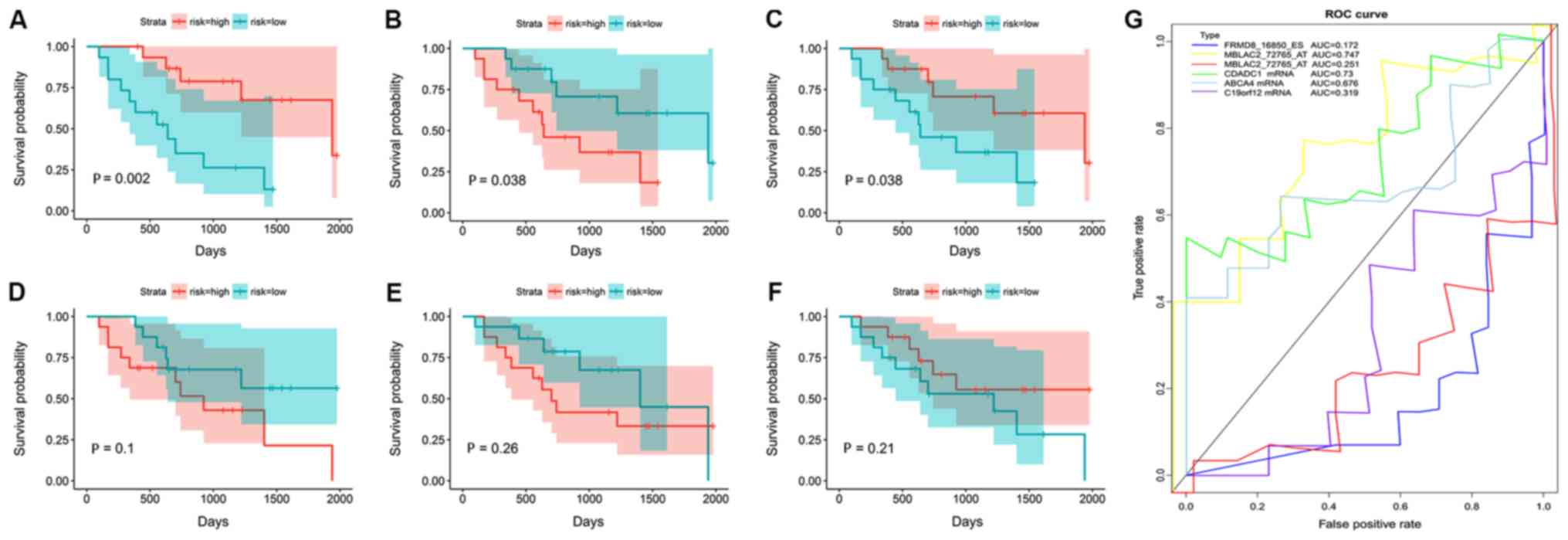
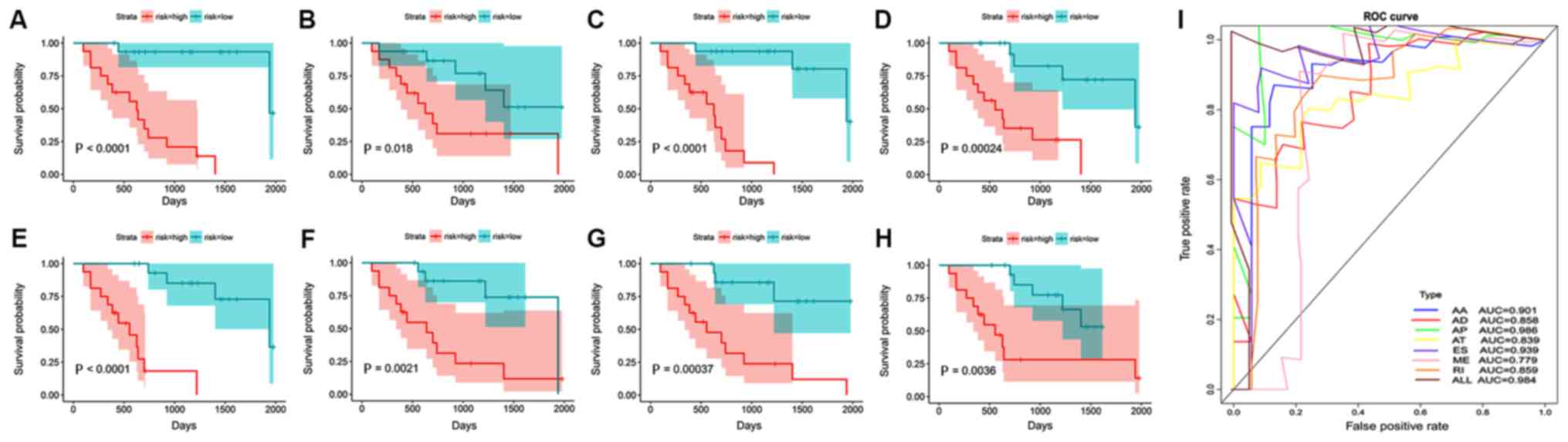
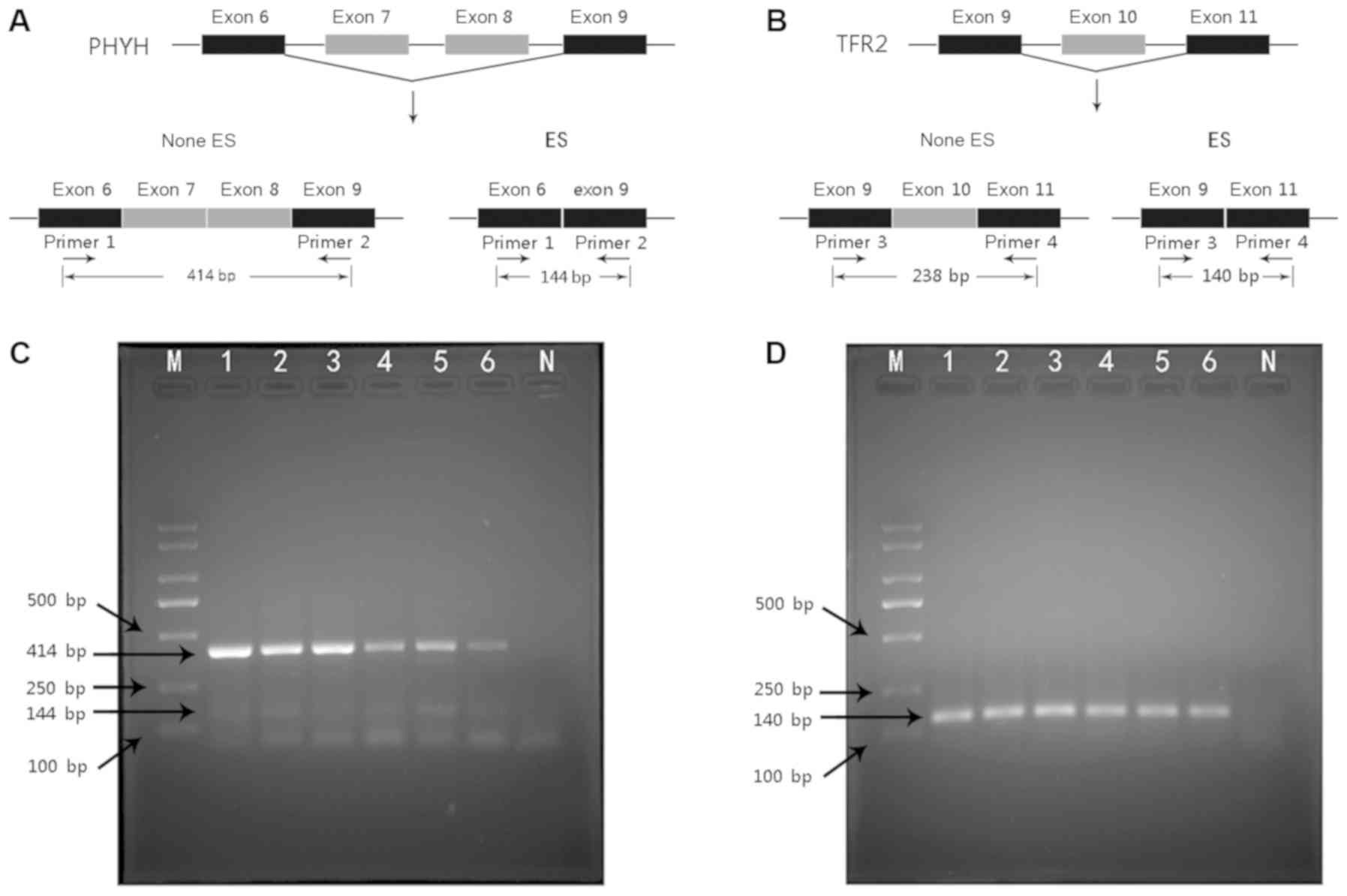
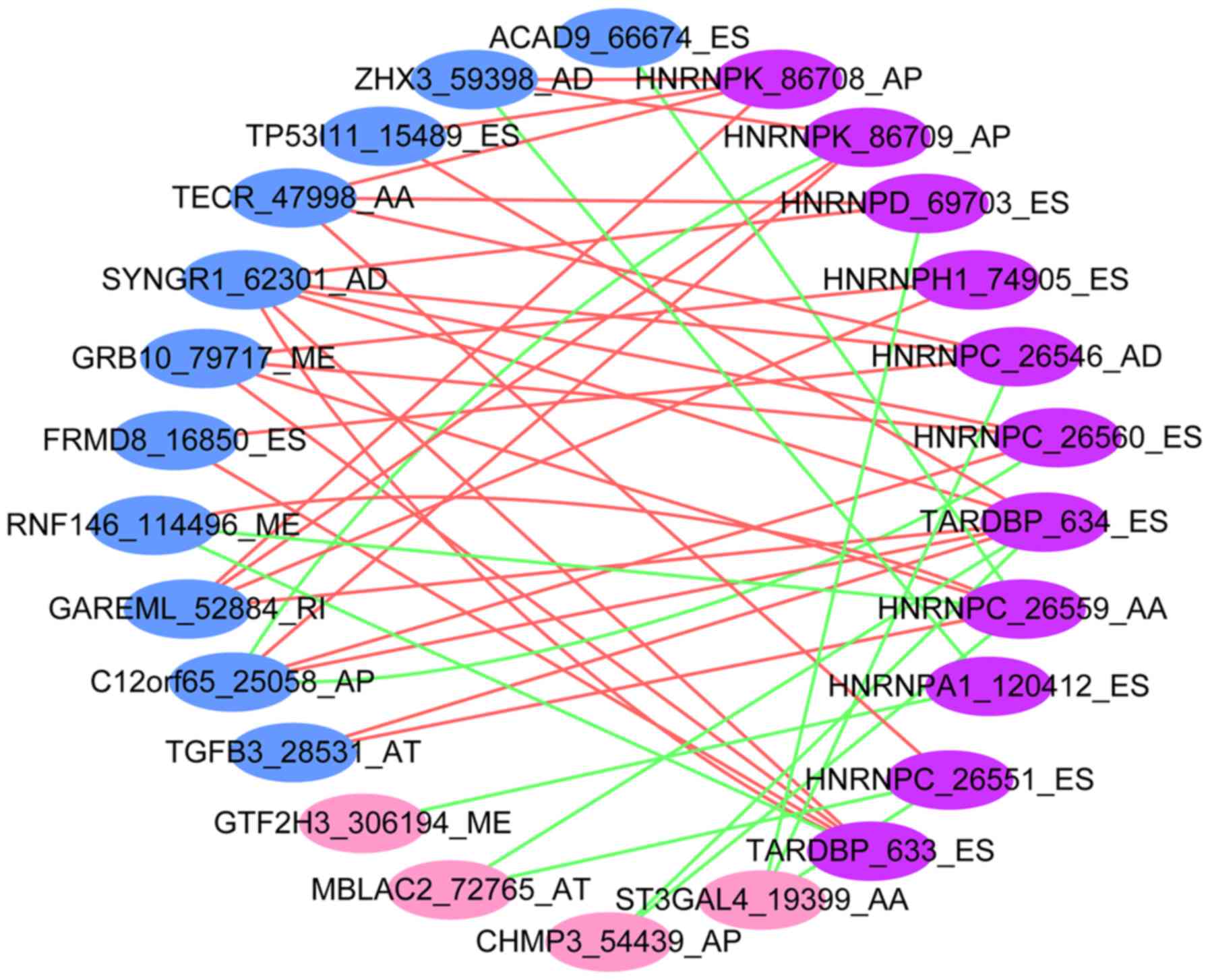
|
1
|
Popat K, McQueen K and Feeley TW: The
global burden of cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol.
27:399–408. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Verathamjamras C, Weeraphan C,
Chokchaichamnankit D, Watcharatanyatip K, Subhasitanont P,
Diskul-Na-Ayudthaya P, Mingkwan K, Luevisadpaibul V,
Chutipongtanate S, Champattanachai V, et al: Secretomic profiling
of cells from hollow fiber bioreactor reveals PSMA3 as a potential
cholangiocarcinoma biomarker. Int J Oncol. 51:269–280. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lu X, Zhou C, Li R, Deng Y, Zhao L and
Zhai W: Long noncoding RNA AFAP1-AS1 promoted tumor growth and
invasion in cholangiocarcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 42:222–230.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cai X, Li J, Yuan X, Xiao J, Dooley S, Wan
X, Weng H and Lu L: CD133 expression in cancer cells predicts poor
prognosis of non-mucin producing intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J
Transl Med. 16:502018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Luo G, Li B, Duan C, Cheng Y, Xiao B, Yao
F, Wei M, Tao Q, Feng C, Xia X, et al: cMyc promotes
cholangiocarcinoma cells to overcome contact inhibition via the
mTOR pathway. Oncol Rep. 38:2498–2506. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Qian Y, Yao W, Yang T, Yang Y, Liu Y, Shen
Q, Zhang J, Qi W and Wang J: aPKC-iota/P-Sp1/Snail signaling
induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and immunosuppression in
cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. 66:1165–1182. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Razumilava N and Gores GJ:
Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet. 383:2168–2179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou G, Yang Z, Wang X, Tao R and Zhou Y:
TRAIL enhances shikonin induced apoptosis through ROS/JNK signaling
in cholangiocarcinoma cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 42:1073–1086.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tang J, Liao Y, He S, Shi J, Peng L, Xu X,
Xie F, Diao N, Huang J, Xie Q, et al: Autocrine parathyroid
hormone-like hormone promotes intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell
proliferation via increased ERK/JNK-ATF2-cyclin D1 signaling. J
Transl Med. 15:2382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chng KR, Chan SH, Ng AHQ, Li C, Jusakul A,
Bertrand D, Wilm A, Choo SP, Tan DMY, Lim KH, et al: Tissue
microbiome profiling identifies an enrichment of specific enteric
bacteria in opisthorchis viverrini associated cholangiocarcinoma.
Ebiomedicine. 8:195–202. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Breitbart RE, Andreadis A and Nadalginard
B: Alternative splicing: A ubiquitous mechanism for the generation
of multiple protein isoforms from single genes. Annu Rev Biochem.
56:467–495. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Blencowe BJ: Alternative splicing: New
insights from global analyses. Cell. 126:37–47. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Oltean S and Bates DO: Hallmarks of
alternative splicing in cancer. Oncogene. 33:5311–5318. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang ET, Rickard S, Luo S, Khrebtukova I,
Zhang L, Mayr C, Kingsmore SF, Schroth GP and Burge CB: Alternative
isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes. Nature.
456:470–476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pan Q, Shai O, Lee LJ, Frey BJ and
Blencowe BJ: Deep surveying of alternative splicing complexity in
the human transcriptome by high-throughput sequencing. Nat Genet.
40:1413–1415. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dvinge H and Bradley RK: Widespread intron
retention diversifies most cancer transcriptomes. Genome Medi.
7:452015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bechara EG, Sebestyén E, Bernardis I,
Eyras E and Valcárcel J: RBM5, 6 and 10 differentially regulate
NUMB alternative splicing to control cancer cell proliferation. Mol
Cell. 52:720–733. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ghigna C, Giordano S, Shen H, Benvenuto F,
Castiglioni F, Comoglio PM, Green MR, Riva S and Biamonti G: Cell
motility is controlled by SF2/ASF through alternative splicing of
the Ron Protooncogene. Mol Cell. 20:881–890. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jung H, Lee D, Lee J, Park D, Kim YJ, Park
WY, Hong D, Park PJ and Lee E: Intron retention is a widespread
mechanism of tumor-suppressor inactivation. Nat Genet.
47:1242–1248. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Goldstein L, Lee J, Gnad F, Klijn C,
Schaub A, Reeder J, Daemen A, Bakalarski CE, Holcomb T, Shames DS,
et al: Recurrent loss of NFE2L2 exon 2 is a mechanism for Nrf2
pathway activation in human cancers. Cell Rep. 16:2605–2617. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kornblihtt AR: Epigenetics at the base of
alternative splicing changes that promote colorectal cancer. J Clin
Invest. 127:3281–3283. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Poulikakos PI, Persaud Y, Janakiraman M,
Kong X, Ng C, Moriceau G, Shi H, Atefi M, Titz B, Gabay MT, et al:
RAF inhibitor resistance is mediated by dimerization of aberrantly
spliced BRAF (V600E). Nature. 480:387–390. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sotillo E, Barrett DM, Black KL, Bagashev
A, Oldridge D, Wu G, Sussman R, Lanauze C, Ruella M, Gazzara MR, et
al: Convergence of acquired mutations and alternative splicing of
CD19 enables resistance to CART-19 immunotherapy. Cancer Discov.
5:1282–1295. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang BD, Ceniccola K, Hwang S, Andrawis R,
Horvath A, Freedman JA, Olender J, Knapp S, Ching T, Garmire L, et
al: Alternative splicing promotes tumour aggressiveness and drug
resistance in African American prostate cancer. Nat Commun.
8:159212017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sebestyén E, Zawisza M and Eyras E:
Detection of recurrent alternative splicing switches in tumor
samples reveals novel signatures of cancer. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:1345–1356. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Trincado JL, Sebestyén E, Pagés A and
Eyras E: The prognostic potential of alternative transcript
isoforms across human tumors. Genome Med. 8:852016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shen S, Wang Y, Wang C, Ying NW and Yi X:
SURVIV for survival analysis of mRNA isoform variation. Nat Commun.
7:115482016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Parsons DW, Li M, Zhang X, Jones S, Leary
RJ, Lin JC, Boca SM, Carter H, Samayoa J, Bettegowda C, et al: The
genetic landscape of the childhood cancer medulloblastoma. Science.
331:435–439. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ghigna C, De Toledo M, Bonomi S, Valacca
C, Gallo S, Apicella M, Eperon I, Tazi J and Biamonti G:
Pro-metastatic splicing of Ron proto-oncogene mRNA can be reversed:
Therapeutic potential of bifunctional oligonucleotides and indole
derivatives. RNA Biol. 7:495–503. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee CW and Abdelwahab O: Therapeutic
targeting of splicing in cancer. Nat Med. 22:976–986. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Koh CM, Bezzi M, Low DH, Ang WX, Teo SX,
Gay FP, Al-Haddawi M, Tan SY, Osato M, Sabò A, et al: MYC regulates
the core pre-mRNA splicing machinery as an essential step in
lymphomagenesis. Nature. 523:96–100. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Havens MA and Hastings ML:
Splice-switching antisense oligonucleotides as therapeutic drugs.
Nucleic Acids Res. 44:6549–6563. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Salton M and Misteli T: Small molecule
modulators of Pre-mRNA splicing in cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med.
22:28–37. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gao L, Xie ZC, Pang JS, Li TT and Chen G:
A novel alternative splicing-based prediction model for uteri
corpus endometrial carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY). 11:263–283. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xiong Y, Deng Y, Wang K, Zhou H, Zheng X,
Si L and Fu Z: Profiles of alternative splicing in colorectal
cancer and their clinical significance: A study based on
large-scale sequencing data. EBioMedicine. 36:183–195. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang ZG, He RQ and Mo ZN: Prognostic
value and potential function of splicing events in prostate
adenocarcinoma. Int J Oncol. 53:2473–2487. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jusakul A, Cutcutache I, Yong CH, Lim JQ,
Huang MN, Padmanabhan N, Nellore V, Kongpetch S, Ng AWT, Ng LM, et
al: Whole-genome and epigenomic landscapes of etiologically
distinct subtypes of cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Discov.
7:1116–1135. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Supek F, Miñana B, Valcárcel J, Gabaldón T
and Lehner B: Synonymous mutations frequently act as driver
mutations in human cancers. Cell. 156:1324–1335. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sterneweiler T and Sanford JR: Exon
identity crisis: Disease-causing mutations that disrupt the
splicing code. Genome Biol. 15:2012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Diederichs S, Bartsch L, Berkmann JC,
Fröse K, Heitmann J, Hoppe C, Iggena D, Jazmati D, Karschnia P,
Linsenmeier M, et al: The dark matter of the cancer genome:
Aberrations in regulatory elements, untranslated regions, splice
sites, non-coding RNA and synonymous mutations. EMBO Mol Med.
8:442–457. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Singh S, Narayanan SP, Biswas K, Gupta A,
Ahuja N, Yadav S, Panday RK, Samaiya A, Sharan SK and Shukla S:
Intragenic DNA methylation and BORIS-mediated cancer-specific
splicing contribute to the Warburg effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
114:11440–11445. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gelfman S, Cohen N, Yearim A and Ast G:
DNA-methylation effect on cotranscriptional splicing is dependent
on GC architecture of the exon-intron structure. Genome Res.
23:789–799. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shukla S, Kavak E, Gregory M, Imashimizu
M, Shutinoski B, Kashlev M, Oberdoerffer P, Sandberg R and
Oberdoerffer S: CTCF-promoted RNA polymerase II pausing links DNA
methylation to splicing. Nature. 479:74–79. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yuan H, Li N, Fu D, Ren J, Hui J, Peng J,
Liu Y, Qiu T, Jiang M, Pan Q, et al: Histone methyltransferase
SETD2 modulates alternative splicing to inhibit intestinal
tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest. 127:3375–3391. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ding X, Liu S, Tian M, Zhang W, Zhu T, Li
D, Wu J, Deng H, Jia Y, Xie W, et al: Activity-induced histone
modifications govern Neurexin-1 mRNA splicing and memory
preservation. Nat Neurosci. 20:690–699. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sharma A, Nguyen H, Geng C, Hinman MN, Luo
G and Lou H: Calcium-mediated histone modifications regulate
alternative splicing in cardiomyocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:E4920–E4928. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kim S, Kim H, Fong N, Erickson B and
Bentley DL: Pre-mRNA splicing is a determinant of histone H3K36
methylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:13564–13569. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Takehara T, Liu X, Fujimoto J, Friedman SL
and Takahashi H: Expression and role of Bcl-xL in human
hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatology. 34:55–61. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Boise LH, Gonzálezgarcía M, Postema CE,
Ding L, Lindsten T, Turka LA, Mao X, Nuñez G and Thompson CB:
bcl-x, a bcl-2-related gene that functions as a dominant regulator
of apoptotic cell death. Cell. 74:597–608. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bingle CD, Craig RW, Swales BM, Singleton
V, Zhou P and Whyte MK: Exon skipping in Mcl-1 results in a Bcl-2
homology domain 3 only gene product that promotes cell death. J
Biol Chem. 275:22136–22146. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bae J, Leo CP, Hsu SY and Hsueh AJ:
MCL-1S, a splicing variant of the antiapoptotic BCL-2 family member
MCL-1, encodes a proapoptotic protein possessing only the BH3
domain. J Biol Chem. 275:25255–25261. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Salton M, Kasprzak WK, Voss T, Shapiro BA,
Poulikakos PI and Misteli T: Inhibition of vemurafenib-resistant
melanoma by interference with pre-mRNA splicing. Nat Commun.
6:71032015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chen K, Xiao H, Zeng J, Yu G, Zhou H,
Huang C, Yao W, Xiao W, Hu J, Guan W, et al: Alternative splicing
of EZH2 pre-mRNA by SF3B3 contributes to the tumorigenic potential
of renal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 23:3428–3441. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Luo C, Cheng Y, Liu Y, Chen L, Liu L, Wei
N, Xie Z, Wu W and Feng Y: SRSF2 regulates alternative splicing to
drive hepatocellular carcinoma development. Cancer Res.
77:1168–1178. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Calabretta S, Bielli P, Passacantilli I,
Pilozzi E, Fendrich V, Capurso G, Fave GD and Sette C: Modulation
of PKM alternative splicing by PTBP1 promotes gemcitabine
resistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene. 35:2031–2039.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li Y, Sun N, Lu Z, Sun S, Huang J, Chen Z
and He J: Prognostic alternative mRNA splicing signature in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 393:40–51. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhu J, Chen Z and Yong L: Systematic
profiling of alternative splicing signature reveals prognostic
predictor for ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 148:368–374. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Miles S, Swift L and Leinster SJ: The
dundee ready education environment measure (DREEM): A review of its
adoption and use. Med Teach. 34:e620–e634. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Shi Y, Chen Z, Gao J, Wu S, Gao H and Feng
G: Transcriptome-wide analysis of alternative mRNA splicing
signature in the diagnosis and prognosis of stomach adenocarcinoma.
Oncol Rep. 40:2014–2022. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lin P, He RQ, Ma FC, Liang L, He Y, Yang
H, Dang YW and Chen G: Systematic analysis of survival-associated
alternative splicing signatures in gastrointestinal
pan-adenocarcinomas. EBioMedicine. 34:46–60. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ryan M, Wong WC, Brown R, Akbani R, Su X,
Broom B, Melott J and Weinstein J: TCGASpliceSeq a compendium of
alternative mRNA splicing in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res.
44:D1018–D1022. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
R Core Team. R, . A language and
environment for statistical computingR Foundation for Statistical
Computing; Vienna, Austria: 2012, ISBN 3-900051-07-0. http://www.R-project.org/
|
|
63
|
Smidt N DJaMT: Guide to the contents of a
Cochrane review and protocol. Cochrane handbook for systematic
reviews of diagnostic test accuracy. 2011.
|
|
64
|
Conway JR, Lex A and Gehlenborg N: UpSetR:
An R package for the visualization of intersecting sets and their
properties. Bioinformatics. 33:2938–2940. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wu G, Dawson E, Duong A, Haw R and Stein
L: ReactomeFIViz: A Cytoscape app for pathway and network-based
data analysis. F1000Res. 3:1462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wickham H: ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for
Data AnalysisSpringer-Verlag; New York, NY: pp. 77–186. 2016
|
|
68
|
Heagerty PJ and Zheng Y: Survival model
predictive accuracy and ROC curves. Biometrics. 61:92–105. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Lee Y and Rio DC: Mechanisms and
regulation of alternative Pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Biochem.
84:291–323. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Piva F, Giulietti M, Burini AB and
Principato G: SpliceAid 2: A database of human splicing factors
expression data and RNA target motifs. Hum Mutat. 33:81–85. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Rahnemai-Azar AA, Weisbrod A, Dillhoff M,
Schmidt C and Pawlik TM: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Molecular
markers for diagnosis and prognosis. Surg Oncol. 26:125–137. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Khan SA, Davidson BR, Goldin RD, Heaton N,
Karani J, Pereira SP, Rosenberg WM, Tait P, Taylor-Robinson SD,
Thillainayagam AV, et al: Guidelines for the diagnosis and
treatment of cholangiocarcinoma: An update. Gut. 61:1657–1669.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Pasquali C, Sperti C, D'Andrea AA,
Costantino V, Filipponi C and Pedrazzoli S: CA50 as a serum marker
for pancreatic carcinoma: Comparison with CA19-9. Eur J Cancer 30A.
1042–1043. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Shan M, Tian Q and Zhang L: Serum CA50
levels in patients with cancers and other diseases. Prog Mol Biol
Transl Sci. 162:187–198. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Dou H, Sun G and Zhang L: CA242 as a
biomarker for pancreatic cancer and other diseases. Prog Mol Biol
Transl Sci. 162:229–239. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Huang CK, Aihara A, Iwagami Y, Yu T,
Carlson R, Koga H, Kim M, Zou J, Casulli S and Wands JR: Expression
of transforming growth factor β1 promotes cholangiocarcinoma
development and progression. Cancer Lett. 380:153–162. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Churi CR, Shroff R, Wang Y, Rashid A, Kang
HC, Weatherly J, Zuo M, Zinner R, Hong D, Meric-Bernstam F, et al:
Mutation profiling in cholangiocarcinoma: Prognostic and
therapeutic implications. PLoS One. 9:e1153832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Dana P, Kariya R, Vaeteewoottacharn K,
Sawanyawisuth K, Seubwai W, Matsuda K, Okada S and Wongkham S:
Upregulation of CD147 promotes metastasis of cholangiocarcinoma by
modulating the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal transitional process.
Oncol Res. 25:1047–1059. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Schweitzer N and Vogel A: Systemic therapy
of cholangiocarcinoma: From chemotherapy to targeted therapies.
Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 29:345–353. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Kamlua S, Patrakitkomjorn S, Jearanaikoon
P, Menheniott TR, Giraud AS and Limpaiboon T: A novel TFF2 splice
variant (ΔEX2TFF2) correlates with longer overall survival time in
cholangiocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 27:1207–1212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Nutthasirikul N, Limpaiboon T, Leelayuwat
C, Patrakitkomjorn S and Jearanaikoon P: Ratio disruption of the
∆133p53 and TAp53 isoform equilibrium correlates with poor clinical
outcome in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Int J Oncol.
42:1181–1188. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Comino-Mendez I, Leandro-Garcia LJ,
Montoya G, Inglada-Pérez L, de Cubas AA, Currás-Freixes M, Tysoe C,
Izatt L, Letón R, Gómez-Graña Á, et al: Functional and in silico
assessment of MAX variants of unknown significance. J Mol Med
(Berl). 93:1247–1255. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Huang X, Wu Z, Mei Y and Wu M: XIAP
inhibits autophagy via XIAP-Mdm2-p53 signalling. EMBO J.
32:2204–2216. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Li Z, Tuteja G, Schug J and Kaestner KH:
Foxa1 and Foxa2 are essential for sexual dimorphism in liver
cancer. Cell. 148:72–83. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
McNeely S, Beckmann R and Bence Lin AK:
CHEK again: Revisiting the development of CHK1 inhibitors for
cancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 142:1–10. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Mo J, Zhang D and Yang R: MicroRNA-195
regulates proliferation, migration, angiogenesis and autophagy of
endothelial progenitor cells by targeting GABARAPL1. Biosci Rep.
36(pii): e003962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Wagner EF and Nebreda AR: Signal
integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:537–549. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Eswaran J, Horvath A, Godbole S, Reddy SD,
Mudvari P, Ohshiro K, Cyanam D, Nair S, Fuqua SA, Polyak K, et al:
RNA sequencing of cancer reveals novel splicing alterations. Sci
Rep. 3:16892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Suo C, Hrydziuszko O, Lee D, Pramana S,
Saputra D, Joshi H, Calza S and Pawitan Y: Integration of somatic
mutation, expression and functional data reveals potential driver
genes predictive of breast cancer survival. Bioinformatics.
31:2607–2613. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Yosudjai J, Inpad C, Chomwong S, Dana P,
Sawanyawisuth K, Phimsen S, Wongkham S, Jirawatnotai S and Kaewkong
W: An aberrantly spliced isoform of anterior gradient-2, AGR2vH
promotes migration and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma cell. Biomed
Pharmacother. 107:109–116. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Mcneely S, Beckmann R and Bence Lin AK:
CHEK again: Revisiting the development of CHK1 inhibitors for
cancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 142:1–10. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zhang H, Yang T, Wu M and Shen F:
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Epidemiology, risk factors,
diagnosis and surgical management. Cancer Lett. 379:198–205. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Goere D, Wagholikar GD, Pessaux P, Carrère
N, Sibert A, Vilgrain V, Sauvanet A and Belghiti J: Utility of
staging laparoscopy in subsets of biliary cancers: Laparoscopy is a
powerful diagnostic tool in patients with intrahepatic and
gallbladder carcinoma. Surg Endosc. 20:721–725. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
He RQ, Zhou XG, Yi QY, Deng CW, Gao JM,
Chen G and Wang QY: Prognostic signature of alternative splicing
events in bladder urothelial carcinoma based on spliceseq data from
317 cases. Cell Physiol Biochem. 48:1355–1368. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Lin P, He RQ, Huang ZG, Zhang R, Wu HY,
Shi L, Li XJ, Li Q, Chen G, Yang H and He Y: Role of global
aberrant alternative splicing events in papillary thyroid cancer
prognosis. Aging (Albany NY). 11:2082–2097. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Zhang D, Duan Y, Cun J and Yang Q:
Identification of prognostic alternative splicing signature in
breast carcinoma. Front Genet. 10:2782019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|