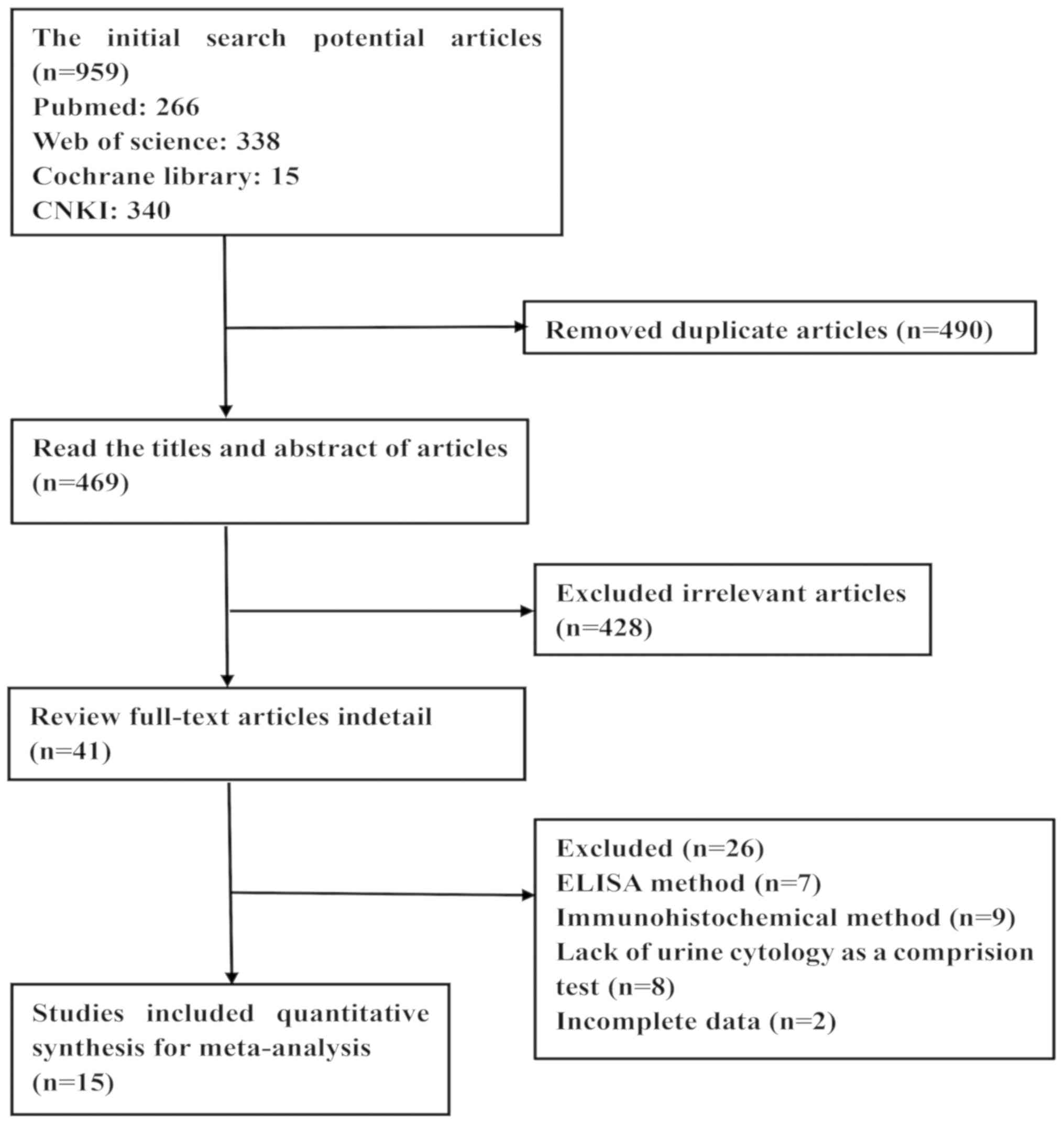
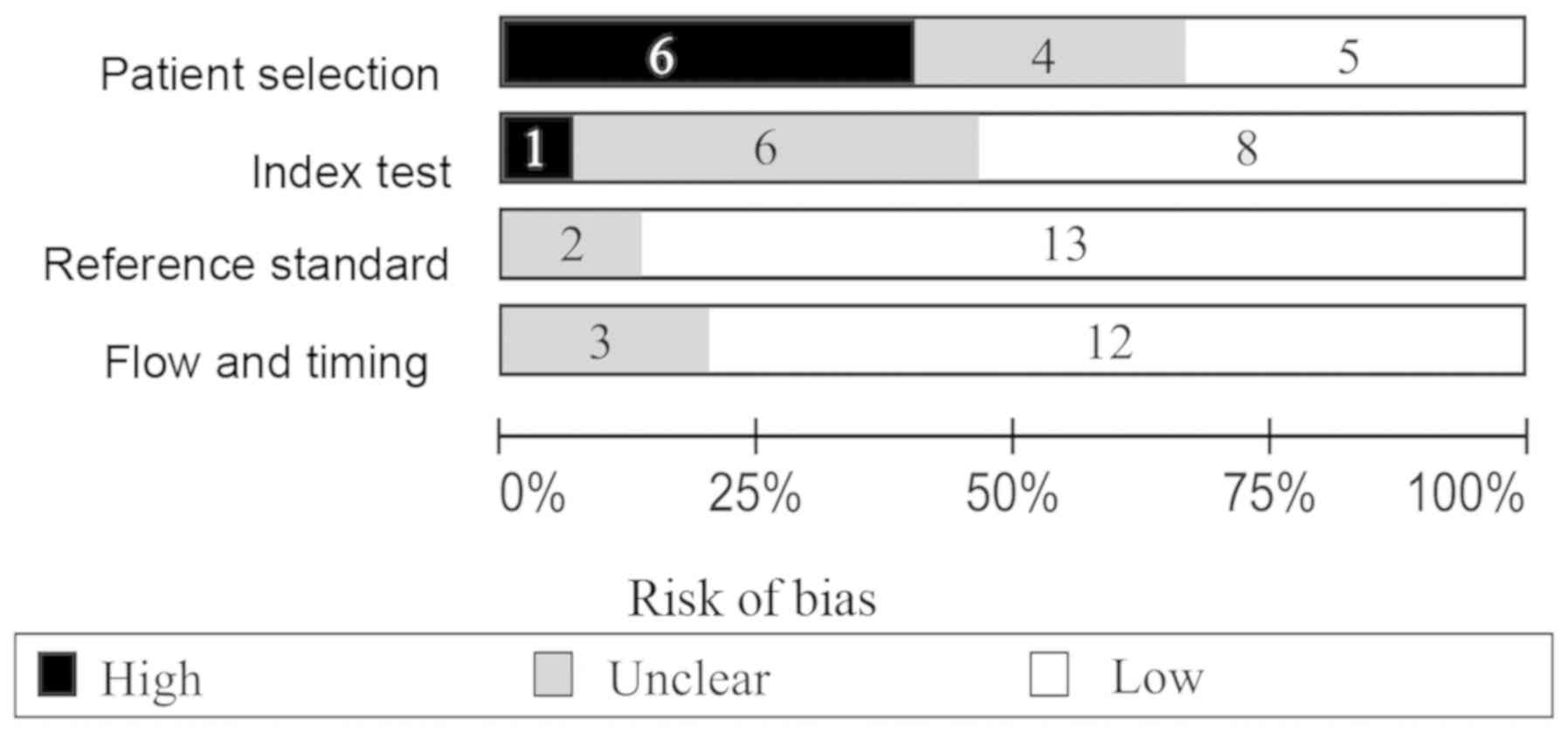
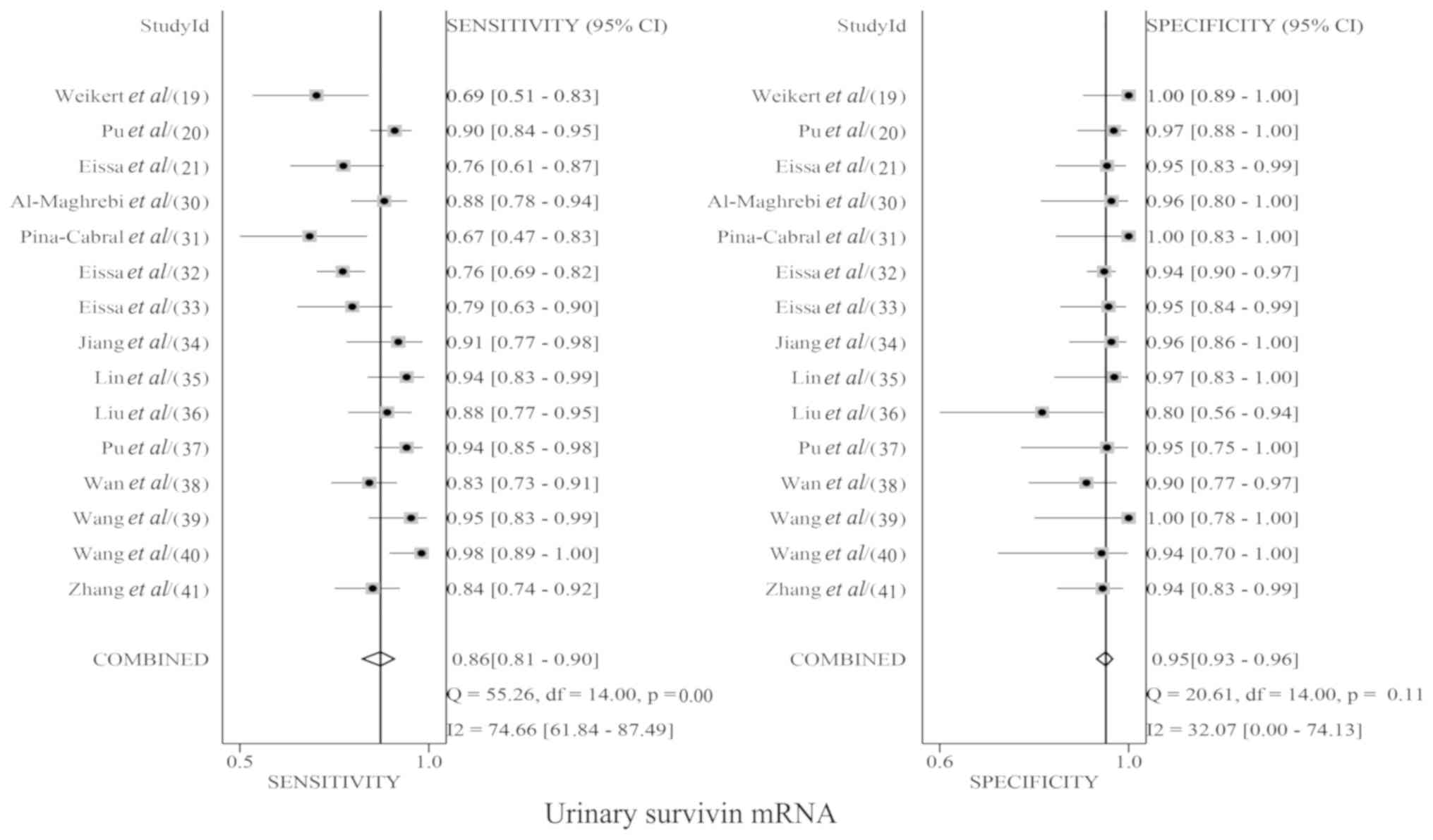
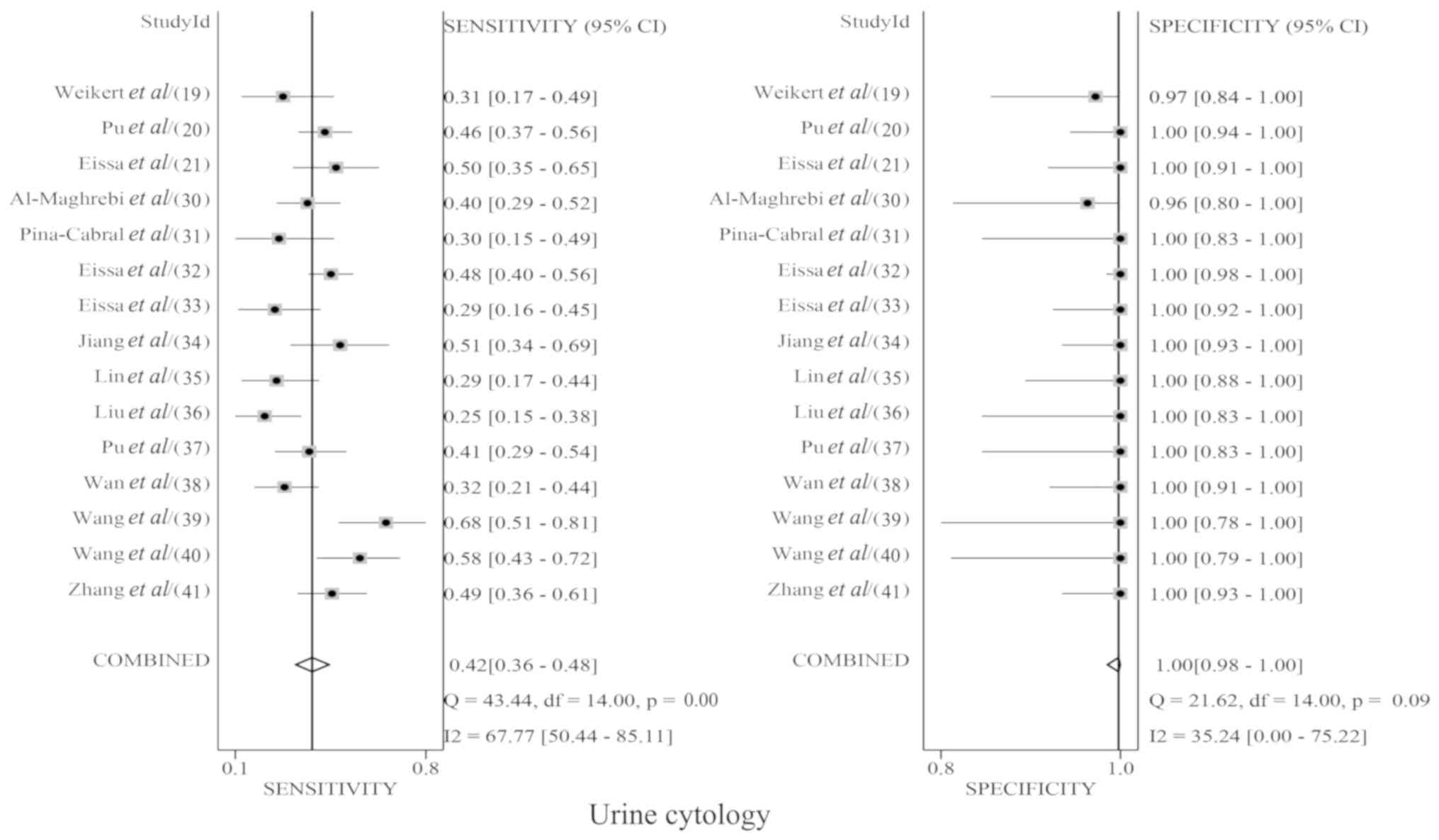
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Witjes JA and Hendricksen K: Intravesical
pharmacotherapy for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A critical
analysis of currently available drugs, treatment schedules, and
long-term results. Eur Urol. 53:45–52. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Babjuk M, Burger M, Zigeuner R, Shariat
SF, van Rhijn BW, Compérat E, Sylvester RJ, Kaasinen E, Böhle A,
Palou Redorta J, et al: EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive
urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: Update 2013. Eur Urol.
64:639–653. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kamat AM, Hegarty PK, Gee JR, Clark PE,
Svatek RS, Hegarty N, Shariat SF, Xylinas E, Schmitz-Dräger BJ,
Lotan Y, et al: ICUD-EAU International Consultation on bladder
cancer 2012: Screening, diagnosis, and molecular markers. Eur Urol.
63:4–15. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Burke DM, Shackley DC and O'Reilly PH: The
community-based morbidity of flexible cystoscopy. BJU Int.
89:347–349. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Biardeau X, Lam O, Ba V, Campeau L and
Corcos J: Prospective evaluation of anxiety, pain, and
embarrassment associated with cystoscopy and urodynamic testing in
clinical practice. Can Urol Assoc J. 11:104–110. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Raitanen MP, Leppilahti M, Tuhkanen K,
Forssel T, Nylund P and Tammela T; FinnBladder Group, : Routine
follow-up cystoscopy in detection of recurrence in patients being
monitored for bladder cancer. Ann Chir Gynaecol. 90:261–265.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lotan Y and Roehrborn CG: Sensitivity and
specificity of commonly available bladder tumour markers versus
cytology: Results of a comprehensive literature review and
meta-analyses. Urology. 61:109–118. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Oeyen E, Hoekx L, De Wachter S, Baldewijns
M, Ameye F and Mertens I: Bladder cancer diagnosis and follow-up:
The current status and possible role of extracellular vesicles. Int
J Mol Sci. 20(pii): E8212019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lokeshwar VB, Habuchi T, Grossman HB,
Murphy WM, Hautmann SH, Hemstreet GP III, Bono AV, Getzenberg RH,
Goebell P, Schmitz-Dräger BJ, et al: Bladder tumour markers beyond
cytology: International consensus panel on bladder tumour markers.
Urology. 66 (6 Suppl 1):35–63. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
D'Costa JJ, Goldsmith JC, Wilson JS, Bryan
RT and Ward DG: A systematic review of the diagnostic and
prognostic value of urinary protein biomarkers in urothelial
bladder cancer. Bladder Cancer. 2:301–317. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Garg H, Suri P, Gupta JC, Talwar GP and
Dubey S: Survivin: A unique target for tumour therapy. Cancer Cell
Int. 16:492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jacob NK, Cooley JV, Shirai K and
Chakravarti A: Survivin splice variants are not essential for
mitotic progression or inhibition of apoptosis induced by
doxorubicin and radiation. Onco Targets Ther. 5:7–20. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ambrosini G, Adida C and Altieri DC: A
novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and
lymphoma. Nat Med. 3:917–921. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Swana HS, Grossman D, Anthony JN, Weiss RM
and Altieri DC: Tumour content of the antiapoptosis molecule
survivin and recurrence of bladder cancer. N Engl J Med.
341:452–453. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Smith SD, Wheeler MA, Plescia J, Colberg
JW, Weiss RM and Altieri DC: Urine detection of survivin and
diagnosis of bladder cancer. JAMA. 285:324–328. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shariat SF, Casella R, Khoddami SM,
Hernandez G, Sulser T, Gasser TC and Lerner SP: Urine detection of
survivin is a sensitive marker for the noninvasive diagnosis of
bladder cancer. J Urol. 171:626–630. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liang Z, Xin R, Yu Y, Wang R, Wang C and
Liu X: Diagnostic value of urinary survivin as a biomarker for
bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of published
studies. World J Urol. 36:1373–1381. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Weikert S, Christoph F, Schrader M, Krause
H, Miller K and Muller M: Quantitative analysis of survivin mRNA
expression in urine and tumour tissue of bladder cancer patients
and its potential relevance for disease detection and prognosis.
Int J Cancer. 116:100–104. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pu XY, Wang ZP, Chen YR, Wang XH, Wu YL
and Wang HP: The value of combined use of survivin, cytokeratin 20
and mucin 7 mRNA for bladder cancer detection in voided urine. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 134:659–665. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Eissa S, Badr S, Elhamid SA, Helmy AS,
Nour M and Esmat M: The value of combined use of survivin mRNA and
matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 for bladder cancer detection in
voided urine. Dis Markers. 34:57–62. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG
and Group P: Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and
meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 6:e10000972009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME,
Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, Leeflang MM, Sterne JA and Bossuyt
PM; QUADAS-2 Group, : QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality
assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med.
155:529–536. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Skupski DW, Rosenberg CR and Eglinton GS:
Intrapartum fetal stimulation tests: A meta-analysis. Obstet
Gynecol. 99:129–134. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deeks JJ, Macaskill P and Irwig L: The
performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size
effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was
assessed. J Clin Epidemiol. 58:882–893. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Glas AS, Lijmer JG, Prins MH, Bonsel GJ
and Bossuyt PM: The diagnostic odds ratio: A single indicator of
test performance. J Clin Epidemiol. 56:1129–1135. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Rutjes AW, Scholten
RJ, Bossuyt PM and Zwinderman AH: Bivariate analysis of sensitivity
and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic
reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 58:982–990. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ and
Altman DG: Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ.
327:557–560. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ye X, Xiao H, Chen B and Zhang S: Accuracy
of lung ultrasonography versus chest radiography for the diagnosis
of adult community-acquired pneumonia: Review of the literature and
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 10:e01300662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Al-Maghrebi M, Kehinde EO, Kapila K and
Anim JT: Urinary survivin mRNA expression and urinary nuclear
matrix protein 22 BladderChek® and urine cytology in the
detection of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Med Princ
Pract. 21:295–297. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pina-Cabral L, Santos L, Mesquita B, Amaro
T, Magalhães S and Criado B: Detection of survivin mRNA in urine of
patients with superficial urothelial cell carcinomas. Clin Transl
Oncol. 9:731–736. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Eissa S, Swellam M, Shehata H, El-Khouly
IM, El-Zayat T and El-Ahmady O: Expression of HYAL1 and survivin
RNA as diagnostic molecular markers for bladder cancer. J Urol.
183:493–498. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Eissa S, Shabayek MI, Ismail MF, El-Allawy
RM and Hamdy MA: Diagnostic evaluation of apoptosis inhibitory gene
and tissue inhibitor matrix metalloproteinase-2 in patients with
bladder cancer. IUBMB Life. 62:394–399. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang G, Zhang JH, Jian RJ and Chen ZD:
Clinical significance of survivin mRNA level and hyaluronic acid
level detection of patients suffered from bladder transitional cell
carcinomas. Sichuan Med J. 11:1162–1164. 2006.
|
|
35
|
Lin Y, Han ZH and Liu T: The clinical
significance of urinary survivin mRNA detection for bladder
transitional cell carcinoma. Zhejiang Journal of Integrated
Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. 17:21–22. 2007.
|
|
36
|
Liu JG, Yang JY and Wei W: The value of
combined detection of urinary cell keratin 19, nuclear matrix
protein 22 and survivin in the early diagnosis of bladder cancer.
China Foreign Medical Treatment. 28:1682009.
|
|
37
|
Pu XY, Wang ZP, Chen YR, Wu YL, Wang HP
and Wang XH: Combined use of uirnary bladder cancer antigen,
hyaluronic aeid and survivin for the detection of bladder cancer.
Chin J Urol. 27:970–973. 2008.
|
|
38
|
Wan JH, Jin FS, Xiang D, Hu B and Gao F:
Value of cytokeratin 20 and survivin in the diagnosis of bladder
tumour. J Clin Res. 25:428–431. 2008.
|
|
39
|
Wang L, Zeng FQ, Liao GY and Chen FM:
Detection of survivin in exfoliated urothelial cells of bladder
cancer. J Clin Urol. 19:489–490. 2004.
|
|
40
|
Wang ZH, Hu ZQ, Ye Q, Ye ZQ, Cai D, Yang
N, Liu H, Zhuang QY, Yang WM, et al: Clinical application of
survivin detection in urothelial cells of patients with
transitional cell carcinoma of bladder. Chin J Exper Surg.
23:959–961. 2006.
|
|
41
|
Zhang WX, Zhen S and Zhen T: Diagnosis of
bladder cancer by detection of survivin and minichromosome
maitence5 protein in urine sediment. Chin J Urol. 26:233–236.
2005.
|
|
42
|
Nicolazzo C, Busetto GM, Del Giudice F,
Sperduti I, Giannarelli D, Gradilone A, Gazzaniga P, de Berardinis
E and Raimondi C: The long-term prognostic value of survivin
expressing circulating tumor cells in patients with high-risk
non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC). J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 143:1971–1976. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gogalic S, Sauer U, Doppler S and
Preininger C: Bladder cancer biomarker array to detect aberrant
levels of proteins in urine. Analyst. 140:724–735. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Herr HW: The risk of urinary tract
infection after flexible cystoscopy in patients with bladder tumor
who did not receive prophylactic antibiotics. J Urol. 193:548–551.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Eissa S, Kassim SK, Labib RA, El-Khouly
IM, Ghaffer TM, Sadek M, Razek OA and El-Ahmady O: Detection of
bladder carcinoma by combined testing of urine for hyaluronidase
and cytokeratin 20 RNAs. Cancer. 103:1356–1362. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chang Y, Xu J and Zhang Q: Microplate
magnetic chemiluminescence immunoassay for detecting urinary
survivin in bladder cancer. Oncol Lett. 14:4043–4052. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Altieri DC: Survivin, versatile modulation
of cell division and apoptosis in cancer. Oncogene. 22:8581–8589.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kitsukawa S, Aoyagi T, Noda K, Ito T,
Yamamoto Y, Hosoda S, Otsuru N and Matsumoto T: Quantitative
analysis of survivin mRNA expression in bladder transitional cell
carcinomas. Hinyokika Kiyo. 54:101–106. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Moussa O, Abol-Enein H, Bissada NK, Keane
T, Ghoneim MA and Watson DK: Evaluation of survivin reverse
transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction for noninvasive detection
of bladder cancer. J Urol. 175:2312–2316. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pormohammad A, Riahi SM, Nasiri MJ, Fallah
F, Aghazadeh M, Doustdar F and Pouriran R: Diagnostic test accuracy
of adenosine deaminase for tuberculous meningitis: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. J Infect. 74:545–554. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|