Introduction
Oral cancer is a common oral and maxillofacial
malignant tumor, among which oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is
the most prevalent (1,2). The reported annual new cases of OSCC
are over 300,000 (3). The diagnosis
and treatment of OSCC are advancing due to the development in
medical fields, but the prognosis is not very good. Data show that
the 5-year survival rate of OSCC is only 50 to 60%, and some
patients have advanced disease and local metastasis at the time of
diagnosis, which is not conducive to clinical treatment (4,5). A
previous study stated that the patients with advanced oral cancer
had a poor 3-year survival rate (6).
At present, the most effective treatment for patients with locally
advanced OSCC suitable for resection is comprehensive treatment
based on radical surgery (7).
In recent years, chemotherapy induced by TPF regimen
(Docetaxel + Cisplatin + Fluorouracil) has been a hotpot of
clinical research of oral cancer (8). TPF regimen helps to downsize the tumor
and reduce the difficulty of radical operation (9). The present clinical evaluation of solid
tumors mainly depends on imaging tests, which, unlike serological
tests, have a high economic cost and high difficulty in sampling,
as well as certain impacts on the patient's body. Therefore, the
search for a serological index to evaluate the efficacy and
prognosis of patients after treatment is crucial (10). The microRNA (miR), a non-coding
short-stranded RNA, 21 to 25 nt long, can bind to the target gene
3′UTR by complementary pairing to degrade or inhibit the expression
of the target gene (11). Several
studies have found that miR is differentially expressed in lung,
liver, breast, oral cancer, and other cancers, and is expected to
be an indicator of cancer observation and prognosis (12–15). As
a member of the miR family, miR-223 was reported to be
differentially expressed in oral cancer in the study by Tachibana
et al (16), and it has
potential to become a diagnostic and therapeutic target in oral
cancer. The study by Soga et al (17) analyzed the miR expression profile of
oral squamous cell carcinoma and discovered a low miR-223
expression in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. However,
the potentiality of miR-223 to function as a short-term efficacy
predictor and long-term prognostic index after chemotherapy has not
been studied.
This study observed the expression of miR-223-3p in
patients treated with TPF chemotherapy and explored its value in
predicting the efficacy of OSCC patients, aiming to provide a
clinical reference.
Patients and methods
Sample collection
Fifty patients with oral cancer treated in the
Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Jiamusi University (Jiamusi,
China) from March 2014 to January 2016 were enrolled in the study
group (aged 50–73 years), while 50 healthy subjects receiving
physical examinations during the same period in the hospital were
enrolled in the control group. This study was approved by the
Medical Ethics Committee of the hospital.
Inclusion criteria: Patients aged >18 years and
diagnosed with OSCC by imaging and pathological biopsy; patients at
stage III and IV according to TNM staging system; patients in line
with the 8th edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer
(AJCC) Cancer Staging Manual issued in 2017 (18); patients willing to cooperate with the
treatment and follow-up.
Exclusion criteria: Patients with other tumors or
congenital defects in liver, kidney, and heart functions; patients
with estimated survival time of less than 1 month; patients with
infections before the admission, patients intolerant of drugs of
this treatment; patients receiving no relevant targeted anticancer
treatments before this treatment.
Main instruments and drugs
Docetaxel was from Shanghai Acebright
Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd., China. Cisplatin was from Guizhou
Hanfang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China. Fluorouracil was from
Hainan Choitec Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd., China. TRIzol reagent and
the mirVanaTM RT-qPCR miRNA detection kit were purchased from
Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA (15590618, AM1558). TaqMan™ microRNA
reverse transcription kit and the PCR instrument were purchased
from Applied Biosystems, Foster, CA, USA (4366596, 4427975,
7500).
Treatment methods
Patients were treated with TPF regimen and oral
radical surgery as follows: 75 mg/m2 of docetaxel (d1), 75 mg/m2 of
cisplatin (d1), 750 mg/m2 of 5-Fluorouracil (d1-d5). One treatment
cycle comprised of 19 days and one course comprised of two cycles.
The efficacy was evaluated 1 week after the chemotherapy. Radical
resection of oral cancer was performed 2 weeks after the
chemotherapy.
Detection of miR-223-3p
expression
A total of 5 ml of peripheral venous blood was
collected from all subjects before and after the treatment. Thirty
minutes later, the blood was centrifuged at 1,500 × g at 24°C for
10 min to obtain the serum for total RNA extraction with TRIzol
reagent. The purity, concentration, and integrity of total RNA were
measured by UV spectrophotometer and agarose gel electrophoresis.
Total RNA was reverse transcribed using the TaqMan™ microRNA
reverse transcription kit in line with the kit instructions. The
miR-223-3p expression in the collected cDNA was detected by
mirVana™RT-qPCR miRNA detection kit and the 7500 PCR instrument.
The detection system consisted of 5 μl of mirVana 5X PCR
Buffer, 0.5 μl of 50X ROX™, 1 μl of cDNA, 0.5
μl of forward primer, 0.5 μl of reverse primer, and
enough nuclease-free water to add the system up to 20 μl.
Amplification conditions: 40 cycles of pre-denaturation at 95°C for
3 min, denaturation at 95°C for 15 sec, annealing and extension at
60°C for 30 sec. Three replicate wells were set for each sample,
and the experiment was carried out 3 times. In the present study,
U6 was used as an internal reference, and the data were analyzed
using 2−ΔΔCq (19).
Follow-up
The survival of patients was followed up for 3 years
by telephone and clinical re-examination, and the follow-up was
performed every 3 months.
Outcome measures
Main outcome measures
The expression of miR-223-3p in the study and the
control group and the expression of miR-223-3p before and after
treatment in the study group were monitored. The short-term
clinical efficacy after treatment was divided into complete
response (CR), partial response (PR), stable disease (SD), and
progressive disease (PD) according to the response evaluation
criteria in solid tumor by WHO (20). Patients with CR and PR were in
remission, while patients with SD and PD were not in remission.
Secondary outcome measures
Patients were divided into the remission group and
the non-remission group based on efficacy. The predictive value of
miR-223-3p for the efficacy was compared between the two groups
before the treatment. Kaplan-Meier survival curve was used to
analyze the relationship between miR-223-3p high/low expression
(median value: 3.22) and OSCC survival, and Cox regression analysis
was performed to analyze OSCC prognosis.
Statistical analysis
The collected data were statistically analyzed using
the SPSS20.0 software and visualized using the GraphPad 7 software.
The distribution of the measurement data were analyzed using the
Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. The measurement data with normal
distribution were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (mean
± SD), the comparison between groups was performed using the
independent sample t-test and the comparison within the group was
performed by paired t-test. The count data were analyzed by the
chi-square test. Spearman's test was used to analyze the
relationship between miR-223-3p and clinical efficacy. ROC curve
was employed to observe the diagnostic value. Kaplan-Meier survival
curve was used to display the 3-year survival which was analyzed by
the log-rank test. Multivariate Cox regression was conducted to
explore the independent risk factors affecting the prognosis of
patients. A statistical difference was recognized at P<0.05.
Results
Baseline data analysis
The study and the control group were not
statistically different in sex, age, BMI, medical history, smoking,
drinking, and place of residence (P>0.05) (Table I).
 | Table I.Baseline data analysis. |
Table I.
Baseline data analysis.
| Factors | Study group
(n=50) | Control group
(n=50) |
χ2/t-test | P-value |
|---|
| Sex |
| Male | 31 (62.00) | 35 (70.00) | 0.713 | 0.398 |
|
Female | 19 (38.00) | 15 (30.00) |
|
|
| Age (year) | 62.4±5.1 | 61.2±5.7 | 1.109 | 0.270 |
| BMI
(kg/m2) | 22.51±2.25 | 22.84±1.72 | 0.824 | 0.412 |
| Medical history |
|
Hypertension | 18 (36.00) | 14 (28.00) | 0.735 | 0.391 |
|
Diabetes | 12 (24.00) | 9 (18.00) | 0.543 | 0.461 |
|
Hyperlipidemia | 8 (46.00) | 5 (10.00) | 0.796 | 0.372 |
| Smoking |
| Yes | 30 (60.00) | 34 (68.00) | 0.694 | 0.405 |
| No | 20 (40.00) | 16 (32.00) |
|
|
| Drinking |
| Yes | 7 (14.00) | 4 (8.00) | 0.919 | 0.338 |
| No | 43 (86.00) | 46 (92.00) |
|
|
| Place of
residence |
| Urban
area | 35 (70.00) | 40 (80.00) | 1.333 | 0.248 |
| Rural
area | 15 (30.00) | 10 (20.00) |
|
|
| Location of
tumor |
|
Glossa | 22 (44.00) |
|
|
|
|
Other | 28 (56.00) |
|
|
|
| Clinical stage |
| III | 35 (70.00) |
|
|
|
| IV | 15 (30.00) |
|
|
|
| Degree of
differentiation |
| High
differentiation | 18 (36.00) |
|
|
|
| Moderate
differentiation | 32 (64.00) |
|
|
|
Expression and efficacy predictive
value of miR-223-3p in patients
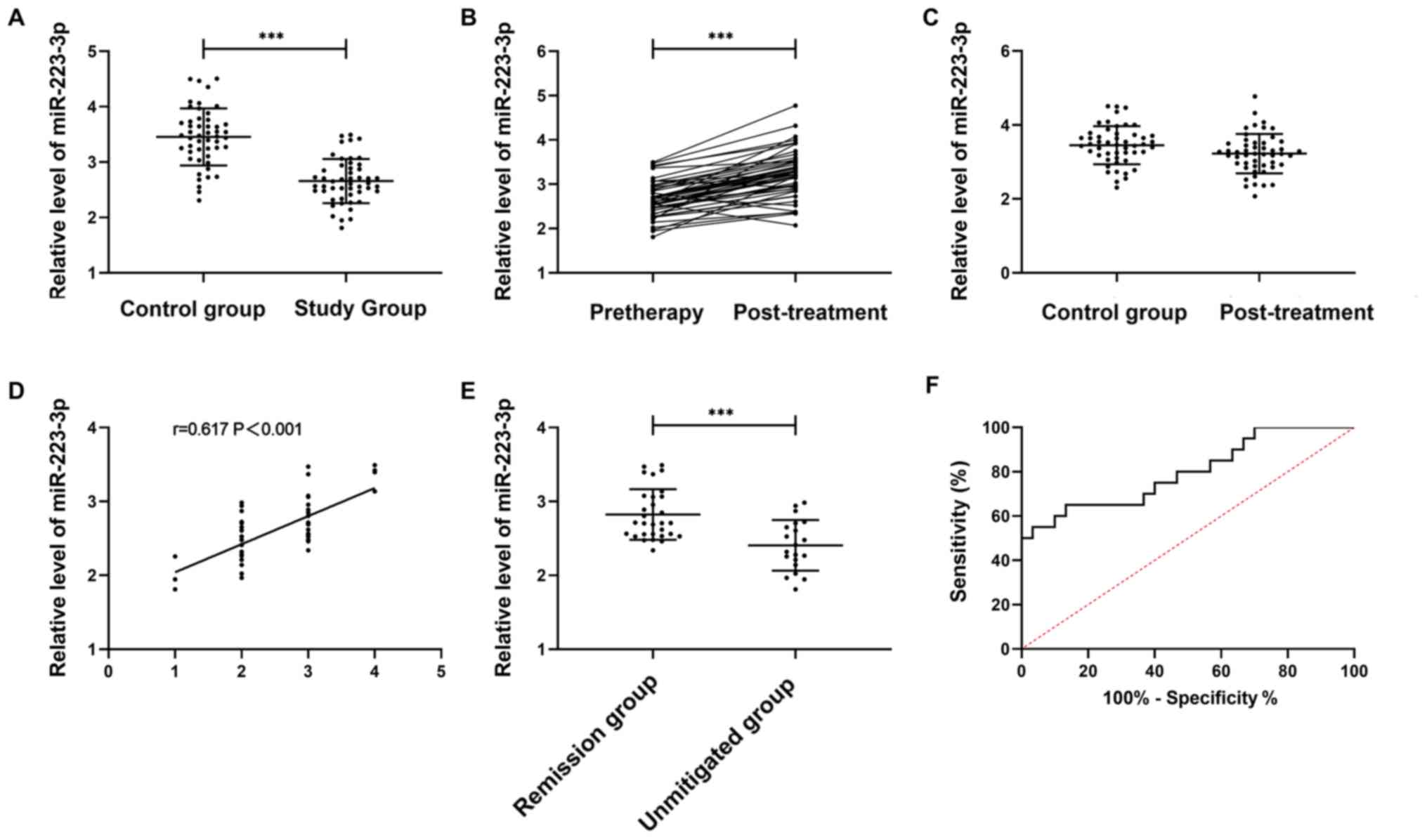
According to the detection of serum miR-223-3p
expression in the study and the control group, the relative serum
miR-223-3p level was lower in the study than in the control group
(P<0.001). The miR-223-3p expression in the study group after
the treatment was significantly higher than before (P<0.05).
After the treatment, no great difference was observed between the
study group and the control group in the miR-223-3p expression
(P>0.05).
The treatment outcome was CR in 4 patients, PR in
26, SD in 17, and PD in 3. Spearman's correlation analysis
indicated that miR-223-3p expression gradually increased with the
improvement of treatment outcome (r=0.617, P<0.001). Patients
were divided into the remission group (n=30) and the non-remission
group (n=20) according to the treatment outcome. The miR-223-3p
level before the treatment was markedly higher in the remission
group than in the non-remission group (P<0.05). The area under
the ROC curve of miR-223-3p was 0.797 (21) (Fig.
1).
Relationship between miR-223-3p and
the prognosis and survival of patients
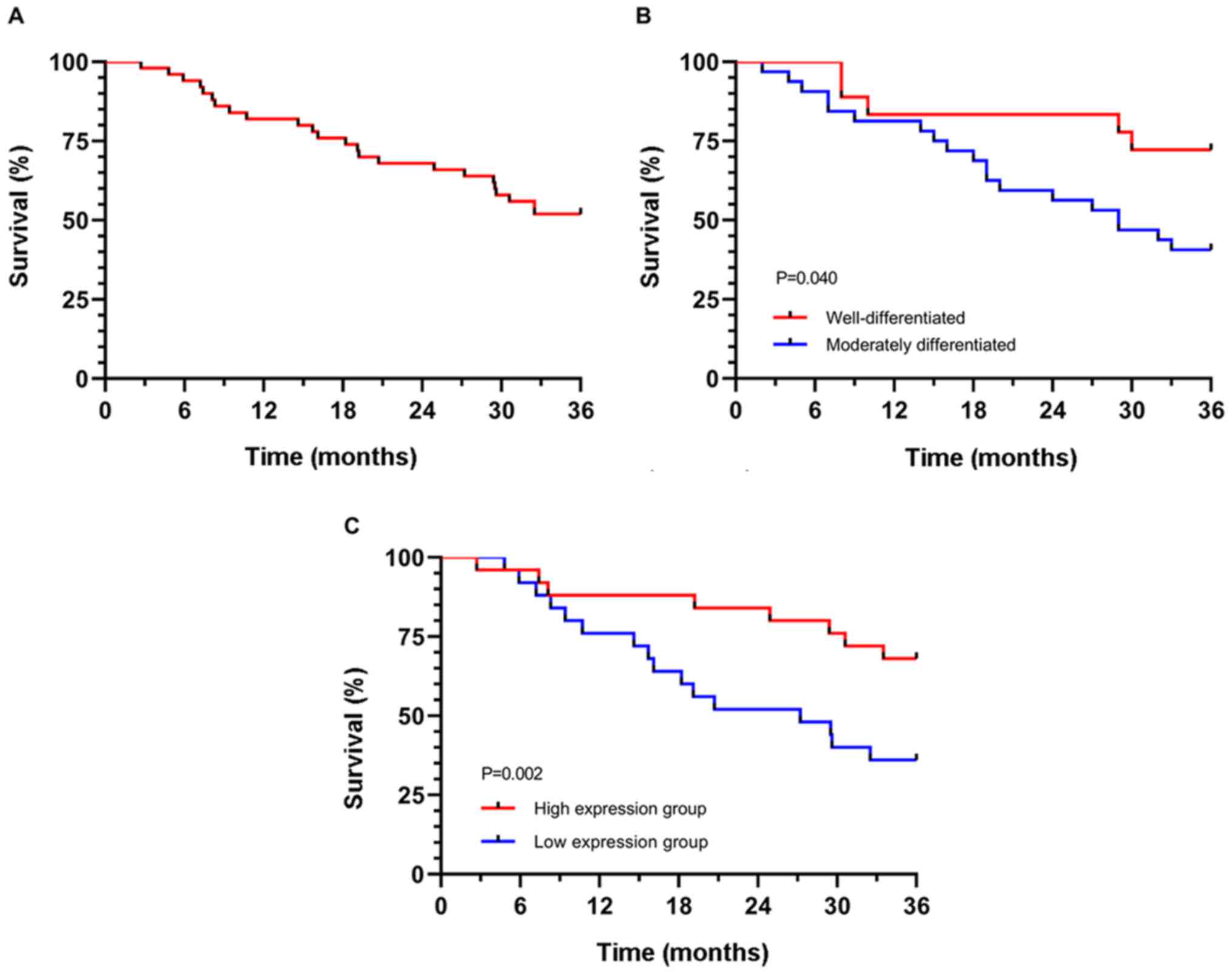
All 50 patients were followed up for three years.
The number of surviving patients was 26, with a survival rate of
52.00%. Univariate Cox regression analysis indicated that the
degree of differentiation and miR-223-3p expression were prognostic
factors. Multivariate Cox regression analysis demonstrated that the
degree of differentiation [HR: 11.862 (95% CI: 2.730–51.547)] and
miR-223-3p [HR: 3.489 (95% CI: 1.447–8.413)] were independent
prognostic factors. According to the survival curve of independent
prognostic factors, the 3-year survival of patients with high
differentiation and high miR-223-3p expression was significantly
higher than that of patients with poor differentiation and low
miR-223-3p expression (P<0.05) (Table II and Fig. 2).
 | Table II.Analysis of 3-year prognostic
factors. |
Table II.
Analysis of 3-year prognostic
factors.
|
| Univariate Cox | Multivariate Cox |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Parameter | P-value | HR | 95% CI | P-value | HR | 95% CI |
|---|
| Sex (male vs.
female) | 0.510 | 0.752 | 0.322~1.758 |
|
|
|
| Age (≤60 vs.
>60) | 0.896 | 0.943 | 0.391~2.275 |
|
|
|
| Location of tumor
(glossa vs. other) | 0.750 | 1.141 | 0.506~2.573 |
|
|
|
| Clinical stage (III
vs. IVA) | 0.219 | 1.679 | 0.734~3.839 |
|
|
|
| Degree of
differentiation (high vs. moderate) | 0.049 | 2.699 | 1.055~7.246 | 0.031 | 2.988 | 1.106~8.071 |
| miR-223-3p expression
(high vs. low) | 0.024 | 2.677 | 1.14~6.287 | 0.014 | 2.933 | 1.241~6.934 |
Discussion
Preoperative induction chemotherapy has been
proposed in recent years as a treatment program. The adoption of
TPF program before the operation can control cancer cell
proliferation and interfere with cell biology functions, thereby
reducing the volume of solid tumors and facilitating surgical
operations (22). Presently, indexes
of short-term clinical efficacy evaluation after TPF treatment are
scarce. The monitoring of related indexes to predict the short-term
clinical efficacy and survival will improve the prognosis of
patients.
A growing number of studies have established the
close relationship between the miR and the occurrence and
development of various tumors (23).
miR-223-3p has low expression in a variety of tumors (24,25). In
the study by Ding et al (26), miR-223-3p was reported to have low
expression in glioblastoma and the overexpression of miR-223-3p can
effectively reduce inflammation-associated cytokines in
glioblastoma to inhibit cell proliferation and migration. However,
little is known about the relationship between miR-223-3p and OSCC.
In the present study, we found the serum expression of miR-223-3p
in OSCC patients was significantly lower than in healthy people,
which is consistent with the findings of Tachibana et al
(16). The present study and that of
Tachibana et al support each other, but this study is more
representative and has a larger sample size. The expression of
miR-223-3p after treatment was also monitored in the present study.
The results demonstrated that the expression of miR-223-3p after
the treatment was significantly higher than before, suggesting that
the expression of miR-223-3p can be improved after TPF treatment,
but its specific mechanism is not clear. The correlation analysis
revealed that the expression of miR-223-3p before the treatment
gradually increased with the improvement of treatment outcome,
indicating that miR-223-3p expression before the treatment can
function as an indicator of the efficacy of OSCC patients. We
divided patients into the remission and non-remission group and
found that the expression of miR-223-3p before treatment was
significantly higher in the remission group than in the
non-remission group. The ROC curve analysis suggested that the area
under the curve of the miR-223-3p expression before the treatment
for OSCC efficacy prediction was 0.797, with high predictive value.
Previous literature (27,28) states that the high expression of
miR-223-3p can increase the sensitivity of cancer cells to
cisplatin, docetaxel, and 5-FU. This may be one of the reasons why
the efficacy in the remission group was better than in the
non-remission group in this study, but the specific mechanism needs
to be further studied.
Cox regression was conducted to analyze the factors
affecting the prognosis of patients. The analysis showed that
miR-223-3p and degree of differentiation were independent factors
influencing the prognosis of patients. One previous study
discovered that the degree of differentiation is related to the
prognosis of patients with OSCC (29). However, previous studies mostly
focused on the difference between poor differentiation and moderate
+ high differentiation. The present study made a comparison between
moderate differentiation and high differentiation and believed
that, like high differentiation, moderate differentiation also has
an impact on the prognosis of patients. However, in the present
study, the prognosis of oral cancer patients was found to be
related with pathological staging but not related with the TNM
staging, which is consistent with the results in the study by Chen
et al (30). We speculate
that this may be the consequence of a small sample size. This study
is the first to discover that miR-223-3p can be used as a potential
independent prognostic indicator for OSCC.
The present study and above-mentioned studies have
proven the clinical value of miR-223-3p in patients with OSCC.
However, the specific mechanism of miR-223-3p were not explored and
the small sample size in this study requires further study for
confirmation.
In summary, miR-223-3p, expression is low in oral
cancer, and it shows potential for predicting the efficacy and
prognosis of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC)
after TPF regimen.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the present
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
CL and YF conceived and designed the study, and
drafted the manuscript. CL, YF and WS collected, analyzed and
interpreted the experimental data. CL revised the manuscript for
important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the
final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of
the Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Jiamusi University
(Jiamusi, China). Signed informed consents were obtained from the
patients and/or the guardians.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Chi AC, Day TA and Neville BW: Oral cavity
and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma - an update. CA Cancer J
Clin. 65:401–421. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li L, Li C, Wang S, Wang Z, Jiang J, Wang
W, Li X, Chen J, Liu K, Li C, et al: Exosomes derived from hypoxic
oral squamous cell carcinoma cells deliver miR-21 to normoxic cells
to elicit a prometastatic phenotype. Cancer Res. 76:1770–1780.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tseng WT, Chiang WF, Liu SY, Roan J and
Lin CN: The application of data mining techniques to oral cancer
prognosis. J Med Syst. 39:592015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Adami GR, Tang JL and Markiewicz MR:
Improving accuracy of RNA-based diagnosis and prognosis of oral
cancer by using noninvasive methods. Oral Oncol. 69:62–67.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sharma A, Agarwal K, Agarwal S, Kumar S
and Bharti AC: 354P-Study of immunohistochemical expression of VEGF
and its association with HPV E6 and E7 oncoproteins in oral and
oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 28:100–110.
2017.
|
|
7
|
Smits RW, Koljenović S, Hardillo JA, Ten
Hove I, Meeuwis CA, Sewnaik A, Dronkers EA, Bakker Schut TC,
Langeveld TP, Molenaar J, et al: Resection margins in oral cancer
surgery: Room for improvement. Head Neck. 38:2197–2203. 2016.
|
|
8
|
Zhong LP, Ma H, Ju W and Zhang ZY:
Relationship of low stathmin expression and benefit from TPF
induction chemotherapy and its role in chemoresistance via mutant
p53 in oral cancer. J Clin Oncol. 36:e180342018.
|
|
9
|
Zhong LP, Zhang CP, Ren GX, Guo W, William
WN Jr, Hong CS, Sun J, Zhu HG, Tu WY, Li J, et al: Long-term
results of a randomized phase III trial of TPF induction
chemotherapy followed by surgery and radiation in locally advanced
oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:18707–18714.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shi J, Bao X, Liu Z, Zhang Z, Chen W and
Xu Q: Serum miR-626 and miR-5100 are promising prognosis predictors
for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Theranostics. 9:920–931.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kasinski AL, Kelnar K, Stahlhut C,
Orellana E, Zhao J, Shimer E, Dysart S, Chen X, Bader AG and Slack
FJ: A combinatorial microRNA therapeutics approach to suppressing
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 34:3547–3555. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Callegari E, Gramantieri L, Domenicali M,
D'Abundo L, Sabbioni S and Negrini M: MicroRNAs in liver cancer: A
model for investigating pathogenesis and novel therapeutic
approaches. Cell Death Differ. 22:46–57. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hannafon BN, Trigoso YD, Calloway CL, Zhao
YD, Lum DH, Welm AL, Zhao ZJ, Blick KE, Dooley WC and Ding WQ:
Plasma exosome microRNAs are indicative of breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res. 18:902016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zeljic K, Jovanovic I, Jovanovic J, Magic
Z, Stankovic A and Supic G: MicroRNA meta-signature of oral cancer:
Evidence from a meta-analysis. Ups J Med Sci. 123:43–49.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tachibana H, Sho R, Takeda Y, Zhang X,
Yoshida Y, Narimatsu H, Otani K, Ishikawa S, Fukao A, Asao H, et
al: Circulating miR-223 in oral cancer: Its potential as a novel
diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target. PLoS One.
11:e01596932016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Soga D, Yoshiba S, Shiogama S, Miyazaki H,
Kondo S and Shintani S: microRNA expression profiles in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 30:579–583. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kukreja P, Parekh D and Roy P: Practical
challenges in measurement of depth of invasion in oral squamous
cell carcinoma: Pictographical documentation to improve consistency
of reporting per the AJCC 8th edition recommendations. Head Neck
Pathol. 2019.doi: 10.1007/s12105-019-01047-9. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCq method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Necchi A, Lo Vullo S, Perrone F, Raggi D,
Giannatempo P, Calareso G, Nicolai N, Piva L, Biasoni D, Catanzaro
M, et al: First-line therapy with dacomitinib, an orally available
pan-HER tyrosine kinase inhibitor, for locally advanced or
metastatic penile squamous cell carcinoma: Results of an
open-label, single-arm, single-centre, phase 2 study. BJU Int.
121:348–356. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hosmer DW Jr, Lemeshow S and Sturdivant
RX: Applied Logistic Regression. (3rd). John Wiley & Sons.
(Hoboken, NJ). 173–182. 2013.
|
|
22
|
Yu CC, Hu FW, Yu CH and Chou MY: Targeting
CD133 in the enhancement of chemosensitivity in oral squamous cell
carcinoma-derived side population cancer stem cells. Head Neck.
38:E231–E238. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Acunzo M, Romano G, Wernicke D and Croce
CM: MicroRNA and cancer - a brief overview. Adv Biol Regul. 57:1–9.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bhattacharya S, Steele R, Shrivastava S,
Chakraborty S, Di Bisceglie AM and Ray RB: Serum miR-30e and
miR-223 as novel noninvasive biomarkers for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 186:242–247. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lu W, Hu Y, Ma Q, Zhou L, Jiang L, Li Z,
Zhao S, Xu Y, Shi W, Li S, et al: miR-223 increases gallbladder
cancer cell sensitivity to docetaxel by downregulating STMN1.
Oncotarget. 7:62364–62376. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ding Q, Shen L, Nie X, Lu B, Pan X, Su Z,
Yan A, Yan R, Zhou Y, Li L, et al: MiR-223-3p overexpression
inhibits cell proliferation and migration by regulating
inflammation-associated cytokines in glioblastomas. Pathol Res
Pract. 214:1330–1339. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bozec A, Zangari J, Butori-Pepino M, Ilie
M, Lalvee S, Juhel T, Butori C, Brest P, Hofman P and
Vouret-Craviari V: MiR-223-3p inhibits angiogenesis and promotes
resistance to cetuximab in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 8:57174–57186. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou X, Jin W, Jia H, Yan J and Zhang G:
MiR-223 promotes the cisplatin resistance of human gastric cancer
cells via regulating cell cycle by targeting FBXW7. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 34:282015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ramos-García P, Bravo M, González-Ruiz L
and González-Moles MÁ: Significance of cytoplasmic cyclin D1
expression in oral oncogenesis. Oral Dis. 24:98–102.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen TC, Wu CT, Wang CP, Hsu WL, Yang TL,
Lou PJ, Ko JY and Chang YL: Associations among pretreatment tumor
necrosis and the expression of HIF-1α and PD-L1 in advanced oral
squamous cell carcinoma and the prognostic impact thereof. Oral
Oncol. 51:1004–1010. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|