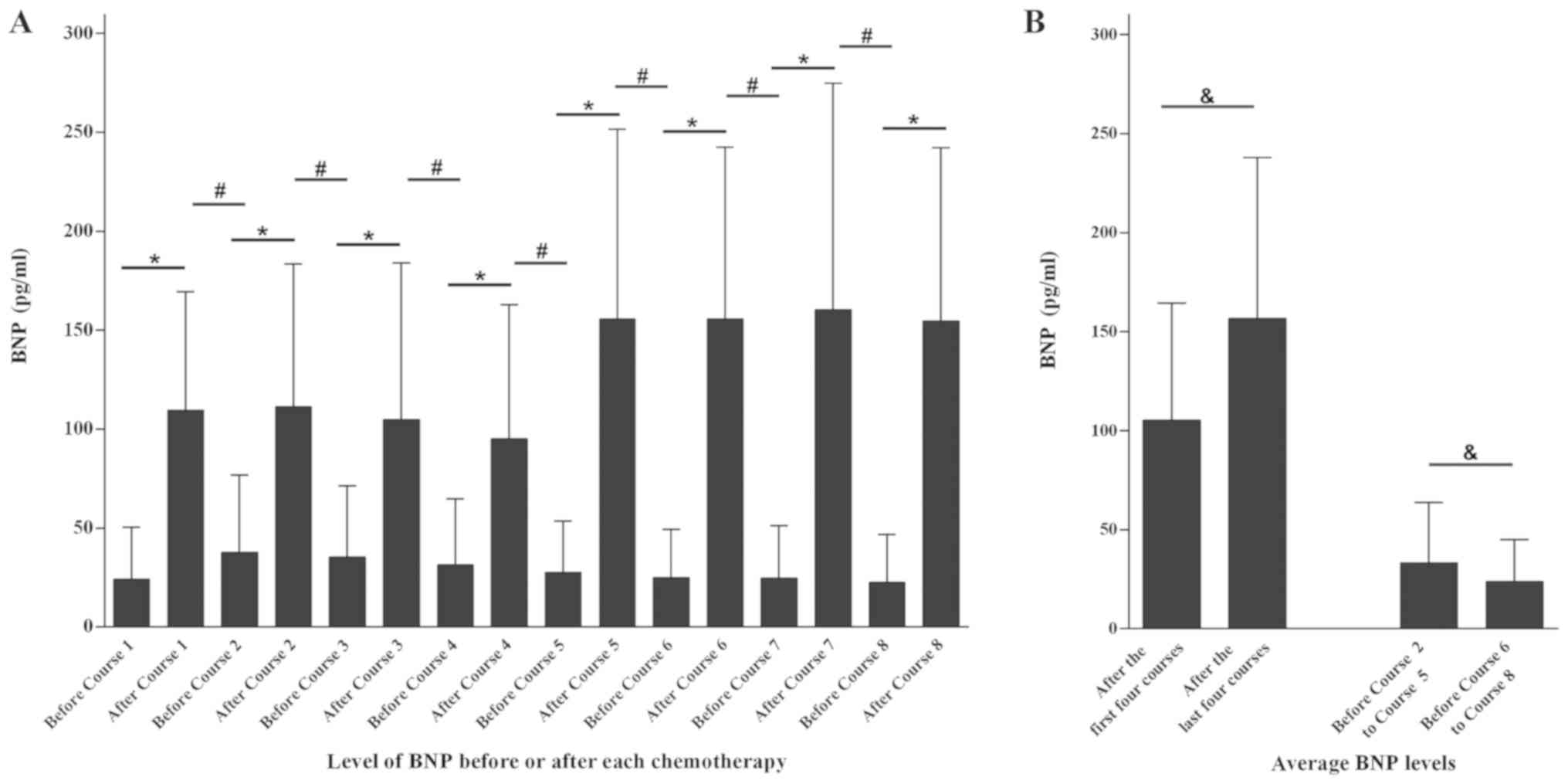
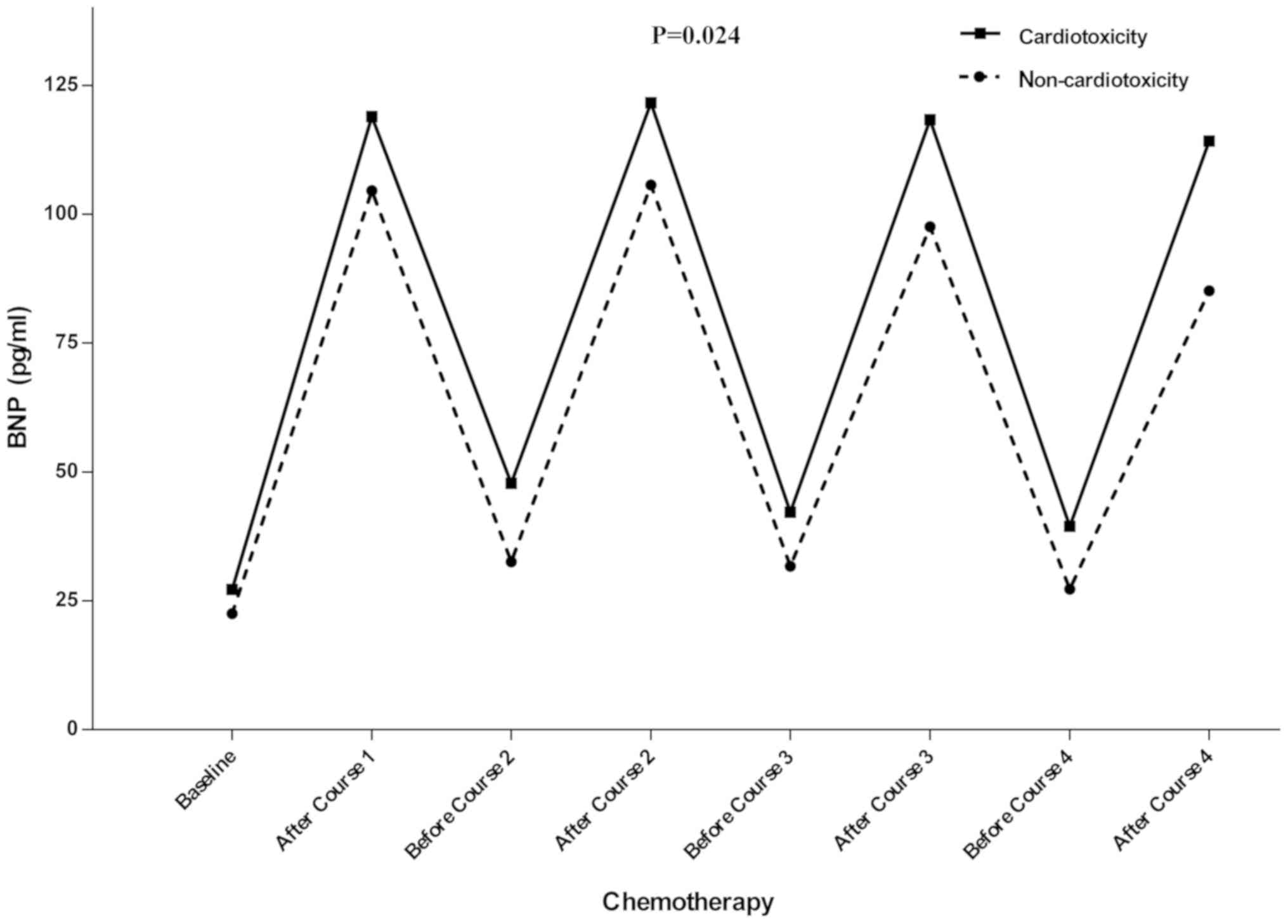
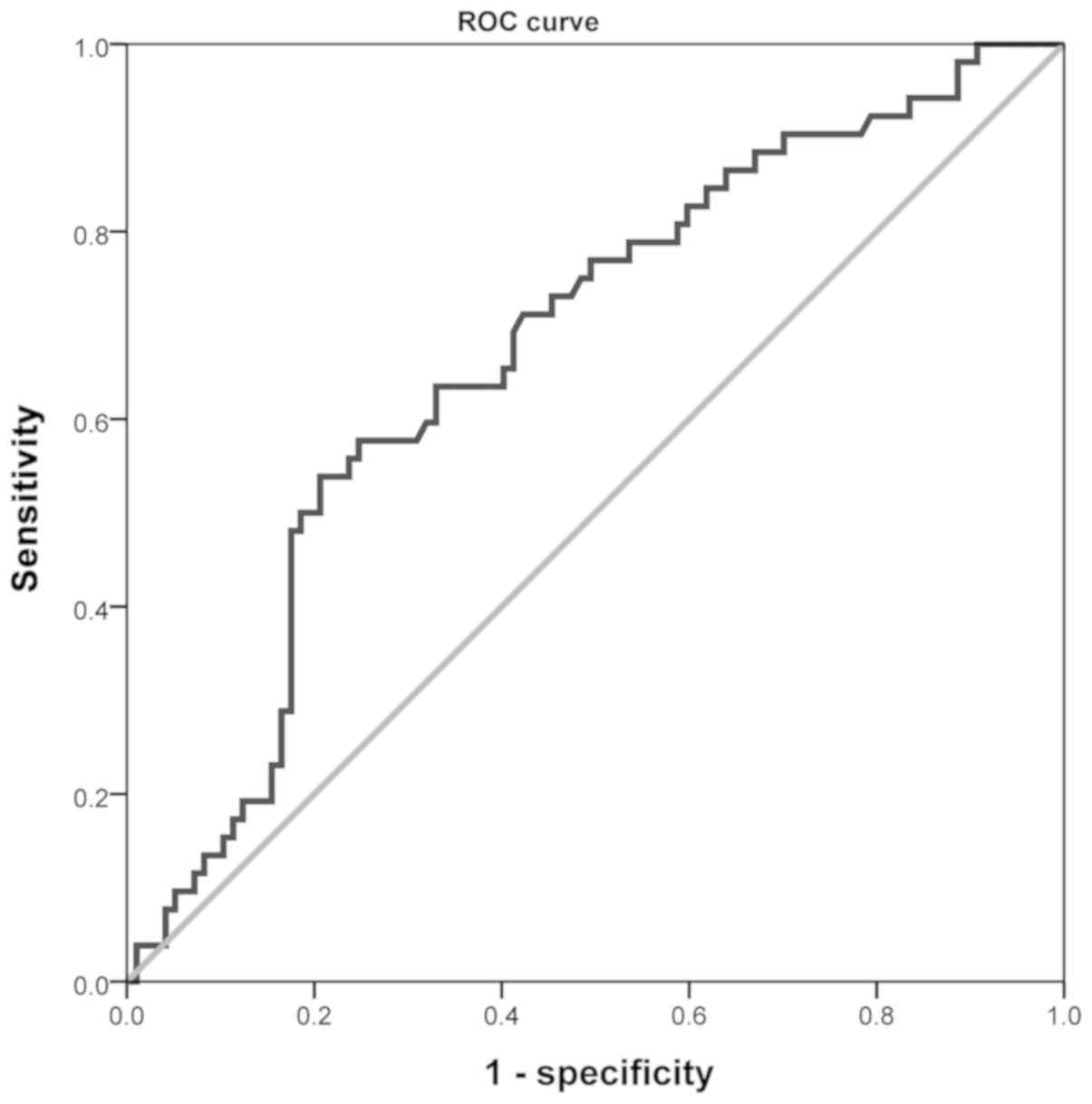
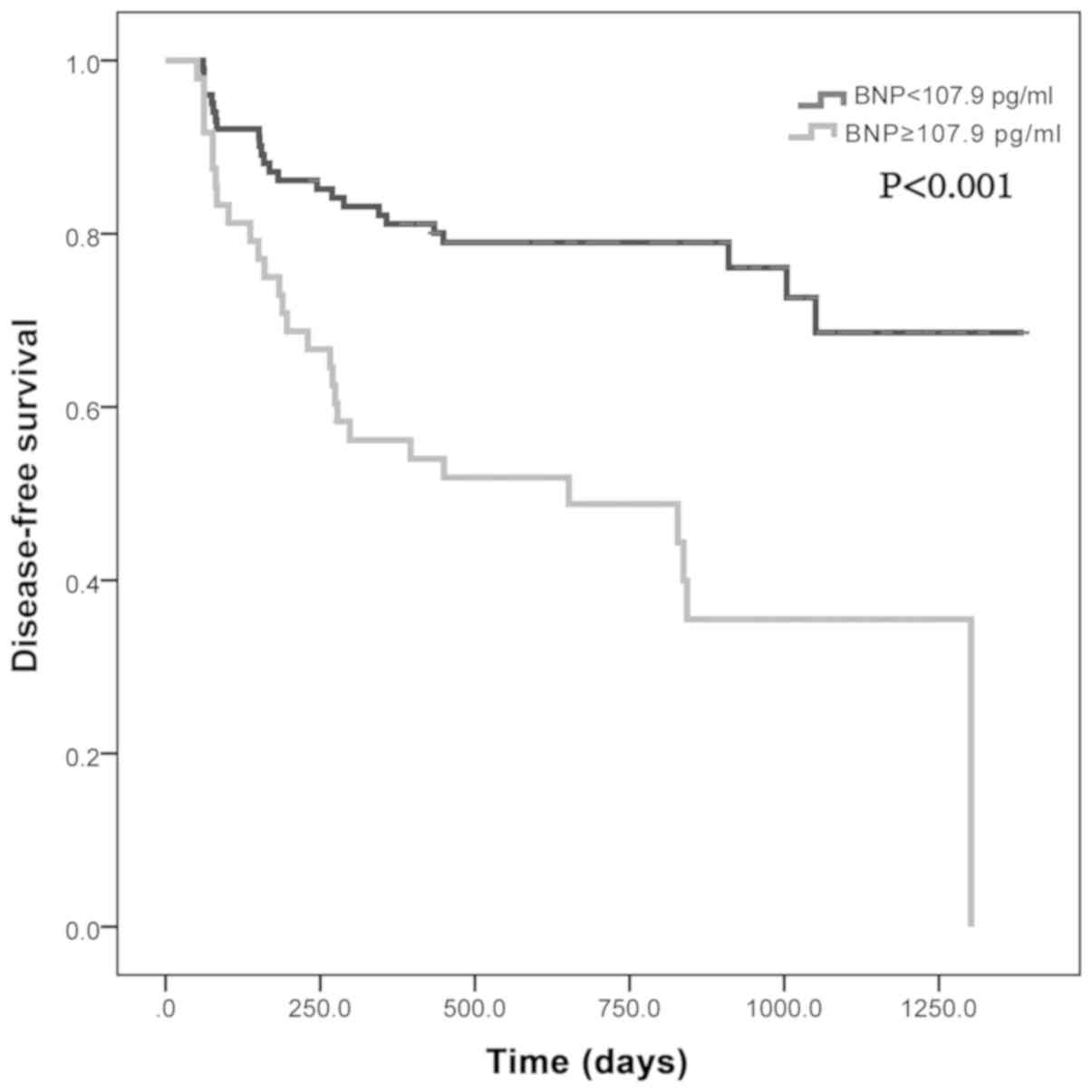
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Meinardi MT, van Veldhuisen DJ, Gietema
JA, Dolsma WV, Boomsma F, van den Berg MP, Volkers C, Haaksma J, de
Vries EG, Sleijfer DT and van der Graaf WT: Prospective evaluation
of early cardiac damage induced by epirubicin- containing adjuvant
chemotherapy and locoregional radiotherapy in breast cancer
patients. J Clin Oncol. 19:2746–2753. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lipshultz SE, Lipsitz SR, Sallan SE,
Dalton VM, Mone SM, Gelber RD and Colan SD: Chronic progressive
cardiac dysfunction years after doxorubicin therapy for childhood
acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 23:2629–2636. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Keefe DL: Anthracycline-induced
cardiomyopathy. Semin Oncol. 28 (Suppl 12):S2–S7. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Armenian SH, Gelehrter SK, Vase T,
Venkatramani R, Landier W, Wilson KD, Herrera C, Reichman L,
Menteer JD, Mascarenhas L, et al: Screening for cardiac dysfunction
in anthracycline-exposed childhood cancer survivors. Clin Cancer
Res. 20:6314–6323. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kilickap S, Barista I, Akgul E, Aytemir K,
Aksoyek S, Aksoy S, Celik I, Kes S and Tekuzman G: cTnT can be a
useful marker for early detection of anthracycline cardiotoxicity.
Ann Oncol. 16:798–804. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Clerico A, Fontana M, Zyw L, Passino C and
Emdin M: Comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of brain natriuretic
peptide (BNP) and the N-terminal part of the propeptide of BNP
immunoassays in chronic and acute heart failure: A systematic
review. Clin Chem. 53:813–822. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ledwidge M, Gallagher J, Conlon C, Tallon
E, O'Connell E, Dawkins I, Watson C, O'Hanlon R, Bermingham M,
Patle A, et al: Natriuretic peptide-based screening and
collaborative care for heart failure: The STOP-HF randomized trial.
JAMA. 310:66–74. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang P, Zhang S, Zhang XB, Li WJ, Hao XM
and Zhang J: Protective effect of dexrazoxane on cardiotoxicity in
breast cancer patients who received anthracycline-containing
chemotherapy. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 35:135–139. 2013.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lipshultz SE, Miller TL, Scully RE,
Lipsitz SR, Rifai N, Silverman LB, Colan SD, Neuberg DS, Dahlberg
SE, Henkel JM, et al: Changes in cardiac biomarkers during
doxorubicin treatment of pediatric patients with high-risk acute
lymphoblastic leukemia: Associations with long-term
echocardiographic outcomes. J Clin Oncol. 30:1042–1049. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
De Iuliis F, Salerno G, Taglieri L, De
Biase L, Lanza R, Cardelli P and Scarpa S: Serum biomarkers
evaluation to predict chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity in breast
cancer patients. Tumour Biol. 37:3379–3387. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lenihan DJ, Stevens PL, Massey M, Plana
JC, Araujo DM, Fanale MA, Fayad LE, Fisch MJ and Yeh ET: The
utility of point-of-care biomarkers to detect cardiotoxicity during
anthracycline chemotherapy: A feasibility study. J Card Fail.
22:433–438. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zidan A, Sherief LM, El-sheikh A, Saleh
SH, Shahbah DA, Kamal NM, Sherbiny HS and Ahmad H: NT-proBNP as
early marker of subclinical late cardiotoxicity after doxorubicin
therapy and mediastinal irradiation in childhood cancer survivors.
Dis Markers. 2015:5132192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sinn HP, Helmchen B and Wittekind CH: TNM
classification of breast cancer: Changes and comments on the 7th
edition. Pathologe. 31:361–366. 2010.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wolff AC, Hammond MEH, Allison KH, Harvey
BE, Mangu PB, Bartlett JMS, Bilous M, Ellis IO, Fitzgibbons P,
Hanna W, et al: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in
breast cancer: American society of clinical oncology/college of
American pathologists clinical practice guideline focused update.
Arch Pathol Lab Med. 142:1364–1382. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pichon MF, Cvitkovic F, Hacene K, Delaunay
J, Lokiec F, Collignon MA and Pecking AP: Drug-induced
cardiotoxicity studied by longitudinal B-type natriuretic peptide
assays and radionuclide ventriculography. In Vivo. 19:567–576.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Potter E and Marwick TH: Assessment of
left ventricular function by echocardiography: The case for
routinely adding global longitudinal strain to ejection fraction.
JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 11:260–274. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chang SA, Lim BK, Lee YJ, Hong MK, Choi JO
and Jeon ES: A novel angiotensin type I receptor antagonist,
fimasartan, prevents doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. J
Korean Med Sci. 30:559–568. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nitta D, Kinugawa K, Imamura T, Kato NP
and Komuro I: High dose β-blocker therapy triggers additional
reverse remodeling in patients with idiopathic non-ischemic
cardiomyopathy. Int Heart J. 57:717–724. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shimomura Y, Baba R, Watanabe A, Horikoshi
Y, Asami K, Hyakuna N, Iwai A, Matsushita T, Yamaji K, Hori T, et
al: Japanese childhood cancer and leukemia study group (JCCLSG):
Assessment of late cardiotoxicity of pirarubicin (THP) in children
with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer.
57:461–466. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bird BR and Swain SM: Cardiac toxicity in
breast cancer survivors: Review of potential cardiac problems. Clin
Cancer Res. 14:14–24. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Visscher H, Ross CJ, Rassekh SR, Barhdadi
A, Dubé MP, Al-Saloos H, Sandor GS, Caron HN, van Dalen EC, Kremer
LC, et al: Canadian pharmacogenomics network for drug safety
consortium: Pharmacogenomic prediction of anthracycline-induced
cardiotoxicity in children. J Clin Oncol. 30:1422–1428. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cao L, Zhu W, Wagar EA and Meng QH:
Biomarkers for monitoring chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity. Crit
Rev Clin Lab Sci. 54:87–101. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Leger KJ, Leonard D, Nielson D, de Lemos
JA, Mammen PP and Winick NJ: Circulating microRNAs: Potential
markers of cardiotoxicity in children and young adults treated with
anthracycline chemotherapy. J Am Heart Assoc. 6:e0046532017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Malik A, Jeyaraj PA, Calton R, Uppal B,
Negi P, Shankar A, Patil J and Mahajan MK: Are biomarkers
predictive of anthracycline-induced cardiac dysfunction? Asian Pac
J Cancer Prev. 17:2301–2305. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Swain SM, Whaley FS and Ewer MS:
Congestive heart failure in patients treated with doxorubicin: A
retrospective analysis of three trials. Cancer. 97:2869–2879. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nachom P and Ratanasit N: Incidence and
predictors of long-term adverse outcomes in patients with rheumatic
mitral stenosis in sinus rhythm. J Med Assoc Thai. 99:374–380.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Singletary GE, Morris NA, Lynne O'Sullivan
M, Gordon SG and Oyama MA: Prospective evaluation of NT-proBNP
assay to detect occult dilated cardiomyopathy and predict survival
in Doberman Pinschers. J Vet Intern Med. 26:1330–1336. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Addetia K, Michel C, Holcroft CA, Sheppard
R and Rudski LG: Early improvement in serial echocardiographic
studies in heart failure patients predicts long term survival-a
pilot study. J Card Fail. 21:470–478. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Inoue T, Kawai M, Nakane T, Nojiri A,
Minai K, Komukai K, Ogawa T, Hongo K, Matsushima M and Yoshimura M:
Influence of low-grade inflammation on plasma B-type natriuretic
peptide levels. Intern Med. 49:2659–2668. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Silva FB, Romero WG, Carvalho AL, Borgo
MV, Amorim MH, Gouvea SA and Abreu GR: Hormone therapy with
tamoxifen reduces plasma levels of NT-B-type natriuretic peptide
but does not change ventricular ejection fraction after
chemotherapy in women with breast cancer. Braz J Med Biol Res.
48:154–160. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sawaya H, Sebag IA, Plana JC, Januzzi JL,
Ky B, Tan TC, Cohen V, Banchs J, Carver JR, Wiegers SE, et al:
Assessment of echocardiography and biomarkers for the extended
prediction of cardiotoxicity in patients treated with
anthracyclines, taxanes, and trastuzumab. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging.
5:596–603. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ponde N, Bradbury I, Lambertini M, Ewer M,
Campbell C, Ameels H, Zardavas D, Di Cosimo S, Baselga J, Huober J,
et al: Cardiac biomarkers for early detection and prediction of
trastuzumab and/or lapatinib-induced cardiotoxicity in patients
with HER2-positive early-stage breast cancer: A NeoALTTO sub-study
(BIG 1–06). Breast Cancer Res Treat. 168:631–638. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Matos E, Jug B, Blagus R and Zakotnik B: A
Prospective cohort study on cardiotoxicity of adjuvant trastuzumab
therapy in breast cancer patients. Arq Bras Cardiol. 107:40–47.
2016.(In English, Portuguese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Criscitiello C and Curigliano G: HER2
signaling pathway and trastuzumab cardiotoxicity. Future Oncol.
9:179–181. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Baldini E, Prochilo T, Salvadori B,
Bolognesi A, Aldrighetti D, Venturini M, Rosso R, Carnino F, Gallo
L, Giannessi P, et al: Multicenter randomized phase III trial of
epirubicin plus paclitaxel vs epirubicin followed by paclitaxel in
metastatic breast cancer patients: Focus on cardiac safety. Br J
Cancer. 91:45–49. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vogelsang TW, Jensen RJ, Hesse B and Kjaer
A: BNP cannot replace gated equilibrium radionuclide
ventriculography in monitoring of anthracycline-induced
cardiotoxity. Int J Cardiol. 124:193–197. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kittiwarawut A, Vorasettakarnkij Y,
Tanasanvimon S, Manasnayakorn S and Sriuranpong V: Serum NT-proBNP
in the early detection of doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction.
Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 9:155–161. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Feola M, Garrone O, Occelli M, Francini A,
Biggi A, Visconti G, Albrile F, Bobbio M and Merlano M:
Cardiotoxicity after anthracycline chemotherapy in breast
carcinoma: Effects on left ventricular ejection fraction, troponin
I and brain natriuretic peptide. Int J Cardiol. 148:194–198. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Skovgaard D, Hasbak P and Kjaer A: BNP
predicts chemotherapy-related cardiotoxicity and death: Comparison
with gated equilibrium radionuclide ventriculography. PLoS One.
9:e967362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Romano S, Fratini S, Ricevuto E,
Procaccini V, Stifano G, Mancini M, Di Mauro M, Ficorella C and
Penco M: Serial measurements of NT-proBNP are predictive of
not-high-dose anthracycline cardiotoxicity in breast cancer
patients. Br J Cancer. 105:1663–1668. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang C, Shi D and Yang P: BNP as a
potential biomarker for cardiac damage of breast cancer after
radiotherapy: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 98:e165072019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Michel L, Rassaf T and Totzeck M:
Biomarkers for the detection of apparent and subclinical cancer
therapy-related cardiotoxicity. J Thorac Dis. 10 (Suppl
35):S4282–S4295. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|