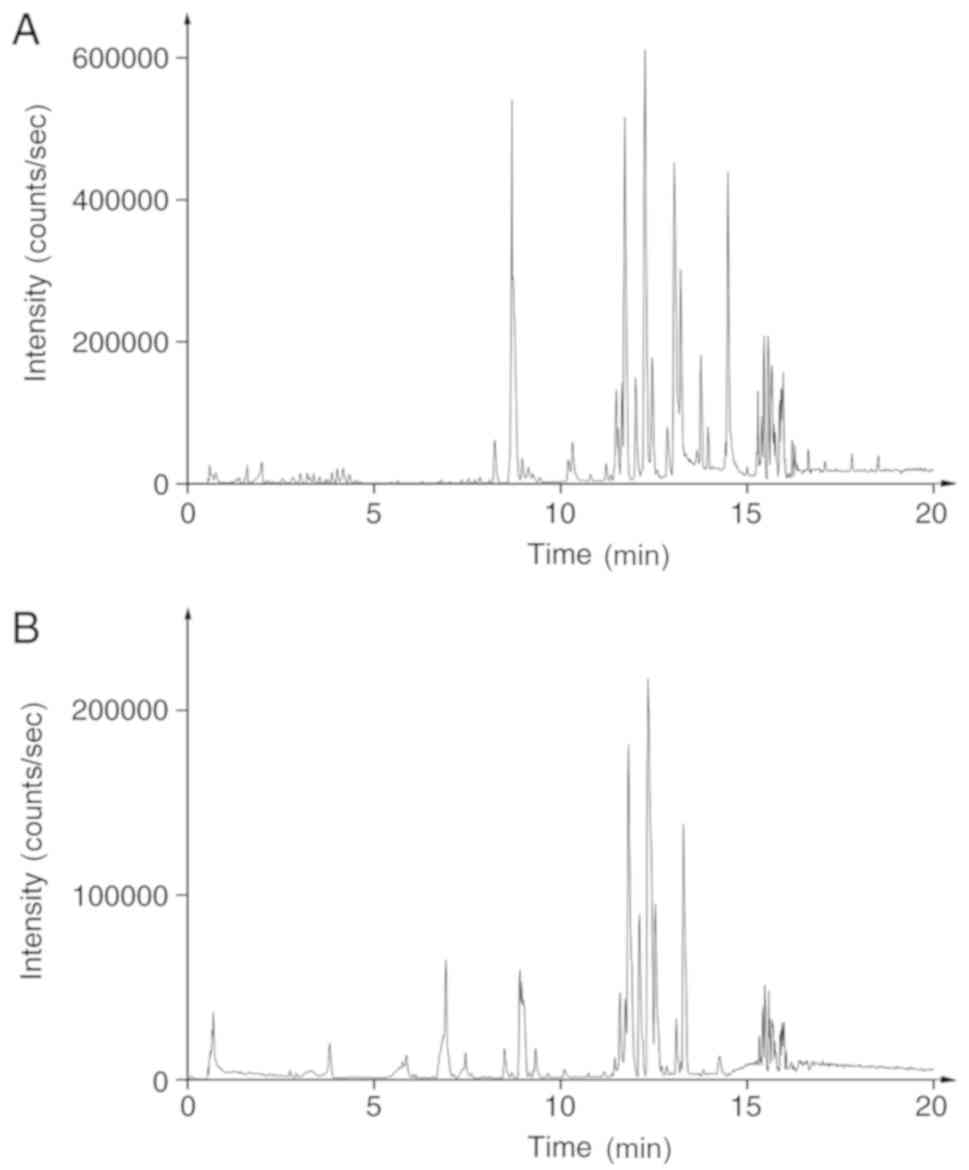
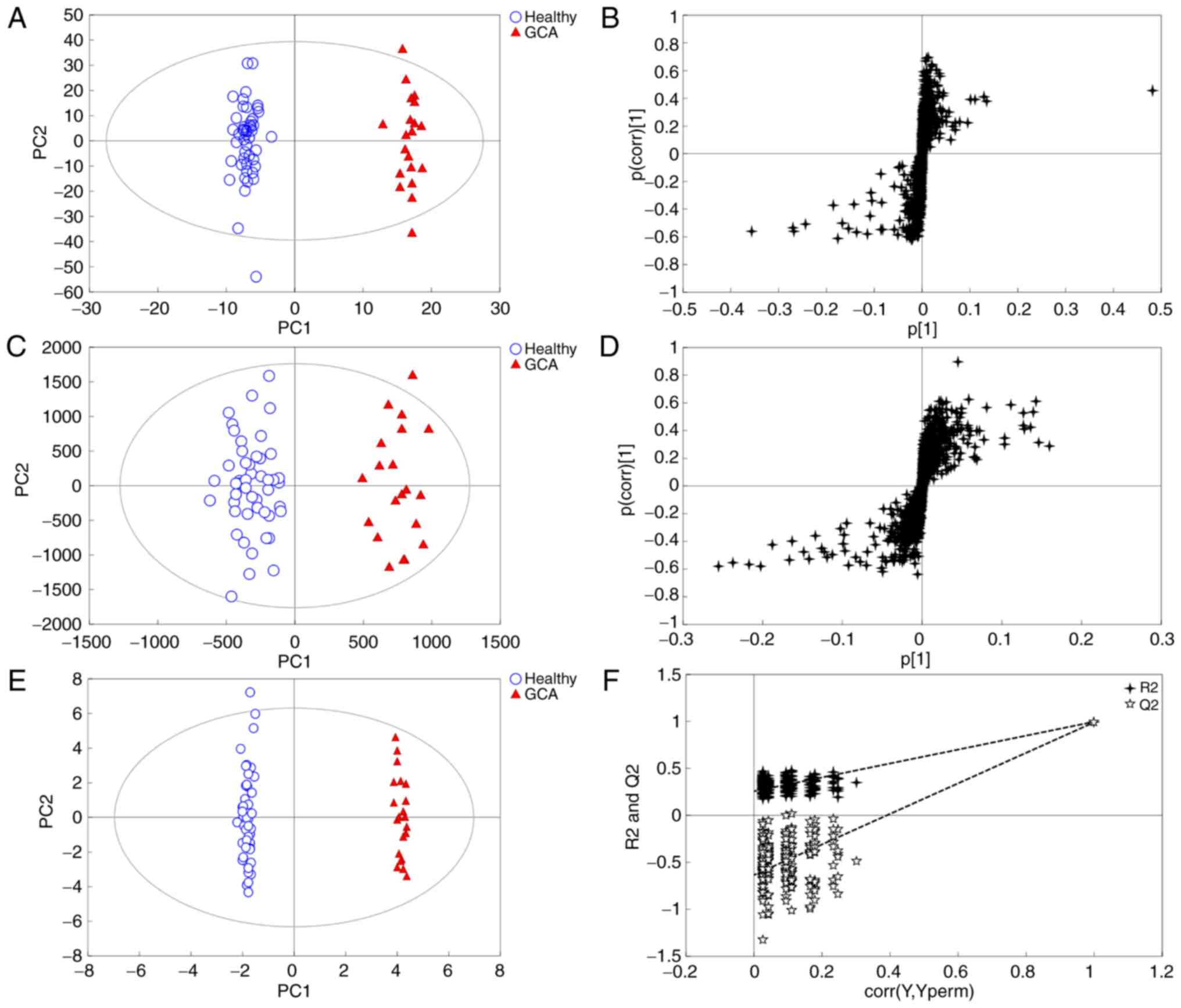
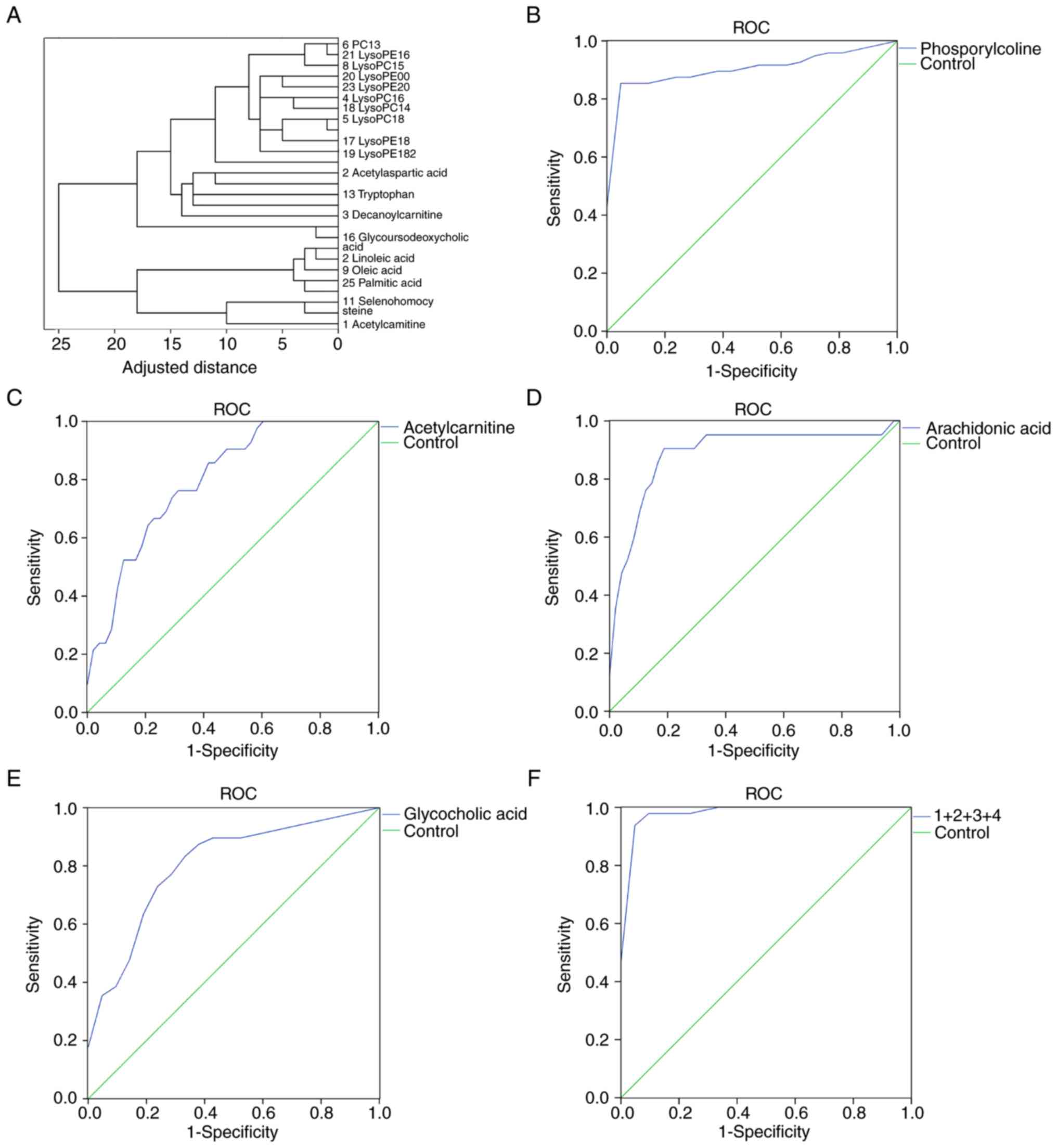
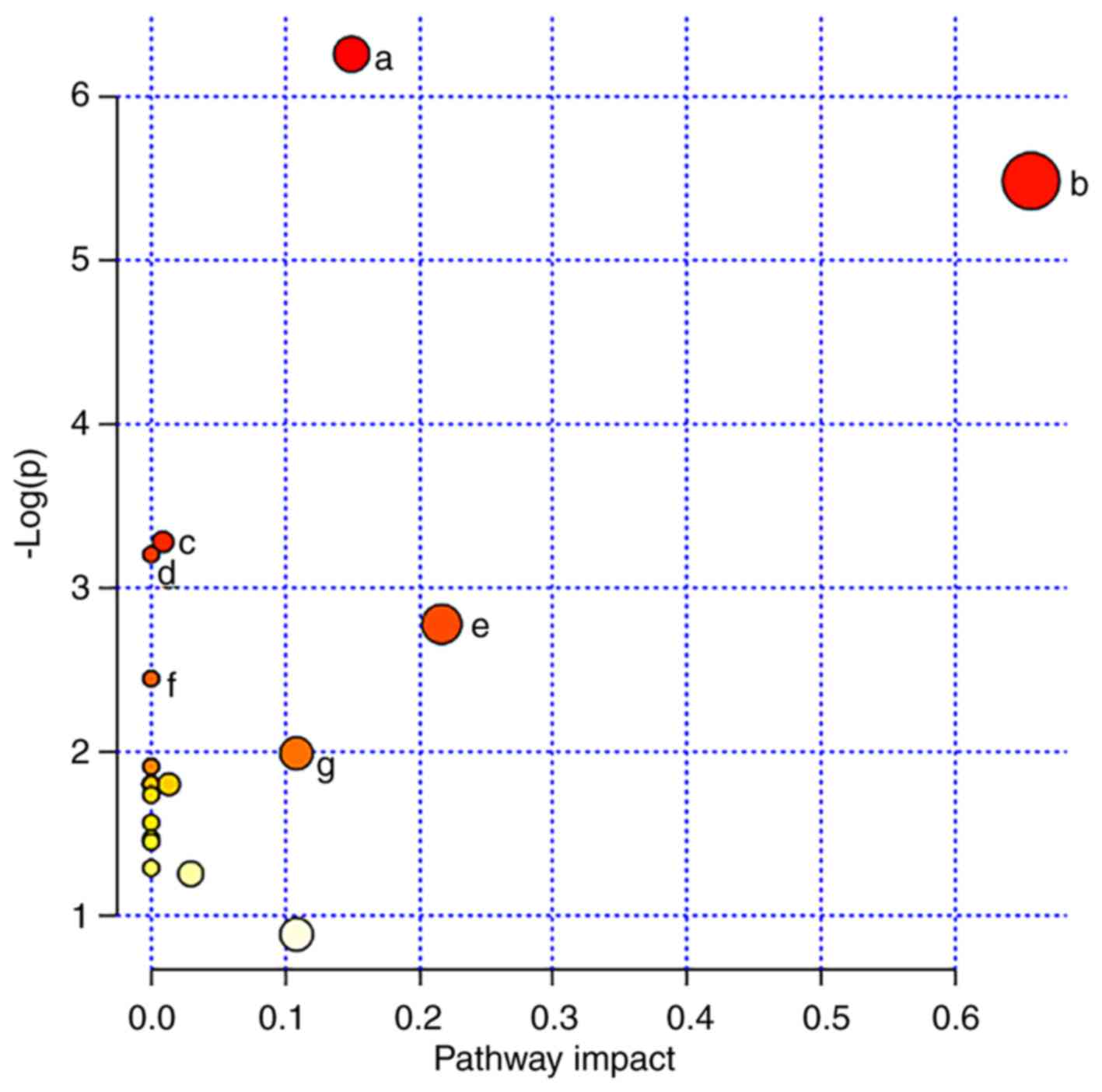
|
1
|
Colquhoun A, Arnold M, Ferlay J, Goodman
KJ, Forman D and Soerjomataram I: Global patterns of cardia and
non-cardia gastric cancer incidence in 2012. Gut. 64:1881–1888.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang LD, Zheng S, Zheng ZY and Casson AG:
Primary adenocarcinomas of lower esophagus, esophagogastric
junction and gastric cardia: In special reference to China. World J
Gastroenterol. 9:1156–1164. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang Q, Li R, Xu GF, Zhou D, Fan XS and
Zou XP: Emerging evidence supports grouping by location of early
gastric carcinoma for appropriate clinical management in Chinese
patients. J Dig Dis. 19:730–736. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Abdi E, Latifi-Navid S, Zahri S, Yazdanbod
A and Pourfarzi F: Risk factors predisposing to cardia gastric
adenocarcinoma: Insights and new perspectives. Cancer Med.
8:6114–6126. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ze-Long Y, Guo-Hui M, Lin Z, Wei-Hong Y,
Ke-Cheng Z and Yan-Wen J: Survival trends of patients with
surgically resected gastric cardia cancer from 1988 to 2015 a
population-based study in the United States. Am J Clin Oncol.
42:581–587. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kutup A, Yekebas EF and Izbicki JR:
Current diagnosis and future impact of micrometastases for
therapeutic strategies in adenocarcinoma of the esophagus, gastric
cardia, and upper gastric third. Recent Results Cancer Res.
182:115–125. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
An JY, Baik YH, Choi MG, Noh JH, Sohn TS,
Bae JM and Kim S: The prognosis of gastric cardia cancer after R0
resection. Am J Surg. 199:725–729. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nishimata H, Maruyama M, Shimaoka S,
Nishimata Y, Ohi H, Niihara T, Nioh T, Matsuda A, Tashiro K and
Torimaru H: Early gastric carcinomas in the cardiac region:
Diagnosis with double-contrast x-ray studies. Abdom Imaging.
28:486–491. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Togo R, Yamamichi N, Mabe K, Takahashi Y,
Takeuchi C, Kato M, Sakamoto N, Ishihara K, Ogawa T and Haseyama M:
Detection of gastritis by a deep convolutional neural network from
double-contrast upper gastrointestinal barium X-ray radiography. J
Gastroenterol. 54:321–329. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Carandang N, Schuman BM and Priest RJ: The
gastrocamera in the diagnosis of stomach disease. JAMA.
204:717–722. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fujiyoshi T, Miyahara R, Funasaka K,
Furukawa K, Sawada T, Maeda K, Yamamura T, Ishikawa T, Ohno E,
Nakamura M, et al: Utility of linked color imaging for endoscopic
diagnosis of early gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol.
25:1248–1258. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shen L, Zhou C, Liu L, Zhang L, Lu D, Cai
J, Zhao L, Chu R, Zhou J and Zhang J: Application of oral contrast
trans-abdominal ultrasonography for initial screening of gastric
cancer in rural areas of China. Dig Liver Dis. 49:918–923. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dai CL, Yang ZG, Xue LP and Li YM:
Application value of multi-slice spiral computed tomography for
imaging determination of metastatic lymph nodes of gastric cancer.
World J Gastroenterol. 19:5732–5737. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang M, Wang X, Shan X, Pan D, Jia Y, Ni
E, Hu Y and Huang H: Value of multi-slice spiral computed
tomography in the diagnosis of metastatic lymph nodes and N-stage
of gastric cancer. J Int Med Res. 47:281–292. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chan AW, Mercier P, Schiller D, Bailey R,
Robbins S, Eurich DT, Sawyer MB and Broadhurst D: (1)H-NMR urinary
metabolomic profiling for diagnosis of gastric cancer. Br J Cancer.
114:59–62. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tatsubayashi T, Tanizawa Y, Miki Y,
Tokunaga M, Bando E, Kawamura T, Sugiura T, Kinugasa Y, Uesaka K
and Terashima M: Treatment outcomes of hepatectomy for liver
metastases of gastric cancer diagnosed using contrast-enhanced
magnetic resonance imaging. Gastric Cancer. 20:387–393. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Van Vliet EP, Hermans JJ, De Wever W,
Eijkemans MJ, Steyerberg EW, Faasse C, van Helmond EP, de Leeuw AM,
Sikkenk AC, de Vries AR, et al: Radiologist experience and CT
examination quality determine metastasis detection in patients with
esophageal or gastric cardia cancer. Eur Radiol. 18:2475–2484.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li L, Pang X, Zhu Z, Lu L, Yang J, Cao J
and Fei S: GTPBP4 promotes gastric cancer progression via
regulating P53 activity. Cell Physiol Biochem. 45:667–676. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou F, Xu Y, Shi J, Lan X, Zou X, Wang L
and Huang Q: Expression profile of E-cadherin, estrogen receptors,
and P53 in early-onset gastric cancers. Cancer Med. 5:3403–3411.
2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yin J, Pan H, Long T, Lv L, Zhai P, Liu C,
Shao A, Shi Y, Sun Y, Zhu J, et al: Polymorphisms of VDR gene and
risk of gastric cardiac adenocarcinoma in Chinese population.
Oncotarget. 8:45531–45543. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou RM, Wang N, Chen ZF, Duan YN, Sun DL
and Li Y: Polymorphisms in promoter region of FAS and FASL gene and
risk of cardia gastric adenocarcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
25:555–561. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang J, Cui Y, Kuang G, Li Y, Wang N,
Wang R, Guo W, Wen D, Wei L, Yu F and Wang S: Association of the
thymidylate synthase polymorphisms with esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma and gastric cardiac adenocarcinoma. Carcinogenesis.
25:2479–2485. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Luo T, Chen W, Wang L and Zhao H: CA125 is
a potential biomarker to predict surgically incurable gastric and
cardia cancer: A retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore).
95:e52972016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Williams GH, Swinn R, Prevost AT, de
Clive-Lowe P, Halsall I, Going JJ, Hales CN, Stoeber K and
Middleton SJ: Diagnosis of oesophageal cancer by detection of
minichromosome maintenance 5 protein in gastric aspirates. Br J
Cancer. 91:714–719. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu M, Li JS, Tian DP, Huang B, Rosqvist S
and Su M: MCM2 expression levels predict diagnosis and prognosis in
gastric cardiac cancer. Histol Histopathol. 28:481–492.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cheng Y, Zhang J, Li Y, Wang Y and Gong J:
Proteome analysis of human gastric cardia adenocarcinoma by laser
capture microdissection. BMC Cancer. 7:1912007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu HN, Liu TT, Wu H, Chen YJ, Tseng YJ,
Yao C, Weng SQ, Dong L and Shen XZ: Serum microRNA signatures and
metabolomics have high diagnostic value in colorectal cancer using
two novel methods. Cancer Sci. 109:1185–1194. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang A, Sun H, Yan G, Wang P, Han Y and
Wang X: Metabolomics in diagnosis and biomarker discovery of
colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 345:17–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang X, Zhang A and Sun H: Power of
metabolomics in diagnosis and biomarker discovery of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 57:2072–2077. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kobayashi T, Nishiumi S, Ikeda A, Yoshie
T, Sakai A, Matsubara A, Izumi Y, Tsumura H, Tsuda M, Nishisaki H,
et al: A novel serum metabolomics-based diagnostic approach to
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 22:571–579.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang G, He P, Tan H, Budhu A, Gaedcke J,
Ghadimi BM, Ried T, Yfantis HG, Lee DH, Maitra A, et al:
Integration of metabolomics and transcriptomics revealed a fatty
acid network exerting growth inhibitory effects in human pancreatic
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 19:4983–4993. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Abbassi-Ghadi N, Kumar S, Huang J, Goldin
R, Takats Z and Hanna GB: Metabolomic profiling of
oesophago-gastric cancer: A systematic review. Eur J Cancer.
49:3625–3637. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang X, Yan SK, Dai WX, Liu XR, Zhang WD
and Wang JJ: A metabonomic approach to chemosensitivity prediction
of cisplatin plus 5-fluorouracil in a human xenograft model of
gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 127:2841–2850. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cai Z, Zhao JS, Li JJ, Peng DN, Wang XY,
Chen TL, Qiu YP, Chen PP, Li WJ, Xu LY, et al: A combined
proteomics and metabolomics profiling of gastric cardia cancer
reveals characteristic dysregulations in glucose metabolism. Mol
Cell Proteomics. 9:2617–2628. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhen C: Glucose metabolic pathway in
gastric cardia cancer and the role of microcilia in tumorogenesis
[Chinese]. Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences; 2011
|
|
36
|
Patriarca S, Ferretti S and Zanetti R: TNM
Classification of malignant tumours-Eighth edition: Which news?
Epidemiol Prev. 41:140–143. 2017.(In Italian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chong J, Soufan O, Li C, Caraus I, Li S,
Bourque G, Wishart DS and Xia J: MetaboAnalyst 4.0: towards more
transparent and integrative metabolomics analysis. Nucleic Acids
Res. 46:W486–W494. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Amini N, Spolverato G, Kim Y, Squires MH,
Poultsides GA, Fields R, Schmidt C, Weber SM, Votanopoulos K,
Maithel SK and Pawlik TM: Clinicopathological features and
prognosis of gastric cardia adenocarcinoma: A multi-institutional
US study. J Surg Oncol. 111:285–292. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang J, Zhang H, Zhou X, Wang T, Zhang J,
Zhu W, Zhu H and Cheng W: Five serum-based miRNAs were identified
as potential diagnostic biomarkers in gastric cardia
adenocarcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 23:193–203. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
von Glutz G and Walter P: Compartmentation
of acetyl-coA in rat-liver mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 60:147–152.
1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Svensson RU, Parker SJ, Eichner LJ, Kolar
MJ, Wallace M, Brun SN, Lombardo PS, Van Nostrand JL, Hutchins A,
Vera L, et al: Inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase suppresses
fatty acid synthesis and tumor growth of non-small-cell lung cancer
in preclinical models. Nat Med. 22:1108–1119. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Scholz R, Olson MS, Schwab AJ, Schwabe U,
Noell C and Braun W: The effect of fatty acids on the regulation of
pyruvate dehydrogenase in perfused rat liver. Eur J Biochem.
86:519–530. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ke J, Behal RH, Back SL, Nikolau BJ,
Wurtele ES and Oliver DJ: The role of pyruvate dehydrogenase and
acetyl-coenzyme A synthetase in fatty acid synthesis in developing
arabidopsis seeds. Plant Physiol. 123:497–508. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lucenteforte E, Bosetti C, Gallus S,
Bertuccio P, Pelucchi C, Tavani A, La Vecchia C and Negri E:
Macronutrients, fatty acids and cholesterol intake and stomach
cancer risk. Ann Oncol. 20:1434–1438. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wen YA, Xing XP, Harris JW, Zaytseva YY,
Mitov MI, Napier DL, Weiss HL, Mark Evers B and Gao T: Adipocytes
activate mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and autophagy to
promote tumor growth in colon cancer. Cell Death Dis. 8:e25932017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Caligiuri G, Khallou-Laschet J, Vandaele
M, Gaston AT, Delignat S, Mandet C, Kohler HV, Kaveri SV and
Nicoletti A: Phosphorylcholine-targeting immunization reduces
atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 50:540–546. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Claflin JL, Lieberman R and Davie JM:
Clonal nature of the immune response to phosphorylcholine. I.
Specificity, class, and idiotype of phosphorylcholine-binding
receptors on lymphoid cells. J Exp Med. 139:58–73. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sigal NH, Pickard AR, Metcalf ES, Gearhart
PJ and Klinman NR: Expression of phosphorylcholine-specific B cells
during murine development. J Exp Med. 146:933–948. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Feldman DA, Rounsifer ME and Weinhold PA:
The stimulation and binding of CTP: Phosphorylcholine
cytidylyltransferase by phosphatidylcholine-oleic acid vesicles.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 833:429–437. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Gasull T, Sarri E, DeGregorio-Rocasolano N
and Trullas R: NMDA receptor overactivation inhibits phospholipid
synthesis by decreasing choline-ethanolamine phosphotransferase
activity. J Neurosci. 23:4100–4107. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mori N, Wildes F, Kakkad S, Jacob D,
Solaiyappan M, Glunde K and Bhujwalla ZM: Choline kinase-alpha
protein and phosphatidylcholine but not phosphocholine are required
for breast cancer cell survival. NMR Biomed. 28:1697–1706. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang H, Song H, Yuan R, Zhang X, Yu H,
Zhao Y and Jiang T: Polyene phosphatidylcholine overcomes
oxaliplatin resistance in human gastric cancer BGC823 cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 497:108–114. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Bereziat G, Chambaz J, Trugnan G, Pepin D
and Polonovski J: Turnover of phospholipid linoleic and arachidonic
acids in human platelets from plasma lecithins. J Lipid Res.
19:495–500. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang D and Dubois RN: Eicosanoids and
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:181–193. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Nieves D and Moreno JJ: Effect of
arachidonic and eicosapentaenoic acid metabolism on RAW 264.7
macrophage proliferation. J Cell Physiol. 208:428–434. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yarla NS, Bishayee A, Sethi G, Reddanna P,
Kalle AM, Dhananjaya BL, Dowluru KS, Chintala R and Duddukuri GR:
Targeting arachidonic acid pathway by natural products for cancer
prevention and therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 40-41:48–81. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Poligone B and Baldwin AS: Positive and
negative regulation of NF-kappaB by COX-2: roles of different
prostaglandins. J Biol Chem. 276:38658–38664. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Bortuzzo C, Hanif R, Kashfi K,
Staiano-Coico L, Shiff SJ and Rigas B: The effect of leukotrienes B
and selected HETEs on the proliferation of colon cancer cells.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1300:240–246. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yu L, Wu WK, Li ZJ, Li HT, Wu YC and Cho
CH: Prostaglandin E-2 promotes cell proliferation via protein
kinase C/extracellular signal regulated kinase pathway-dependent
induction of c-Myc expression in human esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 125:2540–2546. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ul Islam S, Shehzad A and Lee YS:
Prostaglandin E-2 inhibits resveratrol-induced apoptosis through
activation of survival signaling pathways in HCT-15 cell lines.
Anim Cells Syst. 19:374–384. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Kauer WK, Peters JH, DeMeester TR,
Feussner H, Ireland AP, Stein HJ and Siewert RJ: Composition and
concentration of bile acid reflux into the esophagus of patients
with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surgery. 122:874–881. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Fitzgerald RC, Abdalla S, Onwuegbusi BA,
Sirieix P, Saeed IT, Burnham WR and Farthing MJ: Inflammatory
gradient in Barrett's oesophagus: Implications for disease
complications. Gut. 51:316–322. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Tatsugami M, Ito M, Tanaka S, Yoshihara M,
Matsui H, Haruma K and Chayama K: Bile acid promotes intestinal
metaplasia and gastric carcinogenesis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 21:2101–2107. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Messner CJ, Mauch L and Suter-Dick L: Bile
salts regulate CYP7A1 expression and elicit a fibrotic response and
abnormal lipid production in 3D liver microtissues. Toxicol In
Vitro. 60:261–271. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Heubi JE, Setchell KD, Jha P, Buckley D,
Zhang WJ, Rosenthal P, Potter C, Horslen S and Suskind D: Treatment
of bile acid amidation defects with glycocholic acid. Hepatology.
61:268–274. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Abreu MT and Peek RM Jr: Gastrointestinal
malignancy and the microbiome. Gastroenterology. 146:1534–1166.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hu H, Krasinskas A and Willis J:
Perspectives on current tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) staging of
cancers of the colon and rectum. Semin Oncol. 38:500–510. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|