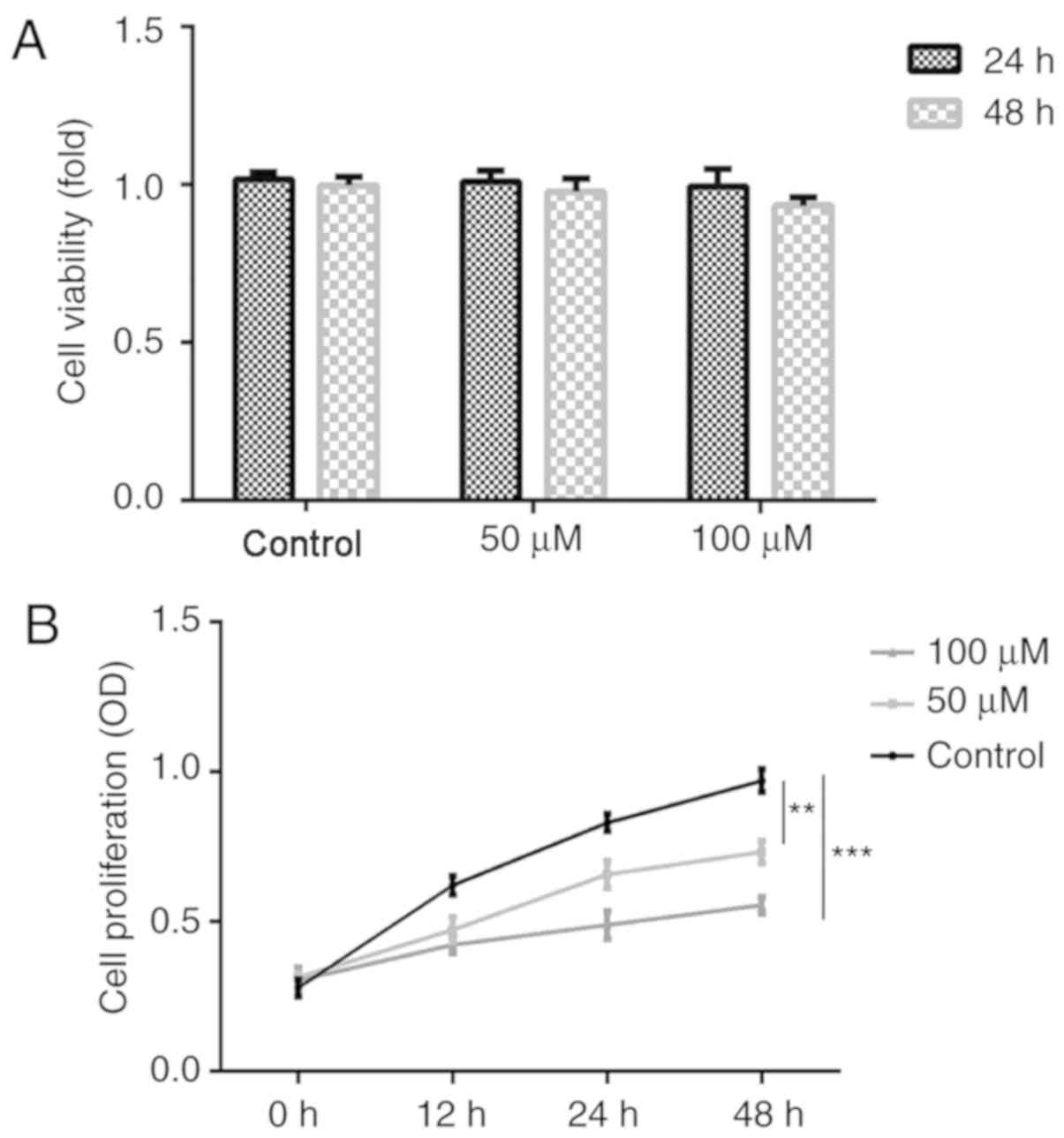
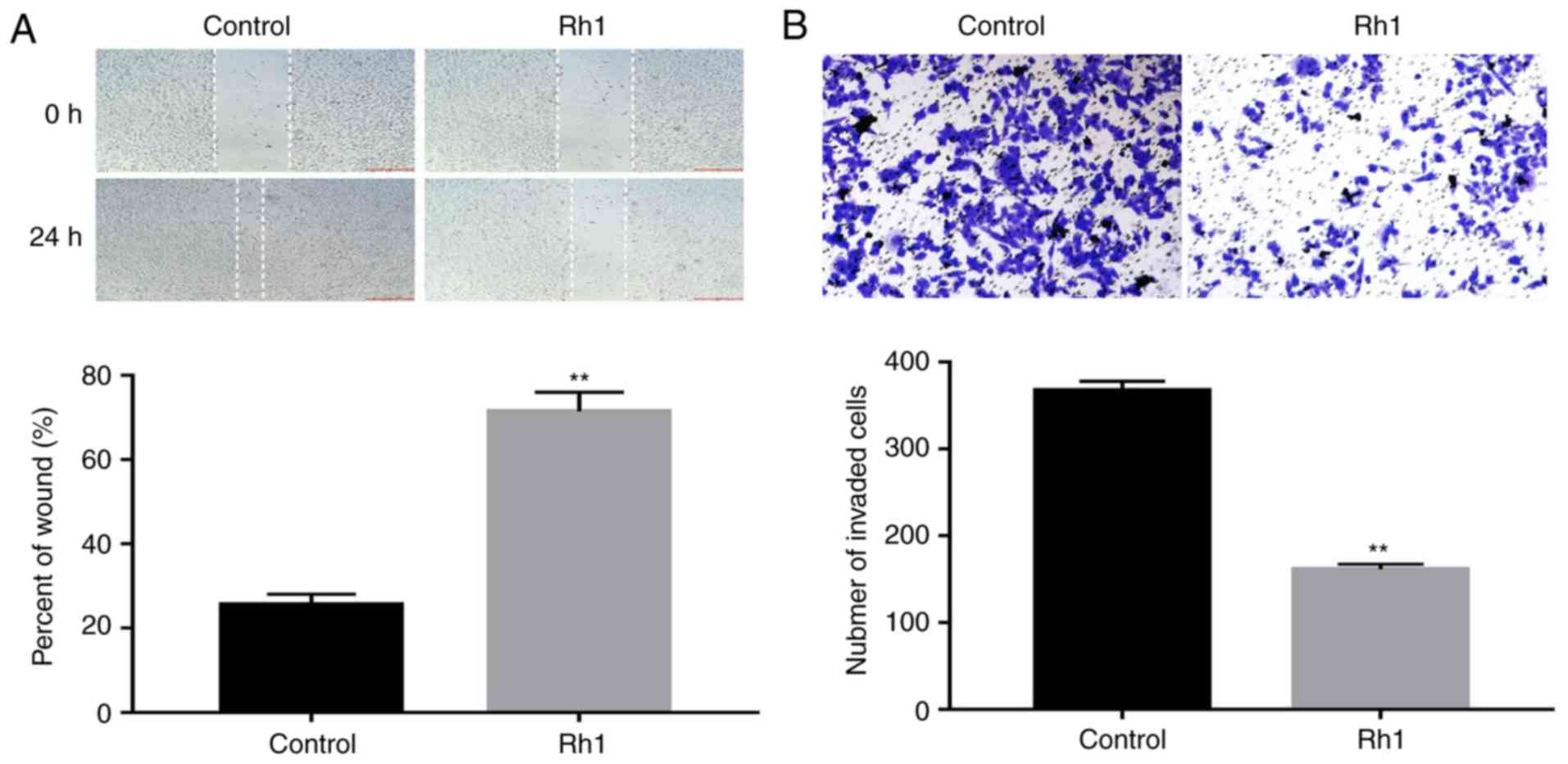
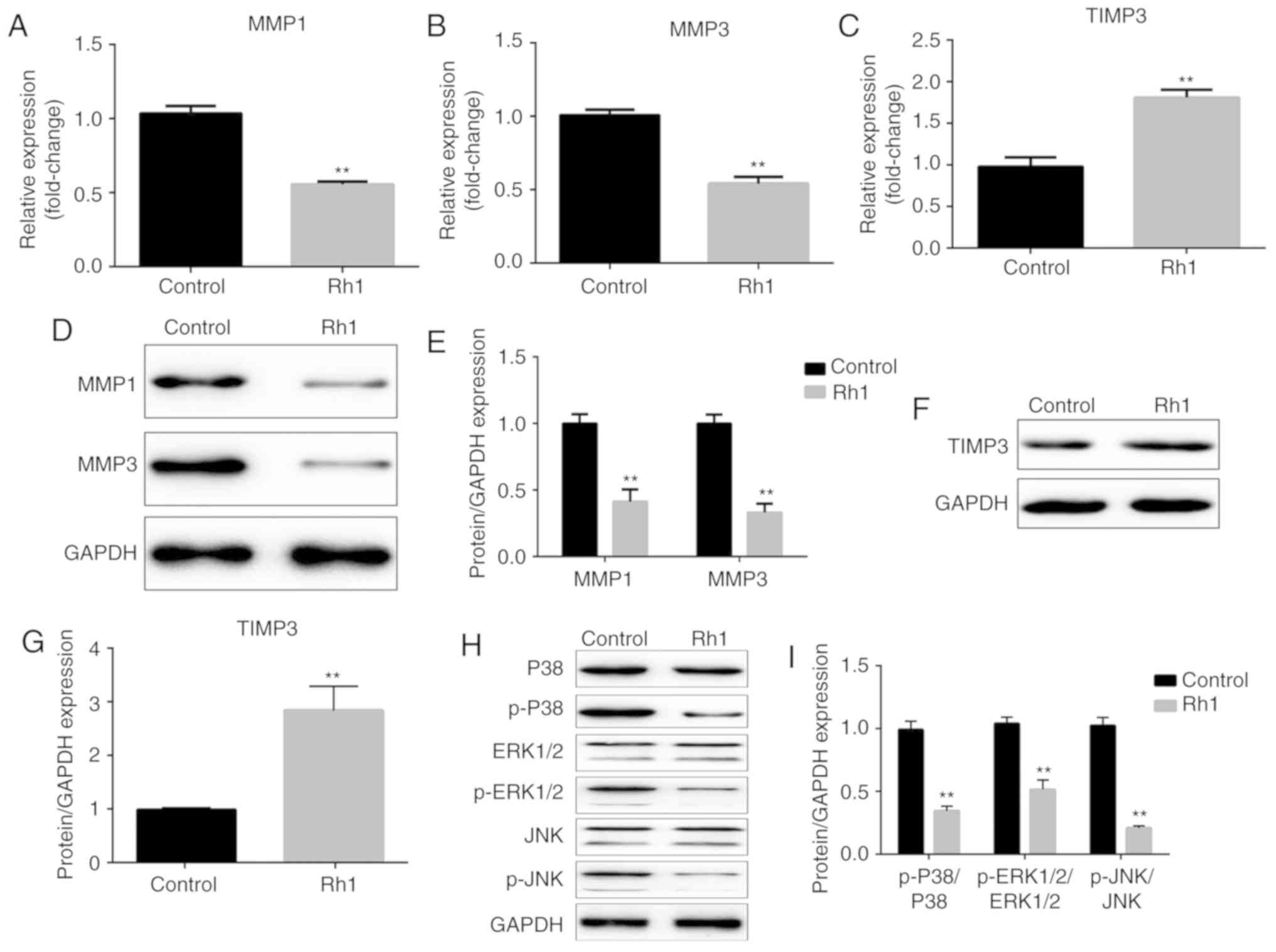
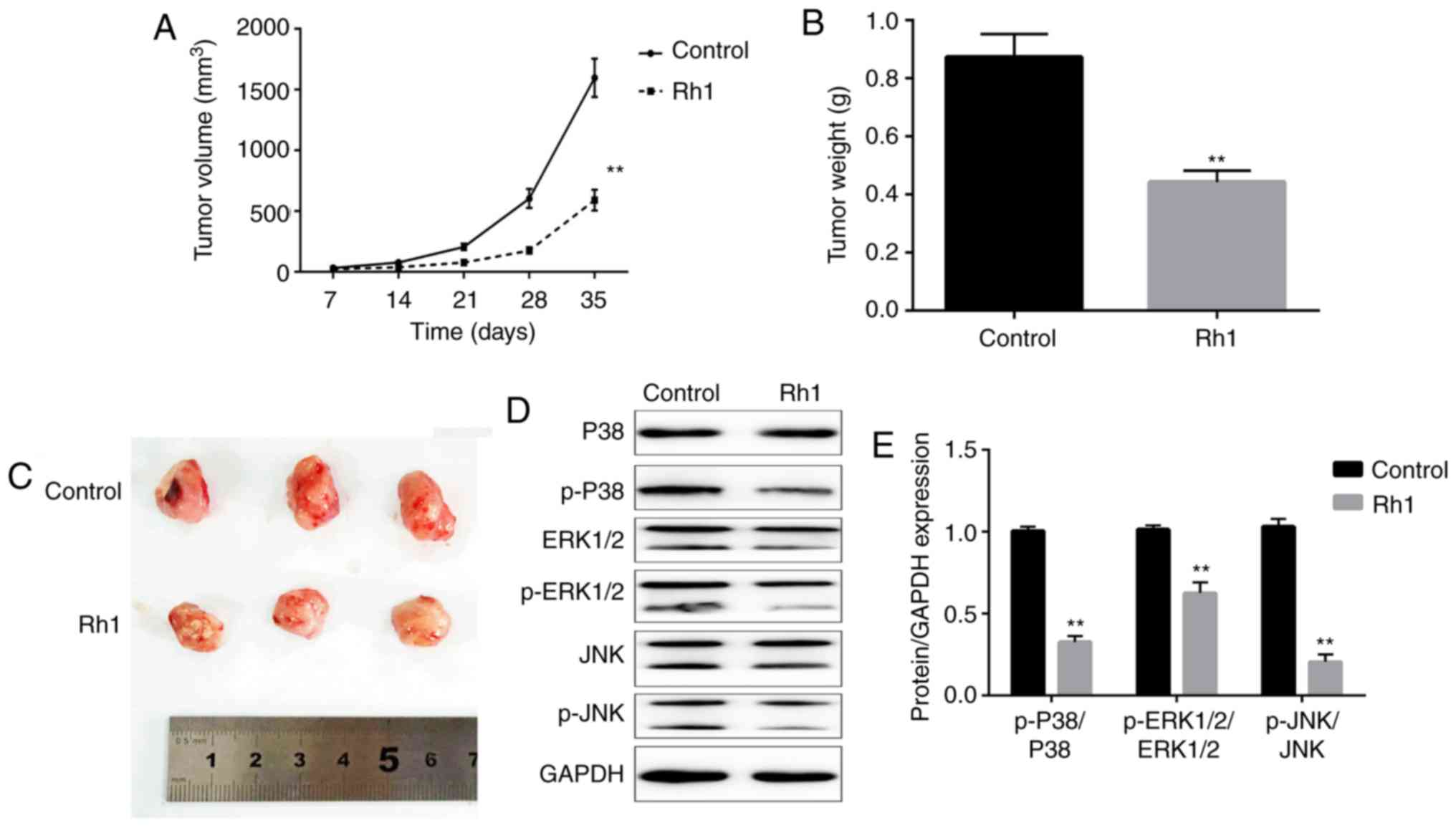
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Binefa G, Rodríguez-Moranta F, Teule A and
Medina-Hayas M: Colorectal cancer: From prevention to personalized
medicine. World J Gastroenterol. 20:6786–6808. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brody H: Colorectal cancer. Nature. 521
(Suppl):S12015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Balaguer F: Hereditary and familial
colorectal cancer. Gastroenterol Hepatol Suppl. 3:77–84. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Vasen HF, Tomlinson I and Castells A:
Clinical management of hereditary colorectal cancer syndromes. Nat
Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 12:88–97. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pellisé M: Colonoscopy in the screening,
follow-up and treatment of colorectal cancer and precursor lesions.
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 38 (Suppl 1):S71–S77. 2015.(In Spanish).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Akgül Ö, Çetinkaya E, Ersöz Ş and Tez M:
Role of surgery in colorectal cancer liver metastases. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:6113–6122. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ting WC, Chen LM, Pao JB, Yang YP, You BJ,
Chang TY, Lan YH, Lee HZ and Bao BY: Common genetic variants in Wnt
signaling pathway genes as potential prognostic biomarkers for
colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 8:e561962013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xiang YZ, Shang HC, Gao XM and Zhang BL: A
comparison of the ancient use of ginseng in traditional Chinese
medicine with modernpharmacological experiments and clinical
trials. Phytother Res. 22:851–858. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee SM, Bae BS, Park HW, Ahn NG, Cho BG,
Cho YL and Kwak YS: Characterization of Korean red ginseng (Panax
ginseng Meyer): History, preparation method and chemical
composition. J Ginseng Res. 39:384–391. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ko SR, Suzuki Y, Choi KJ and Kim YH:
Enzymatic preparation of genuine prosapogenin, 20(S)-ginsenoside
Rh1, from ginsenosides Re and Rg1. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
64:2739–2743. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park EK, Choo MK, Han MJ and Kim DH:
Ginsenoside Rh1 possesses antiallergic and anti-inflammatory
activities. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 133:113–120. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang Y, Liu W, Wang XM, Zhong GG, Zhang
WJ, Chen L, Zhan S, Qi H, Zhao CY, Ma XY, et al: Calcium channel
blockade and anti-free-radical actions of panaxatriol saponins in
cultured myocardiocytes. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 17:138–141.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cheng Y, Shen LH and Zhang JT:
Anti-amnestic and anti-aging effects of ginsenoside Rg1 and Rb1 and
its mechanism of action. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 26:143–149. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang YZ, Chen J, Chu SF, Wang YS, Wang XY,
Chen NH and Zhang JT: Improvement of memory in mice and increase of
hippocampal excitability in rats by ginsenoside Rg1's metabolites
ginsenoside Rh1 and protopanaxatriol. J Pharmacol Sci. 109:504–510.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hou J, Xue J, Lee M, Yu J and Sung C:
Long-term administration of ginsenoside Rh1 enhances learing and
memory by promoting cell survival in the mouse hippocampus. Int J
Mol Med. 33:234–240. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gai Y, Ma Z, Yu X, Qu S and Sui D: Effect
of ginsenoside Rh1 on myocardial injury and heart function in
isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Toxicol Mech Methods.
22:584–591. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gu W, Kim KA and Kim DH: Ginsenoside Rh1
ameliorates high fat diet-induced obesity in mice by inhibiting
adipocyte differentiation. Biol Pharm Bull. 36:102–107. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Teng CM, Kuo SC, Ko FN, Lee JC, Lee LG,
Chen SC and Huang TF: Antiplatelet actions of panaxynol and
ginsenosides isolated from ginseng. Biochim Biophys Acta.
990:315–320. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yoon JH, Choi YJ and Lee SG: Ginsenoside
Rh1 suppresses matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression through
inhibition of activator protein-1 and mitogen-activated protein
kinase signaling pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Eur J Pharmacol. 679:24–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jung JS, Ahn JH, Le TK, Kim DH and Kim HS:
Protopanaxatriol ginsenoside Rh1 inhibits the expression of matrix
metalloproteinases and the in vitro invasion/migration of human
astroglioma cells. Neurochem Int. 63:80–86. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Choi YJ, Yoon JH, Cha SW and Lee SG:
Ginsenoside Rh1 inhibits the invasion and migration of THP-1 acute
monocytic leukemia cells via inactivation of the MAPK signaling
pathway. Fitoterapia. 82:911–919. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lai L, Hao H, Liu Y, Zheng C, Wang Q, Wang
G and Chen X: Characterization of pharmacokinetic profiles and
metabolic pathways of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rh1 in vivo and in vitro.
Planta Med. 75:797–802. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen XJ, Liu WJ, Wen ML, Liang H, Wu SM,
Zhu YZ, Zhao JY, Dong XQ, Li MG, Bian L, et al: Ameliorative
effects of Compound K and ginsenoside Rh1 on non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease in rats. Sci Rep. 7:411442017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang Y, Wang BX, Liu TH, Minami M, Nagata
T and Ikejima T: Metabolism of ginsenoside Rg1 by intestinal
bacteria. II. Immunological activity of ginsenoside Rg1 and Rh1.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 21:792–796. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li XF, Lui CN, Jiang ZH and Ken YK:
Neuroprotective effects of ginsenosides Rh1 and Rg2 on neuronal
cells. Chin Med. 6:192011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kramer N, Walzl A, Unger C, Rosner M,
Krupitza G, Hengstschläger M and Dolznig H: In vitro cell migration
and invasion assays. Mutat Res. 752:10–24. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Deryugina EI and Quigley JP: Matrix
metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
25:9–34. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu M, Hu Y, Zhang MF, Luo KJ, Xie XY, Wen
J, Fu JH and Yang H: MMP1 promotes tumor growth and metastasis in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 377:97–104. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sunami E, Tsuno N, Osada T, Saito S,
Kitayama J, Tomozawa S, Tsuruo T, Shibata Y, Muto T and Nagawa H:
MMP-1 is a prognostic marker for hematogenous metastasis of
colorectal cancer. Oncologist. 5:108–114. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chu C, Liu X, Bai X, Zhao T, Wang M, Xu R,
Li M, Hu Y, Li W, Yang L, et al: MiR-519d suppresses breast cancer
tumorigenesis and metastasis via targeting MMP3. Int J Biol Sci.
14:228–236. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jackson HW, Defamie V, Waterhouse P and
Khokha R: TIMPs: Versatile extracellular regulators in cancer. Nat
Rev Cancer. 17:38–53. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Han XG, Li Y, Mo HM, Li K, Lin D, Zhao CQ,
Zhao J and Tang TT: TIMP3 regulates osteosarcoma cell migration,
invasion and chemotherapeutic resistances. Tumour Biol.
37:8857–8867. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang Z, Wang J, Wang X, Song W, Shi Y and
Zhang L: MicroRNA-21 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion
of cervical cancer through targeting TIMP3. Arch Gynecol Obstet.
297:433–442. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu W, Li M, Chen X, Zhang D, Wei L, Zhang
Z, Wang S, Meng L, Zhu S and Li B: MicroRNA-373 promotes migration
and invasion in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by
inhibiting TIMP3 expression. Am J Cancer Res. 6:1–14.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lin H, Zhang Y, Wang H, Xu D, Meng X, Shao
Y, Lin C, Ye Y, Qian H and Wang S: Tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinases-3 transfer suppresses malignant behaviors of
colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 19:845–851. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cossa G, Gatti L, Cassinelli G, Lanzi C,
Zaffaroni N and Perego P: Modulation of sensitivity to antitumor
agents by targeting the MAPK survival pathway. Curr Pharm Des.
19:883–894. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Burotto M, Chiou VL, Lee JM and Kohn EC:
The MAPK pathway across different malignancies: A new perspective.
Cancer. 120:3446–3456. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yoon JH, Choi YJ, Cha SW and Lee SG:
Anti-metastatic effects of ginsenoside Rd via inactivation of MAPK
signaling and induction of focal adhesion formation. Phytomedicine.
19:284–292. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|