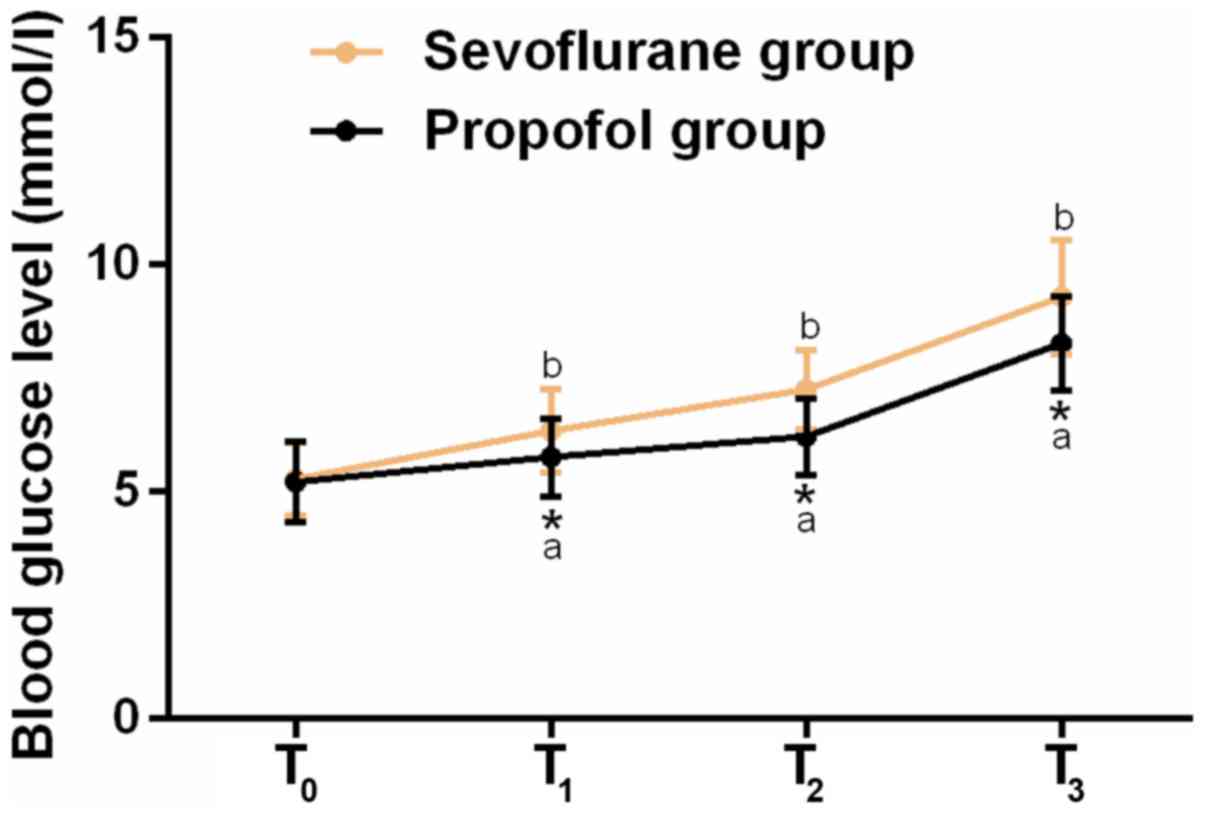
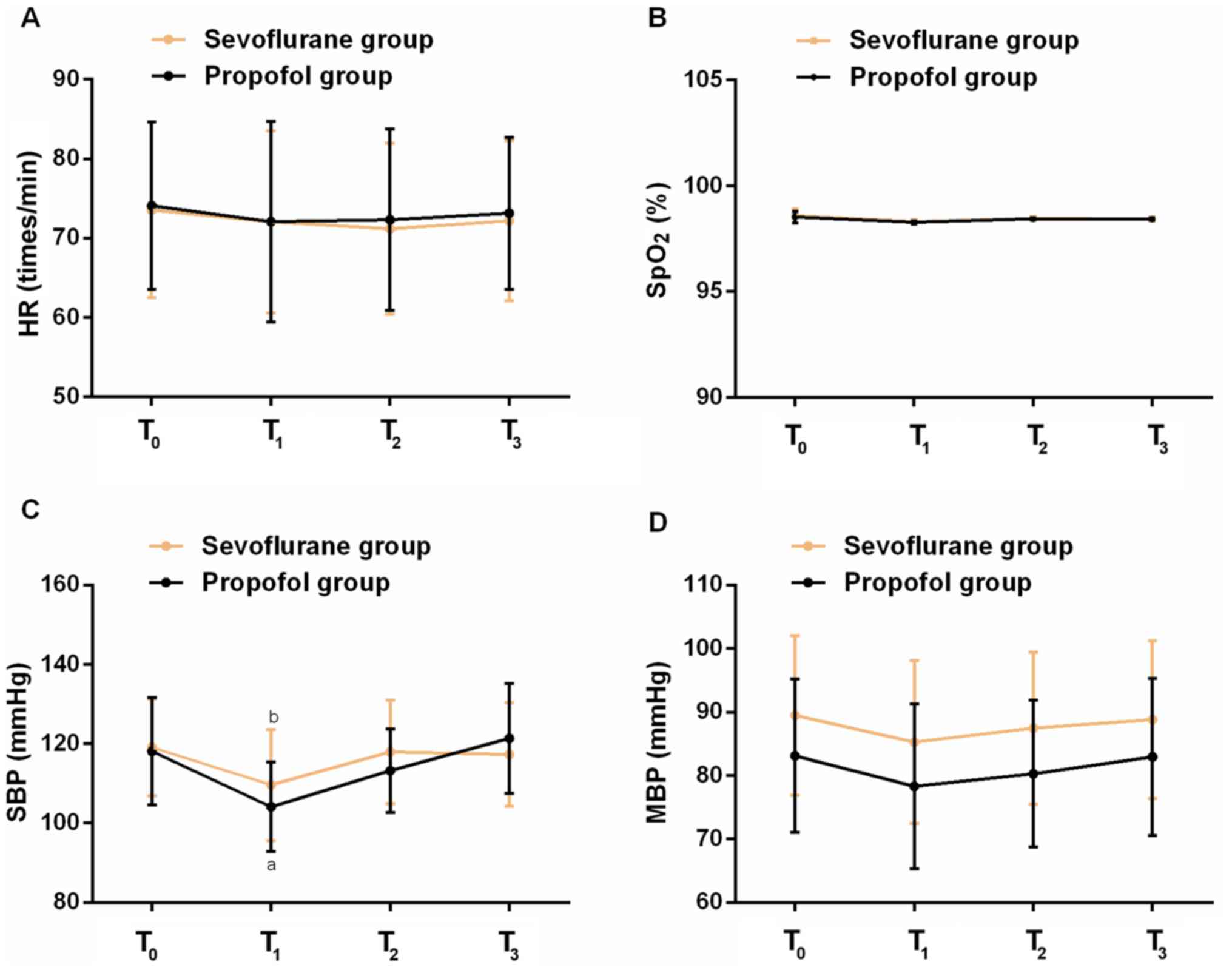
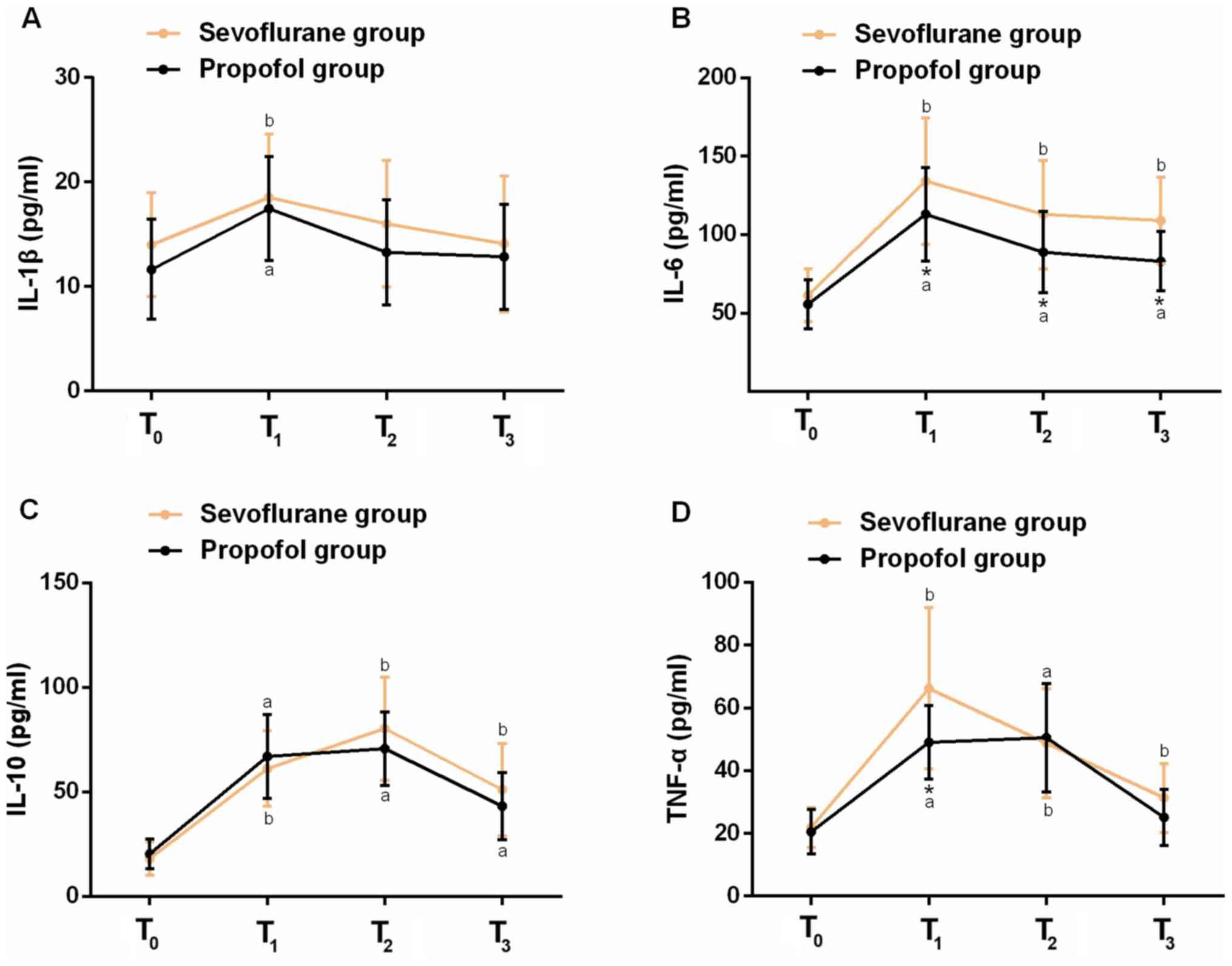
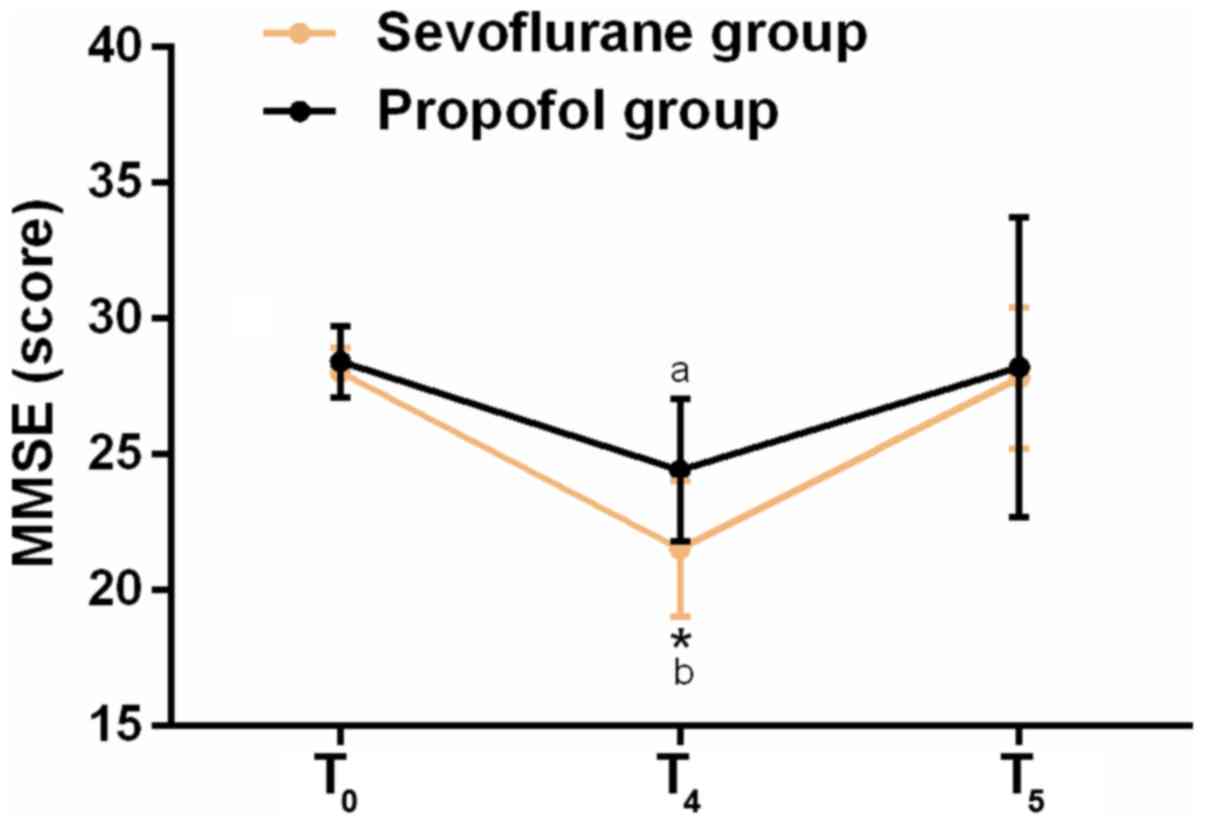
|
1
|
Venerito M, Link A, Rokkas T and
Malfertheiner P: Gastric cancer-clinical aspects (Review).
Helicobacter. 24 (Suppl 1):e126432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sah BR, Owczarczyk K, Siddique M, Cook GJR
and Goh V: Radiomics in esophageal and gastric cancer. Abdom Radiol
(NY). 44:2048–2058. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang SL, Zhuang CL, Huang DD, Pang WY, Lou
N, Chen FF, Zhou CJ, Shen X and Yu Z: Sarcopenia adversely impacts
postoperative clinical outcomes following gastrectomy in patients
with gastric cancer: A prospective study. Ann Surg Oncol.
23:556–564. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Baglia ML, Cui Y, Zheng T, Yang G, Li H,
You M, Xu L, Murff H, Gao YT, Zheng W, et al: Diabetes medication
use in association with survival among patients of breast,
colorectal, lung, or gastric cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 51:538–546.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim JH, Huh YJ, Park S, Park YS, Park DJ,
Kwon JW, Lee JH, Heo Y and Choi SH: Multicenter results of
long-limb bypass reconstruction after gastrectomy in patients with
gastric cancer and type II diabetes. Asian J Surg. May
3–2019.(E-pub ahead of print).
doi.org/10.1016/j.asjsur.2019.03.018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Tseng CH and Tseng FH: Diabetes and
gastric cancer: The potential links. World J Gastroenterol.
20:1701–1711. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Charalampakis N, Economopoulou P,
Kotsantis I, Tolia M, Schizas D, Liakakos T, Elimova E, Ajani JA
and Psyrri A: Medical management of gastric cancer: A 2017 update.
Cancer Med. 7:123–133. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tuttnauer A and Levin PD: Diabetes
mellitus and anesthesia. Anesthesiol Clin. 24:579–597. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qiu Q, Choi SW, Wong SS, Irwin MG and
Cheung CW: Effects of intra-operative maintenance of general
anaesthesia with propofol on postoperative pain outcomes - a
systematic review and meta-analysis. Anaesthesia. 71:1222–1233.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chidambaran V, Costandi A and D'Mello A:
Propofol: A review of its role in pediatric anesthesia and
sedation. CNS Drugs. 29:543–563. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fan W, Zhu X, Wu L, Wu Z, Li D, Huang F
and He H: Propofol: An anesthetic possessing neuroprotective
effects. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 19:1520–1529. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
De Hert S and Moerman A: Sevoflurane.
F1000 Res. 4:(F1000 Faculty Rev). 6262015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kanazawa S, Oda Y, Maeda C and Okutani R:
Electroencephalo-graphic effect of age-adjusted 1 MAC desflurane
and sevoflurane in young, middle-aged, and elderly patients. J
Anesth. 31:744–750. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu Z, Yu J, Wu J, Qi F, Wang H and Wang Z
and Wang Z: The effects of two anesthetics, propofol and
sevoflurane, on liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 38:1631–1642. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zheng X, Wang Y, Dong L, Zhao S, Wang L,
Chen H, Xu Y and Wang G: Effects of propofol-based total
intravenous anesthesia on gastric cancer: A retrospective study.
OncoTargets Ther. 11:1141–1148. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Baynes HW: Classification,
pathophysiology, diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus. J
Diabetes Metab. 6:1–9. 2015.
|
|
17
|
Smyth EC, Verheij M, Allum W, Cunningham
D, Cervantes A and Arnold D; ESMO Guidelines Committee, : Gastric
cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment
and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 27 (Suppl 5):V38–V49. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Doyle DJ and Garmon EH: American Society
of Anesthesiologists Classification (ASA Class) [Updated 2019 May
13]. StatPearls [Internet] Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls
Publishing; 2019
|
|
19
|
Mitchell AJ: The Mini-Mental State
Examination (MMSE): Update on its diagnostic accuracy and clinical
utility for cognitive disorders. Cognitive Screening Instruments.
Larner AJ: 2nd. Springer International Publishing; Switzerland: pp.
37–48. 2017, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kitamura T, Kawamura G and Ogawa Mand
Yamada Y: Comparison of the changes in blood glucose levels during
anesthetic management using sevoflurane and propofol. Masui.
58:81–84. 2009.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Khare A, Mathur V, Jain K, Sethi S, Garg D
and Vishnoi R: A prospective randomized study for comparison of
haemodynamic changes and recovery characteristics with propofol and
sevoflurane anaesthesia during laparoscopic cholecystectomies. Int
J Res Med Sci. 4:5241–5247. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Shen Q, Peng J, Shi Y and Yang LL: Effects
of remifentanil combined with propofol anesthesia on IL-1β, IL-6,
TNF-α and hemodynamics in patients with brain surgery. J Hain Med
Univ. 23:61–64. 2017.
|
|
23
|
Yu W: Anesthesia with propofol and
sevoflurane on postoperative cognitive function of elderly patients
undergoing general thoracic surgery. Pak J Pharm Sci.
30:(3(Special)). 1107–1110. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang L, Chen C, Wang L, Cheng G, Wu WW
and Li YH: Awakening from anesthesia using propofol or sevoflurane
with epidural block in radical surgery for senile gastric cancer.
Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:19412–19417. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Peng K, Liu HY, Wu SR, Liu H, Zhang ZC and
Ji FH: Does propofol anesthesia lead to less postoperative pain
compared with inhalational anesthesia?: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Anesth Analg. 123:846–858. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|