|
1
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W
and Tuschl T: Identification of novel genes coding for small
expressed RNAs. Science. 294:853–858. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG and Bartel
DP: An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles
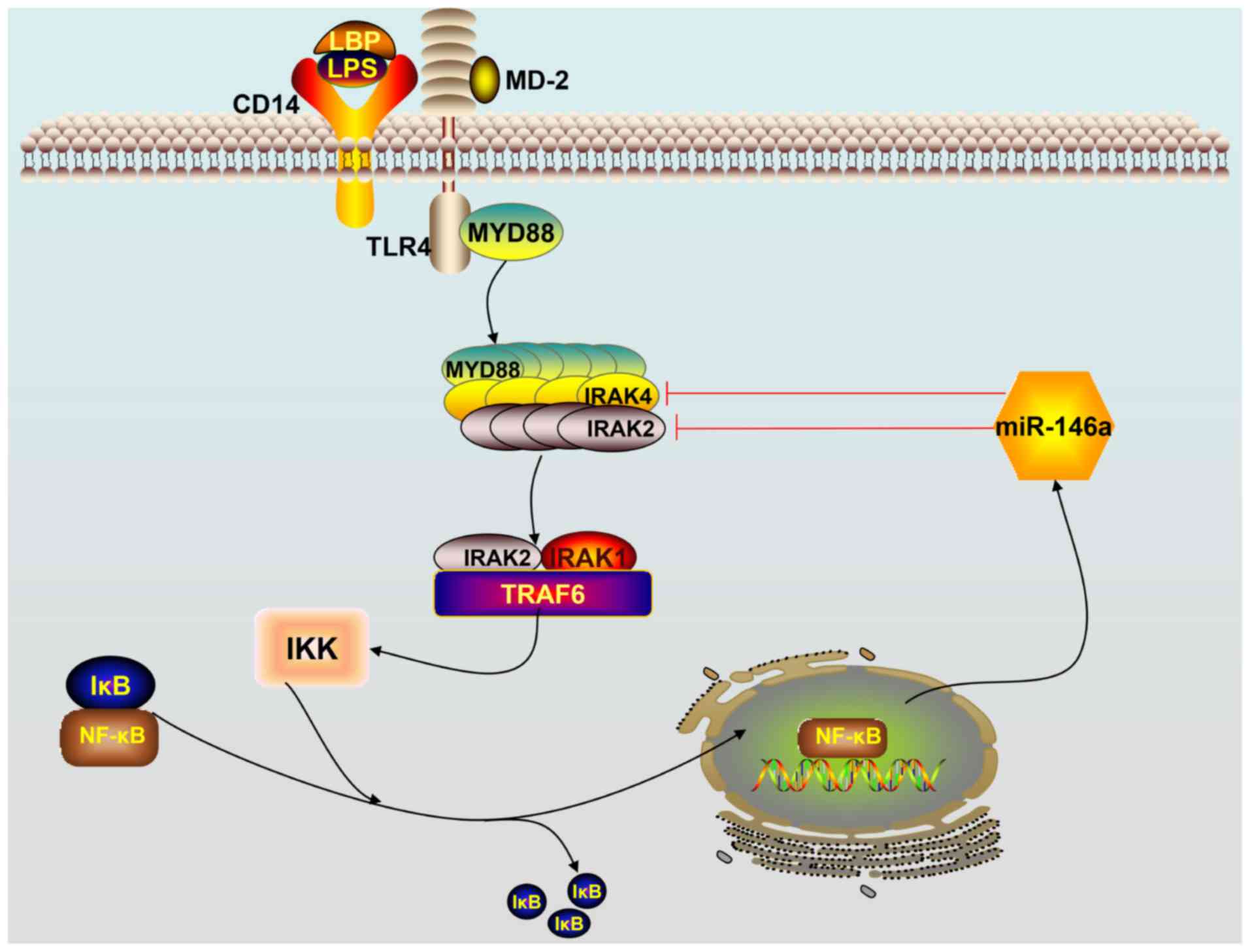
in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 294:858–862. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang H, Qu Y, Duan J, Deng T, Liu R,
Zhang L, Bai M, Li J, Zhou L, Ning T, et al: Integrated analysis of
the miRNA, gene and pathway regulatory network in gastric cancer.
Oncol Rep. 35:1135–1146. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shi XB, Tepper CG and deVere White RW:
Cancerous miRNAs and their regulation. Cell Cycle. 7:1529–1538.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hurst DR, Edmonds MD, Scott GK, Benz CC,
Vaidya KS and Welch DR: Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1
up-regulates miR-146, which suppresses breast cancer metastasis.
Cancer Res. 69:1279–1283. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
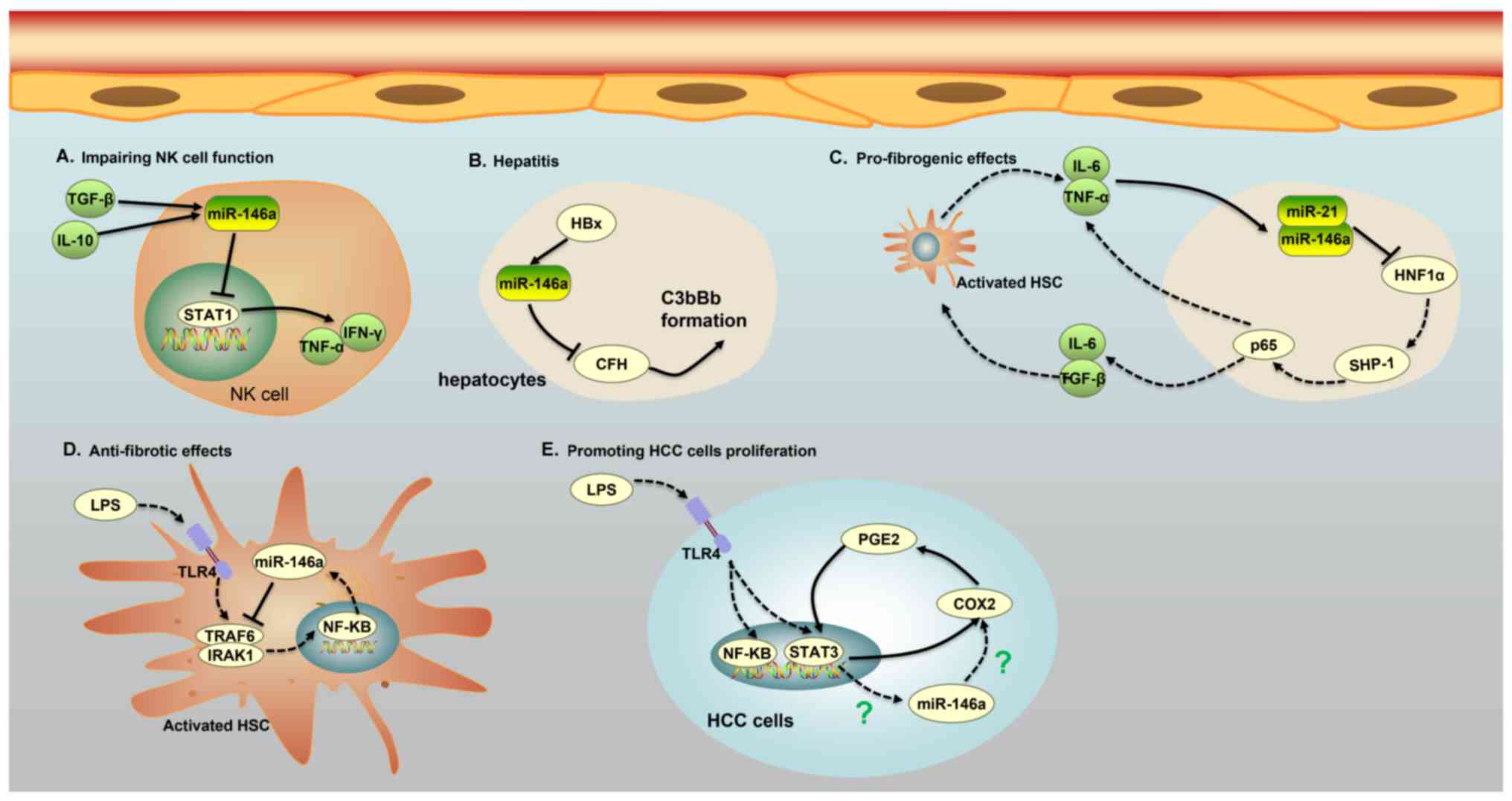
|
8
|
Li Y, Vandenboom TG, Wang Z, Kong D, Ali
S, Philip PA and Sarkar FH: miR-146a suppresses invasion of
pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 70:1486–1495. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kogo R, Mimori K, Tanaka F, Komune S and
Mori M: Clinical significance of miR-146a in gastric cancer cases.
Clin Cancer Res. 17:4277–4284. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Labbaye C and Testa U: The emerging role
of MIR-146A in the control of hematopoiesis, immune function and
cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 5:132012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Thomson JM, Newman M, Parker JS,
Morin-Kensicki EM, Wright T and Hammond SM: Extensive
post-transcriptional regulation of microRNAs and its implications
for cancer. Genes Dev. 20:2202–2207. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ and
Baltimore D: NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an
inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune
responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:12481–12486. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Perry MM, Moschos SA, Williams AE,
Shepherd NJ, Larner-Svensson HM and Lindsay MA: Rapid changes in
microRNA-146a expression negatively regulate the IL-1beta-induced
inflammatory response in human lung alveolar epithelial cells. J
Immunol. 180:5689–5698. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hou J, Wang P, Lin L, Liu X, Ma F, An H,
Wang Z and Cao X: MicroRNA-146a feedback inhibits RIG-I-dependent
type I IFN production in macrophages by targeting TRAF6, IRAK1 and
IRAK2. J Immunol. 183:2150–2158. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu W and Li Y: Lung injury caused by
paraquat poisoning results in increased interleukin-6 and decreased
microRNA-146a levels. Exp Ther Med. 16:406–412. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Peta E, Sinigaglia A, Masi G, Di Camillo
B, Grassi A, Trevisan M, Messa L, Loregian A, Manfrin E, Brunelli
M, et al: HPV16 E6 and E7 upregulate the histone lysine demethylase
KDM2B through the c-MYC/miR-146a-5p axys. Oncogene. 37:1654–1668.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cornett AL and Lutz CS: Regulation of
COX-2 expression by miR-146a in lung cancer cells. RNA.
20:1419–1430. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Iacona JR, Monteleone NJ and Lutz CS:
miR-146a suppresses 5-lipoxygenase activating protein (FLAP)
expression and Leukotriene B4 production in lung cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 9:26751–26769. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Batista PJ and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs: Cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell.
152:1298–1307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xi Y, Jiang T, Wang W, Yu J, Wang Y, Wu X
and He Y: Long non-coding HCG18 promotes intervertebral disc
degeneration by sponging miR-146a-5p and regulating TRAF6
expression. Sci Rep. 7:132342017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ding Y, Guo F, Zhu T, Li J, Gu D, Jiang W,
Lu Y and Zhou D: Mechanism of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 in
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury is mediated by the
miR-146a/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 41:446–454.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou YX, Zhao W, Mao LW, Wang YL, Xia LQ,
Cao M, Shen J and Chen J: Long non-coding RNA NIFK-AS1 inhibits M2
polarization of macrophages in endometrial cancer through targeting
miR-146a. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 104:25–33. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu C, Shi D, Li Z, Wan G and Shi X: Long
noncoding RNA CHRF exacerbates IL-6-induced inflammatory damages by
downregulating microRNA-146a in ATDC5 cells. J Cell Physiol.
234:21851–21859. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu HT, Fang L, Cheng YX and Sun Q: LncRNA
PVT1 regulates prostate cancer cell growth by inducing the
methylation of miR-146a. Cancer Med. 5:3512–3519. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kawai T and Akira S: The role of
pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on
Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol. 11:373–384. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shimazu R, Akashi S, Ogata H, Nagai Y,
Fukudome K, Miyake K and Kimoto M: MD-2, a molecule that confers
lipopolysaccharide responsiveness on Toll-like receptor 4. J Exp
Med. 189:1777–1782. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Meng J, Lien E and Golenbock DT:
MD-2-mediated ionic interactions between lipid A and TLR4 are
essential for receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 285:8695–8702.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guven-Maiorov E, Keskin O, Gursoy A,
VanWaes C, Chen Z, Tsai CJ and Nussinov R: The architecture of the
TIR domain signalosome in the toll-like receptor-4 signaling
pathway. Sci Rep. 5:131282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin SC, Lo YC and Wu H: Helical assembly
in the MyD88-IRAK4-IRAK2 complex in TLR/IL-1R signalling. Nature.
465:885–890. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cameron JE, Yin Q, Fewell C, Lacey M,
McBride J, Wang X, Lin Z, Schaefer BC and Flemington EK:
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 induces cellular
MicroRNA miR-146a, a modulator of lymphocyte signaling pathways. J
Virol. 82:1946–1958. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Iwami KI, Matsuguchi T, Masuda A, Kikuchi
T, Musikacharoen T and Yoshikai Y: Cutting edge: Naturally
occurring soluble form of mouse Toll-like receptor 4 inhibits
lipopolysaccharide signaling. J Immunol. 165:6682–6686. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao X, Huo R, Yan X and Xu T: IRF3
negatively regulates toll-like receptor-mediated NF-κB signaling by
targeting TRIF for degradation in teleost fish. Front Immunol.
9:8672018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schorle H, Holtschke T, Hünig T, Schimpl A
and Horak I: Development and function of T cells in mice rendered
interleukin-2 deficient by gene targeting. Nature. 352:621–624.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Curtale G, Citarella F, Carissimi C,
Goldoni M, Carucci N, Fulci V, Franceschini D, Meloni F, Barnaba V
and Macino G: An emerging player in the adaptive immune response:
microRNA-146a is a modulator of IL-2 expression and
activation-induced cell death in T lymphocytes. Blood. 115:265–273.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang L, Boldin MP, Yu Y, Liu CS, Ea CK,
Ramakrishnan P, Taganov KD, Zhao JL and Baltimore D: miR-146a
controls the resolution of T cell responses in mice. J Exp Med.
209:1655–1670. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhou L, Chong MM and Littman DR:
Plasticity of CD4+ T cell lineage differentiation.
Immunity. 30:646–655. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Murphy KM and Stockinger B: Effector T
cell plasticity: Flexibility in the face of changing circumstances.
Nat Immunol. 11:674–680. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Korn T, Bettelli E, Oukka M and Kuchroo
VK: IL-17 and Th17 cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 27:485–517. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lu LF, Boldin MP, Chaudhry A, Lin LL,
Taganov KD, Hanada T, Yoshimura A, Baltimore D and Rudensky AY:
Function of miR-146a in controlling Treg cell-mediated regulation
of Th1 responses. Cell. 142:914–929. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Luo X, Han M, Liu J, Wang Y, Luo X, Zheng
J, Wang S, Liu Z, Liu D, Yang PC and Li H: Epithelial cell-derived
micro RNA-146a generates interleukin-10-producing monocytes to
inhibit nasal allergy. Sci Rep. 5:159372015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Okoye IS, Czieso S, Ktistaki E, Roderick
K, Coomes SM, Pelly VS, Kannan Y, Perez-Lloret J, Zhao JL,
Baltimore D, et al: Transcriptomics identified a critical role for
Th2 cell-intrinsic miR-155 in mediating allergy and antihelminth
immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:E3081–E3090. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hou T, Liao J, Zhang C, Sun C, Li X and
Wang G: Elevated expression of miR-146, miR-139 and miR-340
involved in regulating Th1/Th2 balance with acute exposure of fine
particulate matter in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 54:68–77. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li B, Wang X, Choi IY, Wang YC, Liu S,
Pham AT, Moon H, Smith DJ, Rao DS, Boldin MP and Yang L: miR-146a
modulates autoreactive Th17 cell differentiation and regulates
organ-specific autoimmunity. J Clin Invest. 127:3702–3716. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pratama A, Srivastava M, Williams NJ, Papa
I, Lee SK, Dinh XT, Hutloff A, Jordan MA, Zhao JL, Casellas R, et
al: MicroRNA-146a regulates ICOS-ICOSL signalling to limit
accumulation of T follicular helper cells and germinal centres. Nat
Commun. 6:64362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Boldin MP, Taganov KD, Rao DS, Yang L,
Zhao JL, Kalwani M, Garcia-Flores Y, Luong M, Devrekanli A, Xu J,
et al: miR-146a is a significant brake on autoimmunity,
myeloproliferation and cancer in mice. J Exp Med. 208:1189–1201.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cho S, Lee HM, Yu IS, Choi YS, Huang HY,
Hashemifar SS, Lin LL, Chen MC, Afanasiev ND, Khan AA, et al:
Differential cell-intrinsic regulations of germinal center B and T
cells by miR-146a and miR-146b. Nat Commun. 9:27572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Guo Q, Zhang J, Li J, Zou L, Zhang J, Xie
Z, Fu X, Jiang S, Chen G, Jia Q, et al: Forced miR-146a expression
causes autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome in mice via
downregulation of Fas in germinal center B cells. Blood.
121:4875–4883. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li Z, Zhang S, Wan Y, Cai M, Wang W, Zhu
Y, Li Z, Hu Y, Wang H, Chen H, et al: MicroRNA-146a overexpression
impairs the positive selection during T cell development. Front
Immunol. 8:20062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
King JK, Ung NM, Paing MH, Contreras JR,
Alberti MO, Fernando TR, Zhang K, Pellegrini M and Rao DS:
Regulation of marginal Zone B-cell differentiation by
MicroRNA-146a. Front Immunol. 7:6702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mao B and Wang G: MicroRNAs involved with
hepatocellular carcinoma (Review). Oncol Rep. 34:2811–2820. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li JF, Dai XP, Zhang W, Sun SH, Zeng Y,
Zhao GY, Kou ZH, Guo Y, Yu H, Du LY, et al: Upregulation of
microRNA-146a by hepatitis B virus X protein contributes to
hepatitis development by downregulating complement factor H. MBio.
6:e02459–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bandiera S, Pernot S, El Saghire H, Durand
SC, Thumann C, Crouchet E, Ye T, Fofana I, Oudot MA, Barths J, et
al: Hepatitis C virus-induced upregulation of MicroRNA miR-146a-5p
in hepatocytes promotes viral infection and deregulates metabolic
pathways associated with liver disease pathogenesis. J Virol.
90:6387–6400. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Visalli M, Bartolotta M, Polito F, Oteri
R, Barbera A, Arrigo R, Di Giorgio RM, Navarra G and Aguennouz M:
miRNA expression profiling regulates necroptotic cell death in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 53:771–780. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Xu D, Han Q, Hou Z, Zhang C and Zhang J:
miR-146a negatively regulates NK cell functions via STAT1
signaling. Cell Mol Immunol. 14:712–720. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang S, Zhang X, Ju Y, Zhao B, Yan X, Hu
J, Shi L, Yang L, Ma Z, Chen L, et al: MicroRNA-146a feedback
suppresses T cell immune function by targeting Stat1 in patients
with chronic hepatitis B. J Immunol. 191:293–301. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Fattovich G, Stroffolini T, Zagni I and
Donato F: Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: Incidence and risk
factors. Gastroenterology. 127 (5 Suppl 1):S35–S50. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Qian H, Deng X, Huang ZW, Wei J, Ding CH,
Feng RX, Zeng X, Chen YX, Ding J, Qiu L, et al: An HNF1α-regulated
feedback circuit modulates hepatic fibrogenesis via the crosstalk
between hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells. Cell Res.
25:930–945. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Weiskirchen R and Tacke F: Cellular and
molecular functions of hepatic stellate cells in inflammatory
responses and liver immunology. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 3:344–363.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chen Y, Wu Z, Yuan B, Dong Y, Zhang L and
Zeng Z: MicroRNA-146a-5p attenuates irradiation-induced and
LPS-induced hepatic stellate cell activation and hepatocyte
apoptosis through inhibition of TLR4 pathway. Cell Death Dis.
9:222018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lin A, Wang G, Zhao H, Zhang Y, Han Q,
Zhang C, Tian Z and Zhang J: TLR4 signaling promotes a
COX-2/PGE2/STAT3 positive feedback loop in
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. Oncoimmunology.
5:e10743762015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Sun X, Zhang J, Hou Z, Han Q, Zhang C and
Tian Z: miR-146a is directly regulated by STAT3 in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells and involved in anti-tumor immune
suppression. Cell Cycle. 14:243–252. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhu K, Pan Q, Zhang X, Kong LQ, Fan J, Dai
Z, Wang L, Yang XR, Hu J, Wan JL, et al: miR-146a enhances
angiogenic activity of endothelial cells in hepatocellular
carcinoma by promoting PDGFRA expression. Carcinogenesis.
34:2071–2079. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Sun XX, Ma X and Chen
ZN: microRNA-146a inhibits cancer metastasis by downregulating VEGF
through dual pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer.
14:52015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhou L, Zhao X, Han Y, Lu Y, Shang Y, Liu
C, Li T, Jin Z, Fan D and Wu K: Regulation of UHRF1 by miR-146a/b
modulates gastric cancer invasion and metastasis. FASEB J.
27:4929–4239. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Xu T, Zhu Y, Wei QK, Yuan Y, Zhou F, Ge
YY, Yang JR, Su H and Zhuang SM: A functional polymorphism in the
miR-146a gene is associated with the risk for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 29:2126–2131. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Peng Q, Li S, Lao X, Chen Z, Li R, Deng Y
and Qin X: The association of common functional polymorphisms in
mir-146a and mir-196a2 and hepatocellular carcinoma risk: Evidence
from a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 93:e2522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Tian T, Wang M, Zhu W, Dai ZM, Lin S, Yang
PT, Liu XH, Liu K, Zhu YY, Zheng Y, et al: miR-146a and miR-196a-2
polymorphisms are associated with hepatitis virus-related
hepatocellular cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Aging (Albany NY).
9:381–392. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Dong S, Miao AY, Lei W and Chen QW:
miR-146a rs2910164 and hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis.
Minerva Med. 108:287–292. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Jazdzewski K, Murray EL, Franssila K,
Jarzab B, Schoenberg DR and de la Chapelle A: Common SNP in
pre-miR-146a decreases mature miR expression and predisposes to
papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:7269–7274.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Moreno R and Berenguer M: Post-liver
transplantation medical complications. Ann Hepatol. 5:77–85. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Hu J, Wang Z, Tan CJ, Liao BY, Zhang X, Xu
M, Dai Z, Qiu SJ, Huang XW, Sun J, et al: Plasma microRNA, a
potential biomarker for acute rejection after liver
transplantation. Transplantation. 95:991–999. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zhuo L, Liu J, Wang B, Gao M and Huang A:
Differential miRNA expression profiles in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells and drug-resistant sublines. Oncol Rep. 29:555–562. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|