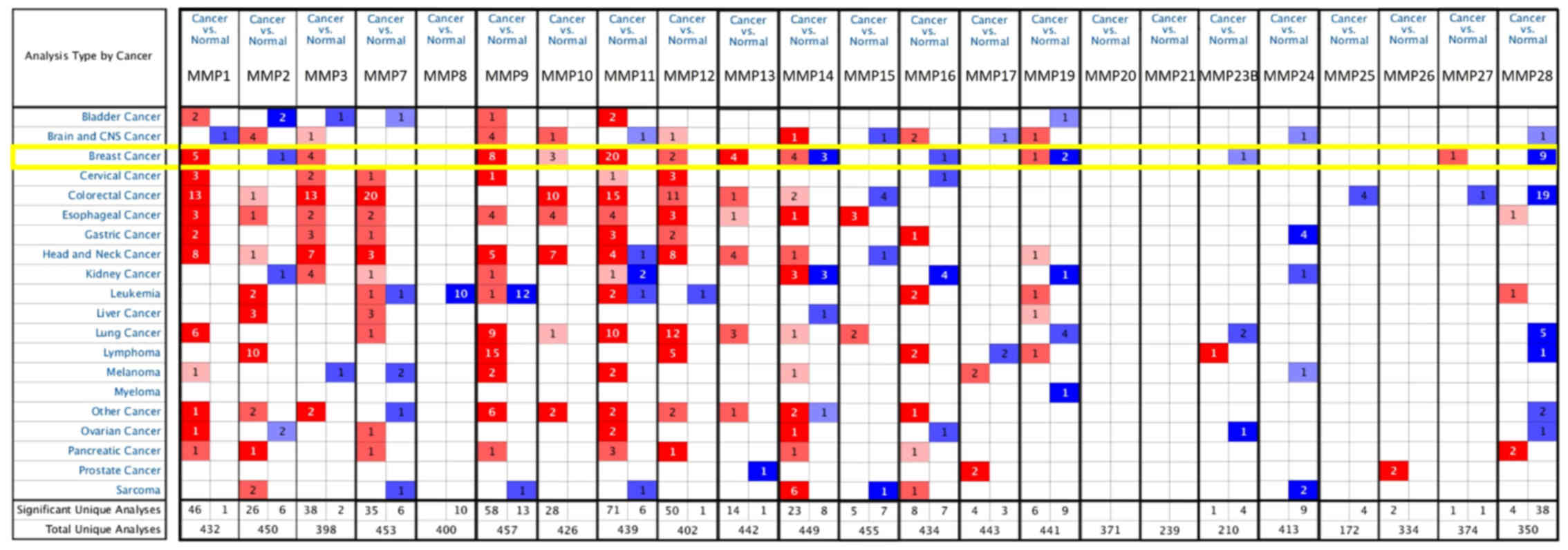
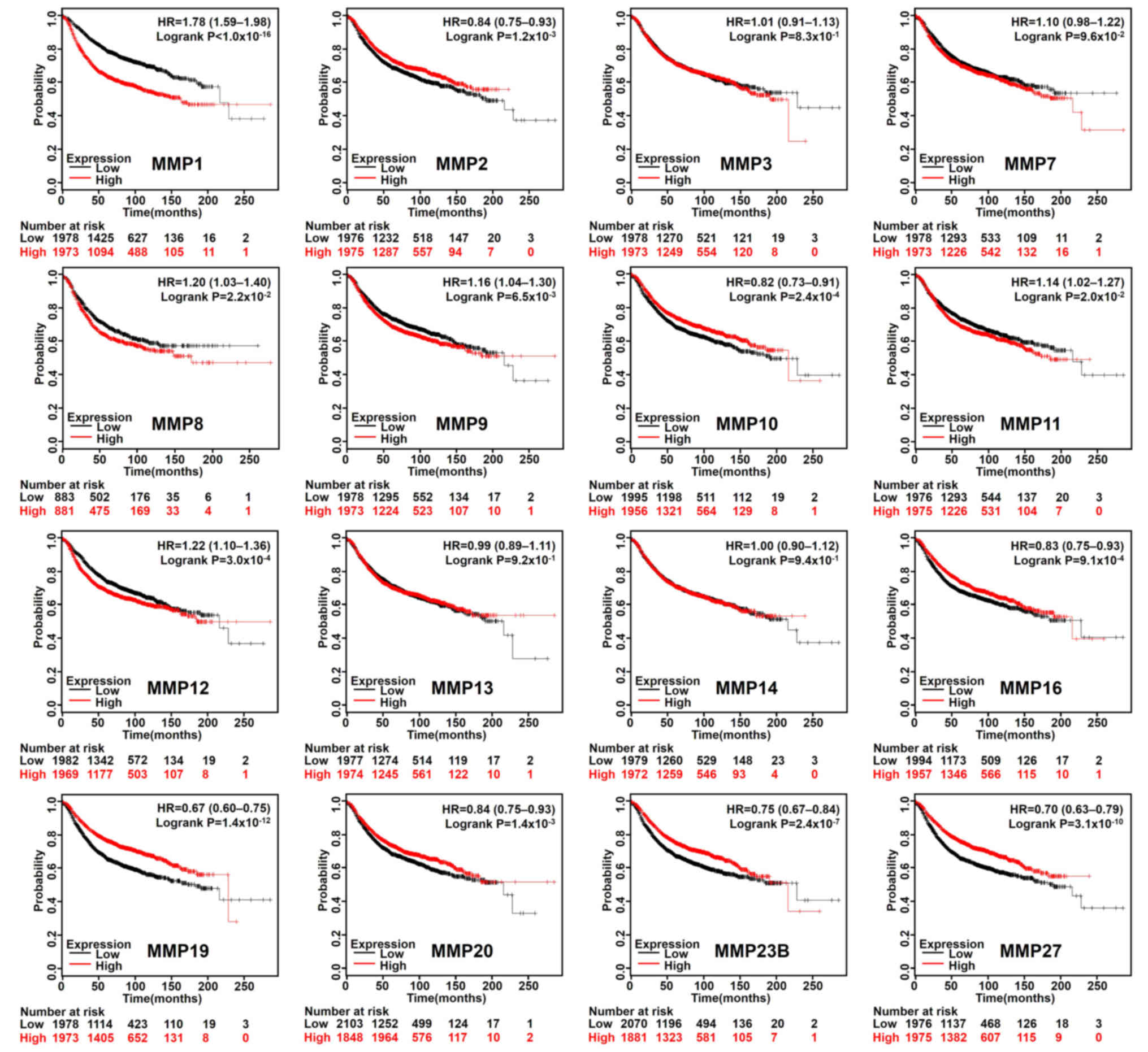
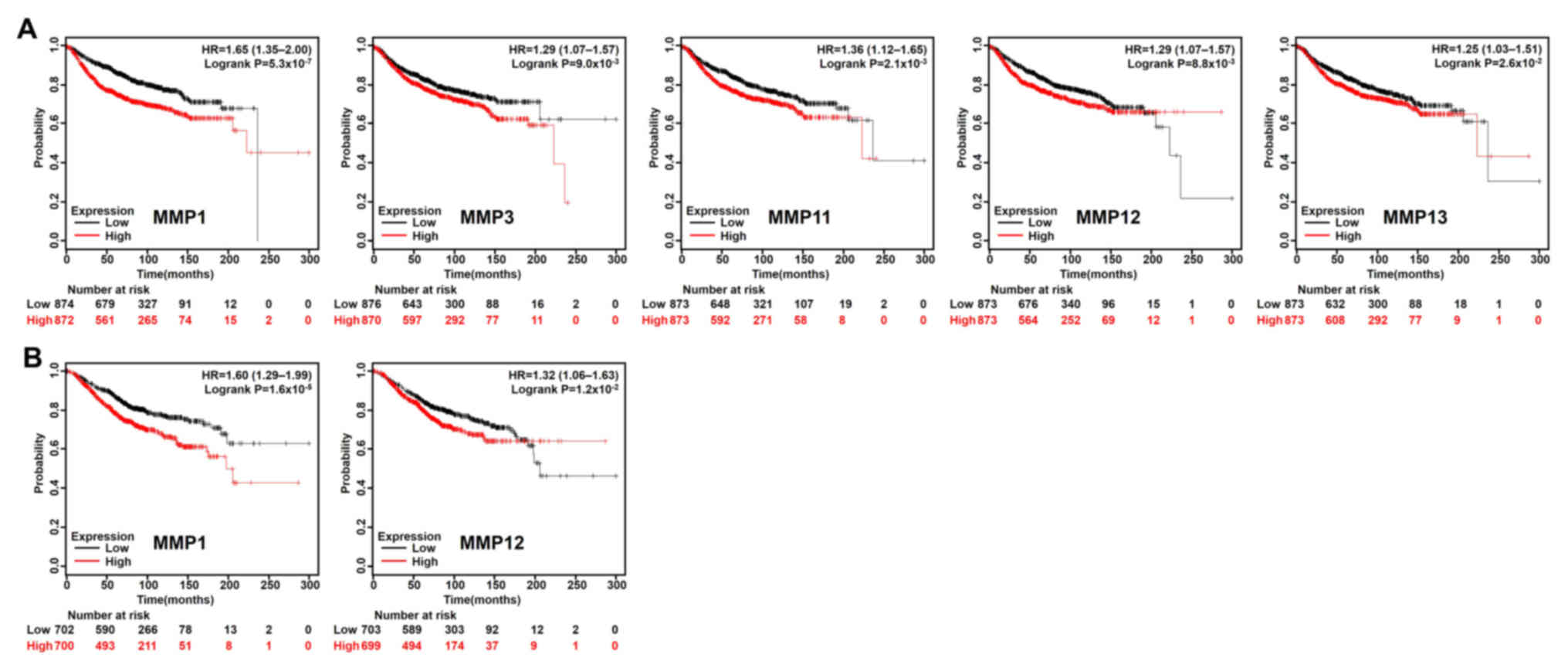
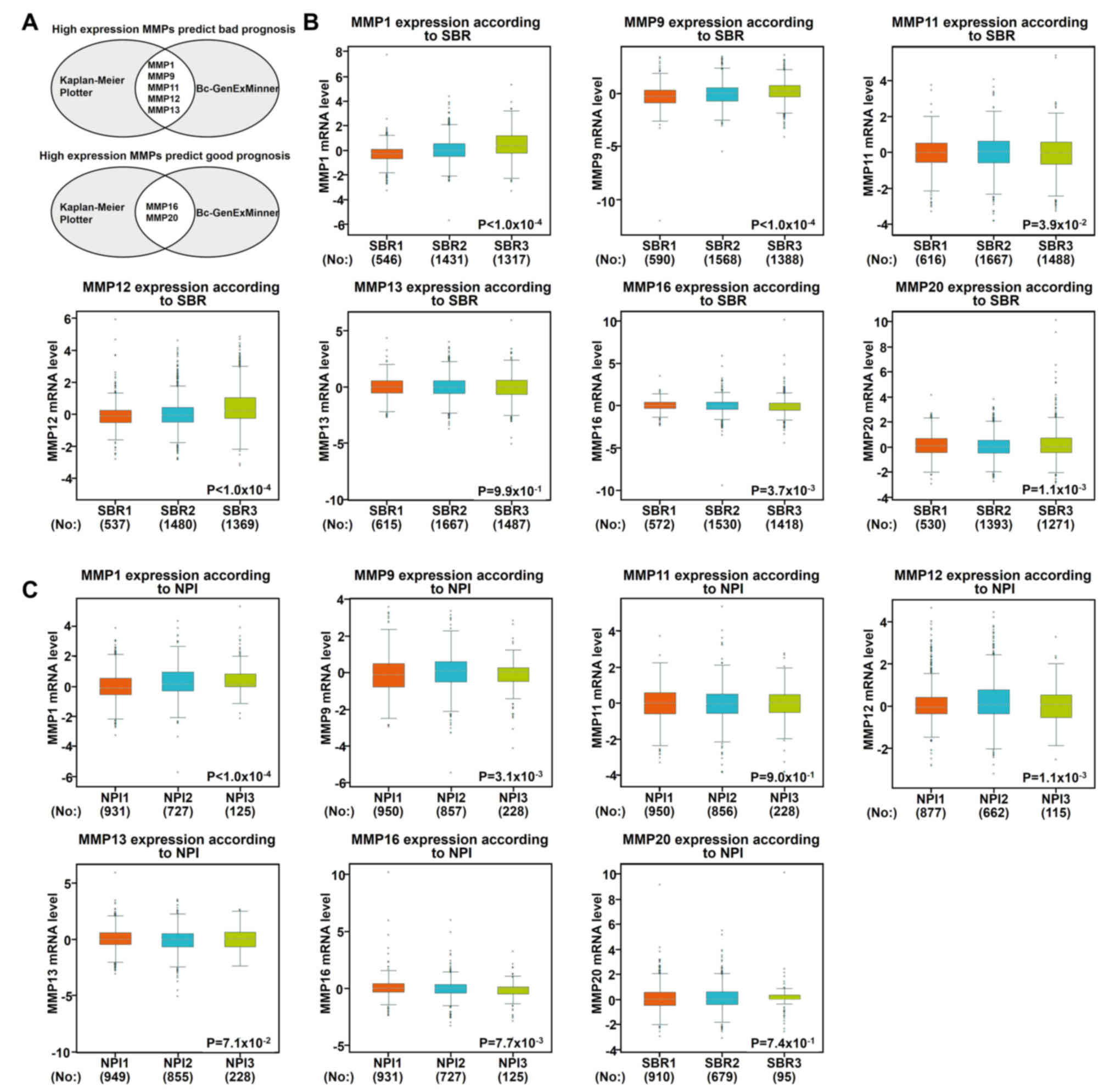
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB,
Kramer JL, Rowland JH, Stein KD, Alteri R and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin.
66:271–289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen E, Qin X, Peng K, Xu X, Li W, Cheng
X, Tang C, Cui Y, Wang Z and Liu T: Identification of potential
therapeutic targets among CXC chemokines in breast tumor
microenvironment using integrative bioinformatics analysis. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 45:1731–1746. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gross J and Lapiere CM: Collagenolytic
activity in amphibian tissues: A tissue culture assay. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 48:1014–1022. 1962. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Takahashi E, Tateyama H, Akatsu H,
Yamakawa Y, Fujii Y and Eimoto T: Expression of matrix
metalloproteinases 2 and 7 in tumor cells correlates with the World
Health Organization classification subtype and clinical stage of
thymic epithelial tumors. Hum Pathol. 34:1253–1258. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Page-McCaw A, Ewald AJ and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:221–233. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cui N, Hu M and Khalil RA: Biochemical and
biological attributes of matrix metalloproteinases. Prog Mol Biol
Transl Sci. 147:1–73. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
141:52–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Alaseem A, Alhazzani K, Dondapati P,
Alobid S, Bishayee A and Rathinavelu A: Matrix metalloproteinases:
A challenging paradigm of cancer management. Semin Cancer Biol.
56:100–115. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fernandez-Garcia B, Eiro N, Marin L,
González-Reyes S, González LO, Lamelas ML and Vizoso FJ: Expression
and prognostic significance of fibronectin and matrix
metalloproteases in breast cancer metastasis. Histopathology.
64:512–522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, Deshpande N,
Varambally R, Ghosh D, Barrette T, Pandey A and Chinnaiyan AM:
ONCOMINE: A cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining
platform. Neoplasia. 6:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gyorffy B, Lanczky A, Eklund AC, Denkert
C, Budczies J, Li Q and Szallasi Z: An online survival analysis
tool to rapidly assess the effect of 22,277 genes on breast cancer
prognosis using microarray data of 1,809 patients. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 123:725–731. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jezequel P, Campone M, Gouraud W,
Guérin-Charbonnel C, Leux C, Ricolleau G and Campion L:
bc-GenExMiner: An easy-to-use online platform for gene prognostic
analyses in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 131:765–775.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G,
Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al:
Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical
profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 6:pl12013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Richardson AL, Wang ZC, De Nicolo A, Lu X,
Brown M, Miron A, Liao X, Iglehart JD, Livingston DM and Ganesan S:
X chromosomal abnormalities in basal-like human breast cancer.
Cancer Cell. 9:121–132. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T,
Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey
SS, et al: Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas
distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:10869–10874. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sorlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J, Hastie
T, Marron JS, Nobel A, Deng S, Johnsen H, Pesich R, Geisler S, et
al: Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent
gene expression data sets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:8418–8423.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Curtis C, Shah SP, Chin SF, Turashvili G,
Rueda OM, Dunning MJ, Speed D, Lynch AG, Samarajiwa S, Yuan Y, et
al: The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2,000 breast
tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature. 486:346–352. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Radvanyi L, Singh-Sandhu D, Gallichan S,
Lovitt C, Pedyczak A, Mallo G, Gish K, Kwok K, Hanna W, Zubovits J,
et al: The gene associated with trichorhinophalangeal syndrome in
humans is overexpressed in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:11005–11010. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Turashvili G, Bouchal J, Baumforth K, Wei
W, Dziechciarkova M, Ehrmann J, Klein J, Fridman E, Skarda J,
Srovnal J, et al: Novel markers for differentiation of lobular and
ductal invasive breast carcinomas by laser microdissection and
microarray analysis. BMC Cancer. 7:552007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Karnoub AE, Dash AB, Vo AP, Sullivan A,
Brooks MW, Bell GW, Richardson AL, Polyak K, Tubo R and Weinberg
RA: Mesenchymal stem cells within tumour stroma promote breast
cancer metastasis. Nature. 449:557–563. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Le Doussal V, Tubiana-Hulin V, Friedman S,
Hacene K, Spyratos F and Brunet M: Prognostic value of histologic
grade nuclear components of Scarff-Bloom-Richardson (SBR). An
improved score modification based on a multivariate analysis of
1262 invasive ductal breast carcinomas. Cancer. 64:1914–1921. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bansal C, Singh US, Misra S, Sharma KL,
Tiwari V and Srivastava AN: Comparative evaluation of the modified
Scarff-Bloom-Richardson grading system on breast carcinoma
aspirates and histopathology. Cytojournal. 9:42012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu K, Lee CH, Tan PH, Hong GS, Wee SB,
Wong CY and Tan P: A molecular signature of the Nottingham
prognostic index in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 64:2962–2968. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gluck S: Extending the clinical benefit of
endocrine therapy for women with hormone receptor-positive
metastatic breast cancer: Differentiating mechanisms of action.
Clin Breast Cancer. 14:75–84. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dawood S: Triple-negative breast cancer:
Epidemiology and management options. Drugs. 70:2247–2258. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Javadian M, Gharibi T, Shekari N,
Abdollahpour-Alitappeh M, Mohammadi A, Hossieni A, Mohammadi H and
Kazemi T: The role of microRNAs regulating the expression of matrix
metalloproteinases MMPs) in breast cancer development, progression,
and meta stasis. J Cell Physiol. 234:5399–5412. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Coussens LM, Fingleton B and Matrisian LM:
Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors and cancer: Trials and
tribulations. Science. 295:2387–2392. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shay G, Lynch CC and Fingleton B: Moving
targets: Emerging roles for MMPs in cancer progression and
metastasis. Matrix Biol. 44-46:200–206. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kohrmann A, Kammerer U, Kapp M, Dietl J
and Anacker J: Expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in
primary human breast cancer and breast cancer cell lines: New
findings and review of the literature. BMC Cancer. 9:1882009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bostrom P, Soderstrom M, Vahlberg T,
Söderström KO, Roberts PJ, Carpén O and Hirsimäki P: MMP-1
expression has an independent prognostic value in breast cancer.
BMC Cancer. 11:3482011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kulic A, Dedic Plavetic N, Vrbanec J and
Sirotković-Skerlev M: Low serum MMP-1 in breast cancer: A negative
prognostic factor? Biomarkers. 17:416–421. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mendes O, Kim HT, Lungu G and Stoica G:
MMP2 role in breast cancer brain metastasis development and its
regulation by TIMP2 and ERK1/2. Clin Exp Metastasis. 24:341–351.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li H, Qiu Z, Li F and Wang C: The
relationship between MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression levels with breast
cancer incidence and prognosis. Oncol Lett. 14:5865–5870.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ren F, Tang R, Zhang X, Madushi WM, Luo D,
Dang Y, Li Z, Wei K and Chen G: Overexpression of MMP family
members functions as prognostic biomarker for breast cancer
patients: A Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One.
10:e01355442015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chu C, Liu X, Bai X, Zhao T, Wang M, Xu R,
Li M, Hu Y, Li W, Yang LU, et al: MiR-519d suppresses breast cancer
tumorigenesis and metastasis via targeting MMP3. Int J Biol Sci.
14:228–236. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Panagopoulos V, Leach DA, Zinonos I,
Ponomarev V, Licari G, Liapis V, Ingman WV, Anderson P, DeNichilo
MO and Evdokiou A: Inflammatory peroxidases promote breast cancer
progression in mice via regulation of the tumour microenvironment.
Int J Oncol. 50:1191–1200. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Slattery ML, John E, Torres-Mejia G, Stern
M, Lundgreen A, Hines L, Giuliano A, Baumgartner K, Herrick J and
Wolff RK: Matrix metalloproteinase genes are associated with breast
cancer risk and survival: The Breast Cancer Health Disparities
Study. PLoS One. 8:e631652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vizoso FJ, Gonzalez LO, Corte MD,
Rodríguez JC, Vázquez J, Lamelas ML, Junquera S, Merino AM and
García-Muñiz JL: Study of matrix metalloproteinases and their
inhibitors in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 96:903–911. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kim GE, Lee JS, Choi YD, Lee KH, Lee JH,
Nam JH, Choi C, Kim SS, Park MH, Yoon JH and Kweon SS: Expression
of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in different
immunohistochemical-based molecular subtypes of breast cancer. BMC
Cancer. 14:9592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sizemore ST and Keri RA: The forkhead box
transcription factor FOXC1 promotes breast cancer invasion by
inducing matrix metalloprotease 7 (MMP7) expression. J Biol Chem.
287:24631–24640. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Aroner SA, Rosner BA, Tamimi RM, Tworoger
SS, Baur N, Joos TO and Hankinson SE: Plasma matrix
metalloproteinase 1, 3, and 7 levels and breast cancer risk in the
Nurses' Health study. Cancer Causes Control. 25:1717–1723. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Van Lint P and Libert C: Matrix
metalloproteinase-8: Cleavage can be decisive. Cytokine Growth
Factor Rev. 17:217–223. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Decock J, Long JR, Laxton RC, Shu XO,
Hodgkinson C, Hendrickx W, Pearce EG, Gao YT, Pereira AC, Paridaens
R, et al: Association of matrix metalloproteinase-8 gene variation
with breast cancer prognosis. Cancer Res. 67:10214–10221. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Decock J, Hendrickx W, Vanleeuw U, Van
Belle V, Van Huffel S, Christiaens MR, Ye S and Paridaens R: Plasma
MMP1 and MMP8 expression in breast cancer: Protective role of MMP8
against lymph node metastasis. BMC Cancer. 8:772008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liu B, Cui J, Sun J, Li J, Han X, Guo J,
Yi M, Amizuka N, Xu X and Li M: Immunolocalization of MMP9 and MMP2
in osteolytic metastasis originating from MDA-MB-231 human breast
cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 14:1099–1106. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang X, Lu H, Urvalek AM, Li T, Yu L,
Lamar J, DiPersio CM, Feustel PJ and Zhao J: KLF8 promotes human
breast cancer cell invasion and metastasis by transcriptional
activation of MMP9. Oncogene. 30:1901–1911. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Prasad CP, Chaurasiya SK, Axelsson L and
Andersson T: WNT-5A triggers Cdc42 activation leading to an ERK1/2
dependent decrease in MMP9 activity and invasive migration of
breast cancer cells. Mol Oncol. 7:870–883. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Muller D, Quantin B, Gesnel MC,
Millon-Collard R, Abecassis J and Breathnach R: The collagenase
gene family in humans consists of at least four members. Biochem J.
253:187–192. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Thakur S, Nabbi A, Klimowicz A and
Riabowol K: Stromal ING1 expression induces a secretory phenotype
and correlates with breast cancer patient survival. Mol Cancer.
14:1642015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
de Vega RC, Sanchez MLF, Eiro N, Vizoso
FJ, Sperling M, Karst U and Medel AS: Multimodal laser
ablation/desorption imaging analysis of Zn and MMP-11 in breast
tissues. Anal Bioanal Chem. 410:913–922. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Han J, Choi YL, Kim H, Choi JY, Lee SK,
Lee JE, Choi JS, Park S, Choi JS, Kim YD, et al: MMP11 and CD2 as
novel prognostic factors in hormone receptor-negative,
HER2-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 164:41–56.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kasper G, Reule M, Tschirschmann M,
Dankert N, Stout-Weider K, Lauster R, Schrock E, Mennerich D, Duda
GN and Lehmann KE: Stromelysin-3 over-expression enhances
tumourigenesis in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell lines:
Involvement of the IGF-1 signalling pathway. BMC Cancer. 7:122007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kwon YJ, Hurst DR, Steg AD, Yuan K, Vaidya
KS, Welch DR and Frost AR: Gli1 enhances migration and invasion via
up-regulation of MMP-11 and promotes metastasis in ERalpha negative
breast cancer cell lines. Clin Exp Metastasis. 28:437–449. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Margheri F, Serrati S, Lapucci A,
Anastasia C, Giusti B, Pucci M, Torre E, Bianchini F, Calorini L,
Albini A, et al: Systemic sclerosis-endothelial cell antiangiogenic
pentraxin 3 and matrix metalloprotease 12 control human breast
cancer tumor vascularization and development in mice. Neoplasia.
11:1106–1115. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Delassus GS, Cho H and Eliceiri GL: New
signaling pathways from cancer progression modulators to mRNA
expression of matrix metalloproteinases in breast cancer cells. J
Cell Physiol. 226:3378–3384. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Hernandez L, Magalhaes MA, Coniglio SJ,
Condeelis JS and Segall JE: Opposing roles of CXCR4 and CXCR7 in
breast cancer metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 13:R1282011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chang HJ, Yang MJ, Yang YH, Hou MF, Hsueh
EJ and Lin SR: MMP13 is potentially a new tumor marker for breast
cancer diagnosis. Oncol Rep. 22:1119–1127. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Nannuru KC, Futakuchi M, Varney ML,
Vincent TM, Marcusson EG and Singh RK: Matrix metalloproteinase
(MMP)-13 regulates mammary tumor-induced osteolysis by activating
MMP9 and transforming growth factor-beta signaling at the
tumor-bone interface. Cancer Res. 70:3494–3504. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Alfranca A, Lopez-Oliva JM, Genis L,
López-Maderuelo D, Mirones I, Salvado D, Quesada AJ, Arroyo AG and
Redondo JM: PGE2 induces angiogenesis via MT1-MMP-mediated
activation of the TGFbeta/Alk5 signaling pathway. Blood.
112:1120–1128. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Turunen SP, Tatti-Bugaeva O and Lehti K:
Membrane-type matrix metalloproteases as diverse effectors of
cancer progression. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res.
1864:1974–1988. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ager EI, Kozin SV, Kirkpatrick ND, Seano
G, Kodack DP, Askoxylakis V, Huang Y, Goel S, Snuderl M, Muzikansky
A, et al: Blockade of MMP14 activity in murine breast carcinomas:
Implications for macrophages, vessels, and radiotherapy. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 107(pii): djv0172015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ma XJ, Dahiya S, Richardson E, Erlander M
and Sgroi DC: Gene expression profiling of the tumor
microenvironment during breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer
Res. 11:R72009.(Table S1). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Finak G, Bertos N, Pepin F, Sadekova S,
Souleimanova M, Zhao H, Chen H, Omeroglu G, Meterissian S, Omeroglu
A, et al: Stromal gene expression predicts clinical outcome in
breast cancer. Nat Med. 14:518–527. 2008.(Table S1). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn
M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA,
et al: Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature.
406:747–752. 2000.(Table S1). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Gluck S, Ross JS, Royce M, McKenna EF Jr,
Perou CM, Avisar E and Wu L: TP53 genomics predict higher clinical
and pathologic tumor response in operable early-stage breast cancer
treated with docetaxel-capecitabine ± trastuzumab. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 132:781–791. 2012.(Table S1). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|