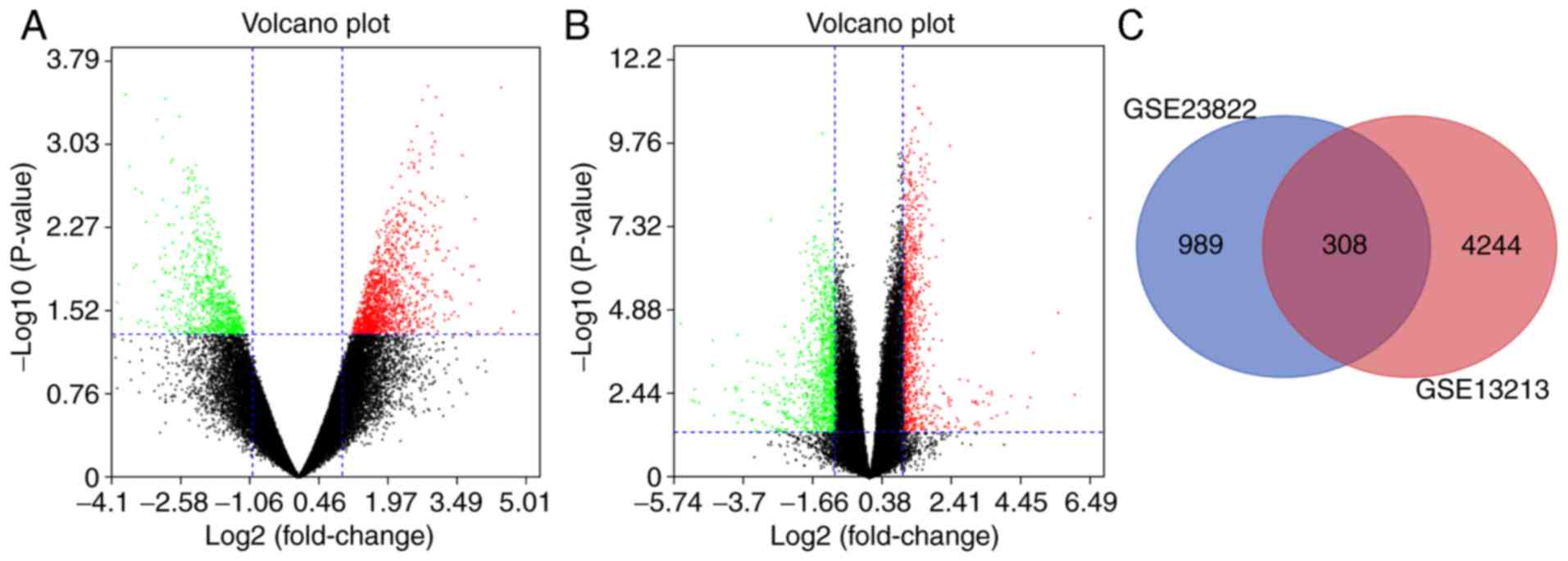
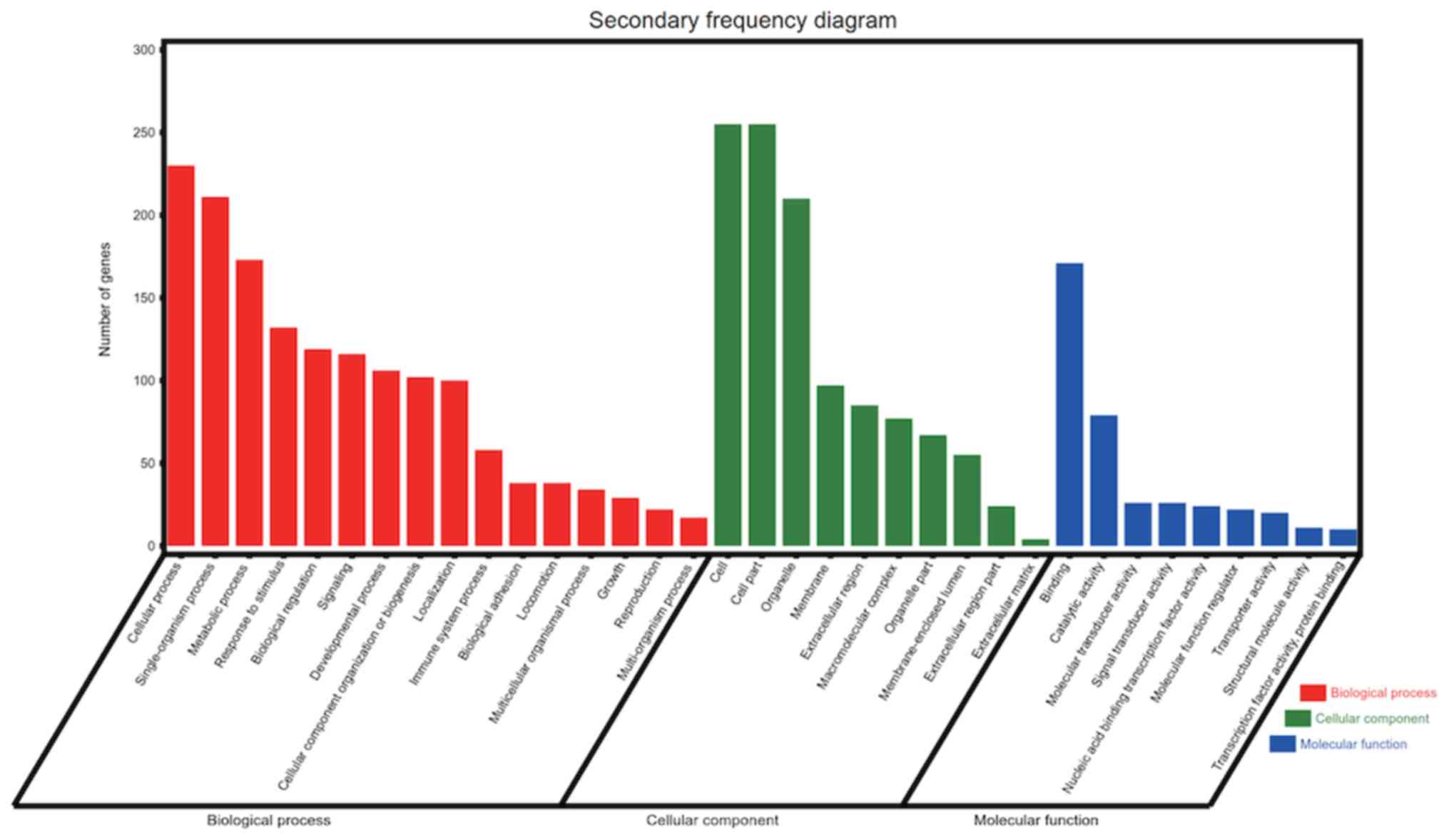
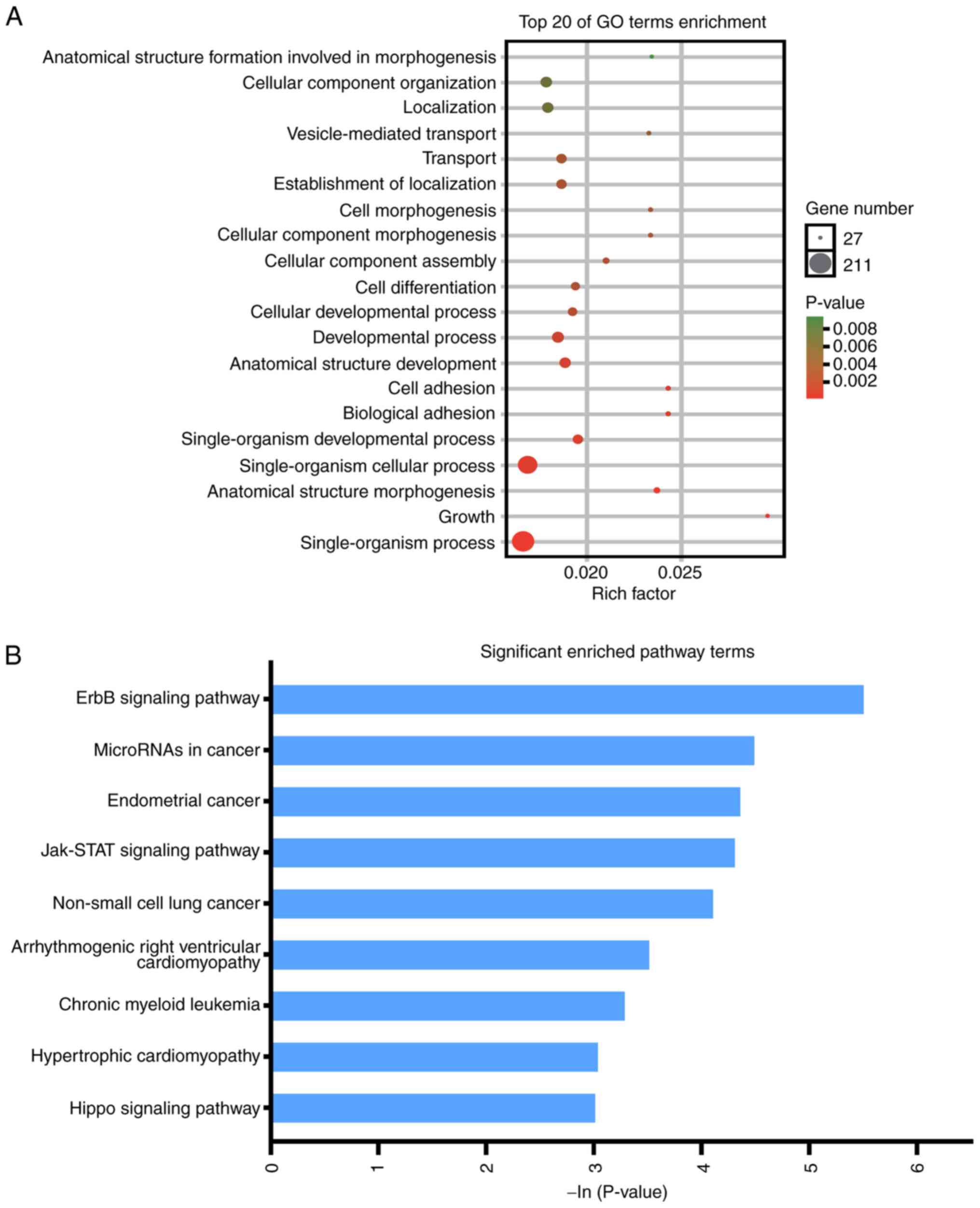
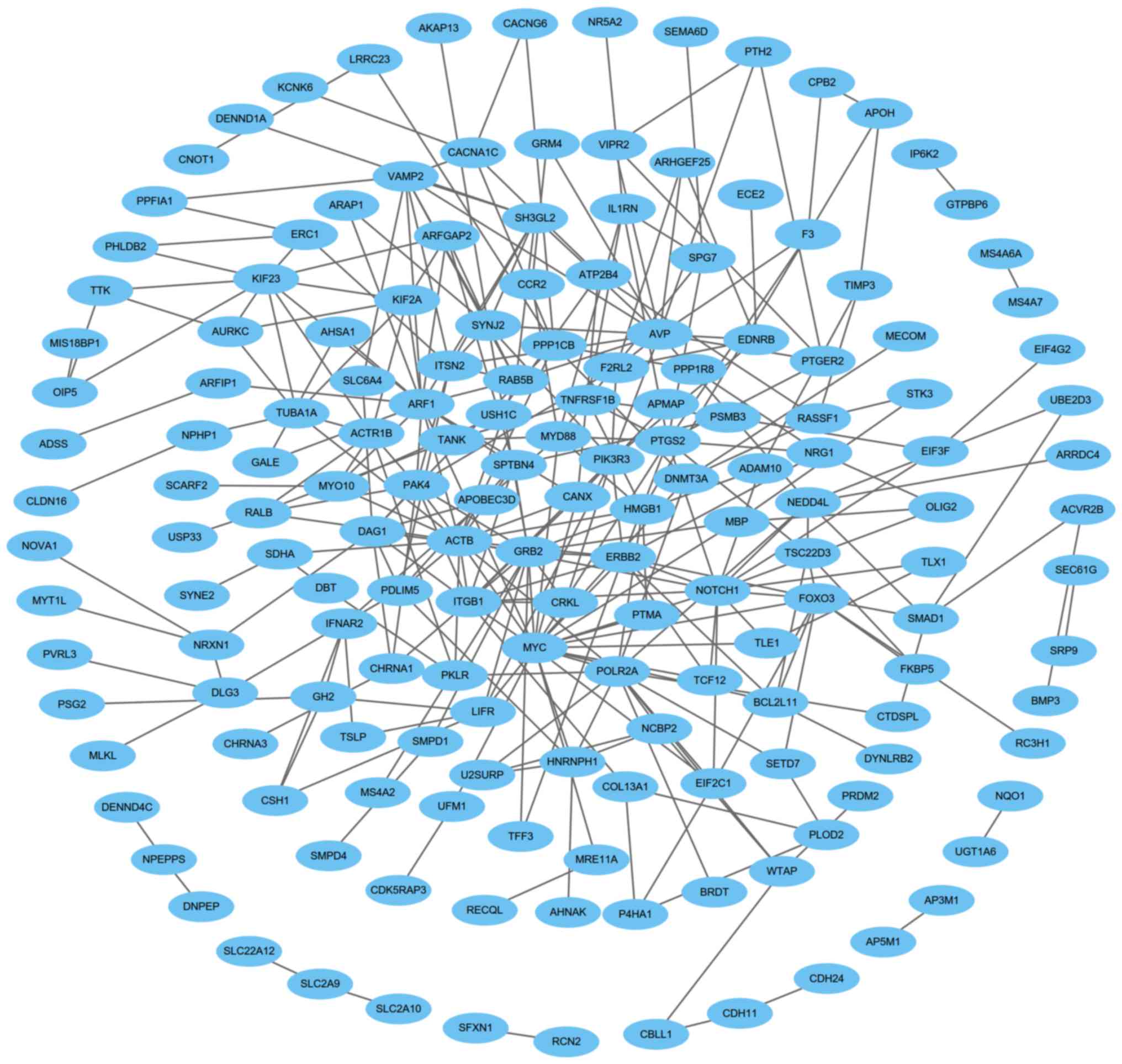
|
1
|
Lopez-Pastorini A, Riedel R, Koryllos A,
Beckers F, Ludwig C and Stoelben E: The impact of preoperative
elevated serum C-reactive protein on postoperative morbidity and
mortality after anatomic resection for lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
109:68–73. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Isaka M, Kojima H, Takahashi S, Omae K and
Ohde Y: Risk factors for local recurrence after lobectomy and lymph
node dissection in patients with non-small cell lung cancer:
Implications for adjuvant therapy. Lung Cancer. 115:28–33. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
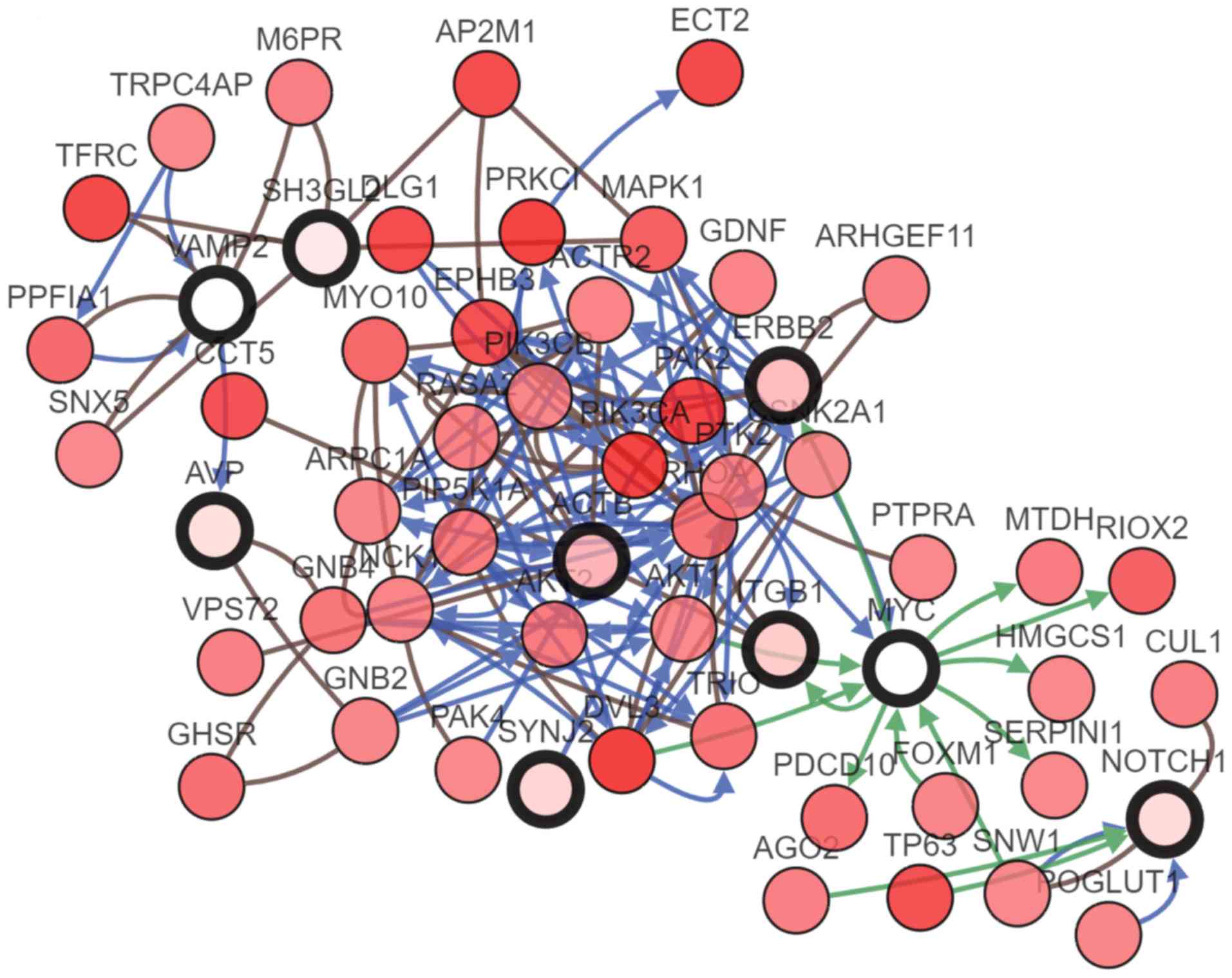
|
4
|
Yeh YC, Kadota K, Nitadori J, Sima CS,
Rizk NP, Jones DR, Travis WD and Adusumilli PS: International
association for the study of lung cancer/American thoracic
society/European respiratory society classification predicts occult
lymph node metastasis in clinically mediastinal node-negative lung
adenocarcinoma. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 49:e9–e15. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang S, Zhou W, Zhang H, Zhao M and Chen
X: Analysis of predictive factors for postoperative survival for
non small cell lung carcinoma patients with unexpected mediastinal
lymph nodes metastasis. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 62:126–132. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ma K, Chang D, He B, Gong M, Tian F, Hu X,
Ji Z and Wang T: Radical systematic mediastinal lymphadenectomy
versus mediastinal lymph node sampling in patients with clinical
stage IA and pathological stage T1 non-small cell lung cancer. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 134:1289–1295. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Saintigny P, Kambouchner M, Ly M, Gomes N,
Sainte-Catherine O, Vassy R, Czernichow S, Letoumelin P, Breau JL,
Bernaudin JF and Kraemer M: Vascular endothelial growth factor-C
and its receptor VEGFR-3 in non-small-cell lung cancer: Concurrent
expression in cancer cells from primary tumour and metastatic lymph
node. Lung Cancer. 58:205–213. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ohtsuka T, Shiomi T, Shimoda M, Kodama T,
Amour A, Murphy G, Ohuchi E, Kobayashi K and Okada Y: ADAM28 is
overexpressed in human non-small cell lung carcinomas and
correlates with cell proliferation and lymph node metastasis. Int J
Cancer. 118:263–273. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Na IK, Scheibenbogen C, Adam C, Stroux A,
Ghadjar P, Thiel E, Keilholz U and Coupland SE: Nuclear expression
of CXCR4 in tumor cells of non-small cell lung cancer is correlated
with lymph node metastasis. Hum Pathol. 39:1751–1755. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Maekawa S, Iwasaki A, Shirakusa T, Enatsu
S, Kawakami T and Kuroki M and Kuroki M: Correlation between lymph
node metastasis and the expression of VEGF-C, VEGF-D and VEGFR-3 in
T1 lung adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res. 27:3735–3741.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li J, Li BL, Zhang HQ, Xu SF, Liu ZD, Yue
WT and Han Y: Relationship between vascular endothelial growth
factor C expression level and lymph node metastasis in non small
cell lung cancer. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 88:2982–2985.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kikuchi T, Daigo Y, Katagiri T, Tsunoda T,
Okada K, Kakiuchi S, Zembutsu H, Furukawa Y, Kawamura M, Kobayashi
K, et al: Expression profiles of non-small cell lung cancers on
cDNA microarrays: Identification of genes for prediction of
lymph-node metastasis and sensitivity to anti-cancer drugs.
Oncogene. 22:2192–2205. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li L, Lei Q, Zhang S, Kong L and Qin B:
Screening and identification of key biomarkers in hepatocellular
carcinoma: Evidence from bioinformatic analysis. Oncol Rep.
38:2607–2618. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kan T, Shimada Y, Sato F, Ito T, Kondo K,
Watanabe G, Maeda M, Yamasaki S, Meltzer SJ and Imamura M:
Prediction of lymph node metastasis with use of artificial neural
networks based on gene expression profiles in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 11:1070–1078. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
O'Donnell RK, Kupferman M, Wei SJ, Singhal
S, Weber R, O'Malley B, Cheng Y, Putt M, Feldman M, Ziober B and
Muschel RJ: Gene expression signature predicts lymphatic metastasis
in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Oncogene.
24:1244–1251. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nguyen ST, Hasegawa S, Tsuda H, Tomioka H,
Ushijima M, Noda M, Omura K and Miki Y: Identification of a
predictive gene expression signature of cervical lymph node
metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 98:740–746.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim TJ, Choi JJ, Kim WY, Choi CH, Lee JW,
Bae DS, Son DS, Kim J, Park BK, Ahn G, et al: Gene expression
profiling for the prediction of lymph node metastasis in patients
with cervical cancer. Cancer Sci. 99:31–38. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Edgar R, Domrachev M and Lash AE: Gene
expression omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array
data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:207–210. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wright CM, Savarimuthu Francis SM, Tan ME,
Martins MU, Winterford C, Davidson MR, Duhig EE, Clarke BE, Hayward
NK, Yang IA, et al: MS4A1 dysregulation in asbestos-related lung
squamous cell carcinoma is due to CD20 stromal lymphocyte
expression. PLoS One. 7:e349432012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tomida S, Takeuchi T, Shimada Y, Arima C,
Matsuo K, Mitsudomi T, Yatabe Y and Takahashi T: Relapse-related
molecular signature in lung adenocarcinomas identifies patients
with dismal prognosis. J Clin Oncol. 27:2793–2799. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P,
Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH,
Sherman PM, Holko M, et al: NCBI GEO: Archive for functional
genomics data sets - update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41(Database issue):
D991–D995. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR,
Alvord WG, Roayaei J, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki
RA: The DAVID gene functional classification tool: A novel
biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large
gene lists. Genome Biol. 8:R1832007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene
ontology consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kanehisa M: The KEGG database. Novartis
Found Symp. 247:91–101. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ni M, Liu X, Wu J, Zhang D, Tian J, Wang
T, Liu S, Meng Z, Wang K, Duan X, et al: Identification of
candidate biomarkers correlated with the pathogenesis and prognosis
of non-small cell lung cancer via integrated bioinformatics
analysis. Front Genet. 9:4692018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43(Database issue): D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL
and Ideker T: Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and
network visualization. Bioinformatics. 27:431–432. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang HM, Jiang X, Hao ML, Shan MJ, Qiu Y,
Hu GF, Wang Q, Yu ZQ, Meng LB and Zou YY: Identification of
biomarkers in macrophages of atherosclerosis by microarray
analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 18:1072019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bader GD and Hogue CW: An automated method
for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction
networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 4:22003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2:401–404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Maere S, Heymans K and Kuiper M: BiNGO: A
cytoscape plugin to assess overrepresentation of gene ontology
categories in biological networks. Bioinformatics. 21:3448–3449.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nagy Á, Lánczky A, Menyhárt O and Győrffy
B: Validation of miRNA prognostic power in hepatocellular carcinoma
using expression data of independent datasets. Sci Rep. 8:92272018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Detterbeck FC, Boffa DJ and Tanoue LT: The
new lung cancer staging system. Chest. 136:260–271. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Suntharalingam M, Paulus R, Edelman MJ,
Krasna M, Burrows W, Gore E, Wilson LD and Choy H: Radiation
therapy oncology group protocol 02-29: A phase II trial of
neoadjuvant therapy with concurrent chemotherapy and full-dose
radiation therapy followed by surgical resection and consolidative
therapy for locally advanced non-small cell carcinoma of the lung.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 84:456–463. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shim SS, Lee KS, Kim BT, Chung MJ, Lee EJ,
Han J, Choi JY, Kwon OJ, Shim YM and Kim S: Non-small cell lung
cancer: Prospective comparison of integrated FDG PET/CT and CT
alone for preoperative staging. Radiology. 236:1011–1019. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
McLoud TC, Bourgouin PM, Greenberg RW,
Kosiuk JP, Templeton PA, Shepard JA, Moore EH, Wain JC, Mathisen DJ
and Grillo HC: Bronchogenic carcinoma: Analysis of staging in the
mediastinum with CT by correlative lymph node mapping and sampling.
Radiology. 182:319–323. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Toloza EM, Harpole L and McCrory DC:
Noninvasive staging of non-small cell lung cancer: A review of the
current evidence. Chest 123(1 Suppl). 137S–146S. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Takamochi K, Yoshida J, Murakami K, Niho
S, Ishii G, Nishimura M, Nishiwaki Y, Suzuki K and Nagai K:
Pitfalls in lymph node staging with positron emission tomography in
non-small cell lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer. 47:235–242. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Billé A, Pelosi E, Skanjeti A, Arena V,
Errico L, Borasio P, Mancini M and Ardissone F: Preoperative
intrathoracic lymph node staging in patients with non-small-cell
lung cancer: Accuracy of integrated positron emission tomography
and computed tomography. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 36:440–445. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Billè A, Okiror L, Skanjeti A, Errico L,
Arena V, Penna D, Ardissone F and Pelosi E: Evaluation of
integrated positron emission tomography and computed tomography
accuracy in detecting lymph node metastasis in patients with
adenocarcinoma vs. squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cardiothorac
Surg. 43:574–579. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pavlyk I, Leu NA, Vedula P, Kurosaka S and
Kashina A: Rapid and dynamic arginylation of the leading edge
β-actin is required for cell migration. Traffic. 19:263–272. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lim YH, Burke AB, Roberts MS, Collins MT
and Choate KA: Multilineage ACTB mutation in a patient with
fibro-osseous maxillary lesion and pilocytic astrocytoma. Am J Med
Genet A. 176:2037–2040. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Antonescu CR, Agaram NP, Sung YS, Zhang L,
Swanson D and Dickson BC: A distinct malignant epithelioid neoplasm
with GLI1 gene rearrangements, frequent S100 protein expression,
and metastatic potential: Expanding the spectrum of pathologic
entities with ACTB/MALAT1/PTCH1-GLI1 fusions. Am J Surg Pathol.
42:553–560. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Castro E, Cortes-Santiago N, Ferguson LM,
Rao PH, Venkatramani R and López-Terrada D: Translocation t(7;12)
as the sole chromosomal abnormality resulting in ACTB-GLI1 fusion
in pediatric gastric pericytoma. Hum Pathol. 53:137–141. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Huang R and Rofstad EK: Integrins as
therapeutic targets in the organ-specific metastasis of human
malignant melanoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:922018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yan M, Zhang L, Li G, Xiao S, Dai J and
Cen X: Long noncoding RNA linc-ITGB1 promotes cell migration and
invasion in human breast cancer. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 64:5–13.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang L, Zhang Y, Lv W, Lu J, Mu J, Liu Y
and Dong P: Long non-coding RNA Linc-ITGB1 knockdown inhibits cell
migration and invasion in GBC-SD/M and GBC-SD gallbladder cancer
cell lines. Chem Biol Drug Des. 86:1064–1071. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Klahan S, Huang WC, Chang CM, Wong HS,
Huang CC, Wu MS, Lin YC, Lu HF, Hou MF and Chang WC: Gene
expression profiling combined with functional analysis identify
integrin beta1 (ITGB1) as a potential prognosis biomarker in triple
negative breast cancer. Pharmacol Res. 104:31–37. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang XM, Li J, Yan MX, Liu L, Jia DS, Geng
Q, Lin HC, He XH, Li JJ and Yao M: Integrative analyses identify
osteopontin, LAMB3 and ITGB1 as critical pro-metastatic genes for
lung cancer. PLoS One. 8:e557142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Qin Q, Wei F, Zhang J and Li B: miR-134
suppresses the migration and invasion of nonsmall cell lung cancer
by targeting ITGB1. Oncol Rep. 37:823–830. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Demin DE, Bogolyubova AV, Zlenko DV,
Uvarova AN, Deikin AV, Putlyaeva LV, Belousov PV, Mitkin NA,
Korneev KV, Sviryaeva EN, et al: The novel short isoform of securin
stimulates the expression of cyclin D3 and angiogenesis factors
VEGFA and FGF2, but does not affect the expression of MYC
transcription factor. Mol Biol (Mosk). 52:508–518. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zaoui K, Benseddik K, Daou P, Salaün D and
Badache A: ErbB2 receptor controls microtubule capture by
recruiting ACF7 to the plasma membrane of migrating cells. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:18517–18522. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Huang CC, Kuo HM, Wu PC, Cheng SH, Chang
TT, Chang YC, Kung ML, Wu DC, Chuang JH and Tai MH: Soluble
delta-like 1 homolog (DLK1) stimulates angiogenesis through
Notch1/Akt/eNOS signaling in endothelial cells. Angiogenesis.
21:299–312. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Joassard OR, Amirouche A, Gallot YS,
Desgeorges MM, Castells J, Durieux AC, Berthon P and Freyssenet DG:
Regulation of Akt-mTOR, ubiquitin-proteasome and autophagy-lysosome
pathways in response to formoterol administration in rat skeletal
muscle. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:2444–2455. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Inoue J, Ninomiya M, Umetsu T, Nakamura T,
Kogure T, Kakazu E, Iwata T, Takai S, Sano A, Fukuda M, et al:
Small interfering RNA screening for the small GTPase rab proteins
identifies Rab5B as a major regulator of hepatitis B virus
production. J Virol. 93:e006212019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yamada K, Nakayama M, Miura Y, Nakano H,
Mimura N and Yoshida S: Role of AVP in the regulation of vascular
tonus and blood pressure in patients with chronic renal failure.
Regul Pept. 45:91–95. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Du Q, Guo X, Zhang X, Zhou W, Liu Z, Wang
J, Zhang T, Mao Z, Luo J, Jin T and Liu C: SYNJ2 variant rs9365723
is associated with colorectal cancer risk in Chinese Han
population. Int J Biol Markers. 31:e138–e143. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Nakatsu F, Perera RM, Lucast L, Zoncu R,
Domin J, Gertler FB, Toomre D and De Camilli P: The inositol
5-phosphatase SHIP2 regulates endocytic clathrin-coated pit
dynamics. J Cell Biol. 190:307–315. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Dasgupta S, Jang JS, Shao C, Mukhopadhyay
ND, Sokhi UK, Das SK, Brait M, Talbot C, Yung RC, Begum S, et al:
SH3GL2 is frequently deleted in non-small cell lung cancer and
downregulates tumor growth by modulating EGFR signaling. J Mol Med
(Berl). 91:381–393. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Caceres PS, Mendez M and Ortiz PA:
Vesicle-associated membrane protein 2 (VAMP2) but not VAMP3
mediates cAMP-stimulated trafficking of the renal Na+-K+-2Cl-
co-transporter NKCC2 in thick ascending limbs. J Biol Chem.
289:23951–23962. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|