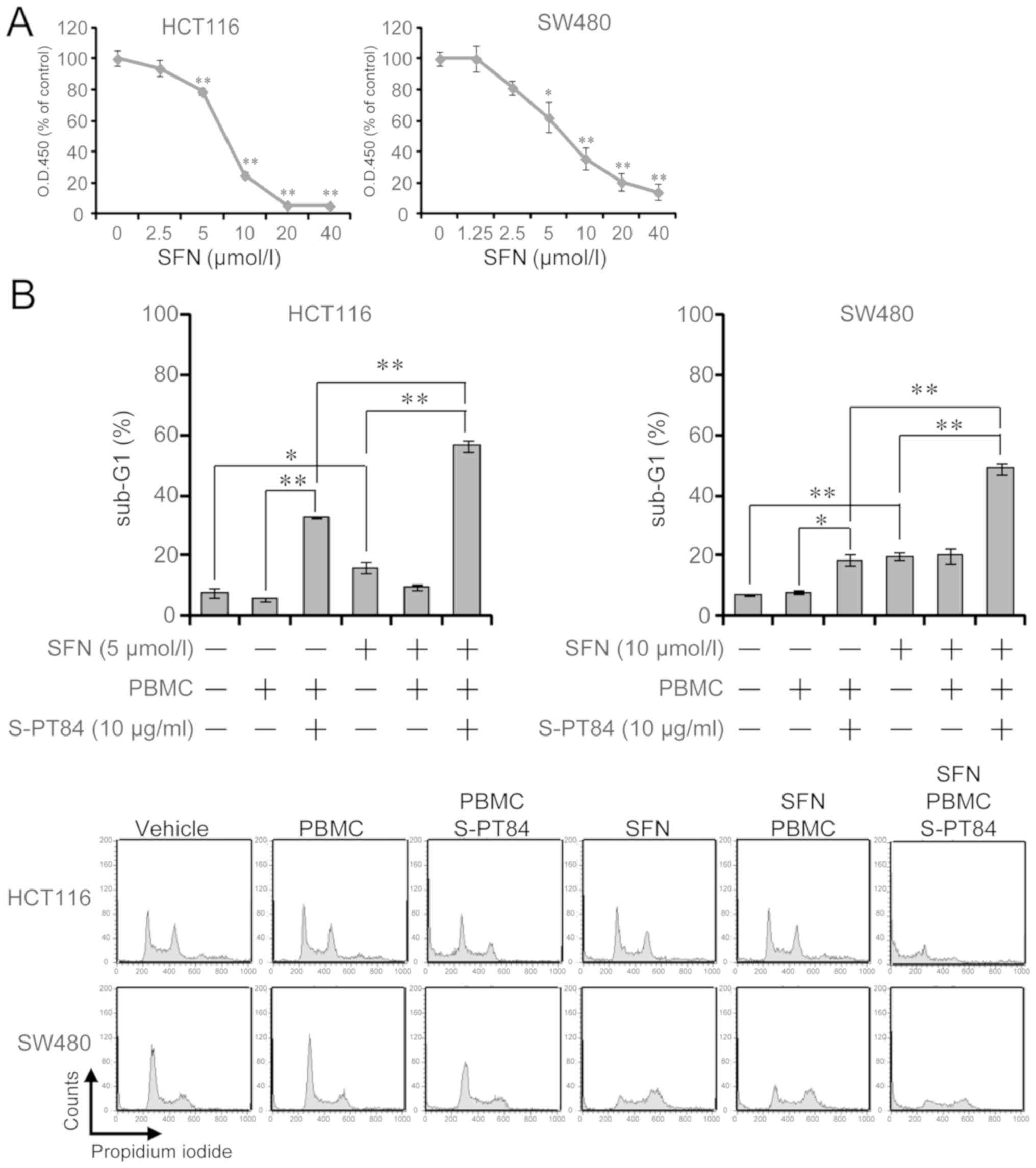
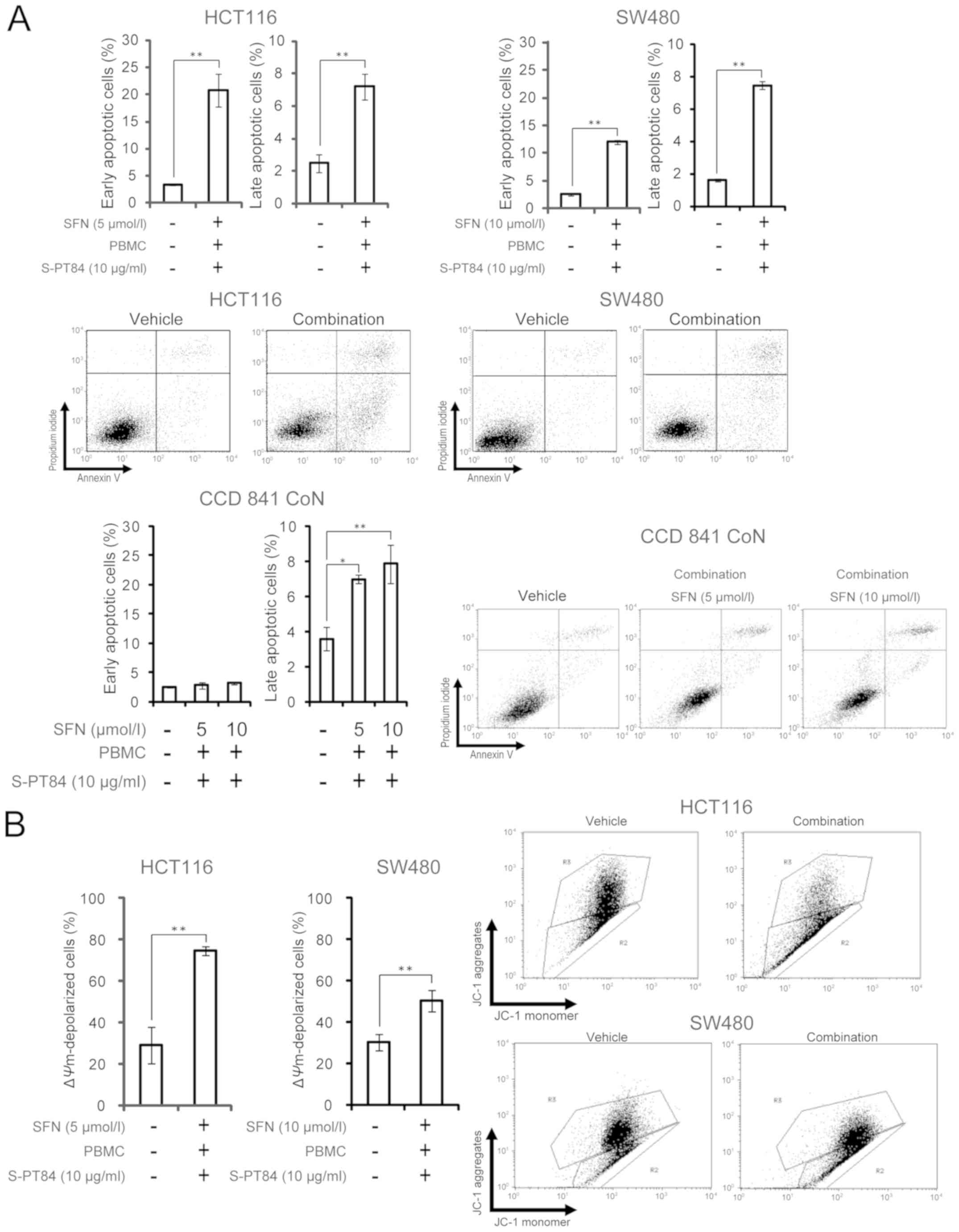
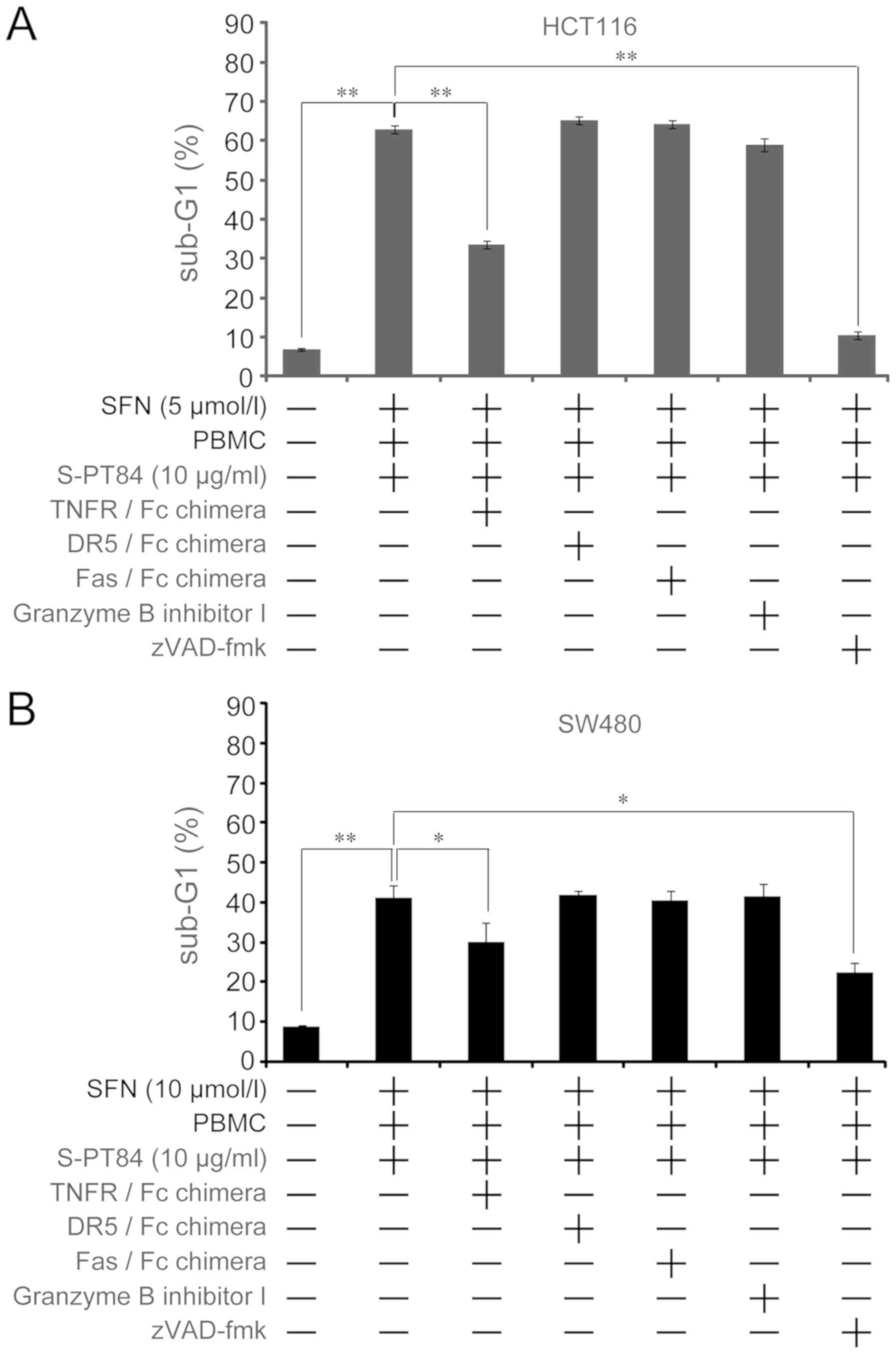
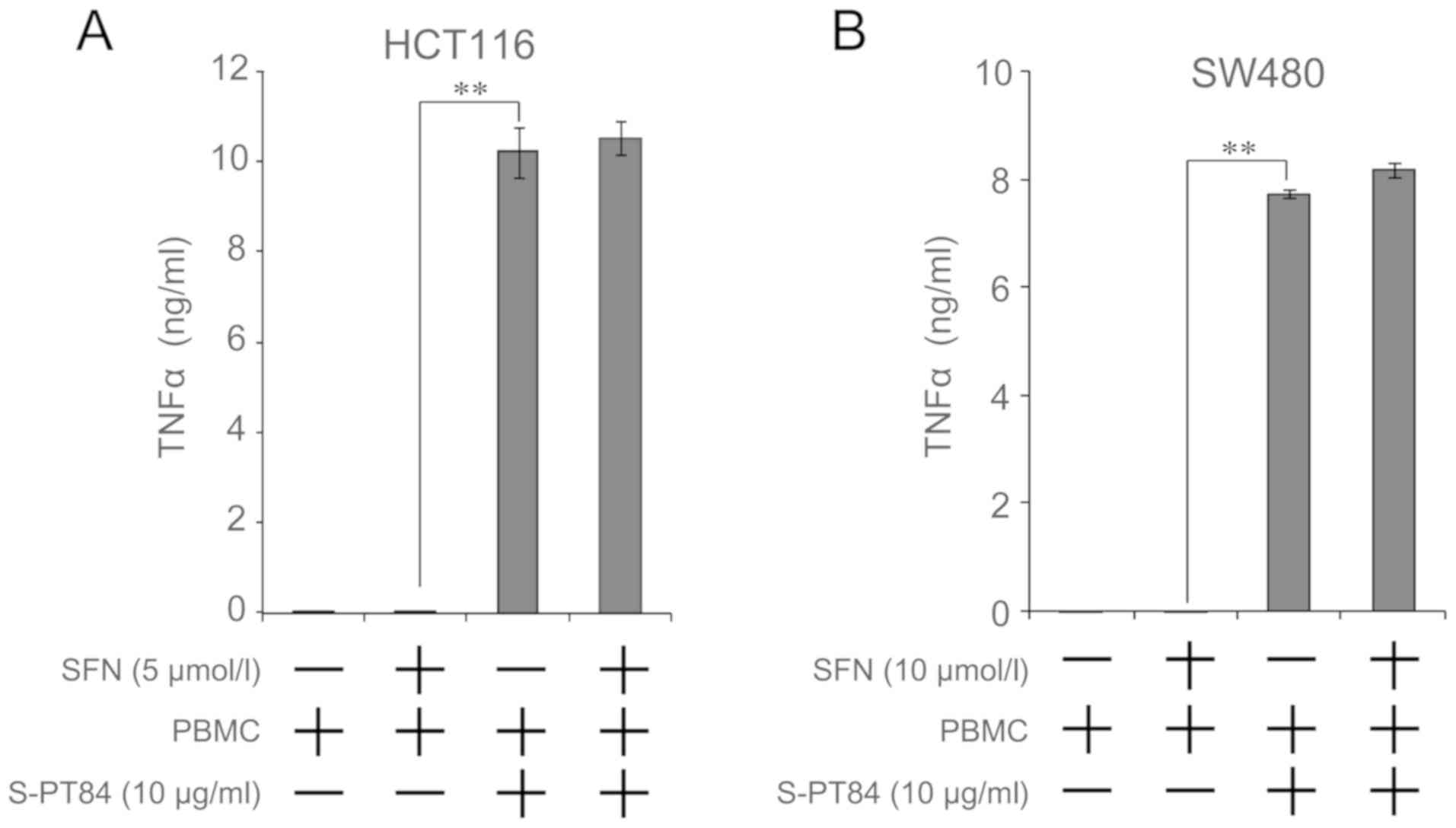
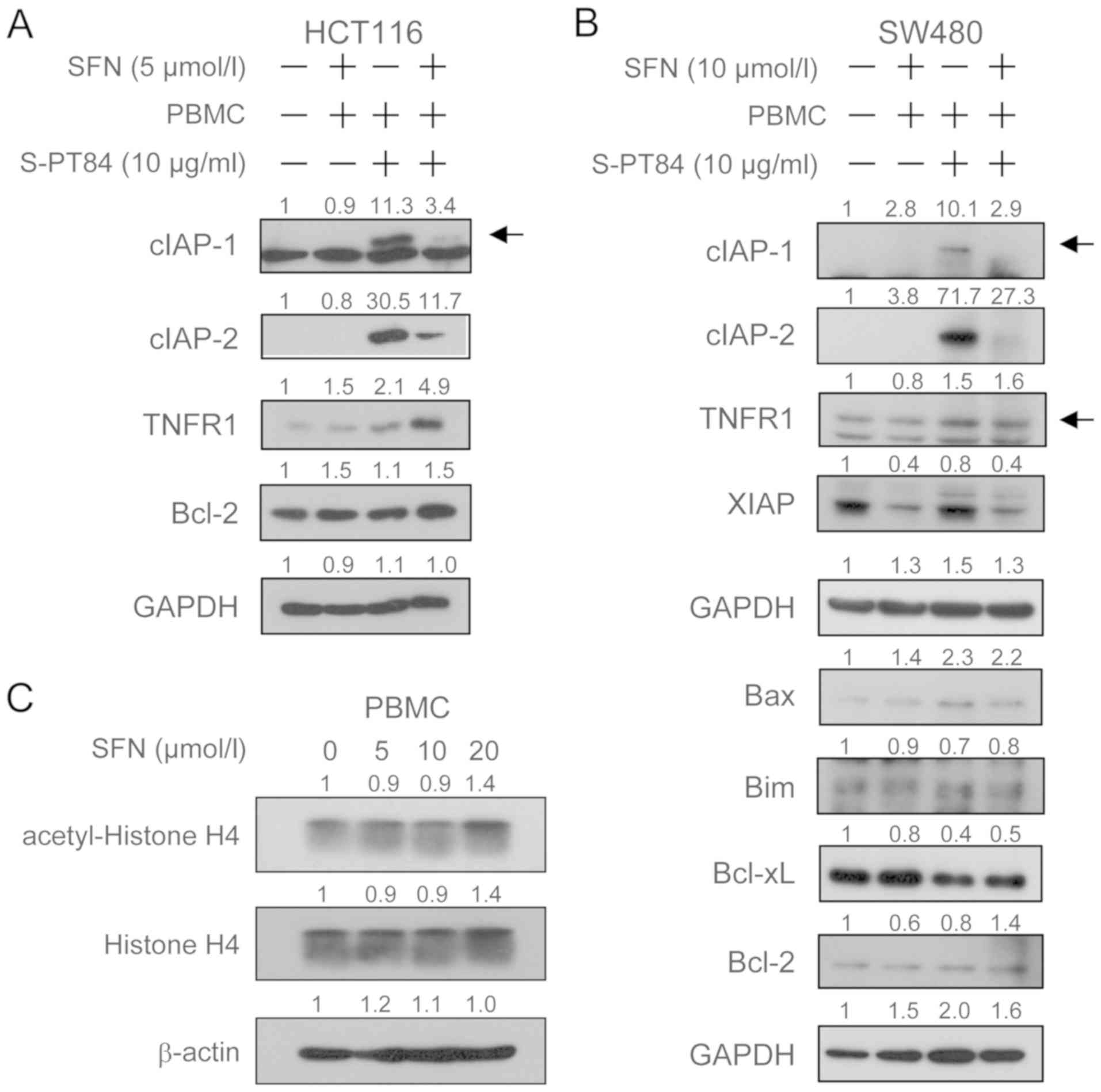
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Terry P, Giovannucci E, Michels KB,
Bergkvist L, Hansen H, Holmberg L and Wolk A: Fruit, vegetables,
dietary fiber, and risk of colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
93:525–533. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sato Y, Tsubono Y, Nakaya N, Ogawa K,
Kurashima K, Kuriyama S, Hazawa A, Nishino Y, Shibuya D and Tsuji
I: Fruit and vegetable consumption and risk of colorectal cancer in
Japan: The Miyagi Cohort Study. Public Health Nutr. 8:309–314.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Aoyama N, Kawado M, Yamada H, Hashimoto S,
Suzuki K, Wakai K, Suuki S, Watanabe Y and Tamakoshi A: Low intake
of vegetables and fruits and risk of colorectal cancer: The Japan
collaborative cohort study. J Epidemiol. 24:353–360. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shemesh N and Arber N: Curcumin alone and
in combination for prevention of colorectal cancer. Curr Colorectal
Cancer Rep. 10:62–67. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sharmila G, Bhat FA, Arunkumar R, Elumalai
P, Raja Singh P, Senthilkumar K and Arunakaran J: Chemopreventive
effect of quercetin, a natural dietary flavonoid on prostate cancer
in in vivo model. Clin Nutr. 33:718–726. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ullah MF, Bhat SH, Husain E, Abu-Duhier F,
Hadi SM, Sarkar FH and Ahmad A: Cancer chemopreventive pharmacology
of phytochemicals derived from plants of dietary and non-dietary
origin: Implication for alternative and complementary approaches.
Phytochem Rev. 13:811–833. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang Y, Talalay P, Cho CG and Posner GH:
A major inducer of anticarcinogenic protective enzymes from
broccoli: Isolation and elucidation of structure. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 89:2399–2403. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fahey JW, Zhang Y and Talalay P: Broccoli
sprouts: An exceptionally rich source of inducers of enzymes that
protect against chemical carcinogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
94:10367–10372. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gamet-Payrastre L, Li P, Lumeau S, Cassar
G, Dupont MA, Chevolleau S, Gasc N, Tulliez J and Terce F:
Sulforaphane, a naturally occurring isothiocyanate, induces cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis in HT29 human colon cancer cells. Cancer
Res. 60:1426–1433. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Singh AV, Xiao D, Lew KL, Dhir R and Singh
SV: Sulforaphane induces caspase-mediated apoptosis in cultured
PC-3 human prostate cancer cells and retards growth of PC-3
×enografts in vivo. Carcinogenesis. 25:83–90. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pledgie-Tracy A, Sobolewski MD and
Davidson NE: Sulforaphane induces cell type-specific apoptosis in
human breast cancer cell lines. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:1013–1021. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Singh SV, Srivastava SK, Choi S, Lew KL,
Antosiewicz J, Xiao D, Zeng Y, Watkins SC, Johnson CS, Trump DL, et
al: Sulforaphane-induced cell death in human prostate cancer cells
is initiated by reactive oxygen species. J Biol Chem.
280:19911–19924. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Choi S, Lew KL, Xiao H, Herman-Antosiewicz
A, Xiao D, Brown CK and Singh SV: D,L-Sulforaphane-induced cell
death in human prostate cancer cells is regulated by inhibitor of
apoptosis family proteins and Apaf-1. Carcinogenesis. 28:151–162.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fimognari C and Hrelia P: Sulforaphane as
a promising molecule for fighting cancer. Mutat Res. 635:90–104.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Myzak MC and Dashwood RH: Chemoprotection
by sulforaphane: Keep one eye beyond Keap1. Cancer Lett.
233:208–218. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Clarke JD, Dashwood RH and Ho E:
Multi-targeted prevention of cancer by sulforaphane. Cancer Lett.
269:291–304. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Juge N, Mithen RF and Traka M: Molecular
basis for chemoprevention by sulforaphane: A comprehensive review.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 64:1105–1127. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yeh CT and Yen GC: Effect of sulforaphane
on metallothionein expression and induction of apoptosis in human
hepatoma HepG2 cells. Carcinogenesis. 26:2138–2148. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Takeda K and Okumura K: Effects of a
fermented milk drink containing Lactobacillus casei strain
Shirota on the human NK-cell activity. J Nutr. 137((3 Suppl 2)):
S791–S793. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Takagi A, Matsuzaki T, Sato M, Nomoto K,
Morotomi M and Yokokura T: Inhibitory effect of oral administration
of Lactobacillus casei on 3-methylcholanthrene-induced
carcinogenesis in mice. Med Microbiol Immunol. 188:111–116. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
de Moreno de LeBlanc A, Matar C, LeBlanc N
and Perdigón G: Effects of milk fermented by Lactobacillus
helveticus R389 on a murine breast cancer model. Breast Cancer
Res. 7:R477–R486. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Orland A, Linsalata M and Russo F:
Antiproliferative effects on colon adenocarcinoma cells induced by
co-administration of vitamin K1 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus
GG. Int J Oncol. 48:2629–2638. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ishikawa H, Akedo I, Otani T, Suzuki T,
Nakamura T, Takeyama I, Ishiguro S, Miyaoka E, Sobue T and Kakizoe
T: Randomized trial of dietary fiber and Lactobacillus casei
administration for prevention of colorectal tumors. Int J Cancer.
116:762–767. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Horinaka M, Yoshida T, Kishi A, Akatani K,
Yausda T, Kouhara J, Wakada M and Sakai T: Lactobacillus
strains induce TRAIL production and facilitate natural killer
activity against cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 584:577–582. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Haller D, Bode C, Hammes WP, Pfeifer AM,
Schiffrin EJ and Blum S: Non-pathogenic bacteria elicit a
differential cytokine response by intestinal epithelial
cell/leucocyte co-cultures. Gut. 47:79–87. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Donkor ON, Ravikumar M, Proudfoot O, Day
SL, Apostolopoulos V, Pukovics G, Vasiljevic T, Nutt SL and Gill H:
Cytokine profile and induction of T helper type 17 and regulatory T
cells by human peripheral mononuclear cells after microbial
exposure. Clin Exp Immunol. 167:282–295. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Izumo T, Maekawa T, Ida M, Noguchi A,
Kitagawa Y, Shibata H, Yasui H and Kiso Y: Effect of intranasal
administration of Lactobacillus pentosus S-PT84 on influenza
virus infection in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 10:1101–1106. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Izumo T, Izumi F, Nakagawa I, Kitagawa Y,
Shibata H and Kiso Y: Influence of Lactobacillus pentosus
S-PT84 ingestion on the mucosal immunity of healthy and
Salmonella Typhimurium-infected mice. Biosci Microflora.
30:27–35. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hayama K, Ishijima S, Ono Y, Izumo T, Ida
M, Shibata H and Abe S: Protective activity of S-PT84, a
heat-killed preparation of Lactobacillus pentosus, against
oral and gastric candidiasis in an experimental murine model. Med
Mycol J. 55:123–129. 2014.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Izumo T, Maekawa T, Ida M, Kishi A,
Akatani K, Kitagawa Y and Kiso Y: Effect of Lactobacillus
pentosus S-PT84 ingestion on IFN-α production from plasmacytoid
dendritic cells by virus stimulation. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
75:370–372. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yoshida T, Horinaka M and Sakai T:
‘Combination-oriented molecular-targeting prevention’ of cancer: A
model involving the combination of TRAIL and a DR5 inducer. Environ
Health Prev Med. 15:203–210. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cheung KL, Khor TO and Kong AN:
Synergistic effect of combination of phenethyl isothiocyanate and
sulforaphane or curcumin and sulforaphane in the inhibition of
inflammation. Pharm Res. 26:224–231. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nair S, Hebbar V, Shen G, Gopalakrishnan
A, Khor TO, Yu S, Xu C and Kong AN: Synergistic effects of a
combination of dietary factors sulforaphane and (−)
epigallocatechin-3-gallate in HT-29 AP-1 human colon carcinoma
cells. Pharm Res. 25:387–399. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Matsui T, Sowa Y, Yoshida T, Murata H,
Horinaka M, Wakada M, Nakanishi R, Sakabe T, Kubo T and Sakai T:
Sulforaphane enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis through the induction
of DR5 expression in human osteosarcoma cells. Carcinogenesis.
27:1768–1777. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shankar S, Ganapathy S and Srivastava RK:
Sulforaphane enhances the therapeutic potential of TRAIL in
prostate cancer orthotopic model through regulation of apoptosis,
metastasis, and angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6855–6866. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nonaka Y, Izumo T, Izumi F, Maekawa T,
Shibata H, Nakano A, Kishi A, Akatani K and Kiso Y: Antiallergic
effects of Lactobacillus pentosus strain S-PT84 mediated by
modulation of Th1/Th2 immunobalance and induction of IL-10
production. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 145:249–257. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nagata S: Apoptosis by death factor. Cell.
88:355–365. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vermijlen D, Froelich CJ, Luo D,
Suarez-Huerta N, Robaye B and Wisse E: Perforin and granzyme B
induce apoptosis in FasL-resistant colon carcinoma cells. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 50:212–217. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Trapani JA and Smyth MJ: Functional
significance of the perforin/granzyme cell death pathway. Nat Rev
Immunol. 2:735–747. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rachid M, Matar C, Duarte J and Perdigon
G: Effect of milk fermented with a Lactobacillus helveticus
R389(+) proteolytic strain on the immune system and on the growth
of 4T1 breast cancer cells in mice. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol.
47:242–253. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Choi WY, Choi BT, Lee WH and Choi YH:
Sulforaphane generates reactive oxygen species leading to
mitochondrial perturbation for apoptosis in human leukemia U937
cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 62:637–644. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jo GH, Kim GY, Kim WJ, Park KY and Choi
YH: Sulforaphane induces apoptosis in T24 human urinary bladder
cancer cells through a reactive oxygen species-mediated
mitochondrial pathway: The involvement of endoplasmic reticulum
stress and the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 45:1497–1506.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Park HS, Han MH, Kim GY, Moon SK, Kim WJ,
Hwang HJ, Park KY and Choi YH: Sulforaphane induces reactive oxygen
species-mediated mitotic arrest and subsequent apoptosis in human
bladder cancer 5637 cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 64:157–165. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Folkard DL, Melchini A, Traka MH,
Al-Bakheit A, Saha S, Mulholland F, Watson A and Mithen RF:
Suppression of LPS-induced transcription and cytokine secretion by
the dietary isothiocyanate sulforaphane. Mol Nutr Food Res.
58:2286–2296. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Myzak MC, Karplus PA, Chung FL and
Dashwood RH: A novel mechanism of chemoprotection by sulforaphane:
Inhibition of histone deacetylase. Cancer Res. 64:5767–5774. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Dashwood RH, Myzak MC and Ho E: Dietary
HDAC inhibitors: Time to rethink weak ligands in cancer
chemoprevention? Carcinogenesis. 27:344–349. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Leoni F, Zaliani A, Bertolini G, Porro G,
Pagani P, Pozzi P, Donà G, Fossati G, Sozzani S, Azam T, et al: The
antitumor histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic
acid exhibits antiinflammatory properties via suppression of
cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:2995–3000. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Leoni F, Fossati G, Lewis EC, Lee JK,
Porro G, Pagani P, Modena D, Moras ML, Pozzi P, Reznikov LL, et al:
The histone deacetylase inhibitor ITF2357 reduces production of
pro-inflammatory cytokines in vitro and systemic inflammation in
vivo. Mol Med. 11:1–15. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bridle BW, Chen L, Lemay CG, Diallo JS,
Pol J, Nguyen A, Capretta A, He R, Bramson JL, Bell JC, et al: HDAC
inhibition suppresses primary immune responses, enhances secondary
immune responses, and abrogates autoimmunity during tumor
immunotherapy. Mol Ther. 21:887–894. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Saleem M, Qadir MI, Perveen N and Ahmad B,
Saleem U, Irshad T and Ahmad B: Inhibitors of apoptotic proteins:
New targets for anticancer therapy. Chem Biol Drug Des. 82:243–251.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|