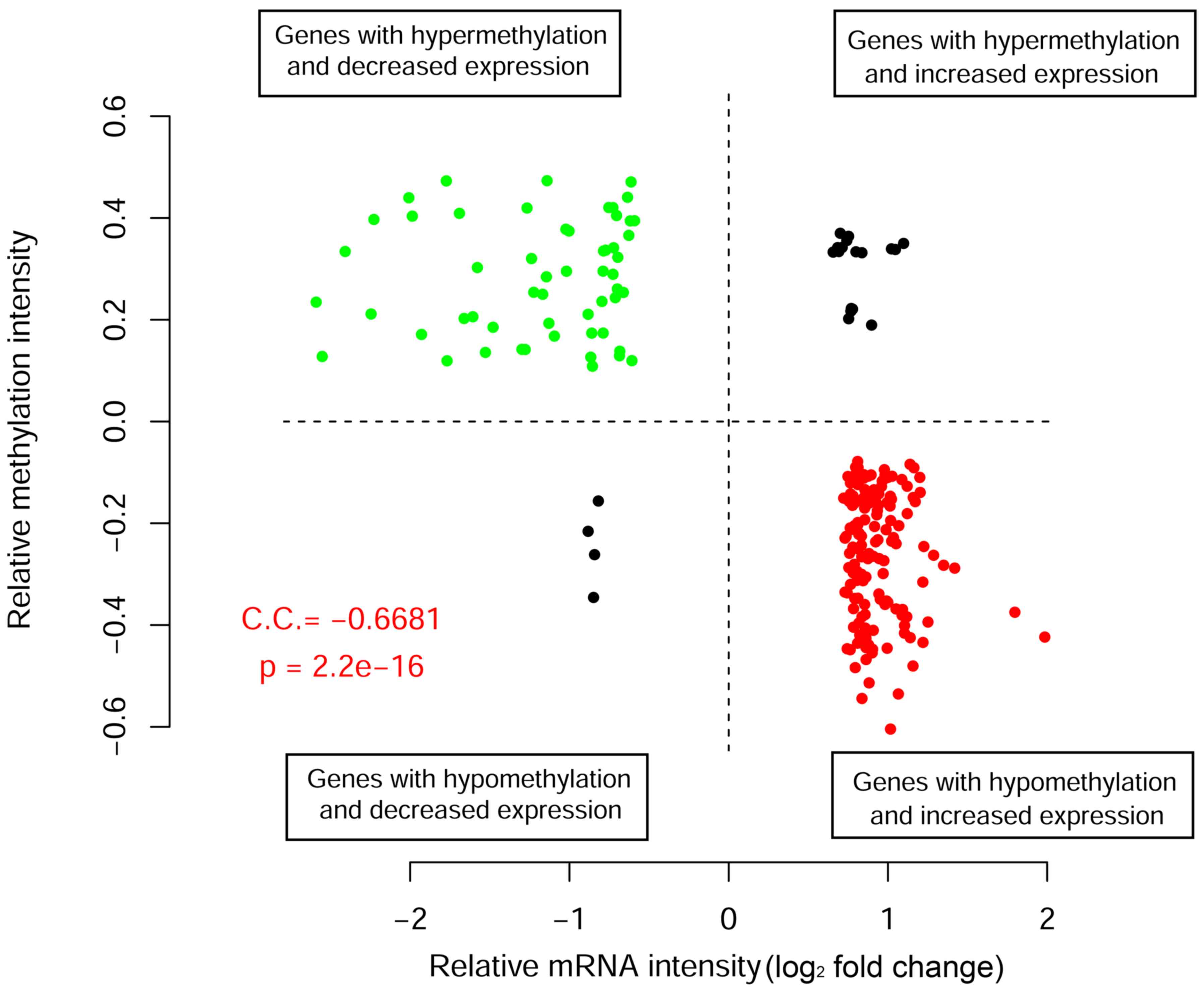
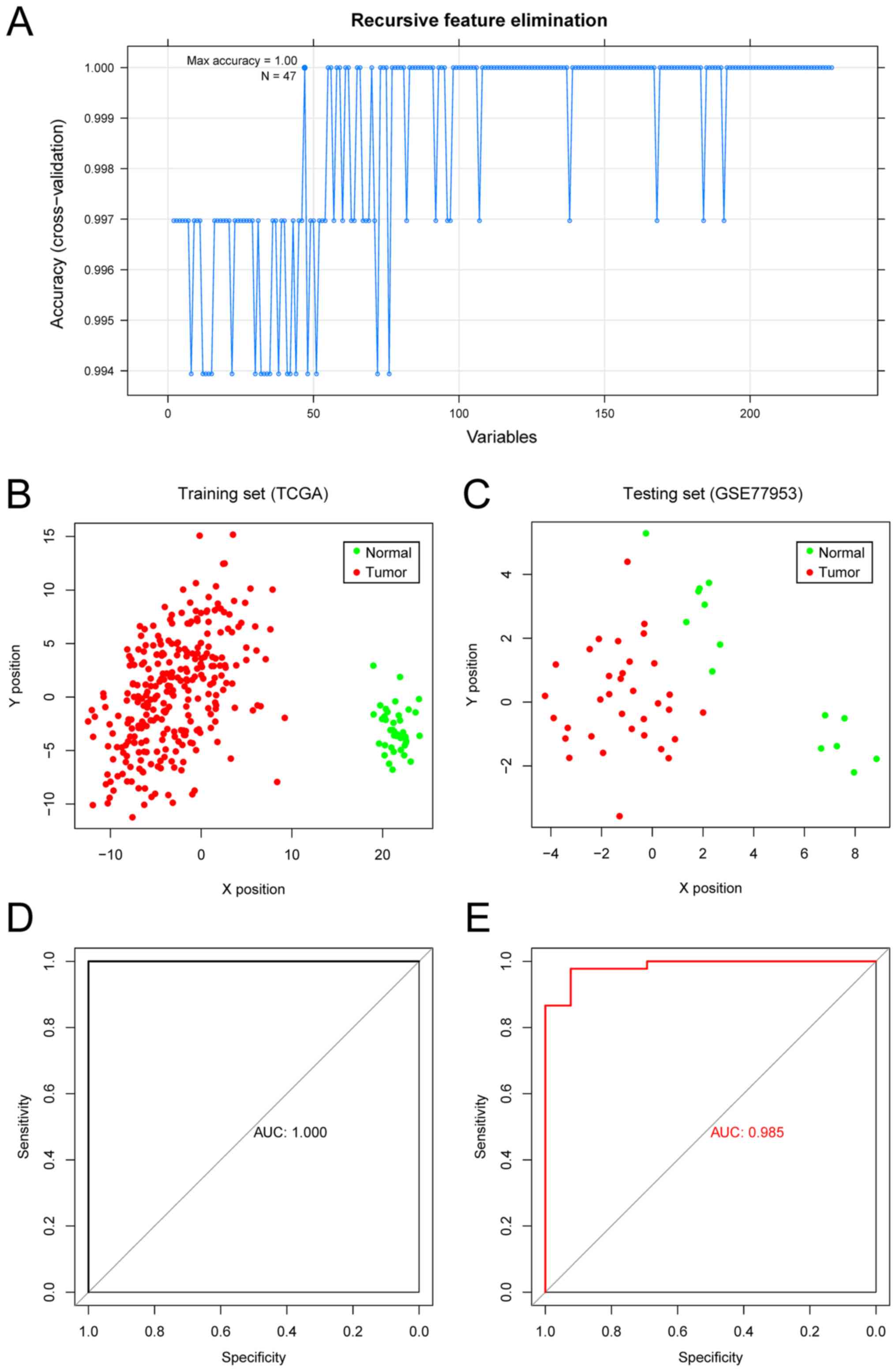
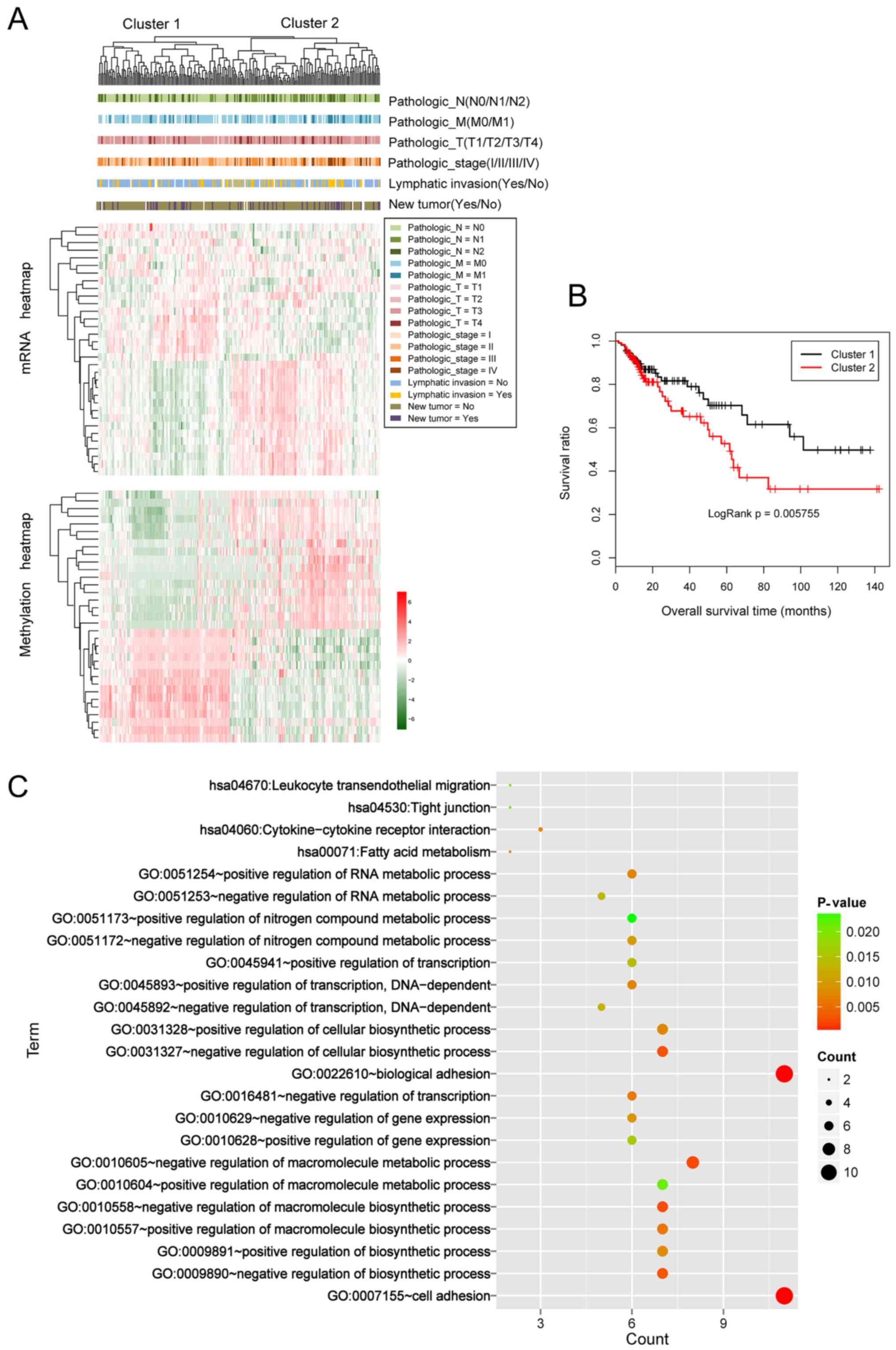
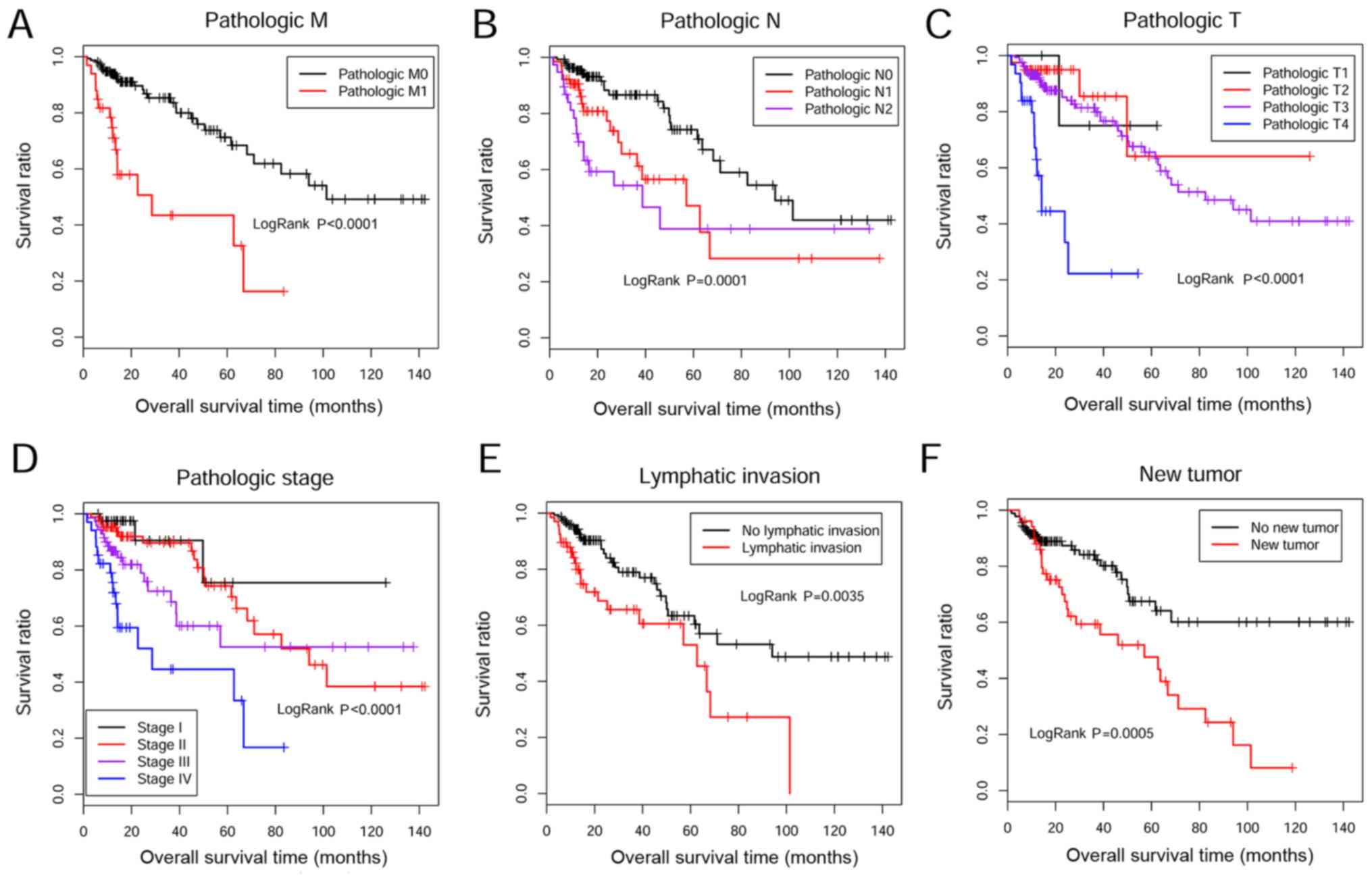
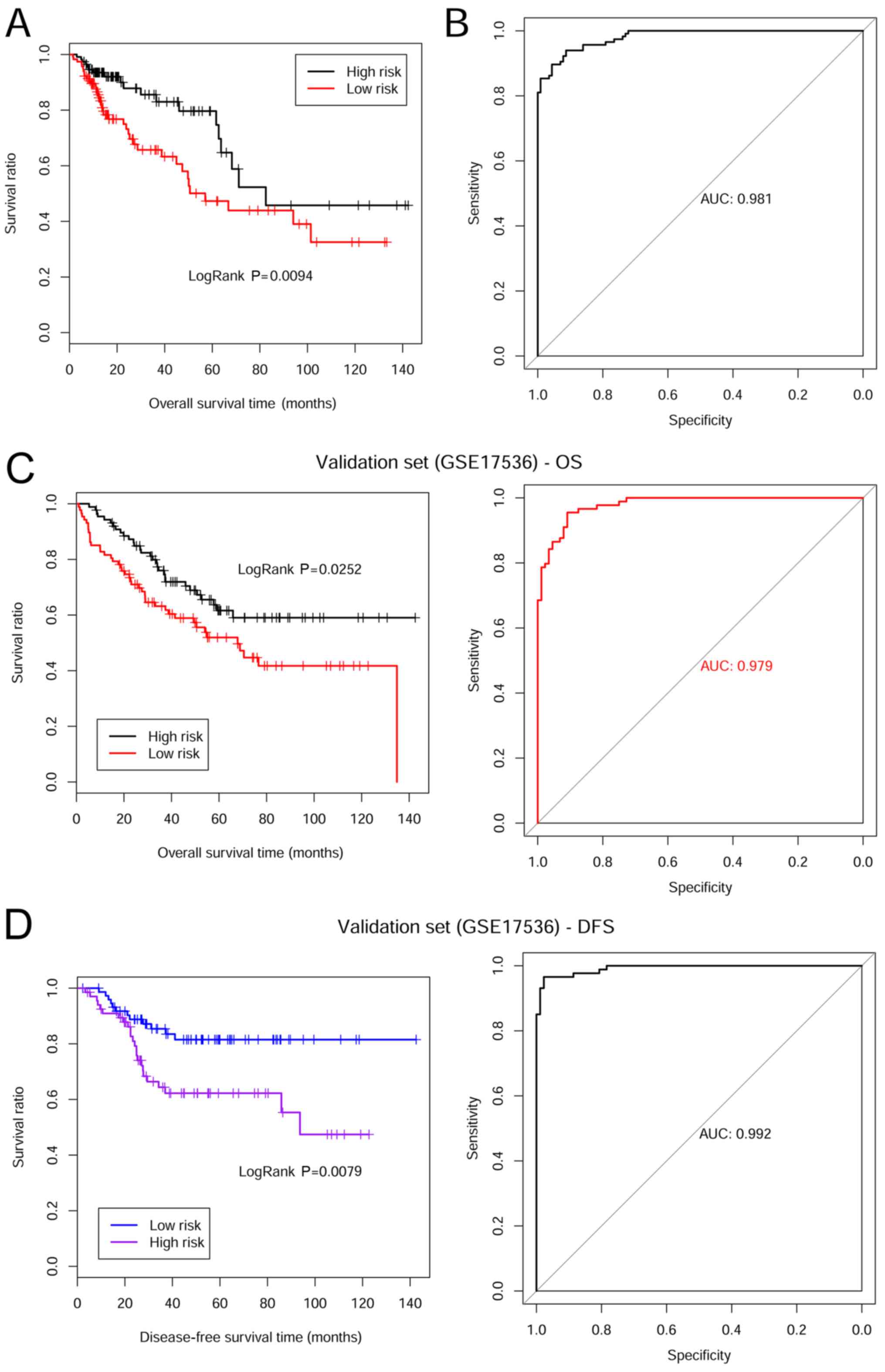
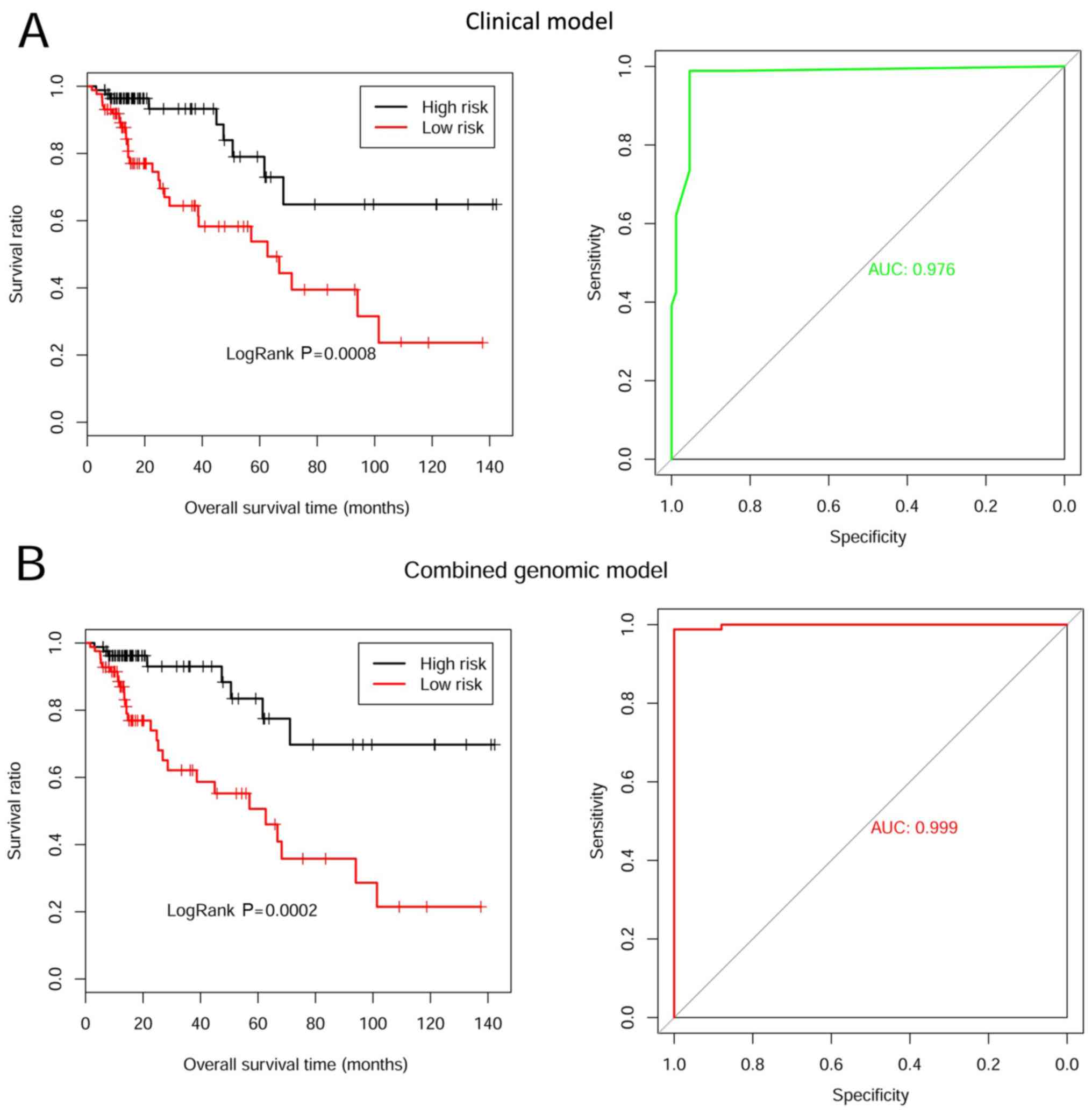
|
1
|
Arnold M, Sierra MS, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global patterns and trends in
colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut. 66:683–691. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rougier P, Sahmoud T, Nitti D, Curran D,
Doci R, De Waele B, Nakajima T, Rauschecker H, Labianca R, Pector
JC, et al: Adjuvant portal-vein infusion of fluorouracil and
heparin in colorectal cancer: A randomised trial. European
Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Gastrointestinal
Tract Cancer Cooperative Group, the Gruppo Interdisciplinare
Valutazione Interventi in Oncologia, and the Japanese Foundation
for Cancer Research. Lancet. 351:1677–1681. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wood LD, D Williams P, Sian J, Lin J,
Sjöblom T, Leary RJ, Shen D, Boca SM, Barber T, Ptak J, et al: The
genomic landscapes of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science.
318:1108–1113. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Van Es JH and Clevers H: Notch and Wnt
inhibitors as potential new drugs for intestinal neoplastic
disease. Trends Mol Med. 11:496–502. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Watt FM: Unexpected hedgehog-Wnt
interactions in epithelial differentiation. Trends Mol Med.
10:577–580. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pasparakis M: Role of NF-κB in epithelial
biology. Immunol Rev. 246:346–358. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xie B, Zhao R, Bai B, Wu Y, Xu Y, Lu S,
Fang Y, Wang Z, Maswikiti EP, Zhou X, et al: Identification of key
tumorigenesisrelated genes and their microRNAs in colon cancer.
Oncol Rep. 40:3551–3560. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Moore LD, Thuc L and Guoping F: DNA
methylation and its basic function. Neuropsychopharmacology.
38:23–38. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fellow DHKLDMCR and Genetics SRiC: DNA
methylation: A form of epigenetic control of gene expression.
Obstetrician & Gynaecologist. 12:37–42. 2011.
|
|
10
|
Gaudet F, Hodgson JG, Eden A,
Jackson-Grusby L, Dausman J, Gray JW, Leonhardt H and Jaenisch R:
Induction of tumors in mice by genomic hypomethylation. Science.
300:489–492. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rodriguez J, Frigola J, Vendrell E,
Risques RA, Fraga MF, Morales C, Moreno V, Esteller M, Capellà G,
Ribas M and Peinado MA: Chromosomal instability correlates with
genome-wide DNA demethylation in human primary colorectal cancers.
Cancer Res. 66:8462–9468. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
McInnes T, Zou D, Rao DS, Munro FM,
Phillips VL, McCall JL, Black MA, Reeve AE and Guilford PJ:
Genome-wide methylation analysis identifies a core set of
hypermethylated genes in CIMP-H colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer.
17:2282017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xue W, Wu X, Wang F, Han P and Cui B:
Genome-wide methylation analysis identifies novel prognostic
methylation markers in colon adenocarcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother.
108:288–296. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qu X, Sandmann T, Frierson H Jr, Fu L,
Fuentes E, Walter K, Okrah K, Rumpel C, Moskaluk C, Lu S, et al:
Integrated genomic analysis of colorectal cancer progression
reveals activation of EGFR through demethylation of the EREG
promoter. Oncogene. 35:6403–6415. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Smith JJ, Deane NG, Fei WU, Merchant NB,
Zhang B, Jiang A, Lu P, Johnson JC, Schmidt C, Bailey CE, et al:
Experimentally derived metastasis gene expression profile predicts
recurrence and death in patients with colon cancer.
Gastroenterology. 138:958–968. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Freeman TJ, Smith JJ, Chen X, Washington
MK, Roland JT, Means AL, Eschrich SA, Yeatman TJ, Deane NG and
Beauchamp RD: Smad4-mediated signaling inhibits intestinal
neoplasia by inhibiting expression of β-catenin. Gastroenterology.
142:562–571-e562. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cortés-Ciriano I, Bender A and Malliavin
T: Prediction of PARP inhibition with proteochemometric modelling
and conformal prediction. Mol Inform. 34:357–366. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu X, Yang Y, Wu F, Gao M, Xu Y, Zhang Y,
Yao Y, Du X, Li C, Wu L, et al: Discriminative analysis of
schizophrenia using support vector machine and recursive feature
elimination on structural MRI images. Medicine (Baltimore).
95:e39732016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Q and Liu X: Screening of feature
genes in distinguishing different types of breast cancer using
support vector machine. Onco Targets Ther. 8:2311–2317.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang L, Cao C, Ma Q, Zeng Q, Wang H, Cheng
Z, Zhu G, Qi J, Ma H, Nian H and Wang Y: RNA-seq analyses of
multiple meristems of soybean: Novel and alternative transcripts,
evolutionary and functional implications. BMC Plant Biol.
14:1692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Eisen MB, Spellman PT, Brown PO and
Botstein D: Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression
patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:14863–14868. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang P, Wang Y, Hang B, Zou X and Mao JH:
A novel gene expression-based prognostic scoring system to predict
survival in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 7:55343–55351.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Goel MK, Khanna P and Kishore J:
Understanding survival analysis: Kaplan-Meier estimate. Int J
Ayurveda Res. 1:274–278. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Young JN, Young-Ho K, Jin JY, Kang YH, Lee
CI, Kim JW, Yeom YI, Chun HK, Choi YH, Kim JH, et al:
Identification of endothelial cell-specific molecule-1 as a
potential serum marker for colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci.
101:2248–2253. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lassalle P, Molet S, Janin A, Heyden JV,
Tavernier J, Fiers W, Devos R and Tonnel AB: ESM-1 is a novel human
endothelial cell-specific molecule expressed in lung and regulated
by cytokines. J Biol Chem. 271:20458–20464. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang H, Fu XG and Chen YT: Serum level of
endothelial cell-specific molecule-1 and prognosis of colorectal
cancer. Genet Mol Res. 14:5519–5526. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kang YH, Ji Ny, Han SR, Lee CI, Kim JW,
Yeom YI, Kim YH, Chun HK, Kim JW, Chung JW, et al: ESM-1 regulates
cell growth and metastatic process through activation of NF-κB in
colorectal cancer. Cell Signal. 24:1940–1949. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tsukita S, Furuse M and Itoh M:
Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
2:285–293. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Feigin ME and Muthuswamy SK: Polarity
proteins regulate mammalian cell-cell junctions and cancer
pathogenesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 21:694–700. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Martin TA and Jiang WG: Tight junctions
and their role in cancer metastasis. Histol Histopathol.
16:1183–1195. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tzelepi VN, Tsamandas AC, Vlotinou HD,
Vagianos CE and Scopa CD: Tight junctions in thyroid
carcinogenesis: Diverse expression of claudin-1, claudin-4,
claudin-7 and occludin in thyroid neoplasms. Mod Pathol. 21:22–30.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Al Moustafa AE, Alaoui-Jamali MA, Batist
G, Hernandez-Perez M, Serruya C, Alpert L, Black MJ, Sladek R and
Foulkes WD: Identification of genes associated with head and neck
carcinogenesis by cDNA microarray comparison between matched
primary normal epithelial and squamous carcinoma cells. Oncogene.
21:2634–2640. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lioni M, Brafford P, Andl C, Rustgi A,
El-Deiry W, Herlyn M and Smalley KS: Dysregulation of claudin-7
leads to loss of E-cadherin expression and the increased invasion
of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Am J Pathol.
170:709–721. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shibutani M, Noda E, Maeda K, Nagahara H,
Ohtani H and Hirakawa K: Low expression of claudin-1 and presence
of poorly-differentiated tumor clusters correlate with poor
prognosis in colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 33:3301–3306.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bujko M, Kober P, Mikula M, Ligaj M,
Ostrowski J and Siedlecki JA: Expression changes of cell-cell
adhesion-related genes in colorectal tumors. Oncol Lett.
9:2463–2470. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hahn-Strömberg V, Askari S, Ahmad A,
Befekadu R and Nilsson TK: Expression of claudin 1, claudin 4, and
claudin 7 in colorectal cancer and its relation with CLDN DNA
methylation patterns. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283176975692017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Guan ZP, Gu LK, Xing BC, Ji JF, Gu J and
Deng DJ: Downregulation of chromobox protein homolog 7 expression
in multiple human cancer tissues. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi.
45:597–600. 2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pallante P, Terracciano L, Carafa V,
Schneider S, Zlobec I, Lugli A, Bianco M, Ferraro A, Sacchetti S,
Troncone G, et al: The loss of the CBX7 gene expression represents
an adverse prognostic marker for survival of colon carcinoma
patients. Eur J Cancer. 46:2304–2313. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tang JY, Yu CY, Bao YJ, Chen L, Chen J,
Yang SL, Chen HY, Hong J and Fang JY: TEAD4 promotes colorectal
tumorigenesis via transcriptionally targeting YAP1. Cell Cycle.
17:102–109. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu Y, Wang G, Yang Y, Mei Z, Liang Z, Cui
A, Wu T, Liu CY and Cui L: Increased TEAD4 expression and nuclear
localization in colorectal cancer promote epithelial mesenchymal
transition and metastasis in a YAP-independent manner. Oncogene.
35:2789–2800. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mito A, Nakano Y, Saitoh T, Gouraud SSS,
Yamaguchi Y, Sato T, Sasaki N and Kojima-Aikawa K: Lectin ZG16p
inhibits proliferation of human colorectal cancer cells via its
carbohydrate-binding sites. Glycobiology. 28:21–31. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Meng H, Li W, Boardman LA and Wang L: Loss
of ZG16 is associated with molecular and clinicopathological
phenotypes of colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 18:4332018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|