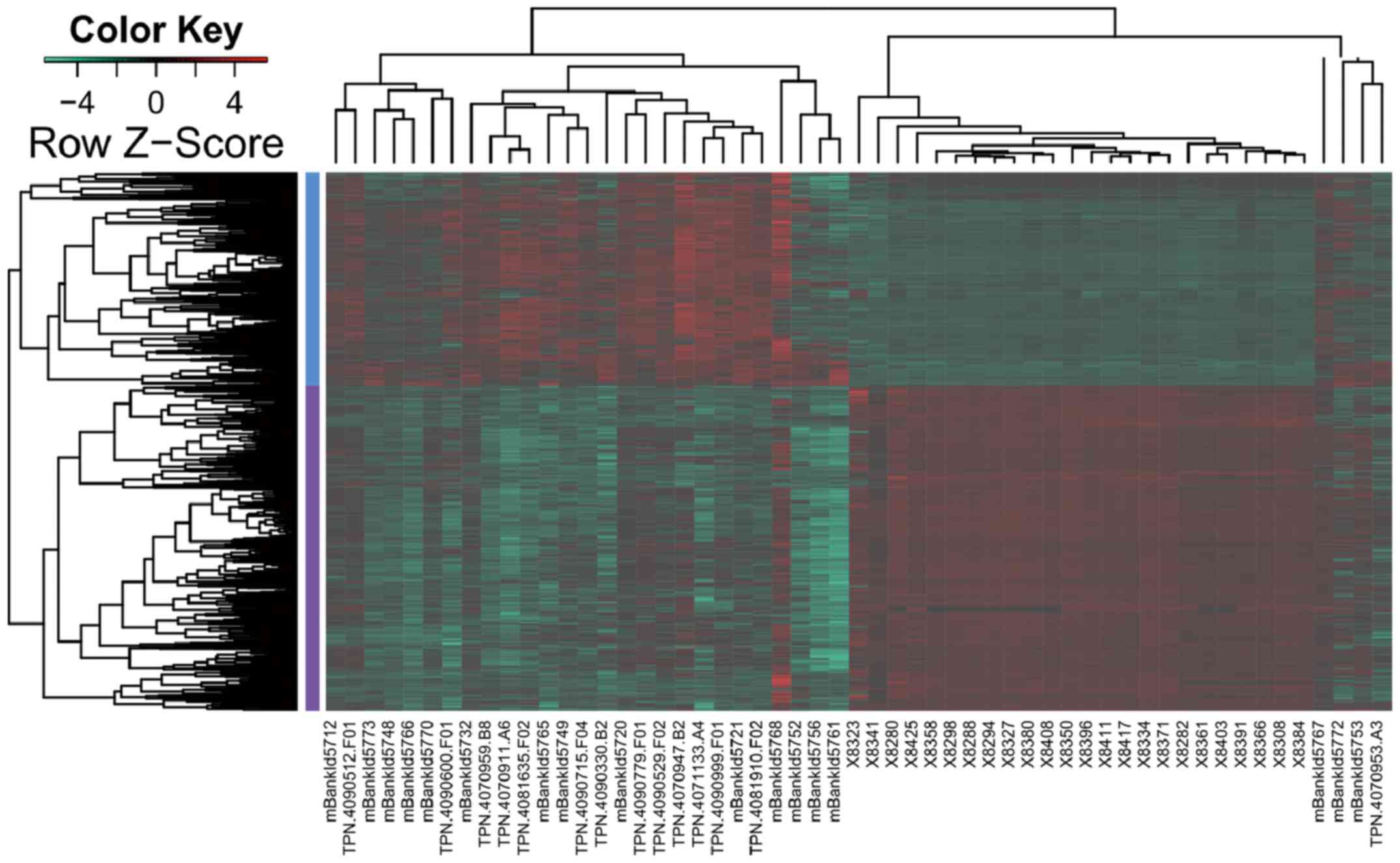
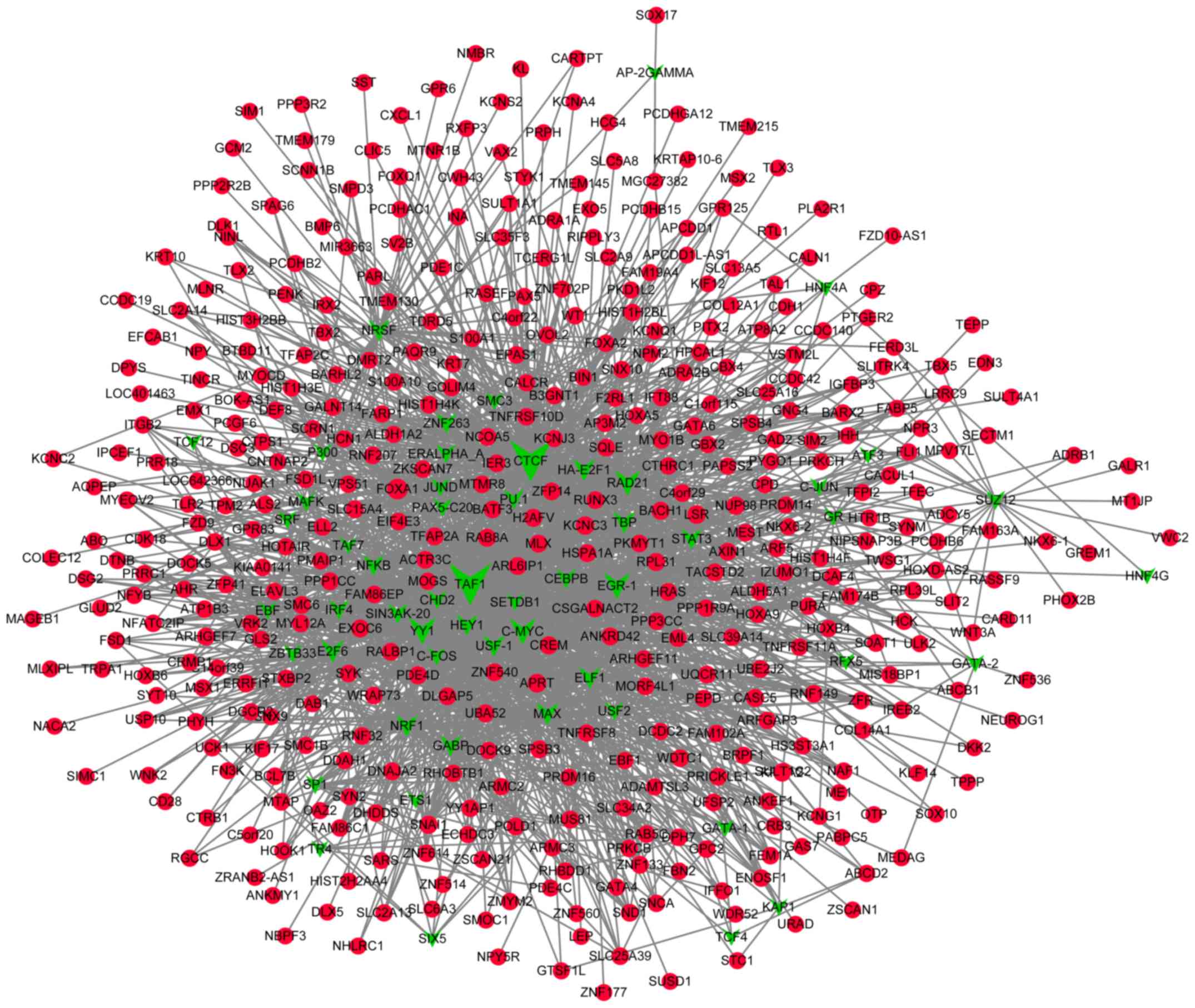
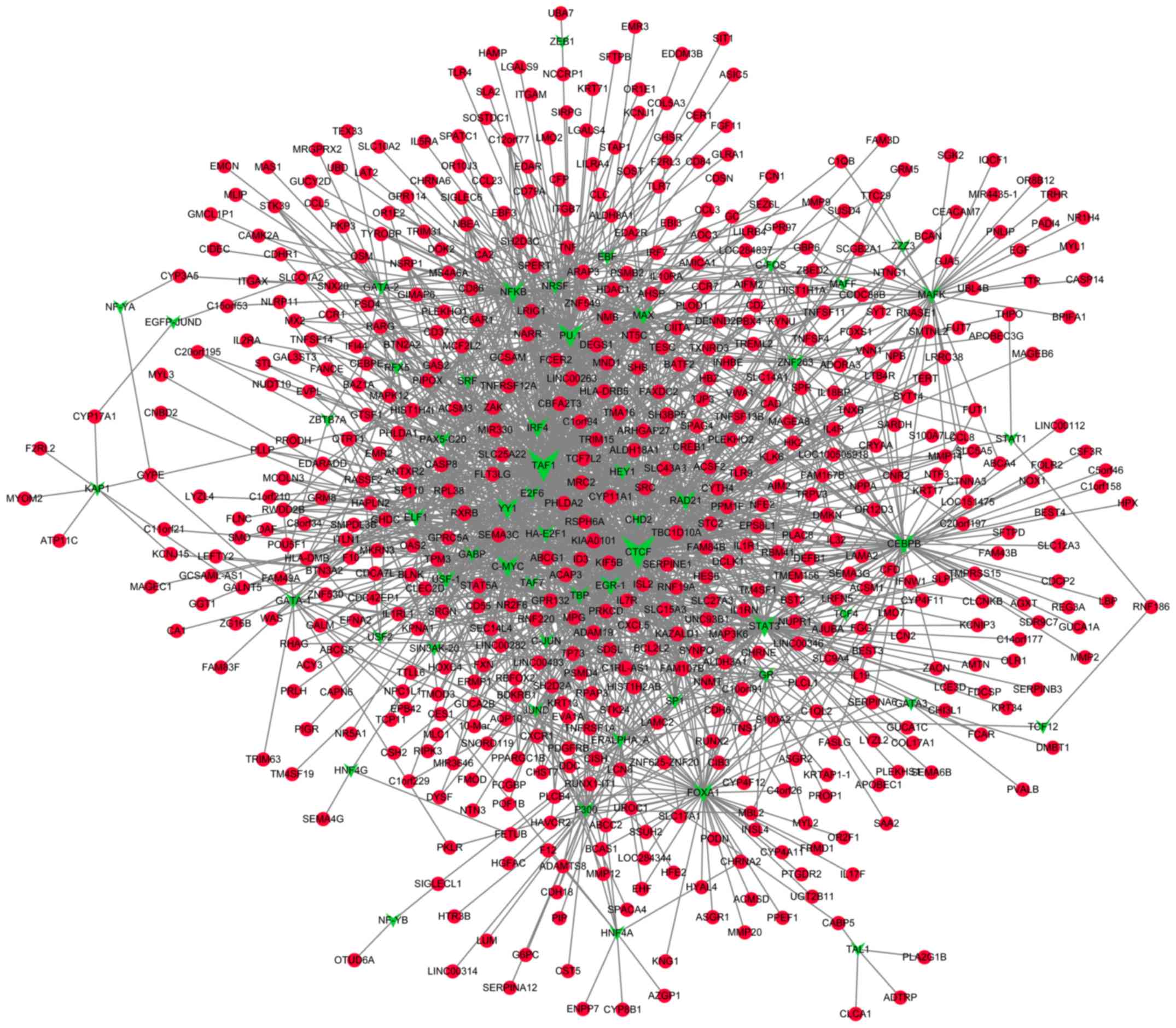
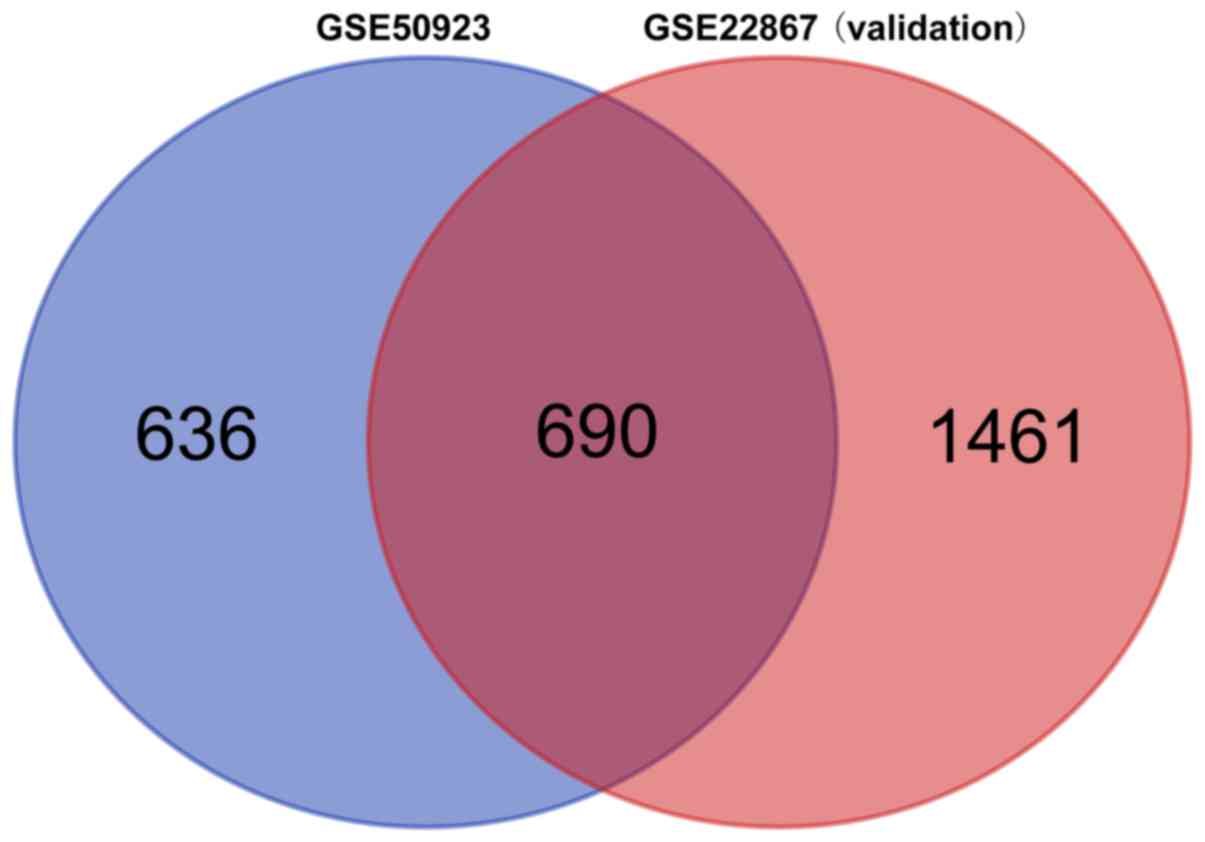
|
1
|
Wen PY and Kesari S: Malignant gliomas in
adults. N Engl J Med. 359:492–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rock K, McArdle O, Forde P, Dunne M,
Fitzpatrick D, O'Neill B and Faul C: A clinical review of treatment
outcomes in glioblastoma multiforme - the validation in a non-trial
population of the results of a randomised phase III: Has a more
radical approach improved survival? Br J Radiol. 85:e729–e733.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Holland EC: Gliomagenesis: Genetic
alterations and mouse models. Nat Rev Genet. 2:120–129. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nagarajan RP and Costello JF: Epigenetic
mechanisms in glioblastoma multiforme. Semin Cancer Biol.
19:188–197. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Herman JG and Baylin SB: Gene silencing in
cancer in association with promoter hypermethylation. N Engl J Med.
349:2042–2054. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Karpf AR and Matsui SI: Genetic disruption
of cytosine DNA methyltransferase enzymes induces chromosomal
instability in human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 65:8635–8639. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nakamura M, Yonekawa Y, Kleihues P and
Ohgaki H: Promoter hypermethylation of the RB1 gene in
glioblastomas. Lab Invest. 81:77–82. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Amatya VJ, Naumann U, Weller M and Ohgaki
H: TP53 promoter methylation in human gliomas. Acta Neuropathol.
110:178–184. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Baeza N, Weller M, Yonekawa Y, Kleihues P
and Ohgaki H: PTEN methylation and expression in glioblastomas.
Acta Neuropathol. 106:479–485. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kreth S, Thon N, Eigenbrod S, Lutz J,
Ledderose C, Egensperger R, Tonn JC, Kretzschmar HA, Hinske LC and
Kreth FW: O-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) mRNA
expression predicts outcome in malignant glioma independent of MGMT
promoter methylation. PLoS One. 6:e171562011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lalezari S, Chou AP, Tran A, Solis OE,
Khanlou N, Chen W, Li S, Carrillo JA, Chowdhury R, Selfridge J, et
al: Combined analysis of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase
protein expression and promoter methylation provides optimized
prognostication of glioblastoma outcome. Neuro Oncol. 15:370–381.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Garcia-Manero G: Demethylating agents in
myeloid malignancies. Curr Opin Oncol. 20:705–710. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li D, Xie Z, Pape ML and Dye T: An
evaluation of statistical methods for DNA methylation microarray
data analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 16:2172015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu C, Zhang JG, Lin D, Zhang L, Shen H and
Deng HW: A systemic analysis of transcriptomic and epigenomic data
to reveal regulation patterns for complex disease. G3 (Bethesda).
7:2271–2279. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Smith AA, Huang YT, Eliot M, Houseman EA,
Marsit CJ, Wiencke JK and Kelsey KT: A novel approach to the
discovery of survival biomarkers in glioblastoma using a joint
analysis of DNA methylation and gene expression. Epigenetics.
9:873–883. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gadaleta F, Bessonov K and Van Steen K:
Integration of gene expression and methylation to unravel
biological networks in glioblastoma patients. Genet Epidemiol.
41:136–144. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lai RK, Chen Y, Guan X, Nousome D, Sharma
C, Canoll P, Bruce J, Sloan AE, Cortes E, Vonsattel JP, et al:
Genome-wide methylation analyses in glioblastoma multiforme. PLoS
One. 9:e893762014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Du P, Kibbe WA and Lin SM: Lumi: A
pipeline for processing Illumina microarray. Bioinformatics.
24:1547–1548. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Du P, Zhang X, Huang CC, Jafari N, Kibbe
WA, Hou L and Lin SM: Comparison of Beta-value and M-value methods
for quantifying methylation levels by microarray analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 11:5872010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Du P and Bourgon R: methyAnalysis: An R
package for DNA methylation data analysis and visualization.
2013.
|
|
21
|
Harris MA, Clark J, Ireland A, Lomax J,
Ashburner M, Foulger R, Eilbeck K, Lewis S, Marshall B, Mungall C,
et al: The gene ontology (GO) database and informatics resource.
Nucleic Acids Res. 32:D258–D261. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Joshi-Tope G, Gillespie M, Vastrik I,
D'Eustachio P, Schmidt E, de Bono B, Jassal B, Gopinath GR, Wu GR,
Matthews L, et al: Reactome: A knowledgebase of biological
pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:D428–D432. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao M, Sun J and Zhao Z: TSGene: A web
resource for tumor suppressor genes. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:D970–D976. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen JS, Hung WS, Chan HH, Tsai SJ and Sun
HS: In silico identification of oncogenic potential of fyn-related
kinase in hepatocellular carcinoma. Bioinformatics. 29:420–427.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
ENCODE Project Consortium: The ENCODE
(ENCyclopedia of DNA elements) project. Science. 306:636–640. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Landt SG, Marinov GK, Kundaje A,
Kheradpour P, Pauli F, Batzoglou S, Bernstein BE, Bickel P, Brown
JB, Cayting P, et al: ChIP-seq guidelines and practices of the
ENCODE and modENCODE consortia. Genome Res. 22:1813–1831. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Etcheverry A, Aubry M, de Tayrac M,
Vauleon E, Boniface R, Guenot F, Saikali S, Hamlat A, Riffaud L,
Menei P, et al: DNA methylation in glioblastoma: Impact on gene
expression and clinical outcome. BMC Genomics. 11:7012010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gentleman R, Carey V, Huber W and Hahne F:
Genefilter: Methods for filtering genes from microarray
experiments. R Package version 1.66.0. 2011.
|
|
31
|
Eiró N and Vizoso FJ: Inflammation and
cancer. World J Gastrointest Surg. 4:62–72. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Spiegelberg BD and Hamm HE: Roles of
G-protein-coupled receptor signaling in cancer biology and gene
transcription. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 17:40–44. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Anglim PP, Alonzo TA and Laird-Offringa
IA: DNA methylation-based biomarkers for early detection of
non-small cell lung cancer: An update. Mol Cancer. 7:812008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hill VK, Ricketts C, Bieche I, Vacher S,
Gentle D, Lewis C, Maher ER and Latif F: Genome-wide DNA
methylation profiling of CpG islands in breast cancer identifies
novel genes associated with tumorigenicity. Cancer Res.
71:2988–2999. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shin SH, Kim BH, Jang JJ, Suh KS and Kang
GH: Identification of novel methylation markers in hepatocellular
carcinoma using a methylation array. J Korean Med Sci.
25:1152–1159. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Knerr I, Schuster S, Nomikos P, Buchfelder
M, Dötsch J, Schoof E, Fahlbusch R and Rascher W: Gene expression
of adrenomedullin, leptin, their receptors and neuropeptide Y in
hormone-secreting and non-functioning pituitary adenomas,
meningiomas and malignant intracranial tumours in humans.
Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 27:215–222. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kore RA and Abraham EC: Inflammatory
cytokines, interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha,
upregulated in glioblastoma multiforme, raise the levels of CRYAB
in exosomes secreted by U373 glioma cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 453:326–331. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang L, Qin H, Li L, Feng F, Ji P, Zhang
J, Li G, Zhao Z and Gao G: Forkhead-box A1 transcription factor is
a novel adverse prognosis marker in human glioma. J Clin Neurosci.
20:654–658. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hurlock EC, McMahon A and Joho RH:
Purkinje-cell-restricted restoration of Kv3.3 function restores
complex spikes and rescues motor coordination in Kcnc3 mutants. J
Neurosci. 28:4640–4648. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Martinez R, Stuhmer W, Martin S, Schell J,
Reichmann A, Rohde V and Pardo L: Analysis of the expression of
Kv10.1 potassium channel in patients with brain metastases and
glioblastoma multiforme: Impact on survival. BMC Cancer.
15:8392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Arvind S, Arivazhagan A, Santosh V and
Chandramouli BA: Differential expression of a novel voltage gated
potassium channel-Kv 1.5 in astrocytomas and its impact on
prognosis in glioblastoma. Br J Neurosurg. 26:16–20. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Qi L, Bellail AC, Rossi MR, Zhang Z, Pang
H, Hunter S, Cohen C, Moreno CS, Olson JJ, Li S and Hao C:
Heterogeneity of primary glioblastoma cells in the expression of
caspase-8 and the response to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis.
16:1150–1164. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|